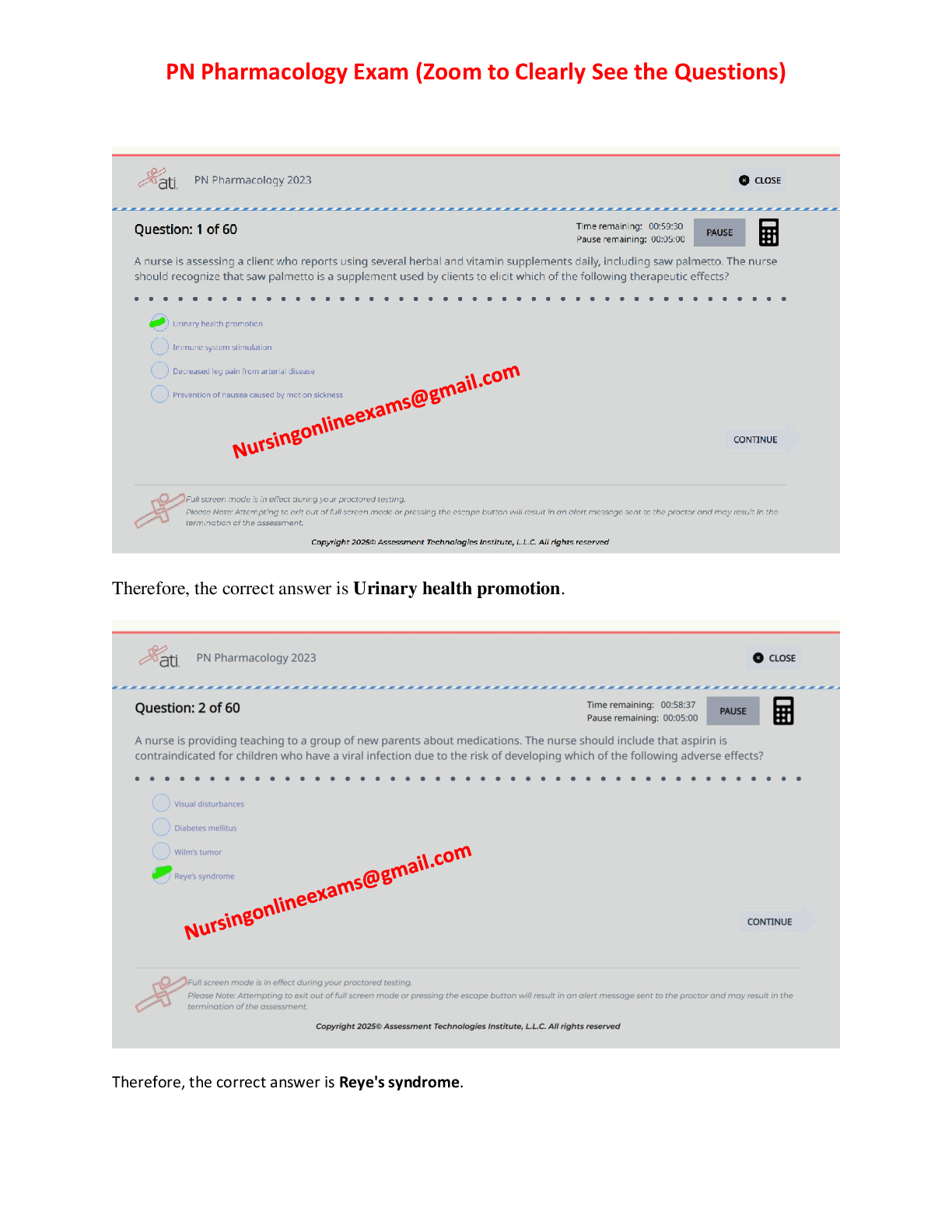
Which of the following is not a benefit associated with the FASB Conceptual Framework
Project?
a. A conceptual framework should increase financial statement users' understanding of
and confidence in financial reportin
...
Which of the following is not a benefit associated with the FASB Conceptual Framework
Project?
a. A conceptual framework should increase financial statement users' understanding of
and confidence in financial reporting.
b. Practical problems should be more quickly solvable by reference to an existing
conceptual framework.
c. A coherent set of accounting standards and rules should result.
d. Business entities will need far less assistance from accountants because the financial
reporting process will be quite easy to apply.
Generally accepted accounting principles
a. are fundamental truths or axioms that can be derived from laws of nature.
b. derive their authority from legal court proceedings.
c. derive their credibility and authority from general recognition and acceptance by the
accounting profession.
d. have been specified in detail in the FASB conceptual framework.
A soundly developed conceptual framework of concepts and objectives should
a. increase financial statement users' understanding of and confidence in financial
reporting.
b. enhance comparability among companies' financial statements.
c. allow new and emerging practical problems to be more quickly solved.
d. All of these answer choices are correct.
What is a purpose of having a conceptual framework?
a. To make sure that economic activity can be identified with a particular legal entity.
b. To segregate activities among different companies.
c. To provide comparable information for different companies.
d. To enable the profession to more quickly solve emerging practical problems and to
provide a foundation from which to build more useful standards.
Which of the following is not true concerning a conceptual framework in accounting?
a. It should be a basis for standard-setting.
b. It should allow practical problems to be solved more quickly by reference to it.
c. It should be based on fundamental truths that are derived from the laws of nature.
d. All of these answer choices are true.
In the conceptual framework for financial reporting, what provides "the why"--the purpose
of accounting?
a. Recognition, measurement, and disclosure concepts such as assumptions, principles,
and constraints
b. Qualitative characteristics of accounting information
c. Elements of financial statements
d. Objective of financial reporting
The underlying theme of the conceptual framework is
a. decision usefulness.
b. understandability.
c. faithful representation.
d. comparability.
The objective of general-purpose financial reporting is to provide financial information
about a reporting entity to each of the following except
a. potential equity investors.
b. potential lenders.
c. present investors.
d. All of these answers are correct.
The objective of general-purpose financial reporting is?
a. to provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful to present and
potential equity investors, lenders, and other creditors in making decisions in their
capacity as capital providers
b. to provide companies with the option to select information that favors one set of
interested parties over another
c. to provide users with financial information that implies total freedom from error.
d. to provide a metric for financial information used to determine when the boundary
between two or more entities should be disregarded and the entities considered to be
a licensing arrangement.
If the LIFO inventory method was used last period, it should be used for the current and
following periods because of
a. consistency.
b. materiality.
c. timeliness.
d. verifiability.
Which of the following is a characteristic describing the fundamental quality of relevance?
a. Predictive value.
b. Neutrality.
c. Verifiability.
d. Understandability
Which of the following is a fundamental quality of useful accounting information?
a. Comparability
b. Relevance
c. Neutrality
d. Materiality
Which of the following is a fundamental quality of useful accounting information?
a. Conservatism
b. Comparability
c. Faithful representation
d. Consistency
What is meant by comparability when discussing financial accounting information?
a. Information has predictive or confirmatory value.
b. Information is reasonably free from error.
c. Information is measured and reported in a similar fashion across companies.
d. Information is timely.
What is meant by consistency when discussing financial accounting information?
a. Information presented by a company applies the same accounting treatment to similar
events, from period to period.
b. Information is timely.
c. Information is classified, characterized, and presented clearly and concisely.
d. Information is verifiable.
Which of the following is an ingredient of relevance?
a. Completeness
b. Neutrality
c. Timeliness
d. Materiality
Which of the following is an ingredient of faithful representation?
a. Predictive value
b. Materiality
c. Neutrality
d. Confirmatory value
Changing the method of inventory valuation should be reported in the financial statements
because of which qualitative characteristic of accounting information?
a. Consistency
b. Verifiability
c. Timeliness
d. Comparability
A company issuing its annual financial reports within one month of the end of the year is
an example of which enhancing quality of accounting information?
a. Comparability
b. Timeliness
c. Understandability
d. Verifiability
What is the quality of information that is capable of making a difference in a decision?
a. Faithful representation
b. Materiality
c. Timeliness
d. Relevance
Neutrality is an ingredient of which fundamental quality of information?
a. Faithful representation
b. Comparability
c. Relevance
d. Understandability
If the FIFO inventory method was used last period, it should be used for the current and
following periods because of
a. relevance.
b. neutrality.
c. understandability.
d. consistency.
The pervasive criterion by which accounting information can be judged is that of
a. decision usefulness.
b. freedom from bias.
c. timeliness.
d. comparability
The two fundamental qualities that make accounting information useful for decision
making are
a. comparability and timeliness.
b. materiality and neutrality.
c. relevance and faithful representation.
d. faithful representation and comparability.
Accounting information is considered to be relevant when it
a. can be depended on to represent the economic conditions and events that it is
intended to represent.
b. is capable of making a difference in a decision.
c. is understandable by reasonably informed users of accounting information.
d. is verifiable and neutral.
The quality of information that means the numbers and descriptions match what really
existed or happened is
a. relevance.
b. faithful representation.
c. completeness.
d. neutrality.
Which of the following does not relate to relevance?
a. Materiality
b. Predictive value
c. Confirmatory value
d. All of these answer choices relate to relevance.
According to Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 8, materiality is an ingredient
of the fundamental quality(ies) of:
Relevance Faithful Representation
a. Yes Yes
b. No Yes
c. Yes No
d. No No
According to Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 8, completeness is an
ingredient of the fundamental quality(ies) of:
Relevance Faithful Representation
a. Yes No
b. Yes Yes
c. No No
d. No Yes
According to Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 8, neutrality is an ingredient
of the fundamental quality(ies) of:
Relevance Faithful Representation
a. Yes Yes
b. No Yes
c. Yes No
d. No No
Neutrality means that information
a. provides benefits which are at least equal to the costs of its preparation.
b. can be compared with similar information about an enterprise at other points in time.
c. would have no impact on a decision maker.
d. cannot favor one set of interested parties over another
The characteristic that is demonstrated when a high degree of consensus can be secured
among independent measurers using the same measurement methods is
a. relevance.
b. faithful representation.
c. verifiability.
d. neutrality.
According to Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 8, predictive value is an
ingredient of the fundamental quality(ies) of:
Relevance Faithful Representation
a. Yes No
b. Yes Yes
c. No No
d. No Yes
Under Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 2, free from error is an ingredient
of the fundamental quality of
Faithful Representation Relevance
a. Yes Yes
b. No Yes
c. Yes No
d. No No
Financial information demonstrates consistency when
a. firms in the same industry use different accounting methods to account for the same
type of transaction.
b. a company changes its estimate of the salvage value of a fixed asset.
c. a company fails to adjust its financial statements for changes in the value of the
measuring unit.
d. None of these answer choices are correct.
Financial information exhibits the characteristic of consistency when
a. expenses are reported as charges against revenue in the period in which they are paid.
b. a company applies the same accounting treatment to similar events, from period to
period.
c. extraordinary gains and losses are not included on the income statement.
d. accounting procedures are adopted which give a consistent rate of net income.
Information about different companies and about different periods of the same company
can be prepared and presented in a similar manner. Comparability and consistency are
related to which of these objectives?
Comparability Consistency
a. Companies Companies
b. Companies Periods
c. Periods Companies
d. Periods Periods
When information about two different enterprises has been prepared and presented in a
similar manner, the information exhibits the characteristic of
a. relevance.
b. faithful representation.
c. consistency.
d. None of these answer choices are correct.
The elements of financial statements include investments by owners. These are increases
in an entity's net assets resulting from owners'
a. transfers of assets to the entity.
b. rendering services to the entity.
c. satisfaction of liabilities of the entity.
d. All of these answer choices are correct.
In classifying the elements of financial statements, the primary distinction between
revenues and gains is
a. the materiality of the amounts involved.
b. the likelihood that the transactions involved will recur in the future.
c. the nature of the activities that gave rise to the transactions involved.
d. the costs versus the benefits of the alternative methods of disclosing the transactions
involved.
A decrease in net assets arising from peripheral or incidental transactions is called a(n)
a. capital expenditure.
b. cost.
c. loss.
d. expense.
One of the elements of financial statements is comprehensive income. As described in
Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts No. 6, "Elements of Financial Statements,"
comprehensive income is equal to
a. revenues minus expenses plus gains minus losses.
b. revenues minus expenses plus gains minus losses plus investments by owners minus
distributions to owners.
c. revenues minus expenses plus gains minus losses plus investments by owners minus
distributions to owners plus assets minus liabilities.
d. None of these answer choices are correct.
Which of the following elements of financial statements is not a component of
comprehensive income?
a. Revenues
b. Distributions to owners
c. Losses
d. Expenses
The calculation of comprehensive income includes which of the following?
Operating Income Distributions to Owners
a. Yes Yes
b. No No
c. No Yes
d. Yes No
According to the FASB conceptual framework, which of the following elements describes
transactions or events that affect a company during a period of time?
a. Assets.
b. Expenses.
c. Equity.
d. Liabilities.
According to the FASB Conceptual Framework, the elementsassets, liabilities, and
equitydescribe amounts of resources and claims to resources at/during a
Moment in Time Period of Time
a. Yes No
b. Yes Yes
c. No Yes
d. No No
Which of the following is not a basic element of financial statements?
a. Assets
b. Balance sheet
c. Losses
d. Revenue
Which of the following basic elements of financial statements is more associated with the
balance sheet than the income statement?
a. Equity
b. Revenue
c. Gains
d. Expenses
Issuance of common stock for cash affects which basic element of financial statements?
a. Revenues
b. Losses
c. Liabilities
d. Equity
Which of these basic elements of financial statements arises from peripheral or incidental
transactions?
a. Assets
b. Liabilities
c. Gains
d. Expenses
Which of the following is not a basic assumption underlying the financial accounting
structure?
a. Economic entity assumption
b. Going concern assumption
c. Periodicity assumption
d. Historical cost assumption
Which basic assumption is illustrated when a firm reports financial results on an annual
basis?
a. Economic entity assumption
b. Going concern assumption
c. Periodicity assumption
d. Monetary unit assumption
Which basic assumption may not be followed when a firm in bankruptcy reports financial
results?
a. Economic entity assumption
b. Going concern assumption
c. Periodicity assumption
d. Monetary unit assumption
Which accounting assumption or principle is being violated if a company provides financial
reports only when it introduces a new product?
a. Economic entity
b. Periodicity
c. Revenue recognition
d. Full disclosure
Which of the following basic accounting assumptions is threatened by the existence of
severe inflation in the economy?
a. Monetary unit assumption
b. Periodicity assumption
c. Going-concern assumption
d. Economic entity assumption
During the lifetime of an entity accountants produce financial statements at artificial points
in time in accordance with the concept of
Relevance Periodicity
a. No No
b. Yes No
c. No Yes
d. Yes Yes
Under current GAAP, inflation is ignored in accounting due to the
a. economic entity assumption.
b. going concern assumption.
c. monetary unit assumption.
d. periodicity assumption.
The economic entity assumption
a. is inapplicable to unincorporated businesses.
b. recognizes the legal aspects of business organizations.
c. requires periodic income measurement.
d. is applicable to all forms of business organizations.
Preparation of consolidated financial statements when a parent-subsidiary relationship
exists is an example of the
a. economic entity assumption.
b. relevance characteristic.
c. comparability characteristic.
d. neutrality characteristic.
During the lifetime of an entity, accountants produce financial statements at arbitrary
points in time in accordance with which basic accounting concept?
a. Cost constraint
b. Periodicity assumption
c. Conservatism
d. Expense recognition principle
What accounting concept justifies the usage of depreciation and amortization policies?
a. Going concern assumption
b. Fair value principle
c. Full disclosure principle
d. Monetary unit assumption
The assumption that a company will not be sold or liquidated in the near future is known
as the
a. economic entity assumption.
b. monetary unit assumption.
c. periodicity assumption.
d. None of these answer choices are correct.
Which of the following is an implication of the going concern assumption?
a. The historical cost principle is credible.
b. Depreciation and amortization policies are justifiable and appropriate.
c. The current-noncurrent classification of assets and liabilities is justifiable and
significant.
d. All of these
Proponents of historical cost ordinarily maintain that in comparison with all other valuation
alternatives for general purpose financial reporting, statements prepared using historical
costs are more
a. verifiable.
b. relevant.
c. indicative of the entity's purchasing power.
d. conservative.
Valuing assets at liquidation values rather than cost is inconsistent with the
a. periodicity assumption.
b. expense recognition principle.
c. materiality constraint.
d. historical cost principle
Revenue is recognized in the accounting period in which the performance obligation is
satisfied. This statement describes the
a. consistency characteristic.
b. expense recognition principle.
c. revenue recognition principle.
d. relevance characteristic.
Generally, revenue from sales should be recognized at a point when
a. management decides it is appropriate to do so.
b. the product is available for sale to the ultimate consumer.
c. the entire amount receivable has been collected from the customer and there remains
no further warranty liability.
d. None of these answer choices are correct.
Revenue generally should be recognized
a. at the end of production.
b. at the time of cash collection.
c. when realized.
d. when the performance obligation is satisfied.
The measurement principle includes the
a. fair value principle only.
b. historical cost principle only.
c. revenue recognition principle and expense recognition principle.
d. historical cost principle and the fair value principle.
Which of the following is commonly referred to as the matching principle?
a. Revenue recognition principle
b. Measurement principle
c. Expense recognition principle
d. Full disclosure principle
Product costs include each of the following except
a. overhead.
b. officer's salaries.
c. material.
d. labor
Recognizing expenses not when a company pays wages, but when the work actually
contributes to revenue in in accordance with the
a. consistency characteristic.
b. expense recognition principle.
c. materiality characteristics.
d. revenue recognition principle.
The accounting principle of expense recognition is best demonstrated by
a. not recognizing any expense unless some revenue is realized.
b. matching effort (expense) with accomplishment (revenue).
c. recognizing prepaid rent received as revenue.
d. establishing an Appropriation for Contingencies account.
Which of the following serves as the justification for the periodic recording of depreciation
expense?
a. Association of efforts (expense) with accomplishments (revenue)
b. Systematic and rational allocation of cost over the periods benefited
c. Immediate recognition of an expense
d. Minimization of income tax liability
Application of the full disclosure principle
a. is theoretically desirable but not practical because the costs of complete disclosure
exceed the benefits.
b. is violated when important financial information is buried in the notes to the financial
statements.
c. is demonstrated by the use of supplementary information explaining the effects of
financing arrangements.
d. requires that the financial statements be consistent and comparable.
Which of the following is an argument against using historical cost in accounting?
a. Fair values are more relevant.
b. Historical costs are based on an exchange transaction.
c. Historical costs are reliable.
d. Fair values are subjective.
When is revenue generally recognized?
a. When cash is received
b. When the warranty expires
c. When production is completed
d. When the company satisfies the performance obligation
Which of the following is a component of the revenue recognition principle?
a. Cash is received and the amount is material.
b. Recognition occurs when the performance obligation is satisfied.
c. Production is complete and there is an active market for the product.
d. Cash is realized or realizable and production is complete.
A company has a performance obligation when it agrees to
a. perform a service for a customer and receives cash payment.
b. sell a product to a customer after receiving payment.
c. perform a service or sell a product to a customer.
d. None of the answer choices are correct
Which of the following is not a required component of financial statements prepared in
accordance with generally accepted accounting principles?
a. President's letter to shareholders.
b. Balance sheet.
c. Income statement.
d. Notes to financial statements
What is the general approach as to when product costs are recognized as expenses?
a. In the period when the expenses are paid
b. In the period when the expenses are incurred
c. In the period when the vendor invoice is received
d. In the period when the related revenue is recognized
Not adjusting the amounts reported in the financial statements for inflation is an example
of which basic assumption or principle of accounting?
a. Economic entity
b. Going concern
c. Monetary unit
d. Full disclosure
Recognition of amortization of an intangible asset illustrates which principle of
accounting?
a. Expense recognition
b. Full disclosure
c. Revenue recognition
d. Historical cost
When should an expenditure be recorded as an asset rather than an expense?
a. Never
b. Always
c. If the amount is material
d. When future benefit exists
Which accounting assumption or principle is being violated if a company reports its
corporate headquarter building at its fair value on the balance sheet?
a. Going concern
b. Monetary unit
c. Historical cost
d. Full disclosure
Which accounting assumption or principle is being violated if a company is a party to
major litigation that it may lose and decides not to include the information in the financial
statements because it may have a negative impact on the company's stock price?
a. Full disclosure.
b. Going concern.
c. Historical cost.
d. Expense recognition.
Which assumption or principle requires that all information significant enough to affect
decisions of reasonably informed users should be reported in the financial statements?
a. Matching.
b. Going concern.
c. Historical cost.
d. Full disclosure.
A company has a factory building that originally cost the company $250,000. The current
fair value of the factory building is $3 million. The president would like to report the
difference as a gain. The write-up would represent a violation of which accounting
assumption or principle?
a. Revenue recognition
b. Going concern
c. Historical cost
d. Monetary unit
Which of the following is a constraint in presenting financial information?
a. Cost
b. Full disclosure
c. Relevance
d. Consistency
All of the following represent costs of providing financial information except
a. processing/preparing.
b. disseminating.
c. accessing capital.
d. auditing.
Which of the following is a benefit of providing financial information?
a. Potential litigation
b. Auditing
c. Disclosure to competition
d. Improved allocation of resources
Materiality is used in all of the following situations of providing financial information,
except
a. where an amount is of relative large size and importance.
b. where it would impact the judgment of a reasonable person.
c. where it would not make a difference in the actions of a decision maker.
d. where omission of the information would result in bias.
. What is prudence or conservatism?
a. Understating assets and net income
b. When in doubt, recognizing the option that is least likely to overstate assets and
income
c. Recognizing the option that is least likely to overstate assets and income
d. Recognizing revenue when earned and realized
Expensing the cost of copy paper when the paper is acquired is an example
a. materiality.
b. expense recognition.
c. conservatism.
d. industry practices.
Which of the following statements concerning the cost-benefit relationship is not true?
a. Business reporting should exclude information outside of management's expertise.
b. Management should not be required to report information that would significantly harm
the company's competitive position.
c. Management should not be required to provide forecasted financial information.
d. If needed by financial statement users, management should gather information not
included in the financial statements that would not otherwise be gathered for internal
use.
Which of the following relates to both relevance and faithful representation?
a. Cost constraint
b. Predictive value
c. Verifiability
d. Neutrality
Expensing the cost of a wastebasket with an estimated useful life of 10 years when
purchased is an example of the application of the
a. consistency characteristic.
b. expense recognition principle.
c. materiality ingredient.
d. historical cost principle.
Which of the following statements about materiality is correct?
a. An item must make a difference or it need not be disclosed.
b. Materiality is a matter of relative size or importance.
c. An item is material if its inclusion or omission would influence or change the judgment
of a reasonable person.
d. All of these answers are correct.
Which of the following is considered a pervasive constraint by Statement of Financial
Accounting Concepts No. 8?
a. Comparability
b. Timeliness
c. Verifiability
d. Cost constraint
The cost constraint is also referred to as the
a. cost-benefit relationship.
b. materiality quality.
c. monetary unit assumption.
d. measurement principle.
The second level of the conceptual framework includes each of the following except
a. elements.
b. principles.
c. enhancing qualities.
d. fundamental qualities.
Trade-offs between the characteristics that make information useful may be necessary or
beneficial. Issuance of interim financial statements is an example of a trade-off between
a. relevance and faithful representation.
b. faithful representation and periodicity.
c. timeliness and materiality.
d. understandability and timeliness.
Allowing firms to estimate rather than physically count inventory at interim (quarterly)
periods is an example of a trade-off between
a. verifiability and faithful representation.
b. faithful representation and comparability.
c. timeliness and verifiability.
d. neutrality and consistency.
The third level of the conceptual framework does not include
a. assumptions.
b. constraint.
c. elements.
d. principles.
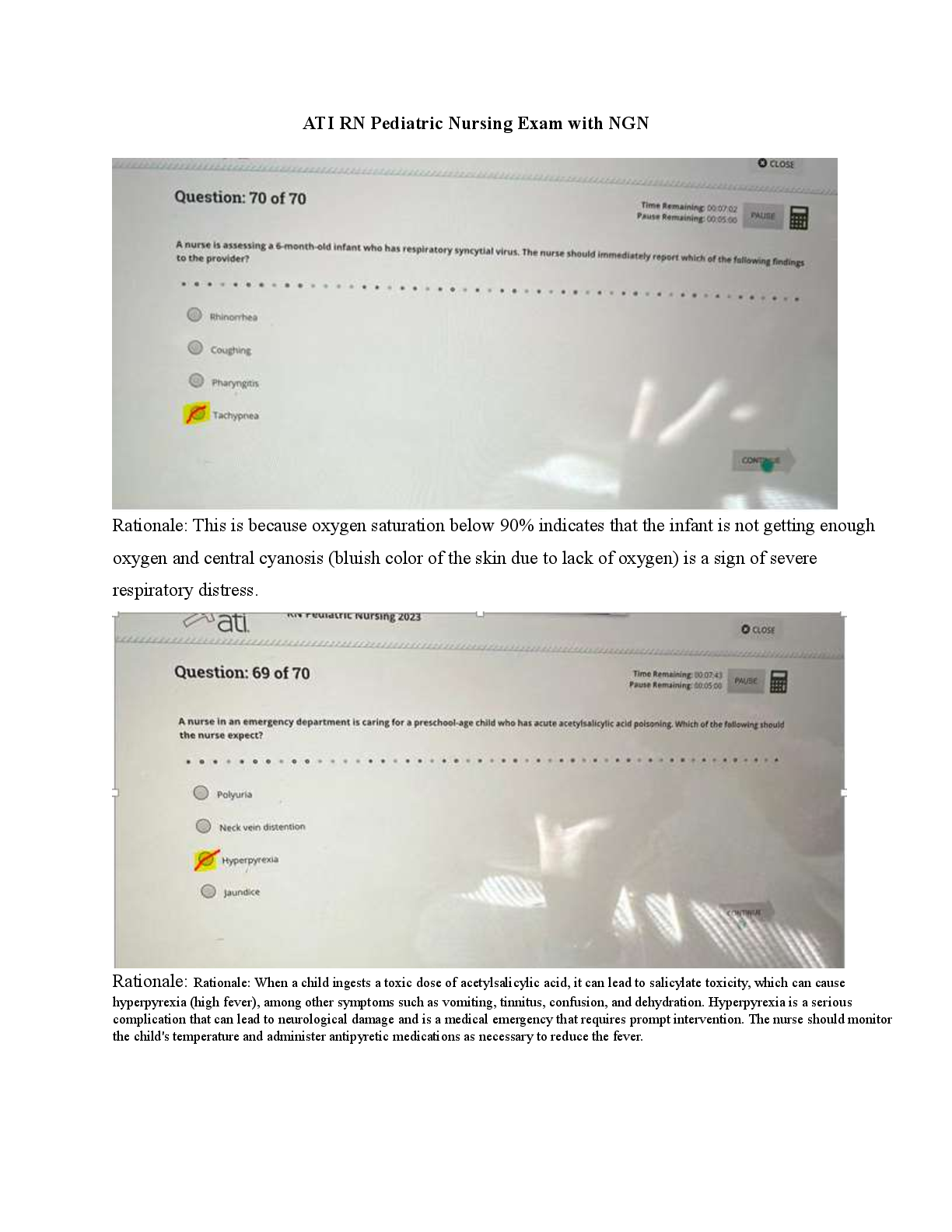
[Show More]
.png)


.png)
.png)


 (Q&A).png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)