BIOS 255 New final Exam study guide 65 MCQ (65X2=130)
Heart
Changes happening in damage to different areas of the heart – right heart failure, lung edema etc membranes that surrounds and protects the heart
structures
...
BIOS 255 New final Exam study guide 65 MCQ (65X2=130)
Heart
Changes happening in damage to different areas of the heart – right heart failure, lung edema etc membranes that surrounds and protects the heart
structures of the heart – atria, ventricles, valves, routes of blood passage through these structures. Blood entering and leaving the heart, pulmonary circulation, systemic circulation
Blood vessels & blood
Types of blood cells, functions of each type, Erythrocytes, leukocytes (all types), thrombocytes/platelets, proerythroblast, megakaryoblast, hematopoiesis,
plasma proteins that play a role in blood clotting Lymphatic system & immunity
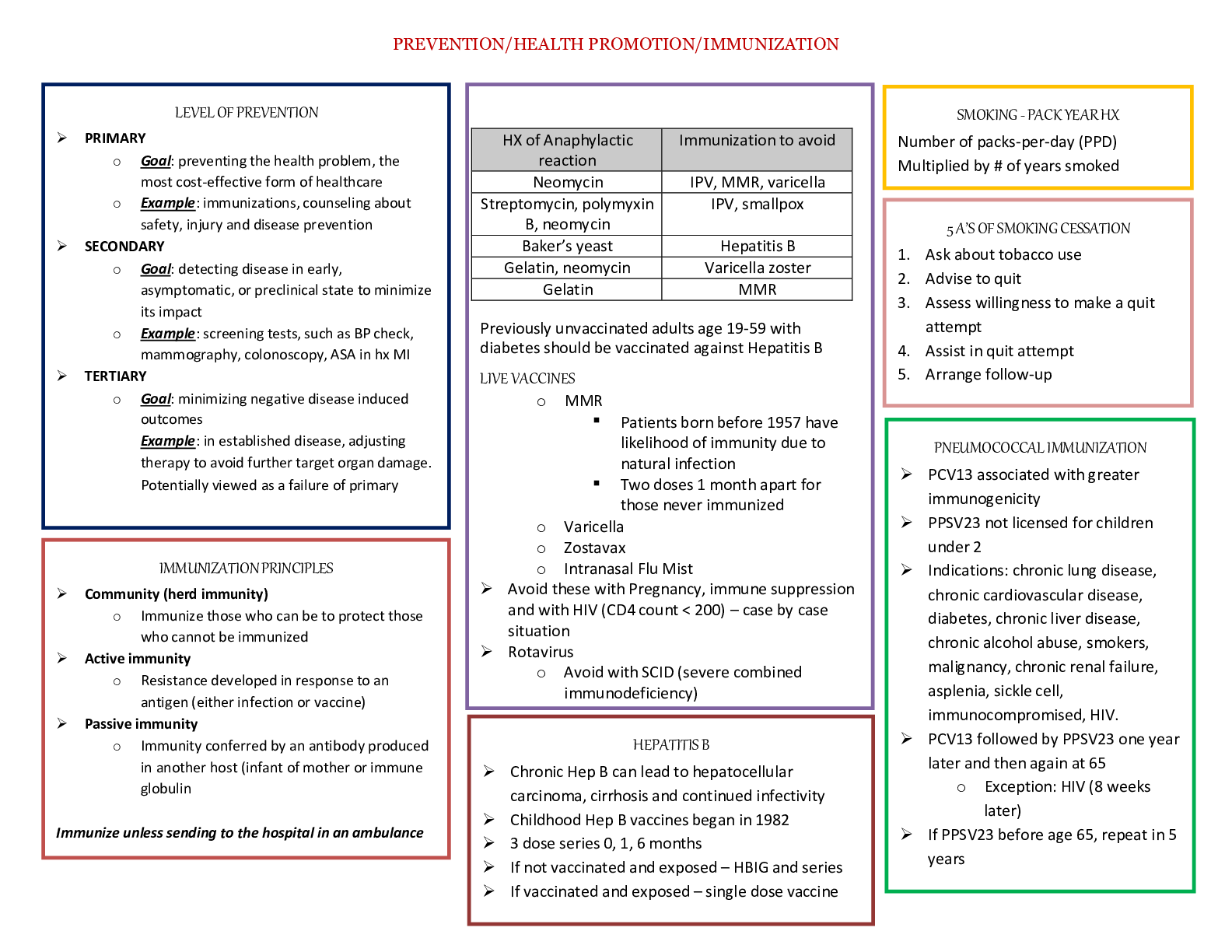
Types of immunity, examples- naturally acquired active immunity, naturally acquired passive immunity, artificially acquired active immunity, artificially acquired passive immunity, naturally acquired innate immunity
Components of the lymphatic system, locations, functions of each component (thymus, spleen, Functions of the lymphatic and immune system, contents of lymph, Cells of the immune system – T & B cells, cytotoxic T cells, Helper T cells, Memory T cells, plasma B cells, Memory B cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells and dendritic cells, Antigen presenting cells, T cell receptors, B cell receptors, CD4+, CD8+, MHC Class I and II antigens presentation on T and B cells
Allergies (types of allergies), acute allergic response, immune responses involving all the types of immune cells, contact dermatitis, positive selection of T cells, B cell formation, maternal antibodies attacking fetal blood cells during a second pregnancy
Antigens, class of antibodies, IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE – where/what body fluids are they found, structures/configuration, functions of each type
Innate & adaptive immunity, active & passive immunity, Primary and secondary immune response, antimicrobial proteins, functions of histamines, perforins, granzymes, cytokines, signs of inflammation, immunodeficiency disease, HIV, membrane attack complexes to eliminate cytolysis in pathogenic cells
Respiratory system & respiration
Structures of the respiratory system - cardiac notch, false vocal cord, terminal bronchiole, oropharynx, thyroid cartilage, bronchial arteries, pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries- functions of these structures, gaseous exchange, the conductive and respiratory portion of respiratory system, Which vessel carries highly oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart, muscles that are important to you when blowing up a balloon, muscles that are important to you when taking a deep breath into your lungs
Inspiration & expiration- muscles involved, neural mechanisms of respiratory control, internal & external respiration, gaseous transport (oxygen and carbon dioxide transport mechanisms), Ferritin, gaseous exchange
cells of the alveoli - Type I alveolar cells, Type II alveolar cells, Type III alveolar cells, their functions lung volumes-vital capacity, residual volume, tidal volume, expiratory reserve capacity
Factors affecting affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and oxygen delivery to tissues,
Sites of gas exchange, direction of the diffusion of gases at the alveoli and tissue, relationship between the pressure and volume of gases, solubility of gases - Dalton’s law, Boyle’s law, Henry’s law
what happens in Asthma, Voice pitch control, Eupnea, 20 SA questions (20X2=40)
Structure labelling - great saphenous vein, popliteal vein, femoral artery, common carotid artery vertebral artery, vena cava, common iliac vein, radial artery, aorta
chambers of the heart, valves, papillary muscles, chordae tendinae
nasal meatuses, uvula, epiglottis, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, trachea, bronchi, carina
This study source was downloaded by 100000849840424 from CourseHero.com on 11-03-2022 07:43:16 GMT -05:00
thoracic duct, thymus, MALT, cisterna chyli, spleen, peyer’s patch, Bone marrow (B-cells formation)
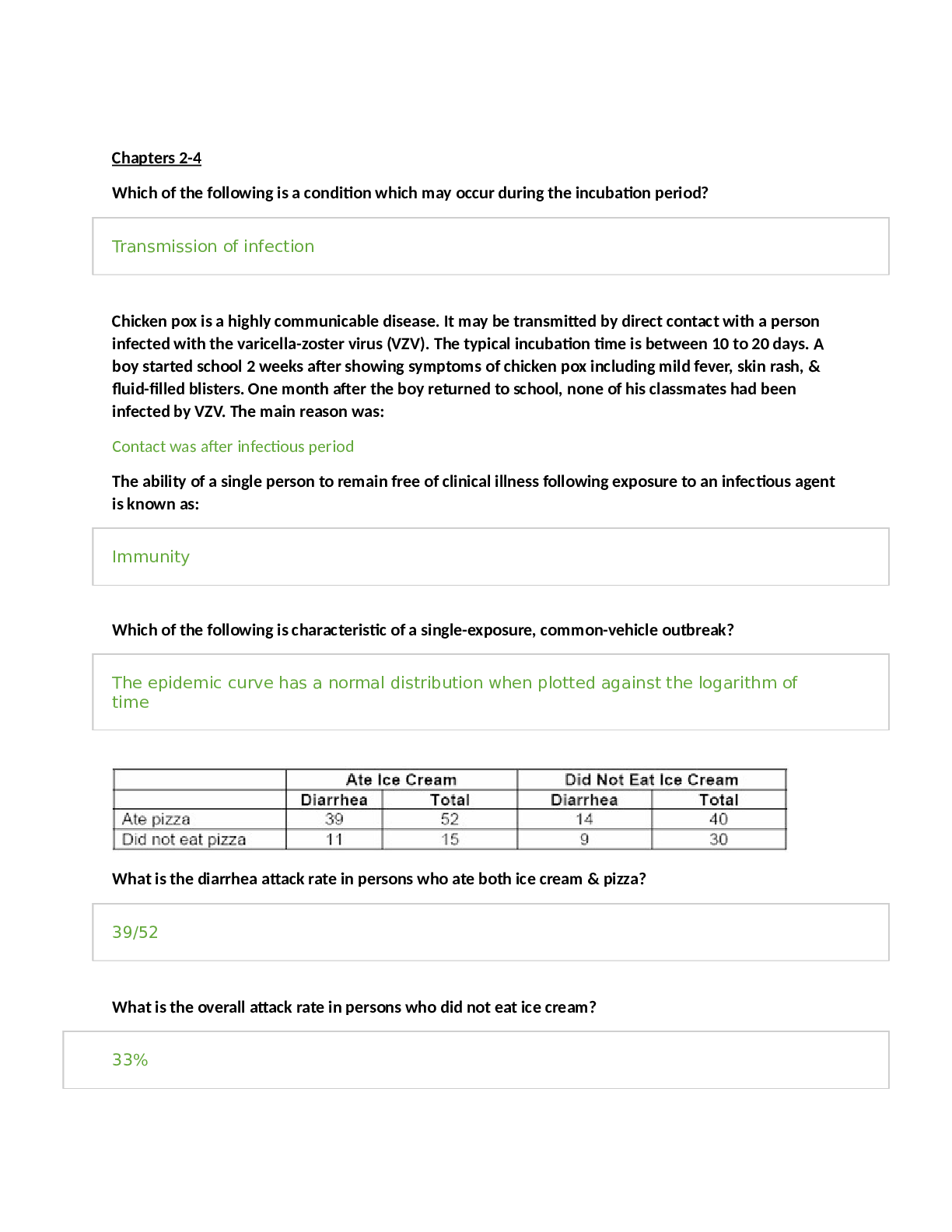
5 Calculations (6X5=30)
Minute ventilation
MV= 12 breath /min X 500 = 6 liters/min (minute ventilation ) Respiration Rate :
Tidal Volume - Anatomic Dead Space * numbers of breaths
ex: (500-150mL)*12 = 4,200mL/min350ml/breath X 12 breath per min = 4200 ml/min Tidal Volume
The volume of air inhaled and exhaled in a normal, resting breath - 500 mL. heart rate from ECG tracing=???
Cardiac cycle= 60sec/ any heart rate she gives Mean Arterial Pressure= 1/3(SBP-DBP)+ DBP Stroke volume = EDV- ESV
Ejection volume= ( SV / EDV)100 Pulse pressure = Systolic – diastolic 2 Long answer essay (2X15=30)
(A) Describe the innate and adaptive immune systems, how they work and how they interact.
(B) Explain the similarities and differences between primary and secondary responses of the adaptive immune system
(C) List and briefly describe the major functions of the various subclasses of T-cells.
(D) Explain the various subclasses of antibodies - how they are similar, how they differ.
A) Define ventialtion, external respiration and internal respiration. Be sure to identify their functions and where they occur.
(B) Explain the neural control of ventilation including brain centers, sensory and motor signals.
(C) Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood with a special emphasis on the factors that affect the loading/unloading of these gases in the lungs vs. tissues.
[Show More]
.png)

.png)