BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > 150 Biochemistry Exam 1 practice questions with correct answers (All)
150 Biochemistry Exam 1 practice questions with correct answers
Document Content and Description Below
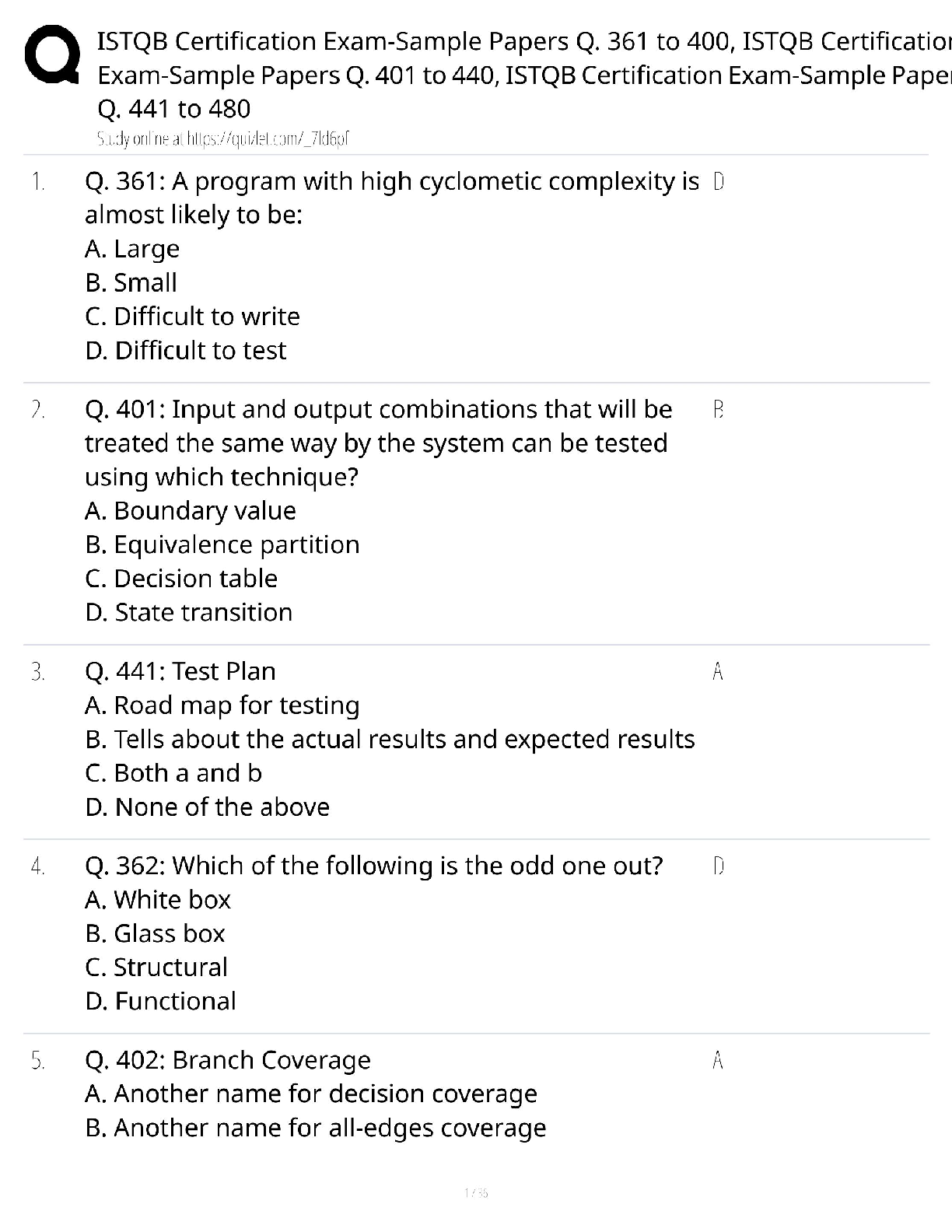
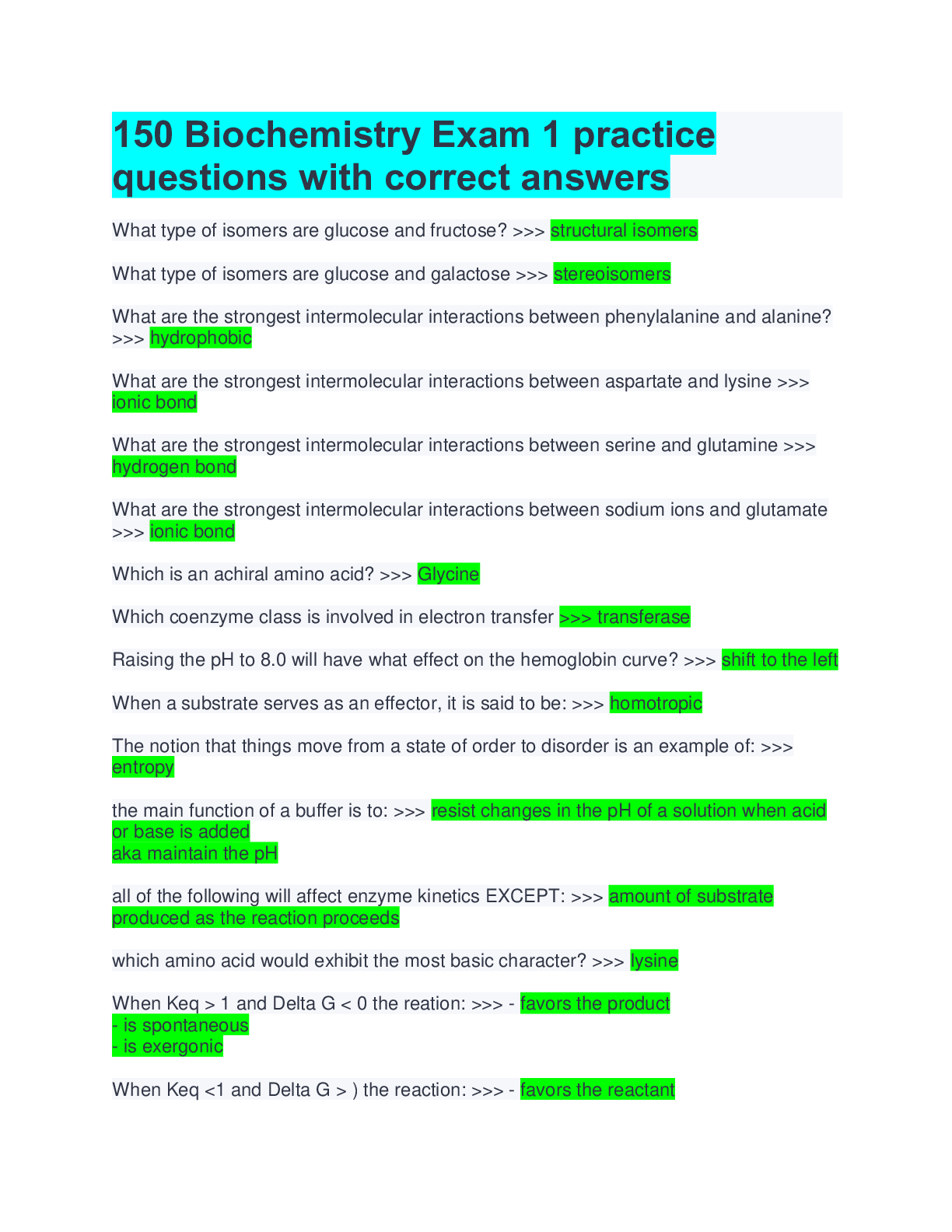
150 Biochemistry Exam 1 practice questions with correct answers What type of isomers are glucose and fructose? >>> structural isomers What type of isomers are glucose and galactose >>> stereoisome ... rs What are the strongest intermolecular interactions between phenylalanine and alanine? >>> hydrophobic What are the strongest intermolecular interactions between aspartate and lysine >>> ionic bond What are the strongest intermolecular interactions between serine and glutamine >>> hydrogen bond What are the strongest intermolecular interactions between sodium ions and glutamate >>> ionic bond Which is an achiral amino acid? >>> Glycine Which coenzyme class is involved in electron transfer >>> transferase Raising the pH to 8.0 will have what effect on the hemoglobin curve? >>> shift to the left When a substrate serves as an effector, it is said to be: >>> homotropic The notion that things move from a state of order to disorder is an example of: >>> entropy the main function of a buffer is to: >>> resist changes in the pH of a solution when acid or base is added aka maintain the pH all of the following will affect enzyme kinetics EXCEPT: >>> amount of substrate produced as the reaction proceeds which amino acid would exhibit the most basic character? >>> lysine When Keq > 1 and Delta G < 0 the reation: >>> - favors the product - is spontaneous - is exergonic When Keq <1 and Delta G > ) the reaction: >>> - favors the reactant - is not spontaneous - is endergonic non-competitive inhibition: >>> decrease the vmax Km stays the same glucose and galactose form: >>> lactose glucose and fructose form: >>> sucrose glucose and glucose form: >>> maltose What is an epimer of glucose? >>> galactose What is the 1st Law of Thermodynamics? >>> Energy cannot be created or destroyed only converted into different forms Gibbs Free Energy Formula: >>> DeltaG = DeltaH - TDeltaS True or false: spontaneous and instantaneous are the same thing >>> false What is Hess's Law >>> as long as the reaction ends up in a egative number the process will occur spontaneously Endogonic reactions are ______________ and Exergonic reactions are __________ >>> anabolic; catabolic When the free energy of a reaction is zero: >>> equilibrium What do enzymes do to the energy required for activation? >>> lowers energy Is the enzyme consumed during a reaction? >>> No Acids with a high Ka are >>> strong (wants to lose hydrogen) Acids with a low Ka are >>> weak (wants to gain a hydrogen) High Ka = what pKa? >>> Low pKa (strong acid) Low Ka = what pKa? >>> High oKa (weak acid) What is the range that buffers work well in? >>> plus or minus 1 of pka of pH What is a good buffer range for pKa = 10? >>> pH range 9-11 What is it called if the pH is < pKa >>> protinated [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 21, 2022
Number of pages
9
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 21, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
184




 v.png)