Human Resource Management > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > SHRM-CP 2021 Questions and Answers Already Passed.2022/2023, updates (All)
SHRM-CP 2021 Questions and Answers Already Passed.2022/2023, updates
Document Content and Description Below
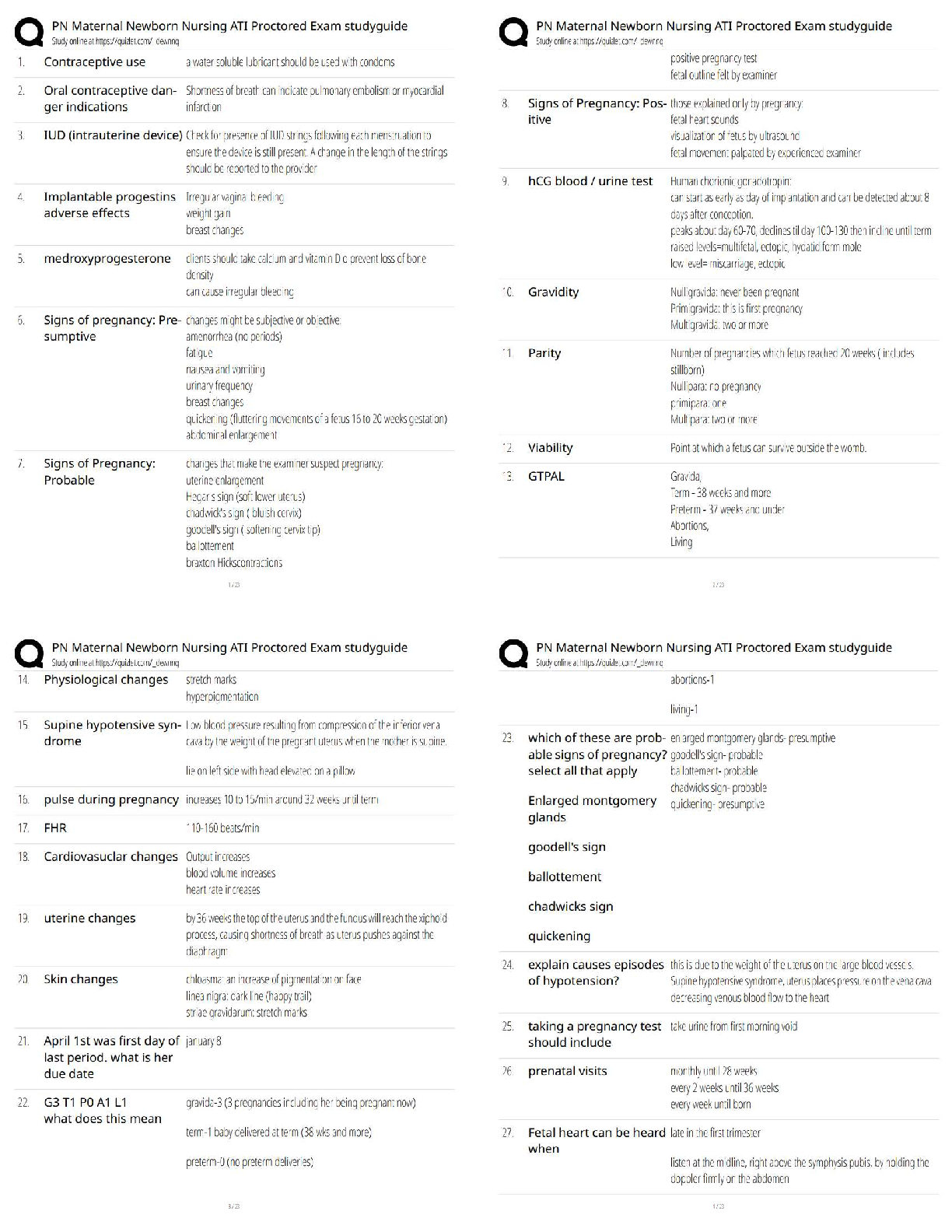
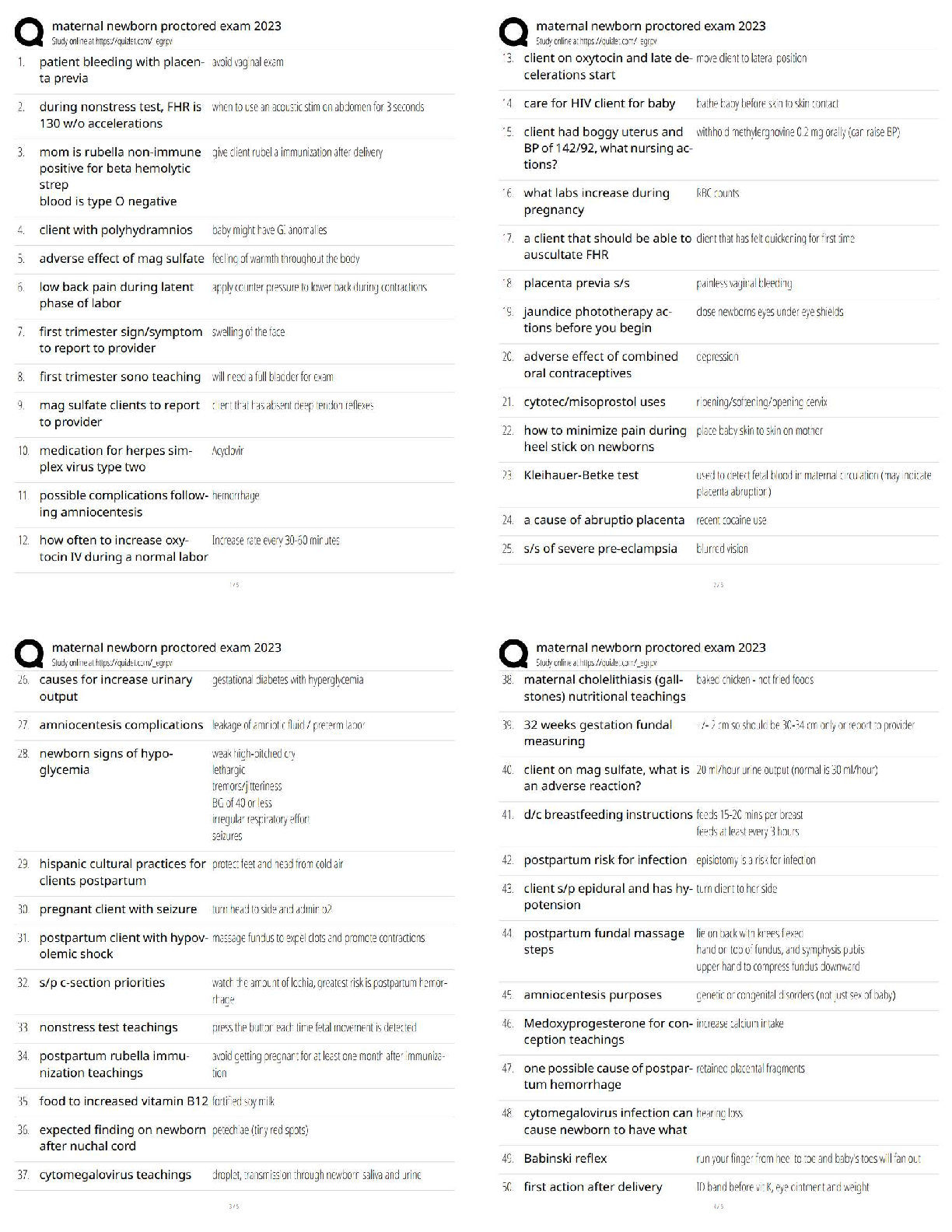
SHRM-CP 2021 Questions and Answers Already Passed PESTLE ✔✔Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental Globalization ✔✔web of interconnectedness or the movement of peop ... le (labor) and knowledge (technology) across borders Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) ✔✔the investment of foreign assets into domestic structures, equipment, and organizations Global Remittances ✔✔Monies sent back home by migrants working in foreign countries. Diaspora ✔✔A mass migration of a group from its homeland to multiple destinations Demographic Dichotomy ✔✔Workforce in emerging countries becoming disproportionately young, but in developing countries, aging rapidly. Reverse Innovation ✔✔Innovations created for or by emerging-economy markets and then imported to developed-economy markets. hyperconnectivity ✔✔increasing digital interconnection of people—and things—anytime and anyplace pushes and pulls ✔✔Organizations have been pushed toward globalization in reaction to changes in the business environment. They have been pulled toward change through the promise of achieving greater organizational value through globalization.globalization push factors ✔✔A need for new markets; Increased cost pressures and competition; Shortfalls in natural resources and talent supply; Government policies; Trade agreements; A globalized supply chain tax inversion, aka expatriation ✔✔seeking to avoid higher corporation taxation rates by acquiring foreign-based competitors and then moving headquarters to their acquisition's home base globalization pull factors ✔✔Greater strategic control; Government policies that promote outward foreign investment; Trade agreements Turnkey Operation ✔✔An existing facility and its operations are acquired and run by the purchaser without major changes Greenfield Operation ✔✔Building a new operation from the ground up Brownfield Operation ✔✔Repurposing an existing disused facility Perlmutter's four orientations for multinational corporations ✔✔Ethnocentric, Polycentric, Regiocentric, Geocentric Ethnocentric ✔✔Headquarters maintains tight control over subsidiaries, who are expected to follow strategic pattern, values, policies, and practices expressed by headquarters; "one best way" Polycentric ✔✔Subsidiaries are allowed a large measure of independence as long as they are profitable; "many best ways" Regiocentric ✔✔Subsidiaries are grouped into regions (Such as North America, Europe and Asia Pacific) Communication and coordination are high within the region but not as high between the region and headquarters.Geocentric ✔✔Subsidiaries are neither satellites taking orders nor independent bodies setting their own course. Headquarters and subsidiaries are participants in a network, each contributing to its unique expertise; "a team way" global integration and local responsiveness ✔✔Organizational continuum strategies to meet the needs of customers and expand their growth opportunities. global integration ✔✔Emphasizes consistency of approach, standardization of processes, and a common corporate culture across global operations local responsiveness ✔✔Emphasizes adapting to the needs of local markets and allows subsidiaries to develop unique products, structures, and systems. Market, Cost, Governmental, Competitive ✔✔Four drivers that determine an organization's choice of whether to emphasize global integration or local responsiveness Assignees ✔✔Employees who work outside their home countries. Global, Transnational, International, Mulitdomestic ✔✔Matrix that describes ways in which an organization can combine GI and LR elements into a single globalization strategy International Strategy ✔✔strategy that is low in global integration - in that there is little pressure to increase efficiency - and also low in local responsiveness - in that there is little advantage in tailoring products or services to individual foreign markets; suits organizations with strong global brand identity or very specialized products or services that enjoy weak local competition Multidomestic Strategy ✔✔organizations with subsidiaries in multiple countries that operate with a fair degree of independence from each other and from headquarters, which remains in the home country; decentralized federations; portfolio of independent businesses; low in GI and high in LRGlobal Strategy ✔✔high in GI but low on the LR scale; the headquarters (which may or may not be in the originating country) maintains a strong relationship with each subsidiary, integrating operations to take advantage of conditions in subsidiary markets, such as inexpensive labor or materials, and standardizing its products or services "hub and spoke" - the centralized hub makes key strategic decisions and exerts tight but simple controls on subsidiaries Transnational organizational structure ✔✔Strong links between headquarters and subsidiaries and among subsidiaries; high GI and high LR Glocalization ✔✔an organization with a strong global image but equally strong local identity Upstream Strategies ✔✔Decisions made at HQ-workforce alignment, organizational development, knowledge and experience sharing. Downstream Strategies ✔✔Decisions make at local level. Identity Alignment ✔✔Extent to which diversity is embraced in management of people, products/services, and branding. Process Alignment ✔✔Extent to which underlying operations such as IT, finance, or HR integrate across locations. outsourcing ✔✔A practice where a company transfers portions of work (e.g. processes or production) to outside suppliers rather than completing it internally. Offshoring ✔✔The practice of relocating processes or productions to another country; historically, has largely involved movement from developed countries to distant developing countries.Onshoring ✔✔Refers to the relocation of business processes or production to a lower-cost location inside the same country as the business; sometimes called "home-shoring."; can also include where businesses allow employees to work from home. Near-shoring ✔✔Refers to a company contracting a part of its business processes or production to an external company located in a country that is relatively close (e.g. within its own region). International Assignee (IA) ✔✔an employee who is being reassigned to an international jurisdiction; traditional expatriates on full relocation assignments lasting from one to three years. Expat ✔✔Generally refers to anyone who is not a citizen of the country in which they reside and doesn't intent to become a permanent resident. Globalists ✔✔Spend their entire careers in international assignments, moving from one locale to another Local Hires ✔✔Hired locally in subsidiary countries (and are also known as HCs, host-country nationals) Short-term assignees ✔✔On assignment for less than a year but more than a few weeks, often without moving the family Commuters ✔✔Travel across a country border for work regularly. Just-in-time expatriates ✔✔These are ad hoc or contract expatriates, who are hired from outside the firm just as they are needed and just for one assignment. Global Assignment Process ✔✔Stage 1: Assessment and selection Stage 2: Management and assignee decision Stage 3: Pre-departure and preparationStage 4: On assignment Stage 5: Completing the assignment Repatriation ✔✔involves reintegrating the employee back into the home country after an international assignment Redeployment ✔✔Process by which an organization moves an employee out of an international assignment; can involve moving back to the home country, moving to a different global location, or moving to a new location or position in the current host country. Diversity ✔✔the similarities and differences between individuals, accounting for all aspects of one's personality and individual identity Diversity of thought ✔✔view that focuses on valuing the unique perspectives individuals bring to an organization Principle of Equal Opportunity ✔✔where the employer needs to provide a level playing field for all groups and minorities without discrimination Principle of Reservation ✔✔where laws mandate a percentage quota or other special considerations for specified minority or ethnic groups Equity ✔✔refers to a focus on promoting fairness and justice via organizational structure, distinct from the notion of equality; the goal is to use the available support systems to ensure everyone ends up at the same level Four-Layer Model of Diversity Dimensions ✔✔Organizational Dimensions External Dimensions Internal Dimensions PersonalityEmployee Resources Groups (ERGs) ✔✔voluntary groups for employees who share a particular diversity dimension Inclusion ✔✔Extent to which each person in an organization feels welcomed, respected, supported, and valued as a team member. Covering ✔✔defensive behavior that occurs when an organization recruits a diverse workforce, but consciously or otherwise, promotes assimilation rather than inclusion; "you are welcome despite of who you are, not because of who you are" similarity bias ✔✔tends to reward (with assignments, promotions, etc.) people who share the same traits DEI Strategic Process ✔✔1. Executive Commitment 2. Preliminary Assessment 3. Infrastructure Creation 4. System Changes 5. Training 6. Measurement and Evaluation 7. Evolution and Integration diversity council ✔✔Task force created to define a diversity and inclusion initiative and guide the development and implementation process. Risk Management ✔✔The identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks and the application of resources, to minimize, monitor, and control their probability and impact. moral hazar ✔✔that alignment and balance (not just alignment) between an organization's goals and associated risks is a necessary requirement for a sustainable business modelantifrag ✔✔the ability to not just withstand high-impact events or shocks, but to improve and benefit from them black swan events ✔✔incidents that describe highly improbable but high-impact events ERM Framework - Risk Categories ✔✔Strategy Operations Financial Reporting Compliance risk position ✔✔An organization's desired gain or acceptable loss in value. Risk Appetite & Risk Tolerance ✔✔the amount of uncertainty the organization is willing to pursue or to accept to attain its risk management goals Appetite= acceptable or not Tolerance = defined range Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) ✔✔Expected monetary loss every time a risk occurs; calculated by multiplying asset value by exposure factor. Annualized ✔✔Expected monetary loss for an asset due to a risk over a one-year period. It is calculated by multiplying single loss expectancy (SLE) by an annualized rate of return (ARO) moral hazard ✔✔Exists when one party engages in risky behavior knowing that it is protected against risk because another party will incur the resulting loss. principal-agent ✔✔An economic concept often associated with moral hazard in employment; the problem arises when an agent (such as an employee) makes decisions or takes actions on behalf ofa principal (an employer or owner) but has personal incentives that may not align with those of the principal. conflict of interest ✔✔a person or organization has the potential to be influenced by two opposing sets of incentives, is exemplified in both moral hazard and the principal-agent dilemma risk control ✔✔An action taken to manage a risk. Duty of Care ✔✔The organizations should take all the steps that are reasonably possible to ensure the health, safety, and well-being of employees and protect them from foreseeable injury hazard ✔✔defined as the potential for harm, often associated with a condition or activity that, if left uncontrolled, can result in injury or illness Risk Level Equation ✔✔Probability of occurrence x Magnitude of impact risk scorecard ✔✔Tool used to gather individual assessments of various characteristics of risk (e.g., frequency of occurrence, degree of impact/loss/gain for the organization, degree of efficacy of current controls). event probability ✔✔how likely a risk was to occur speed of onset ✔✔how quickly a risk would materialize if it occurred existing mitigation ✔✔how well the organization if currently prepared for a risk severity of impact ✔✔the possible effects if the risk event occursrisk matrix ✔✔a simple grid in which the horizontal axis represents the probability that an event will occur and the vertical axis relates to the severity of the impact on the organization or function if the event occurs Prepare, Act, Park and Adapt ✔✔PAPA model - risk prioritization matrix Key risk indicators (KRIs) ✔✔Metrics that provide an early signal of increasing risk exposures in the various areas of an enterprise. Secondary Risk ✔✔A risk that arises as a direct result of implementing a risk response. Residual Risk ✔✔Amount of uncertainty that remains after all risk management efforts have been exhausted. contingency plan ✔✔Protocol that an organization implements to respond to an unplanned but identified risk event. after-action debrief ✔✔it is usually applied to meetings to examine the effectiveness of a risk response strategy, such as workplace evacuations, in-place lockdowns for security reasons, a workplace injury or act of violence whistleblowing ✔✔the act of an employee exposing an employer's wrongdoing to outsiders, such as the media or government regulatory agencies Quality Assurance ✔✔the actions an organization takes to be sure that it is performing work according to the standards it has set and that it is using specified processes correctly and completely Corporate Social Responsibility ✔✔the organization's commitment to operate in an ethical and sustainable manner, by engaging in activities that promote and support philanthropy, transparency, sustainability, and ethically sound governance practicesTriple Bottom Line ✔✔recognition of the need for organizations to improve the state of people, the planet, and profit (economic, environment, social) simultaneously if they are to achieve sustainable, long-term growth Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) ✔✔A non-profit organization that works toward a sustainable global economy by providing guidance in sustainability reporting. social audit ✔✔a systematic evaluation of an organization's progress toward implementing socially responsible and responsive programs compliance ✔✔being in accordance with all national, federal, regional, or local laws, regulations and government authority requirements for all the locations in which the organization operates Ethics ✔✔a set of behavioral guidelines that an organization expects all of its directors, managers, and employees to follow to ensure appropriate moral and ethical business standards Ethical Universalism ✔✔Concept that argues that there are fundamental ethical principles that apply across cultures and that organizations must apply these principles when making decisions in a country, without regard to local ethical norms. cultural relativism ✔✔argues that ethical behavior is determined by local culture, laws, and business practices Governance ✔✔System of rules and processes an organization puts in place to ensure its compliance with local and international laws, accounting rules, ethical norms, and its own codes of conduct. sustainability sweet spot ✔✔that place where an action can fulfill expectations in all three categories: it benefits people, the environment, and the organization's budgetshared values ✔✔resolves what had been viewed as conflicting sets of values - corporate financial goals on one hand and societal and environmental concerns on the other Global Reporting Initiative Sustainability Reporting Standards (GRI Standards) ✔✔a universally accepted standard for reporting the results of an organization's sustainability programs ISO 26000 ✔✔the international standard developed to help organizations effectively assess and address those social responsibilities that are relevant and significant to their mission and vision; operations and processes; customers, employees, communities, and other stakeholders; and environmental impact. Consititution ✔✔the highest law in the country and the foundation on which all U.S. law has been built; defines the powers of the different federal government branches (executive, legislative, judicial) and how these entities operate and interrelate; provides basic principles such as fundamental freedoms and rights Statutes ✔✔actions passed by legislative bodies, such as Congress and state legislatures, and by local government units, such as cities and counties Regulations ✔✔proposed, adopted, and enforced by administrative agencies to whom government units have delegated specific rule-making authority; reflect how lows will be implemented and often have the force of law; they may have just as profound an effect on organizations as laws Agency Guidelines ✔✔Administrative agencies may also issue guidelines that interpret how laws and regulations will be enforces Executive Orders ✔✔Directives by the chief executive of a governmental unit (e.g. the president of the US) telling that governmental unit how it will act or interact with members of its community.Common Law ✔✔A legal system based on custom and court decisions, rather than statutory law, and is recognized on the federal level and in whole or in part in nearly all states. Amendment ✔✔Modification of the U.S. Constitution or a U.S. law. Bill ✔✔a proposed law presented to a legislative body for possible enactment to a statute Public comment period ✔✔Time allowed for the public to express its views and concerns regarding an action of an administrative agency. Regulation ✔✔a rule or order issued by an executive authority or regulatory agency of a government and having the force of law Veto ✔✔Action of rejecting a bill or statute Employment practices liability insurance (EPLI) ✔✔Type of liability insurance covering an organization against claims by employees, former employees, and employment candidates alleging that their legal rights in the employment relationship have been violated. Directors and Officers Liability Insurance ✔✔Insurance that covers a corporation's directors and officers against liability for their wrongful acts covered by the policy and also covers the sums that the insured corporation is required or permitted by law to pay to the directors and officers as indemnification. privileged and confidential ✔✔a discussion between a client and an attorney related to securing legal advice; not subject to the discovery process (in which each party learns the facts about the other side's case) within certain limits protected class ✔✔within the context of equal employment opportunity (EEO), describes people who are covered under a particular federal, state, or local antidiscrimination law1. disparate treatment 2. disparate impact ✔✔Two primary types of discrimination Disparate Treatment ✔✔discrimination which occurs when an applicant or employee is treated differently because of his or her membership in a protected class Disparate Impact (Adverse Impact) ✔✔discrimination that results when a policy that appears to be neutral has a discriminatory effect Civil Rights Act of 1964 ✔✔federal law which outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin national origin ✔✔Refers to the country (including those that no longer exist) of one's birth or of one's ancestors' birth. gender identity ✔✔Refers to one's internal, personal sense of being a man or a woman (or boy or girl), which may or may not be the same as one's sexual assignment at birth. Gender ✔✔Refers to the socially constructed roles, behaviors, activities, and attributes that a given society considers appropriate for men and women. Sex ✔✔classification of people as male or female based on biological characteristics sexual orientation ✔✔the sexual, romantic, or emotional/spiritual attraction that one feels for the persons of the opposite sex or gender, the same sex or gender, or both sexes and more than one genderTitle IV of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 ✔✔it is unlawful to discriminate against any individual based on race, color, religion, sex, and national origin in regard to all terms, conditions, or privileges of employment Bona Fide Occupational Qualification (BFOQ) ✔✔an exception in employment law that permits sex, age, religion, and the like to be used when making employment decisions, but only if they are "reasonably necessary to the normal operation of that particular business." Race can never be one. Equal Employment Opportunity Act of 1972 ✔✔Amended Title VII of Civil Rights Act of 1964 and gave the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission authority to implement its administrative findings and conduct its own enforcement litigation. Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 ✔✔prohibits discrimination against women in employment decisions on the basis of pregnancy, childbirth, and related medical decisions; requires employers to treat pregnancy the same as any other disability Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures ✔✔documents a uniform federal position about prohibiting discrimination in employment practices on the bases of race, color, religion, sex or national origin; covers all aspects of the selection process, including recruiting, testing, interviewing, and performance appraisals (to the extent they are used to make employment decisions) 80% rule or 4/5 rule ✔✔Under the Uniform Guidelines on EE Selection Procedures, adverse impact occurs when the selection rate for an employment decision works to the disadvantage of a protected class. As a rule of thumb, this occurs when the selection rate for the protected class is less than 80% of the rate for the class with the highest selecti [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 62 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

THE SHRM BUNDLE. DIFFERENT VERSIONS OF QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS. 100% COMPREHENSIVE. LATEST PREDICTOR PAPERS. RATED A
ALL YOU NEED TO PASS THE SHRM EXAMS. DIFFERENT VERSIONS. DOWNLOAD FOR EASY REVISION.
By bundleHub Solution guider 3 years ago
$26
19
Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 30, 2022
Number of pages
62
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 30, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
238