*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ACE Personal Trainer Exam Prep 195 Questions with preceding answers. Graded A+ (All)
ACE Personal Trainer Exam Prep 195 Questions with preceding answers. Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
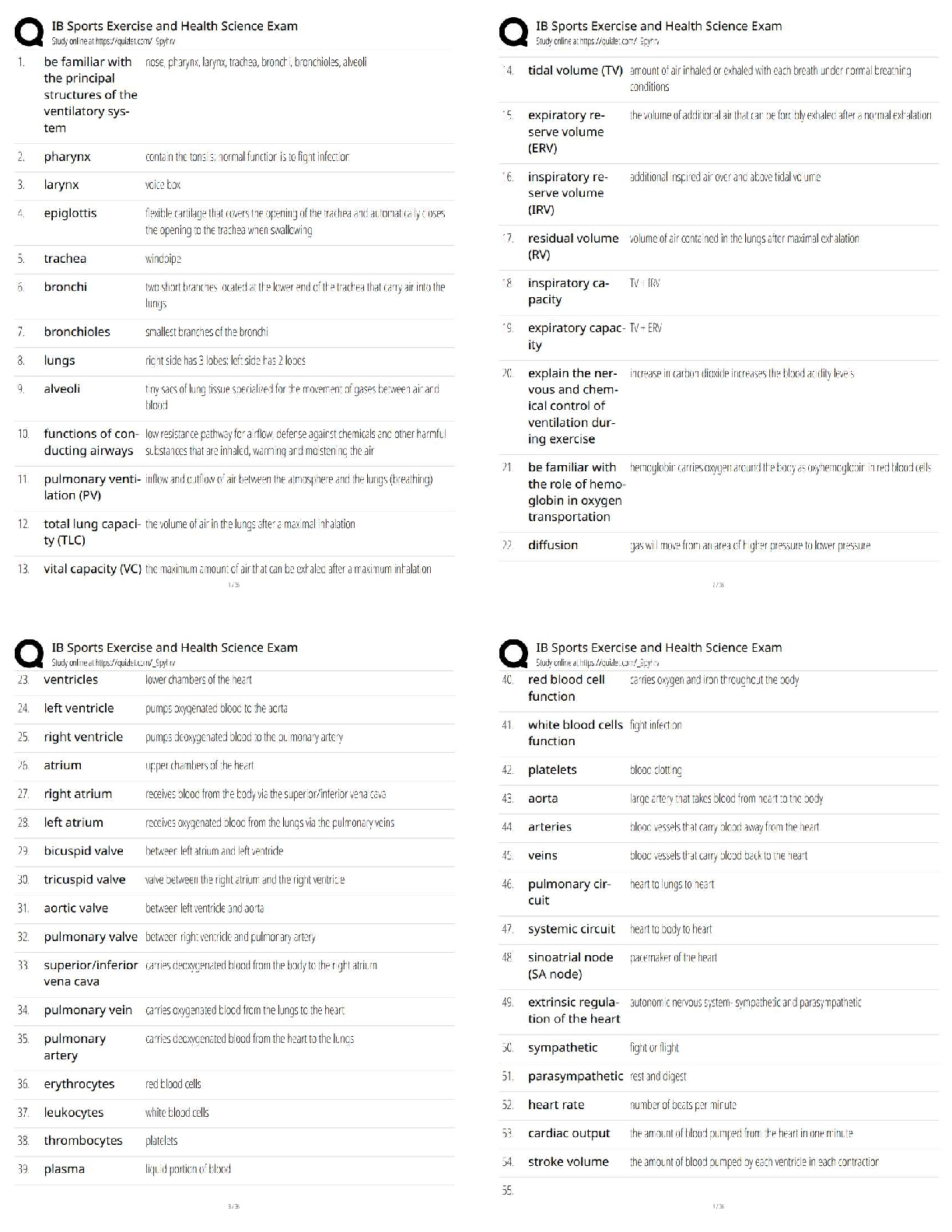
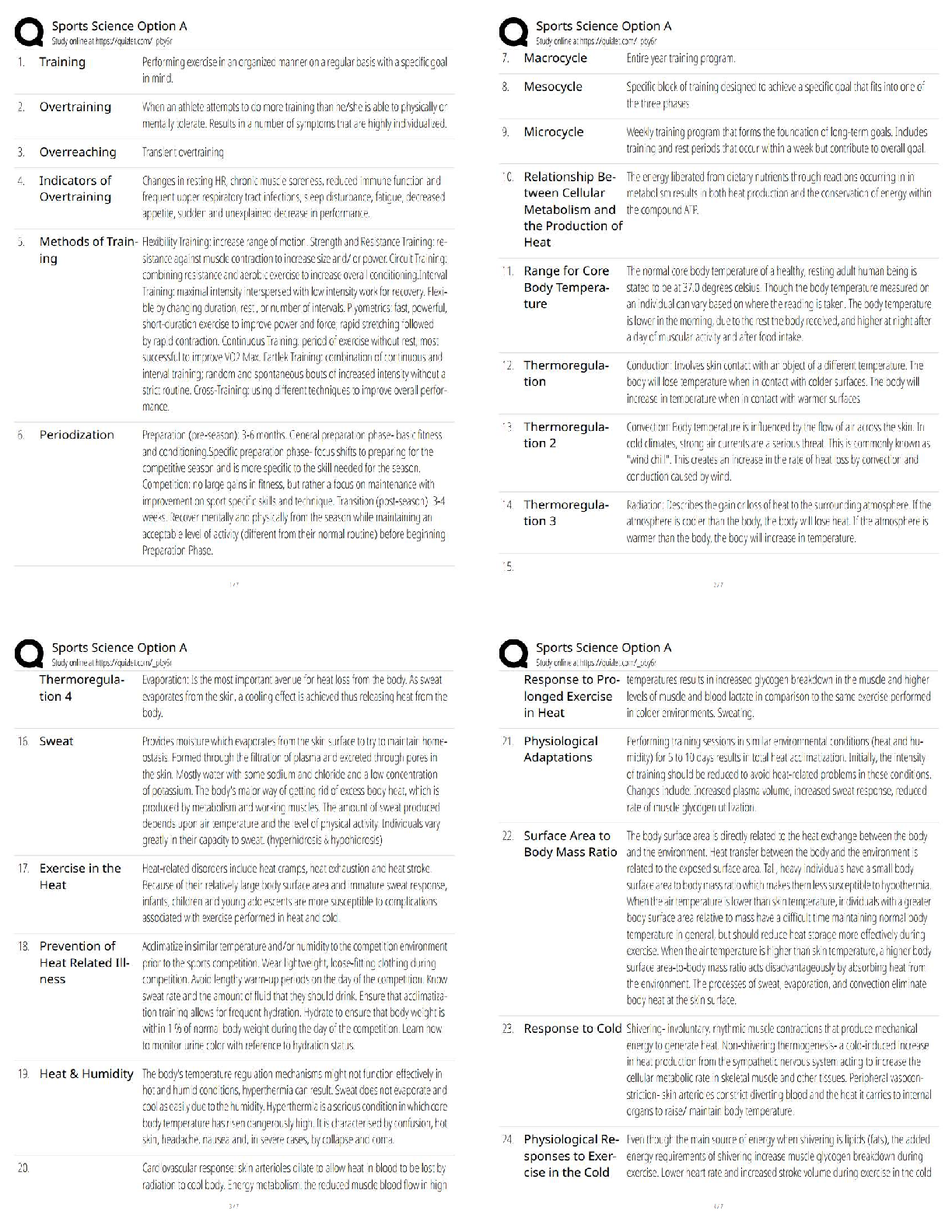
ACE Personal Trainer Exam Prep 195 Questions with preceding answers. Graded A+ 70 percent - ✔✔-chronic diseases account for what percentage of deaths in the US? 80 percent - ✔✔-what perc ... entage of deaths could have been prevented if a healthy lifestyle were followed? less than 200 mg/dl - ✔✔-healthy total cholesterol level between 200 and 239 mg/dl - ✔✔-borderline high total cholesterol level more than 240 mg/dl - ✔✔-high risk total cholesterol level BMI - ✔✔-weight over height essentially, 703 times weight over height squared for US (703*lbs / in^2) or kg / m^2 overseas 50 percent - ✔✔-percentage of adults with cholesterol 200 mg/dl and over 80 percent - ✔✔-percentage of adults with low back pain 80 thou to 100 thou - ✔✔-amount of ACL injuries that occur in the US annually 70 percent - ✔✔-amount of ACL injuries that are non-contact stabilization endurance phase, stabilization level training strategy - ✔✔-low loads, high reps strength endurance phase, strength level training strategy - ✔✔-superset, moderate loades and reps (8- 12) hypertrophy phase, strength level training strategy - ✔✔-high volume, moderate to high loads, moderate or low reps (6-12 max strength phase, strength level training strategy - ✔✔-high loads, low reps (1-5), longer rest periods obesity - ✔✔-bmi of 30+, at least 30 lbs over recommended weight for their height blood lipids - ✔✔-carried in the bloodstream by protein molecules known as HDL and LDL, aka cholesterol and triglycerides overweight - ✔✔-bmi of 25 to 29.9, between 25 to 30 lbs over recommended weight for their height muscle imbalance - ✔✔-alteration of muscle length surrounding a joint type 2 diabetes - ✔✔-associated w obesity, particularly abdominal obesity, and accounts for 90 percent to 95 percent of all diabetes. type 1 diabetes - ✔✔-often referred to as juvenile diabetes bc symptoms of the disease typically first appear in childhood as a result of the pancreas not producing insulin 66 percent - ✔✔-percentage of Americans older than age 20 that are overweight 72 million - ✔✔-# of Americans that are obese 34 percent - ✔✔-percentage of overweight Americans that are actually obese five - ✔✔-of the six leading causes of death in the US in 2006, how many were chronic diseases responsible for 57 percent - ✔✔-of the leading causes of death in the US, what percentage were caused by cardiovascular disease and cancer rate of force production - ✔✔-the power training level of the OPT strives most to improve? at least three BUSINESS days - ✔✔-how long must you wait before scheduling a retest for the CPT? at least two business days - ✔✔-how long must you wait to schedule an exam after purchasing a retest for the CPT? non-confidential info - ✔✔-cert status, cert # issued with NASM, NASM certs held in good standing with NASM BOC confidential info - ✔✔-application status, cert exam results, phone #s, email and residential addresses writing - ✔✔-a name change notification must be submitted in criteria that CPR/AED cert must meet - ✔✔-hands-on training component, skills demonstration evaluation from instructor, must require the passing of a standardized exam four years - ✔✔-you should maintain accurate financial, contract, appt, and tax records including original receipts for a minimum of? every 2 years - ✔✔-how often do i need to recertify? requirements for recert - ✔✔-1. pay recert fee 2. send in copy of current cpr/aed cert 3. docuz verify 20 contact hrs with continuing education providers aka 2.0 CEUs 4. completed recert app reputation - ✔✔-success depends on, do a great degree uncompromising customer service - ✔✔-being unwavering in providing an experience and level of assistance that is rarely, if ever, experienced anywhere else the four p's of marketing - ✔✔-product, price, place, promotion stages of change - ✔✔-precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance price - ✔✔-the amount charged for a product or service promote - ✔✔-the communication of information about a product or service with the goal of generating a positive customer response place - ✔✔-the channels that a product or service will go through to reach the customer product - ✔✔-the specific product or service offered precontemplation - ✔✔-people in this stage do not exercise and do not intend to start in the next 6 months contemplation - ✔✔-people in this stage do not exercise but are thinking about becoming more active in the next 6 months preparation - ✔✔-people in this stage exercise occasionally but are planning to begin exercising regularly in the next month action - ✔✔-people in this stage are active but have not yet maintained this behavior for 6 months maintenance - ✔✔-people in this stage have maintained change for 6 months or more stages of verbal communication - ✔✔-WHAT SPEAKER MEANS to WHAT SPEAKER SAYS to WHAT LISTENER HEARS to WHAT LISTENER THINKS SPEAKER MEANS communication - ✔✔-number one impt thing in the initial session the relationship between summarizing and reflecting (in effective communication) - ✔✔-summaries are a series of reflections the difference between affirmations and compliments - ✔✔-compliments typically have an evaluative judgment implicit within them. compliments usually begin with "i" statements... active listening - ✔✔-having an attitude and genuine interest in seeking a client's perspective and getting to know him or her 75 percent - ✔✔-what percentage of the US population is estimated not to engage in 30 minutes of low to moderate physical activity? human movement system - ✔✔-the combo and interrelation of the nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems nervous system - ✔✔-a conglomeration of billions of cells specifically designed to provide a communication network within the human body sensory function - ✔✔-the ability of the nervous system to sense changes in either the internal or external environment integrative function - ✔✔-the ability of the nervous system to analyze and interpret sensory info to allow for proper decision making, which produces the appropriate response motor function - ✔✔-the neuromuscular response to the sensory information proprioception - ✔✔-the cumulative sensory input to the central nervous system from all mechanoreceptors that sense body position and limb movement neuron - ✔✔-the functional unit of the nervous system Sensory (Afferent) Neurons - ✔✔-transmit nerve impulses from effector sites (such as muscles and organs) via receptors to the brain and spinal cord Interneurons - ✔✔-transmit nerve impulses from one neuron to another Motor (Efferent) Neurons - ✔✔-transmit nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to effector sites Central Nervous System - ✔✔-the portion of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System - ✔✔-cranial and spinal nerves that spread throughout the body mechanoreceptors - ✔✔-sensory receptors responsible for sensing distortion in body tissues muscle spindles - ✔✔-receptors sensitive to change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change golgi tendon organs - ✔✔-receptors sensitive to change in tension of the muscle and the rate of that change joint receptors - ✔✔-receptors surrounding a joint that response to pressure acceleration and deceleration of the joint Skeletal System - ✔✔-the body's framework, composed of bones and joints Bones - ✔✔-provide a resting ground for muscles and protection of vital organs Joints - ✔✔-junctions of bones, muscles, and connective tissues at which movement occurs. Also known as an articulation. Axial Skeleton - ✔✔-portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column Appendicular Skeleton - ✔✔-portion of the skeletal system that includes the upper and lower extremities Remodeling - ✔✔-the process of resorption and formation of bone Osteoclassts - ✔✔-a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue Osteoblasts - ✔✔-a type of cell that is responsible for bone formation Epiphysis - ✔✔-the end of long bones, which is mainly composed of cancellous bone, and house much of the red marrow involves in red blood cell production. They are also one of the primary sites for bone growth. Diaphysis - ✔✔-The shaft portion of the long bone. Epiphyseal Plate - ✔✔-The region of long bone connecting the diaphysis to the epiphysis. It is a layer of subdividing cartilaginous cells in which growth in length of the diaphysis occurs. Periosteum - ✔✔-A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue that closely wraps (invests) all bone, except that of the articulating surfaces in joints, which are covered by a synovial membrane. Medullar Cavity - ✔✔-The central cavity of bone shafts where marrow is stored. Articular (Hyaline) Cartilage - ✔✔-Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones. Depressions - ✔✔-Flattened or indented portions of bone, which can be muscle attachment sites. Processes - ✔✔-Projections protruding from the bone where muscles, tendons, and ligaments can attach. Vertebral Column - ✔✔-A series of irregularly shaped bones called vertebrae that houses the spinal cord. Arthrokinematics - ✔✔-Joint motion Synovial Joints - ✔✔-Joints that are held together by a joint capsule and ligaments and are most associated with movement in the body. Nonsynovial Joints - ✔✔-Joints that do not have a joint cavity, connective tissue, or cartilage. Ligament - ✔✔-primary connective tissue that connects bones together and provides stability, input to the nervous syste, guidance, and the limitation of improper joint movement. Muscular System - ✔✔-Series of muscles that moves the skeleton. Epimysium - ✔✔-A layer of connective tissue that is underneath the fascia and surrounds the muscle. Perimysium - ✔✔-The connective tissue that surrounds fascicles. Endomysium - ✔✔-The deepest layer of connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle fibers. Tendsons - ✔✔-Connective tissues that attach muscle to bone and provide an anchor for muscles to produce force Sarcomere - ✔✔-The functional unit of muscle that produces muscular contraction and consists of repeating sections of actin and myosin. Neural Activation - ✔✔-The contraction of a muscle generated by neural stimulation Motor Unit - ✔✔-A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates. Neurotransmitters - ✔✔-Chemical messengers that cross the neuromuscular junction (synapse) to transmit electrical impulses from the nerve to the muscle. agonist, chest press - ✔✔-pectoralis major agonist, overhead press - ✔✔-deltoid agonist, row - ✔✔-latissimus dorsi agonist, squat - ✔✔-gluteus maximus, quadriceps synergist, chest press - ✔✔-anterior deltoid, triceps synergist, overhead press - ✔✔-triceps synergist, row - ✔✔-posterior deltoid, biceps synergist, squat - ✔✔-hamstring complex stabilizer, squat - ✔✔-transversus abdominis stabilizer, chest press, overhead press, row - ✔✔-rotator cuff antagonist, chest press - ✔✔-posterior deltoid antagonist, overhead press - ✔✔-latissimus dorsi antagonist, row - ✔✔-pectoralis major antagonist, squat - ✔✔-psoas (deep hip flexor) carpals of the hands, tarsals of the feet - ✔✔-examples of short bones sternum - ✔✔-example of flat bones vertebrae - ✔✔-example of irregular bones describe regulation mechanism of the blood - ✔✔-regulates body temp and acid balance in the body describe protection mechanism of the blood - ✔✔-protects the body from excessive bleeding by clotting, contains specialized immune cells to help fight disease and sickness describe transportation mechanism of the blood - ✔✔-transports oxygen and nutrients to tissues, transports waste products from tissues, transports hormones to organs and tissues, carries heat throughout the body structures of the respiratory pump (bones) - ✔✔-sternum, ribs, vertebrae structures of the respiratory pump (muscles, inspiration) - ✔✔-diaphragm, external intercostals, scalenes, sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis minor structures of the respiratory pump (muscles, expiration) - ✔✔-internal intercoastals, abdominals 2 subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system - ✔✔-somatic and automatic nervous systems somatic nervous system - ✔✔-nerves that serve the outer areas of the body and skeletal muscle and are largely responsible for the voluntary control of movement autonomic nervous system - ✔✔-supplies neural input to the involuntary systems (heart, digestive systems, and endocrine glands) of the body 2 subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system - ✔✔-sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems 7-12-5 - ✔✔-number of vertebrae in the cervical, thoracic, and lumpar spine example of ball-and-socket joint - ✔✔-shoulder, moves in all 3 planes of motion example of pivot joint - ✔✔-radioulnar joint, moves in one plane of motion (transverse) example of saddle joint - ✔✔-moves predominantly in 2 planes of motion, only carpometacarpal example of hinge joint - ✔✔-only moves in sagittal plane...elbow joint example of condyloid joint - ✔✔-knee, moves mostly in 1 plane example of gliding joint - ✔✔-carpals of the hand, no axis of rotation example of synovial joint - ✔✔-knee.... example of nonsynovial joint - ✔✔-sutures of the skill...little or no movement cardiorespiratory system - ✔✔-a system of the body composed of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems heart - ✔✔-a hollow muscular organ that pumps a circulation of blood through the body by means of rhythmic contraction mediastinum - ✔✔-the space in the chest between the lungs that contains all the internal organs of the chest except the lungs sinoatrial (sa) node - ✔✔-a specialized area of cardiac tissue located in the right atrium of the heart, which initiates the electrical impulses that determine the heart rate; often termed the pacemaker for the heart atrioventricular (av) node - ✔✔-a small mass of specialized cardiac muscle fibers, located in the wall of the right atrium of the heart, that receives heartbeat impulses from the sinoatrial node and directs them to the walls of the ventricles atrium - ✔✔-the superior chamber of the heart that receives blood from the veins and forces it into the ventricles ventricles - ✔✔-the inferior chamber of the heart that receives blood from its corresponding atrium and, in turn, forces blood into the arteries stroke volume - ✔✔-the amount of blood pumped out of [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

ACE FINAL Exam BUNDLE, Approved Exam predictor.
ACE FINAL Exam. Top Questions with accurate answers. 100% Verified Predictor paper. 24 exam versions.
By Topmark 2 years ago
$38
23
Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 14, 2023
Number of pages
17
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 14, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
131