Software QA C857 WGU Latest 2022
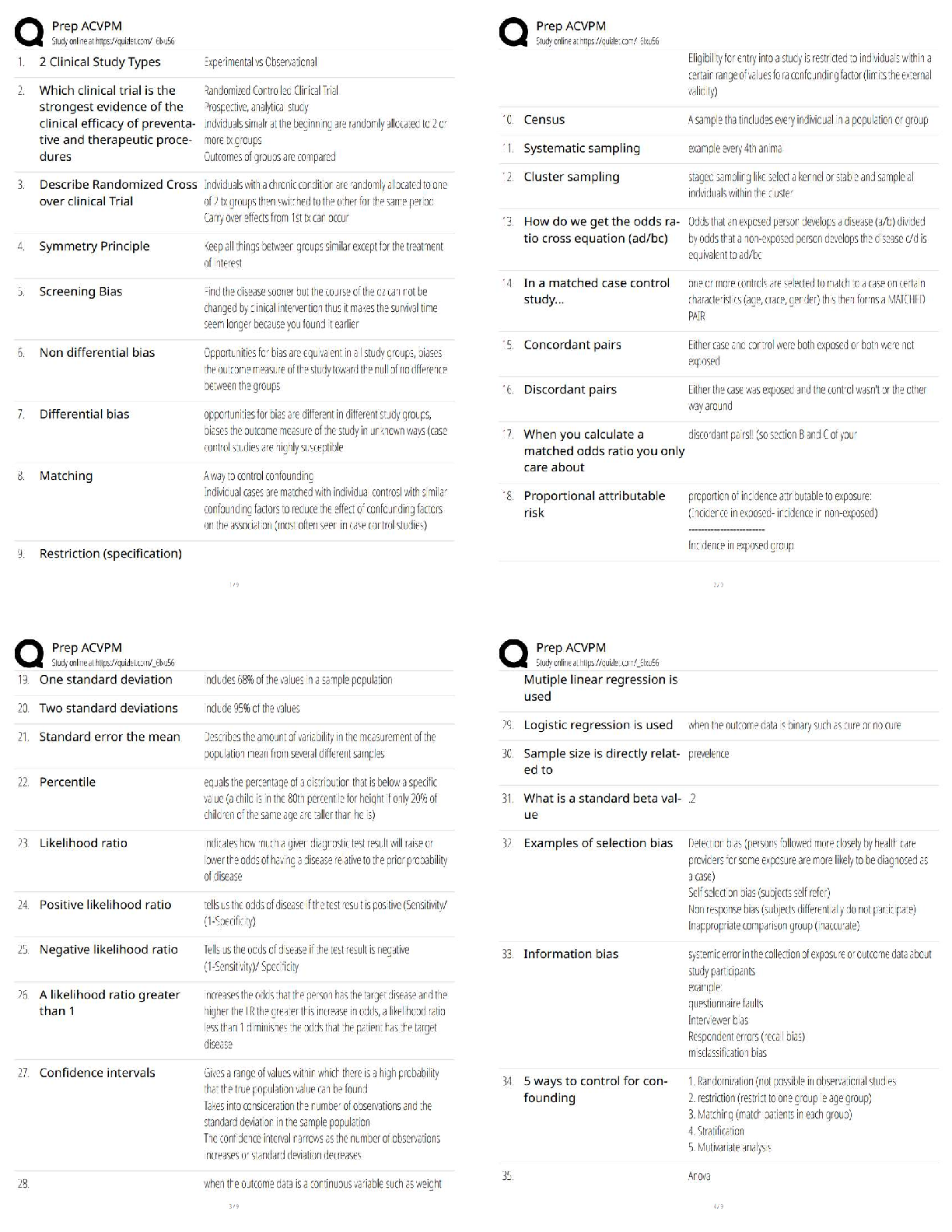
Rated A+
Facility Test case ✔✔Ensure that the functionality in the objectives is implemented.
Volume test case ✔✔Subject the program to abnormally large volumes of data to process.
St
...
Software QA C857 WGU Latest 2022
Rated A+
Facility Test case ✔✔Ensure that the functionality in the objectives is implemented.
Volume test case ✔✔Subject the program to abnormally large volumes of data to process.
Stress test case ✔✔Subject the program to abnormally large loads, generally concurrent
processing.
Usability test case ✔✔Subject the program to abnormally large loads, generally concurrent
processing.
Security test case ✔✔Try to subvert the program's security measures.
Performance test case ✔✔Determine whether the program meets response and throughput
requirements.
Storage test case ✔✔Ensure the program correctly manages its storage needs, both system and
physical.
Configuration test case ✔✔Check that the program performs adequately on the recommended
configurations.
Compatibility/Conversion test case ✔✔Determine whether new versions of the program are
compatible with previous releases.
Installation test case ✔✔Ensure the installation methods work on all supported platforms.
Reliability test case ✔✔Determine whether the program meets reliability specifications such as
uptime and MTBF.
Serviceability/Maintenance test case ✔✔Determine whether the application correctly provides
mechanisms to yield data on events requiring technical support.
Documentation test case ✔✔Validate the accuracy of all user documentation.
Procedure test case ✔✔Determine the accuracy of special procedures required to use or maintain
the program.
Black box tests ✔✔1. Equivalence partitioning
2. Boundary analysis
3. Cause-effect graphing
4. Error guessing
White box tests ✔✔1. Statement coverage
2. Decision coverage
3. Condition coverage
4. Decision/condition coverage
5. Multiple-condition coverage
Test completion criteria ✔✔1. Stop when the scheduled time for testing expires.
2. Stop when all the test cases execute without detecting errors—that is, stop when the test cases
are unsuccessful.
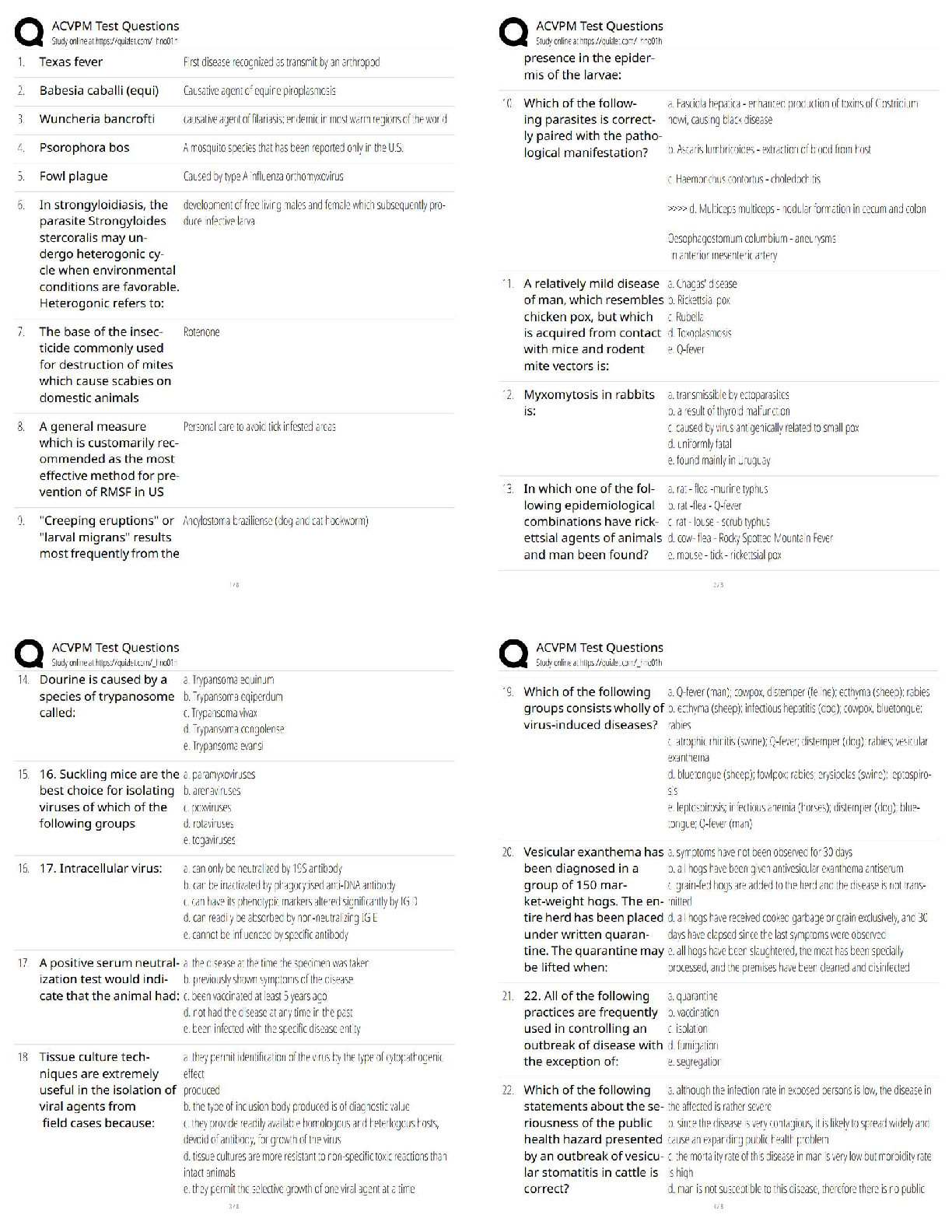
First phase / SDLC Requirements Phase ✔✔Acceptance test
Second phase / SDLC Objectives Phase ✔✔System Test
Third phase / SDLC External Specification ✔✔Function test
Fourth phase / SDLC System Design ✔✔Integration test
Fifth phase / Program structure design ✔✔Integration test
Sixth phase / Module interface specifications ✔✔Module test
ROESPM ✔✔Requirements
Objectives
External Specification
System Design
Program Structure Design
Module Interface Specifications
ASFIIM ✔✔Acceptance - test
System - test
Function - test
Integration - test
Integration - test
Module - test
R -> A
O -> S
E -> F
S -> I
P -> I
M -> M ✔✔Requirements -> Acceptance - test
Objectives -> System - test
External Specification -> Function - test
System Design -> Integration - test
Program Structure Design -> Integration - test
Module Interface Specs -> Module - test
R -> A ✔✔Requirements -> Acceptance - test
O -> S ✔✔Objectives -> System - test
E -> F ✔✔External Specification -> Function - test
S -> I ✔✔System Design -> Integration - test
P -> I ✔✔Program Structure Design -> Integration - test
M -> M ✔✔Module Interface Specs -> Module - test
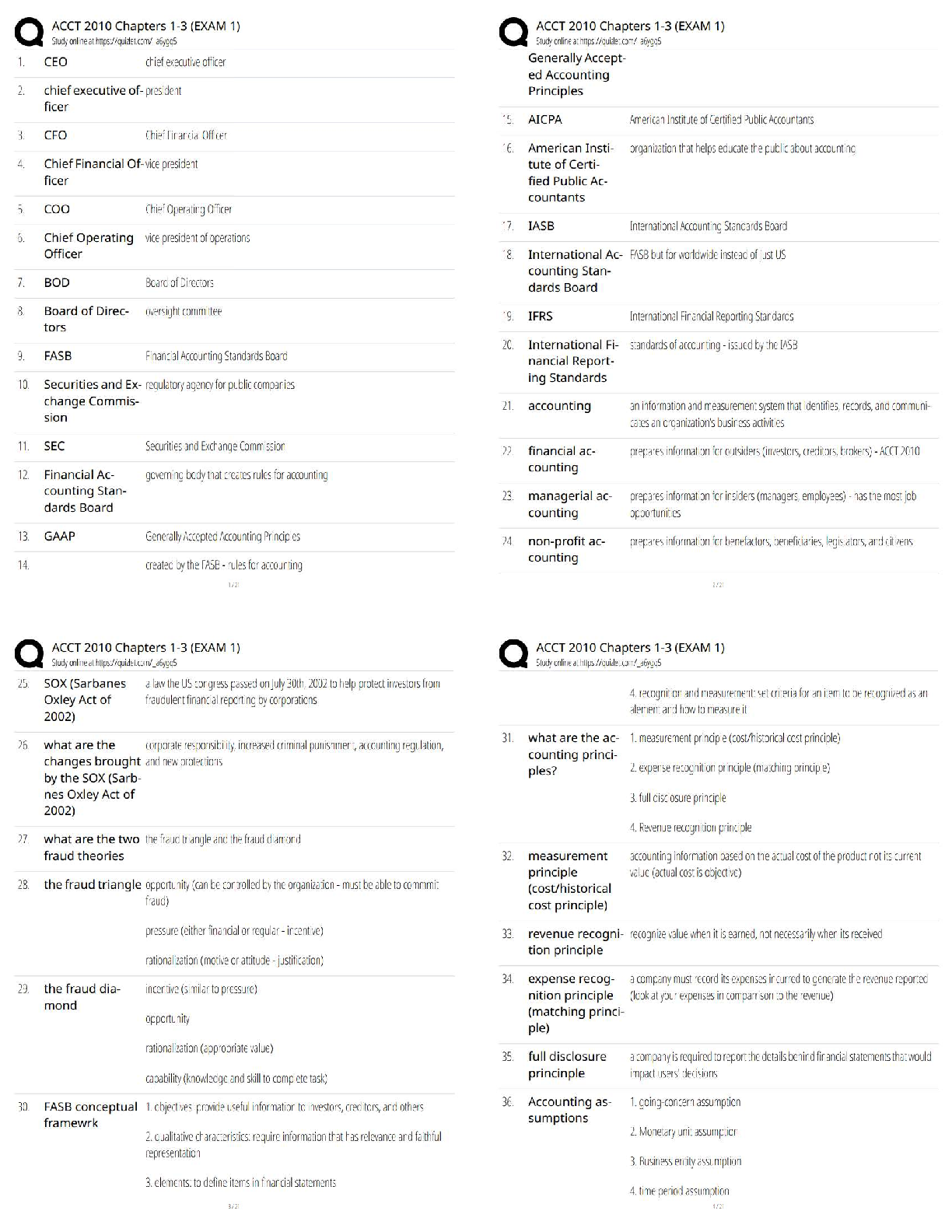
Peer Ratings ✔✔Technique of evaluating anonymous programs in terms of their overall quality,
maintainability, extensibility, usability, and clarity. The purpose of the technique is to provide
programmer self-evaluation.
Code Inspections ✔✔Code-oriented - Error identification
· Data Reference
· Data Declaration
· Computation
· Comparison
· Control-Flow
· Interface
· Input/Output
Desk Checking ✔✔Unproductive, undisciplined
Walkthroughs ✔✔Code-oriented
Jakob Nielsen ✔✔E=100*(1-L)^n)
where:
E = percent of errors found n = number of testers
L = percent of usability problems found by a tester
Module Testing ✔✔You need two types of information when designing test cases for a module
test: a specification for the module and the module's source code. The specification typically
defines the module's input and output parameters and its function.
Incremental ✔✔modules are tested in steps
Top-down - start at main entry point
Bottom-up - start with terminal node modules
Top-down ✔✔start at main entry point
Bottom-up ✔✔start with terminal node modules
Function test is ✔✔to show that a program does not match its external specifications.
Module test is ✔✔to find discrepancies between the program's modules and their interface
specifications.
System test is ✔✔to show that the product is inconsistent with its original objectives.
Logic coverage ✔✔Tests that exercise all decision point outcomes at least once, and ensure that
all statements or entry points are executed at least once.
Equivalence partitioning ✔✔Defines condition or error classes to help reduce the number of finite
tests. Assumes that a test of a representative value within a class also tests all values or conditions
within that class.
Boundary value analysis. ✔✔Tests each edge condition of an equivalence class; also considers
output equivalence classes as well as input classes.
Cause-effect graphing ✔✔Produces Boolean graphical representations of potential test case results
to aid in selecting efficient and complete test cases.
Error guessing ✔✔Produces test cases based on intuitive and expert knowledge of test team
members to define potential software errors to facilitate efficient test case design.
[Show More]
.png)

.png)