Pathophysiology Final Exam Study Guide
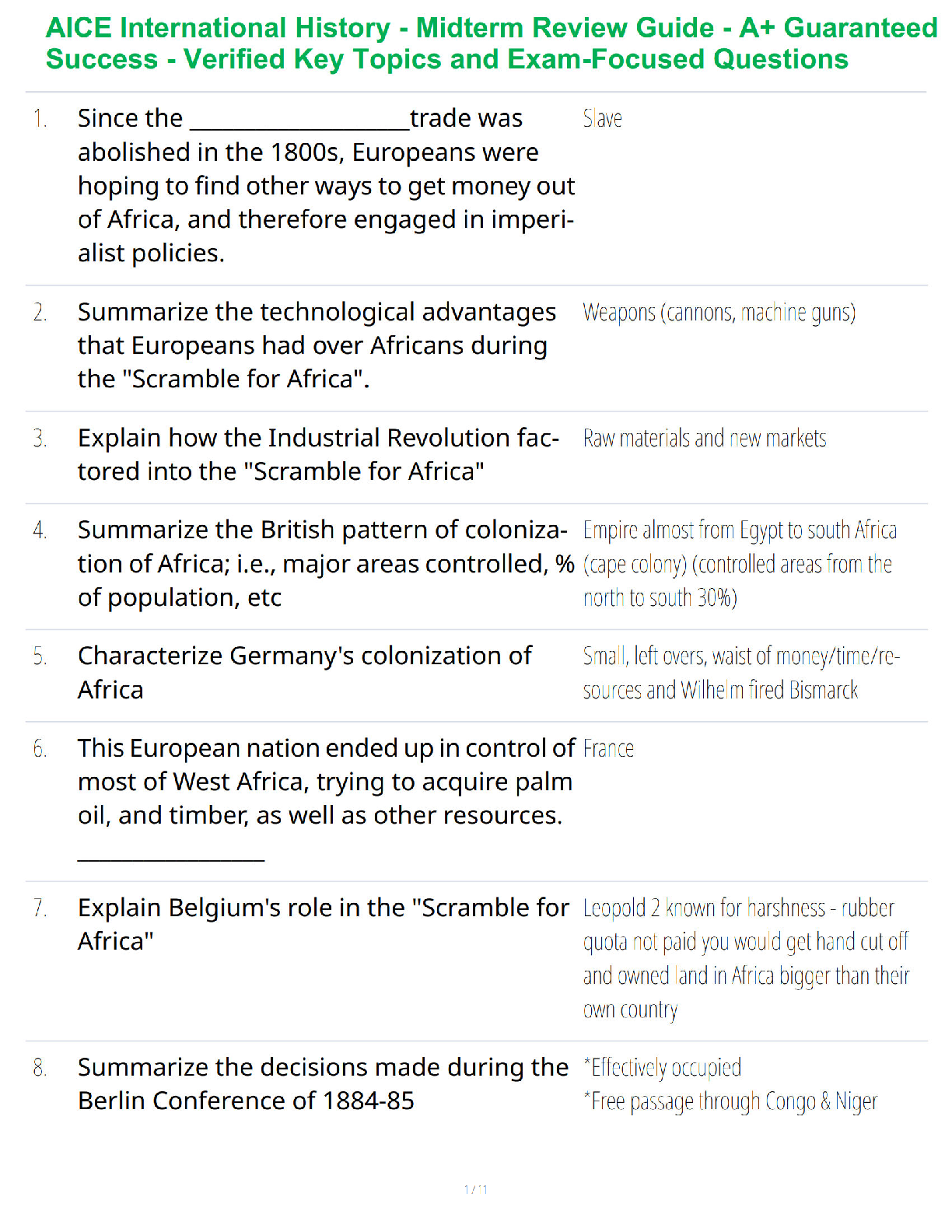
i. Altered Cell Biology (1 question)
a. Atrophy – decrease in cellular size
b. Hypertrophy – increase in cell size
c. Hyperplasia – increase in the number of cells
d. Metapl
...
Pathophysiology Final Exam Study Guide
i. Altered Cell Biology (1 question)
a. Atrophy – decrease in cellular size
b. Hypertrophy – increase in cell size
c. Hyperplasia – increase in the number of cells
d. Metaplasia – replacement of one mature cell by another
e. Dysplasia – abnormal changes in the size, shape and organization of mature cell
f. Cellular Adaptation
i. Allows the stressed tissue to survive or maintain function
ii. Genetics (2 questions)
a. Autosomal dominant disorders
i. Male/female offspring affected equally
ii. One of the parents is usually affected
iii. If one of the parents is heterozygous affected, the children have a 50% chance of being affected
iv. If both parents are heterozygous affected, the children have a 75 % chance of being affected
b. Marfan Syndrome
i. Etiology – disease of the connective tissue
1. Ocular, skeletal, and CV anomalies
2. It is an autosomal dominant disease – linked to chromosome 15
3. Affects men and women equally
ii. Signs and symptoms
1. Joint hypermobility
2. Spinal deformity
3. Mitral valve prolapse
4. Aortic valve disease
c. Tay Sachs Disease
i. Etiology – accumulation of glycolipids in the brain neurons & retina b/c of deficiency in Hexosaminidase A enzyme
ii. Signs and symptoms
1. Mental retardation and motor problems
2. Blindness and seizures
3. Death in 2-5 years
4. Cherry red spot in retina will occur
d. Turner Syndrome
i. Etiology – partial or full inactivation of X chromosomes
1. 45 chromosomes instead of 46, b/c only one X
2. Diagnosed through genetic testing
3. Associated with Coronary Heart Disease
ii. Signs and symptoms
1. Affects girls, typically are shorter, no breasts/ovaries, sterile
2. Webbing of neck
3. Amenorrhea
4. May have signs of mental retardation
iii. Fluid and Electrolytes / Acid-Base Balance (6 questions)
a. Interpret ABGs
i. Compensation of disorders
Acid/Base
Ph Range 7.35-7.45
C02 35-45 mm Hg
HC03 22-26 mEq/L
PaO2 80-100mm Hg
02 Stat 95% or greater
b. Acidosis
i. H+ diffuses into cells and drives out K+, elevating K+ concentration in ECF
ii. Compensate by excreting hydrogen ions
c. Alkalosis
i. H+ diffuses out of cells and K+ diffuses in
ii. Excrete bicarbonate and hold hydrogen ions
d. Compensation
i. Acute vs. Chronic
1. Acute compensation of acid base balance is done by the respiratory system
2. Chronic compensation is done by the kidneys to slowly but completely balance the disorder
ii. The body’s attempt to return the ratio of acid to base back toward 1:20(1 acid for every 20 bases) to maintain the pH between 7.35-7.45
iii. The patient is not considered to be compensated unless pH is within normal range
iv. If changes in tha
[Show More]