Applied Science > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Btec Applied Science Unit One Biology, Questions and answers, 100% Accurate. Graded A+ (All)
Btec Applied Science Unit One Biology, Questions and answers, 100% Accurate. Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
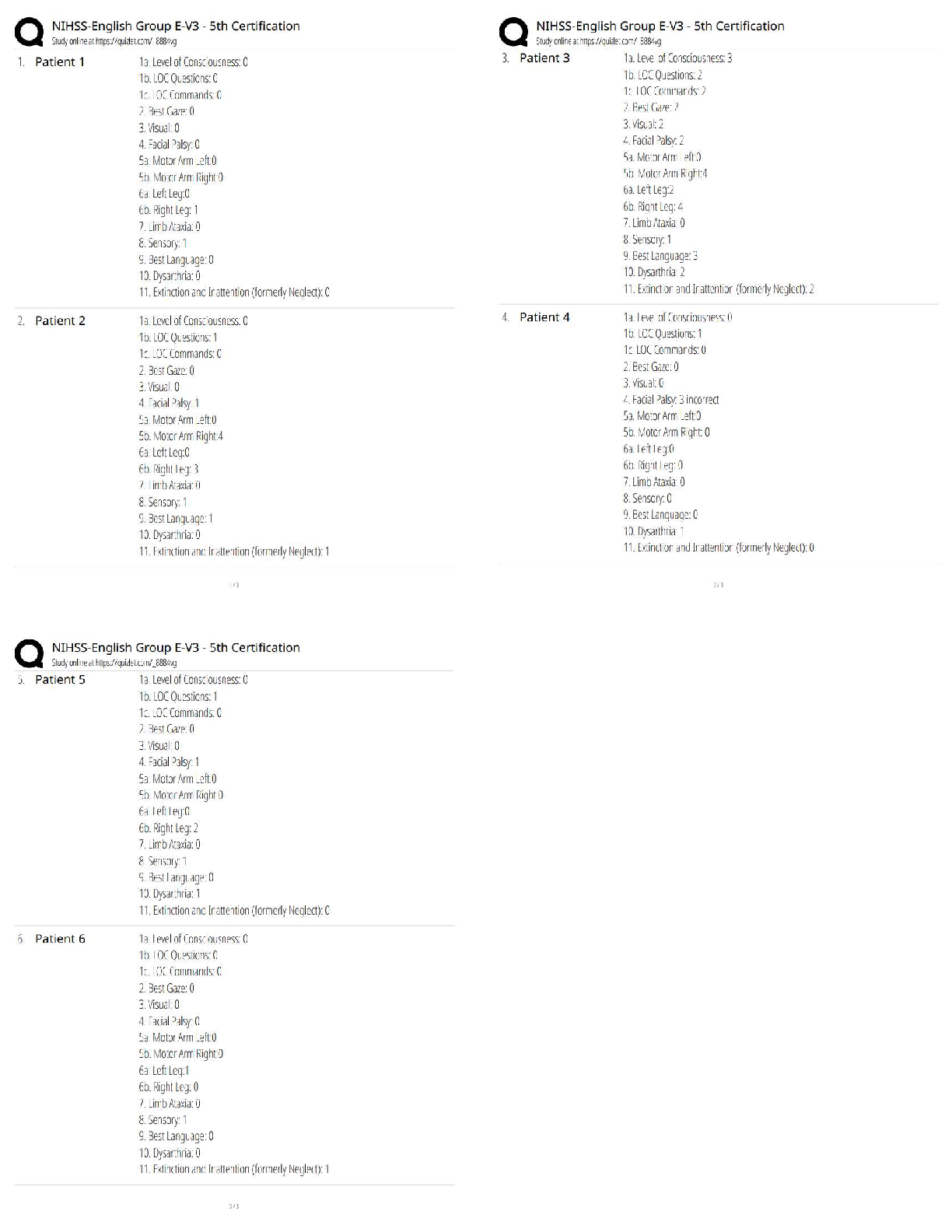
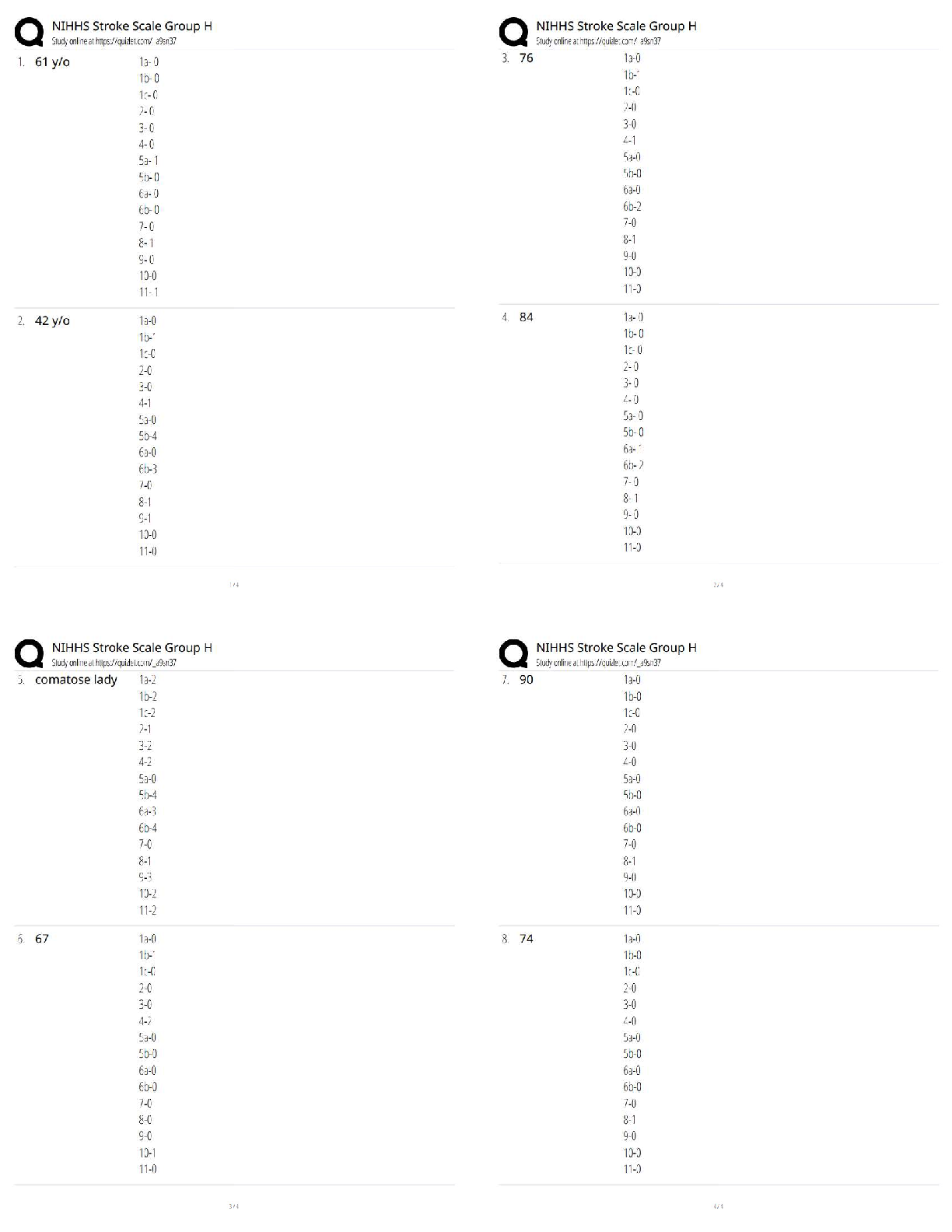
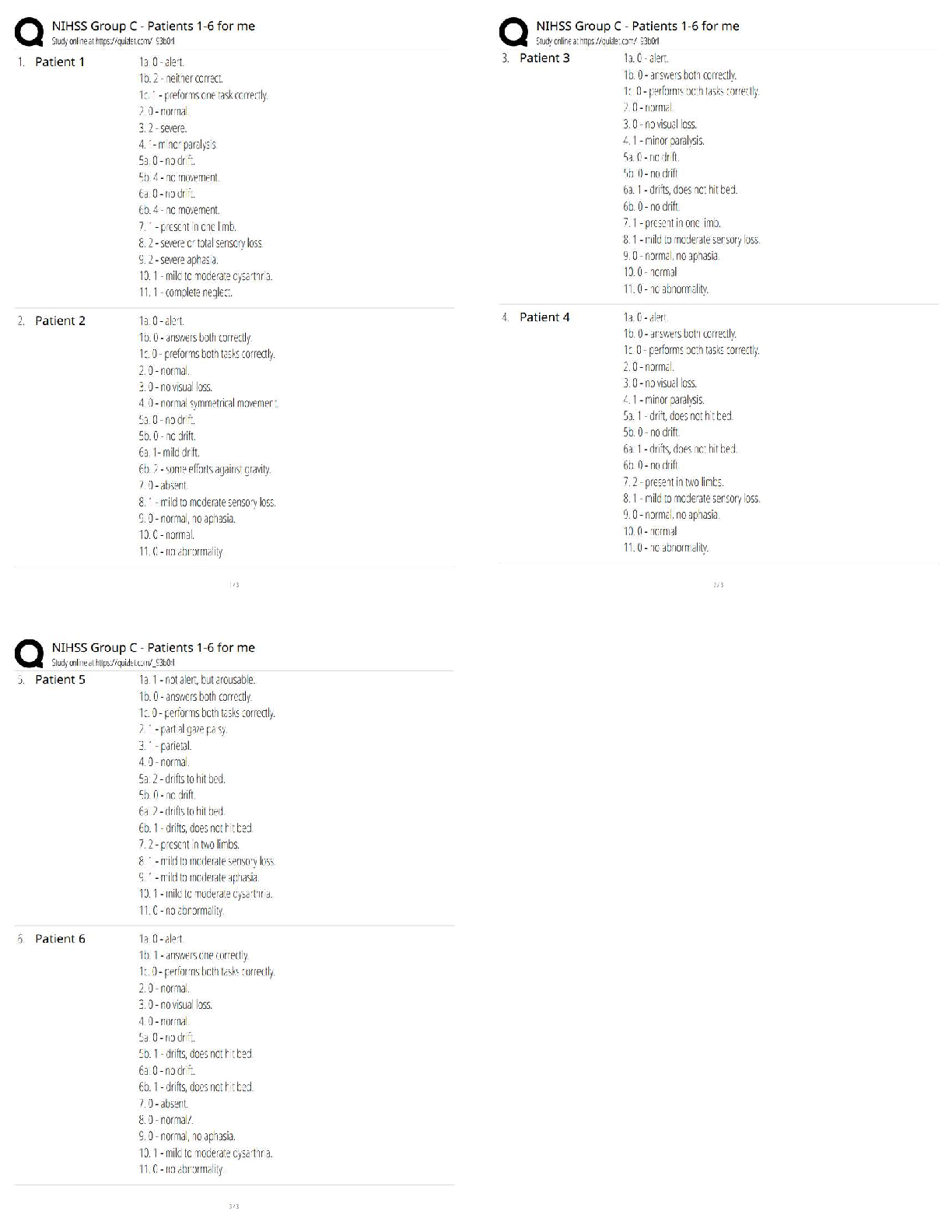
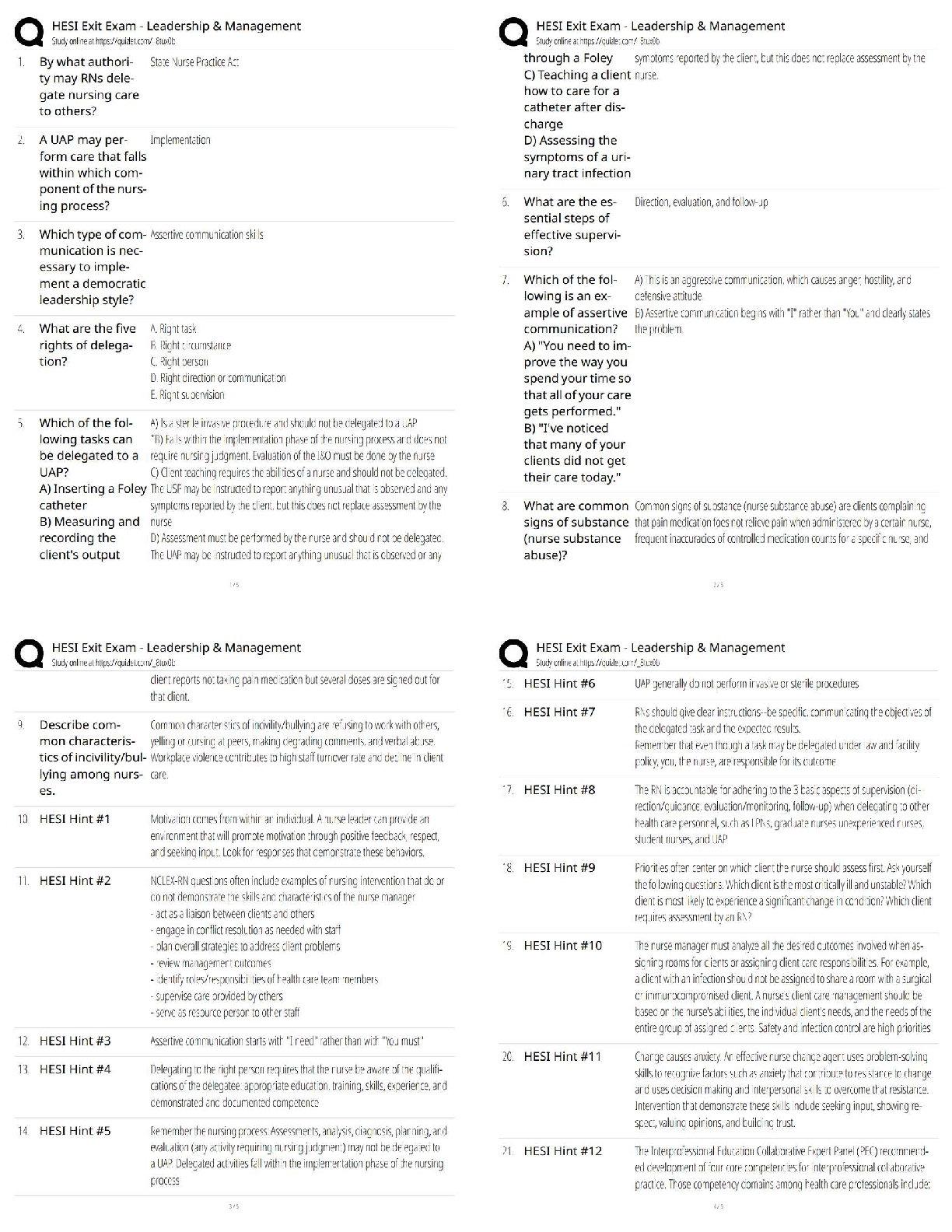
Btec Applied Science Unit One Biology, Questions and answers, 100% Accurate. Graded A+ What is the function of the mitochondria? - ✔✔-cellular respiration What is the function of the ribosom ... es? - ✔✔-protein synthesis What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum? - ✔✔-Synthesis and transport of lipids and carbohydrates What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? - ✔✔-Modified and packaged proteins into vesicles for transport What is the function of the lysosomes? - ✔✔-Digests old cell material and waste What is the function of the centrioles? - ✔✔-Form into spindle fibres for cell division What is the function of the chloroplasts? - ✔✔-photosynthesis What is the function of the tonoplasts? - ✔✔-The membrane around the vacuole to keep it together What is the function of the vacuole? - ✔✔-Maintain turgid pressure in the plant cell What is the function of the plasmodestmata? - ✔✔-To allow materials to pass through the cell wall What is the function of the amyloplasts? - ✔✔-Starch synthesis and storage Name three organelles which are only in plant cells - ✔✔-Vacuole, chloroplasts, cell wall Define eukaryotic cells - ✔✔-Are part of a multicellular organisms Define prokaryotic cells - ✔✔-Are unicellular organisms Name two differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? - ✔✔-Eukaryotic has a nucleus but prokaryotic doesn't my eukaryotic has a membrane bound organelles while prokaryotic doesn't What two dyes are used to show gram positive and gram negative bacteria? - ✔✔-Crystal violet and safranin Describe the difference between gram positive and gram negative? - ✔✔-Gram negative has thin cell walls so the ethanol washes out the crystal violet, so they appear safranin pink. Gram positive appears purple Describe the key features of a sperm cell? - ✔✔-Across one to penetrate the egg, tail for swimming, lots of mitochondria for energy Describe the features of egg cells? - ✔✔-Hormones to attract the speed, zona pellucuda to protect the egg, corona radiate to supply protein to developing foetus What is TEM? - ✔✔-Transmission electron microscope What is SEM? - ✔✔-Scanning electron microscope Compare TEM and SEM - ✔✔-TEM produces images of thin slices of material whereas SEM looks at the surface topography. Both are very magnified compared to the light microscopes and require dead samples. Describe how a light microscope works - ✔✔-Light microscopes use visible light and magnifying lenses to observe small objects Describe how an electron microscope works - ✔✔-They use a beam of electrons in a vacuum with a wavelength of less than 1 nm to visualise the specimen Give one positive and one limitation of light microscopes - ✔✔-Positive - can observe living structures Negative - relatively low magnification (x500) and resolution (x200nm) Give one positive and one negative of electron microscopes - ✔✔-Positive - high magnification (x500000) and resolution (0.1nm) Negative - destroys the sample Magnification equation - ✔✔-magnification = image size/actual size Describe the key features of a palisade cell - ✔✔-Found in leaves, they are rectangular box shaped cells that contain chloroplasts. The chloroplasts can absorb light for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts move around in the cytoplasm to maximise the amount of light absorbed Describe the key features of a root hair cell - ✔✔-Found in a plants roots near the growing tip. They have long hair like extensions called root hairs. They increase the surface area of the cell to maximise the movement of water and minerals. Describe the key features of a red blood cell (erythrocytes) - ✔✔-Biconcave in shape increases the surface area to volume ratio. They are flexible so that they can squeeze through the narrow capillaries. They have no nucleus, this increases space for haemoglobin to carry oxygen Describe the key features of white blood cells (neutrophils) - ✔✔-Multi-over nuclei which help them to squeeze through small gaps when travelling to the site of infection. Cytoplasms holds lysosomes that contain enzymes which breakdown pathogens and then ingest them Describe the location of the squamous epithelial tissue - ✔✔-Lines organs Describes the function of the squamous epithelial tissue - ✔✔-It is one cell thick and forms thin, smooth, flat layers, ideal for rapid diffusion Describe the location of the ciliated columnar epithelial tissue - [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 15, 2023
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 15, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
100