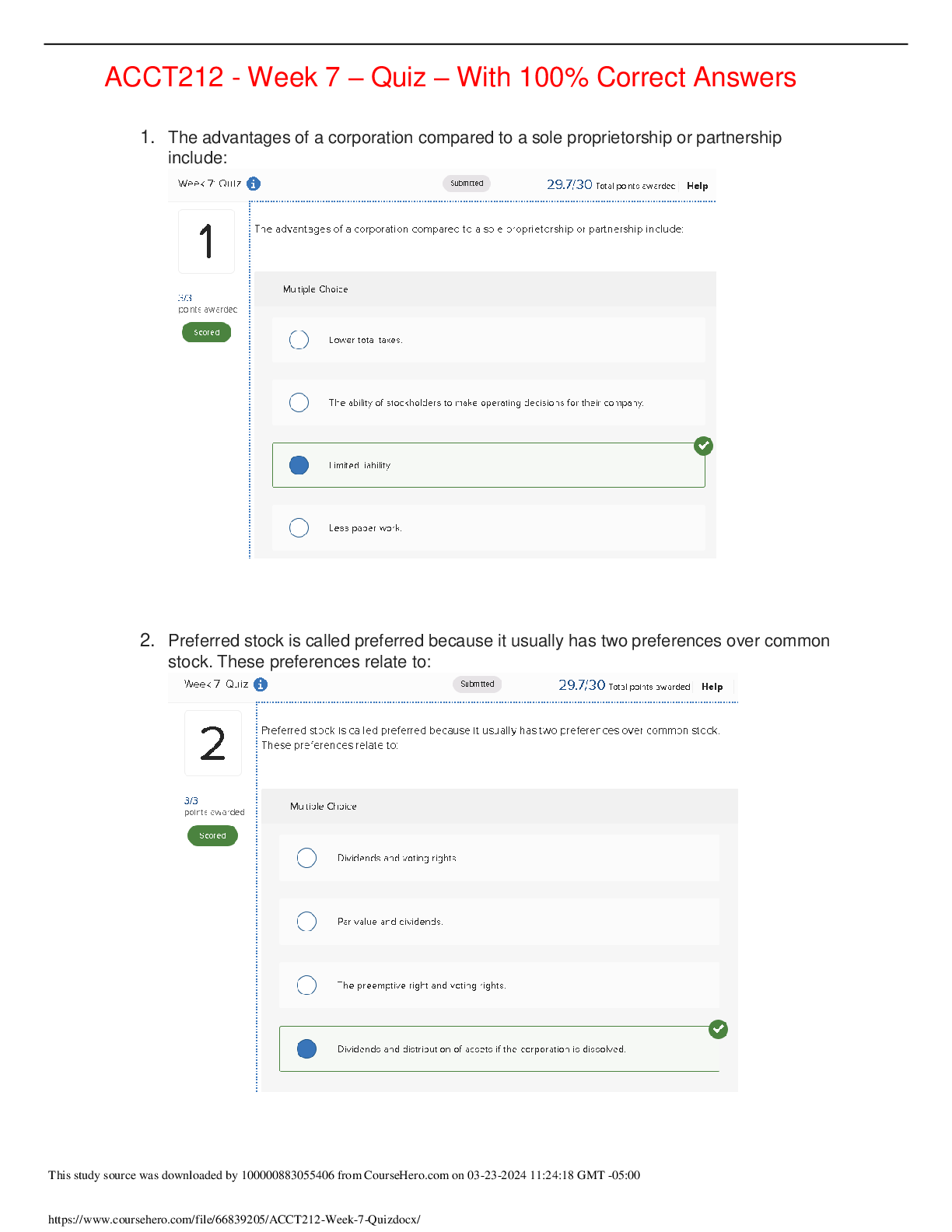
Philosophy > Quiz > PHIL 347 Week 6 Checkpoint Quiz -100% Correct Answers (All)
PHIL 347 Week 6 Checkpoint Quiz -100% Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
Instructions What are the three fundamental reasoning strategies listed in the text? Answer: 1. Comparative reasoning 2. Ideological reasoning 3. Empirical reasoning What is comparative r... easoning? On what skill is it based? Answer: Comparative reasoning is used to illustrate, illuminate, suggest, or hypothesize the process of using what is familiar to make interpretations, explanations, or inferences about what is less familiar. Based on critical thinking skills. We learned four tests for evaluating arguments: truthfulness of the premises, logical strength, relevance, and non-circularity. How well do these tests work with respect to evaluating comparative reasoning? Consider each of the four tests. Answer: Test 1: Are the premises all true? This test will not work with evaluating comparative reasoning because true or false are used mainly for evaluating the comparison. Test 2: Are there counterexamples and how difficult is it to imagine them? This question helps measure the logical strength of the analogy and categorize comparisons' plausibility. Nonetheless, it will not work well with comparative reasoning because there are too many cases of similarities and dissimilarities. Test 3: Are the premises relevant to the truth of the conclusion? The conclusion is the claim about the characteristics of the unfamiliar topic or content. It will help establish the relevance of comparisons between topics. Test 4: Does the truth of any premise depend on the truth of the conclusion? Comparative interference should flow from what we know to what we claim to be true. Nonetheless, it does not work because in comparative reasoning there is unfamiliarity. Thus, if something is unfamiliar it is challenging to connect premise and conclusion. Lastly, the four tests for evaluating comparative reasoning do not work to evaluating comparative reasoning. Briefly explain how we can determine if one comparison is more comprehensive than another. Answer: To determine if one comparison is more comprehensive than another, we can utilize the four tests for evaluating comparative reasoning stated in question 3. Are the premises all true? Are there any counter-examples and how difficult is it to imagine? Are the premises relevant to the truth of the conclusion? Does the truth of any premise depend on the truth of the conclusion? According to the text, the basic question to ask when evaluating a comparison between two objects or ideas, or events is “Are they alike enough in important ways or not?” (p. 248). What are those “important ways” that determine the credibility of conclusions based on similarities? Answer: The 5 criteria that can be utilized when evaluating comparative reasoning: 1. Familiarity 2. Simplicity 3. comprehensiveness 4. Productivity 5. Testability In your own words, define empirical reasoning. Answer: Empirical reasoning is using own personal experiences and premises that hold true to the individual and uses their own experiences to support their argument. What are the three defining characteristics of empirical reasoning? Answer: The three defining characteristics of empirical reasoning is as follows: 1. Inductive 2. Self-corrective 3. Independent verification What is meant by “the null hypothesis”? Answer: "the null hypothesis" is an empirically testable hypothesis that two incidents are entirely unrelated except by random chance What is the purpose of empirical reasoning? Answer: The purpose of empirical reasoning is to explain, predict, or control what happens. They are three powerful and interconnected purposes. Question 10 How do we evaluate empirical reasoning? Answer: We evaluate empirical reasoning by evaluating through the following: 1: The truthfulness of the premises 2. Logical strength 3. Relevancy 4. Non-circularity or not 5. Peer review What part of a research study addresses the test for logical strength, and how is it addressed? Answer: Operational design is the part of a research study that defines logical strength. It addressed three major sub-parts to guide test results. 1. Presentations 2. Analysis 3. Interpretation Briefly explain the process of peer review. What is the process of peer review designed to do? Answer: Peer review is a process in which a group of authors or a single author's work is evaluated (reviewed) under scrutiny by experts in the same field. Furthermore, it is designed to assess the validity, quality, and originality of the report for publications. It is a measure taken to provide ensure the quality of the content that is deemed qualified for publication in various fields of study. The authors of our text state: “We have 40 years of data across multiple studies that confirm the positive correlation between taking a course in critical thinking and improvements in the students’ pretest to post-test critical thinking skills scores. It would be a mistake, therefore, all things being equal, to say that growth in critical thinking and taking a course in critical thinking are unrelated” (p. 290). The null hypothesis is false. Does that mean, therefore, that taking a critical thinking course causes students to become more skilled at critical thinking and more motivated to use those skills? Explain your answer. Answer: Taking a critical reasoning course will aid to develop the skills and knowledge needed to recognize strategies that are utilized or can be utilized in an argument. Gaining the ability to recognize and implement the skills gained through the critical reasoning course will strengthen our professional field and daily encounters with others. Because the null hypothesis is false does not imply that the opposite is true If the reasoning is empirical, contains statistics, and appears in print, should we take for granted that it has passed the four tests of the truthfulness of the premises, logical strength, relevance, and non-circularity? Explain your answer. Answer: If the reasoning is empirical, contains statistics, and appears in print, we should not take for granted that it has passed the four tests of the truthfulness of the premises, logical strength, relevance, and non-circularity unless it has not been processed through peer-view. It should not be taken for granted until researched and examined. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (2)

PHIL 347 PACKAGE DEAL - DOWLOAD TO SCORE AN A+
PHIL 347 Week 8 Assignment: Journal - Download Paper For An A PHIL 347N Week 6 Discussion 2 Empirical Reasoning PHIL 347 Week 6 Discussion 1: Comparative Reasoning- Download Paper To Get A Pass...
By Doc.Mukai Edyth 1 year ago
$30
19

PHIL 347 Package Deal Critical Reasoning
PHIL 347 Week 1 Assignment: Journal PHIL-347 Week 1 Course Project: Topic Selection PHIL 347 Week 2 Assignment: Journal PHIL-347 Week 3 Course Project: Issue Review PHIL 347 Week 4 Assignm...
By Doc.Mukai Edyth 2 years ago
$25
10
Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 24, 2023
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 24, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
76