NURSING 101 Exam 1 Med
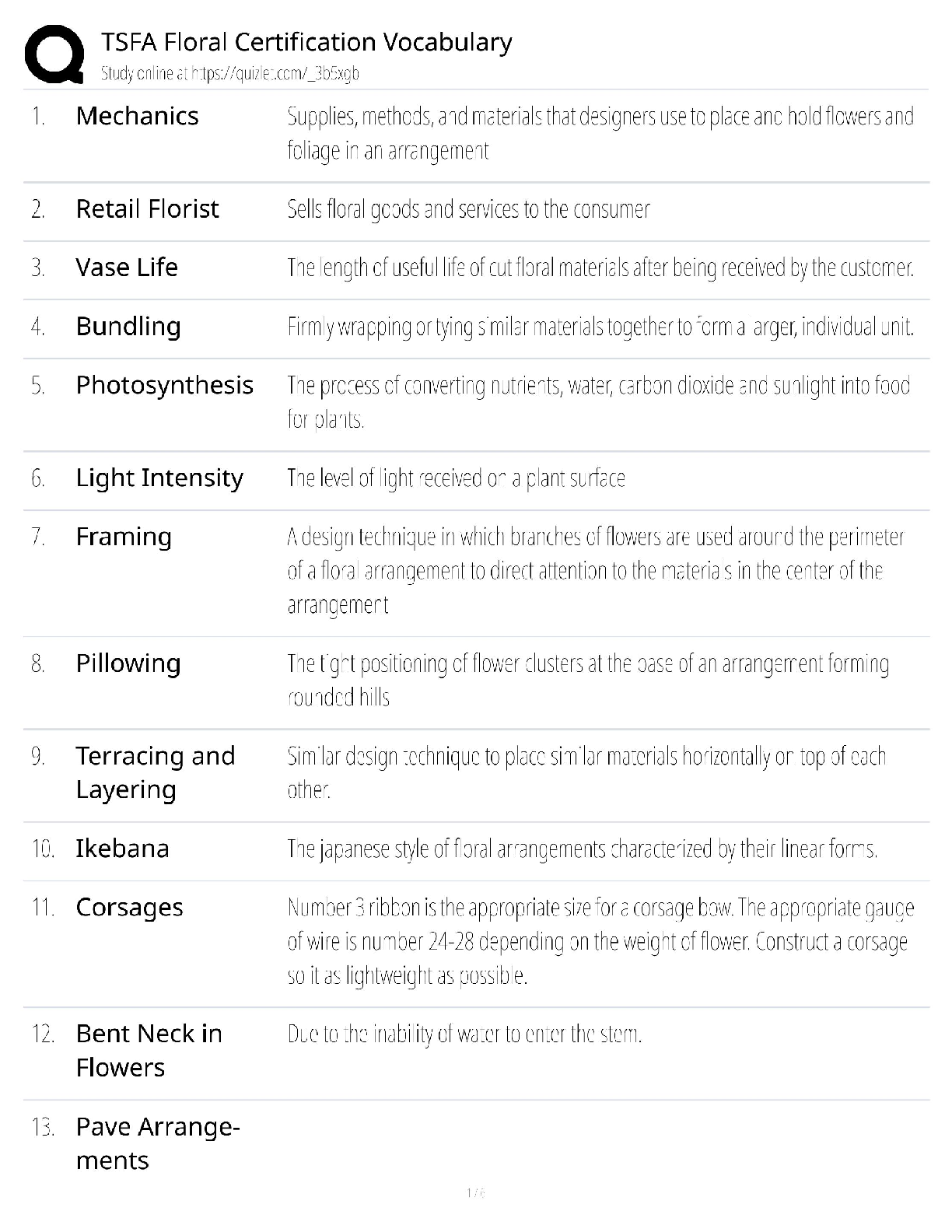
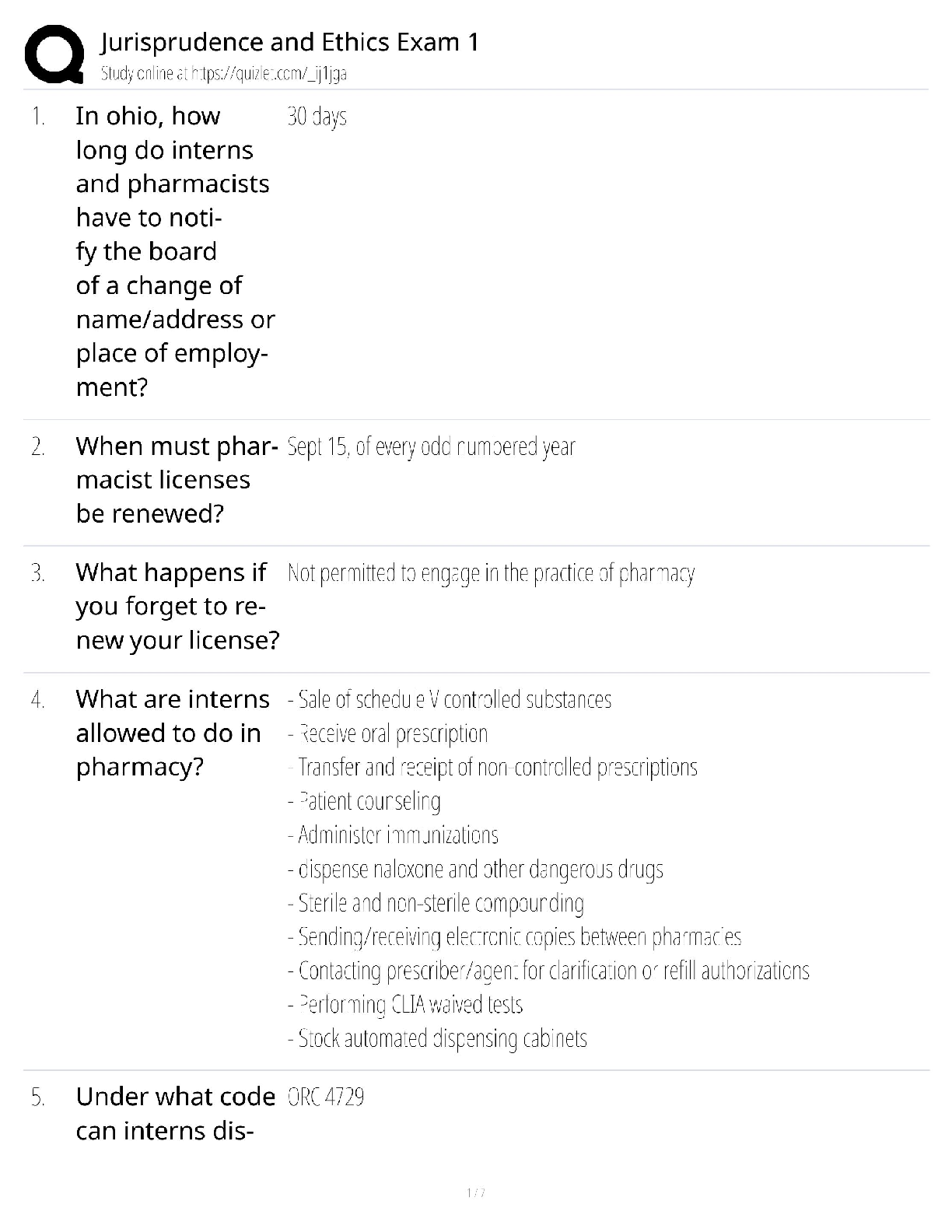
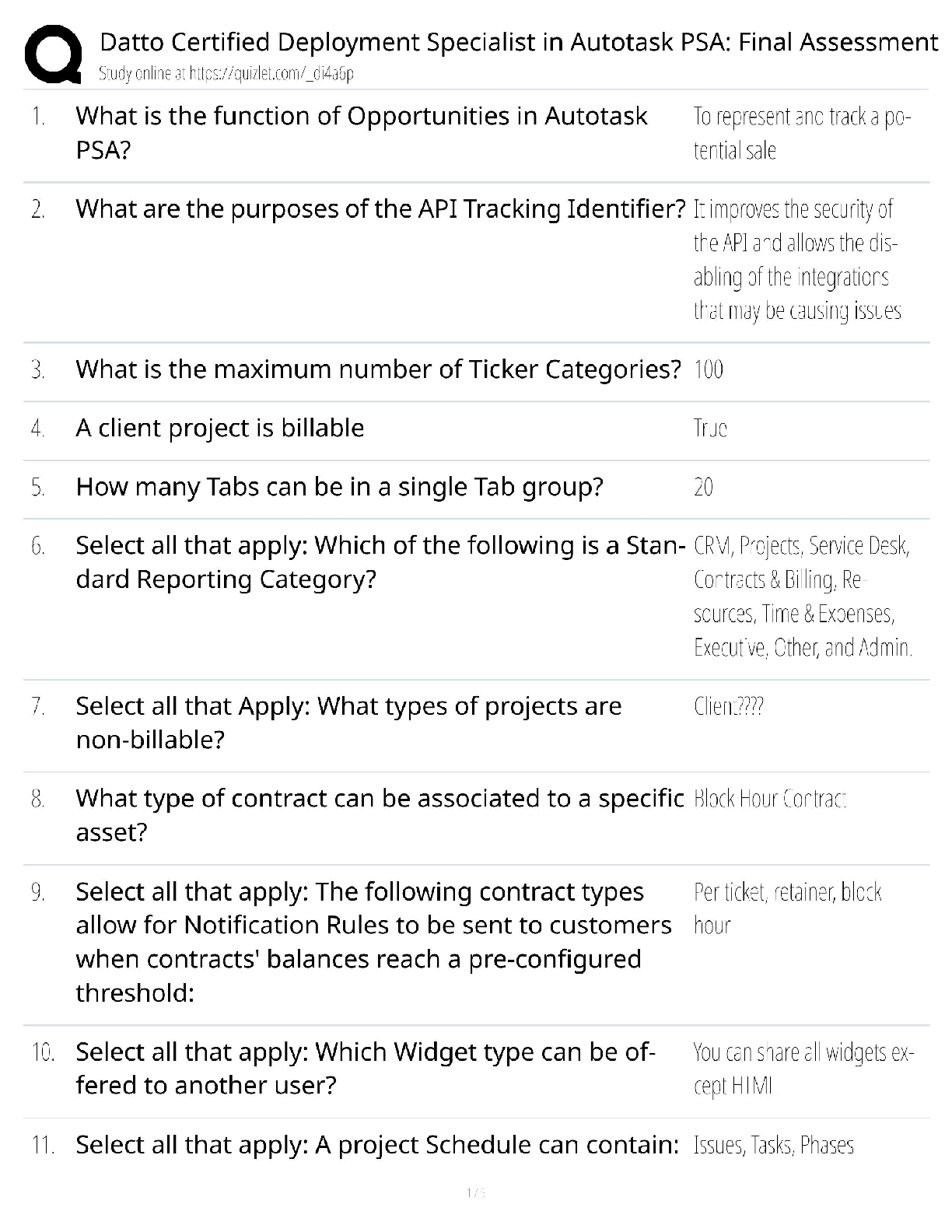
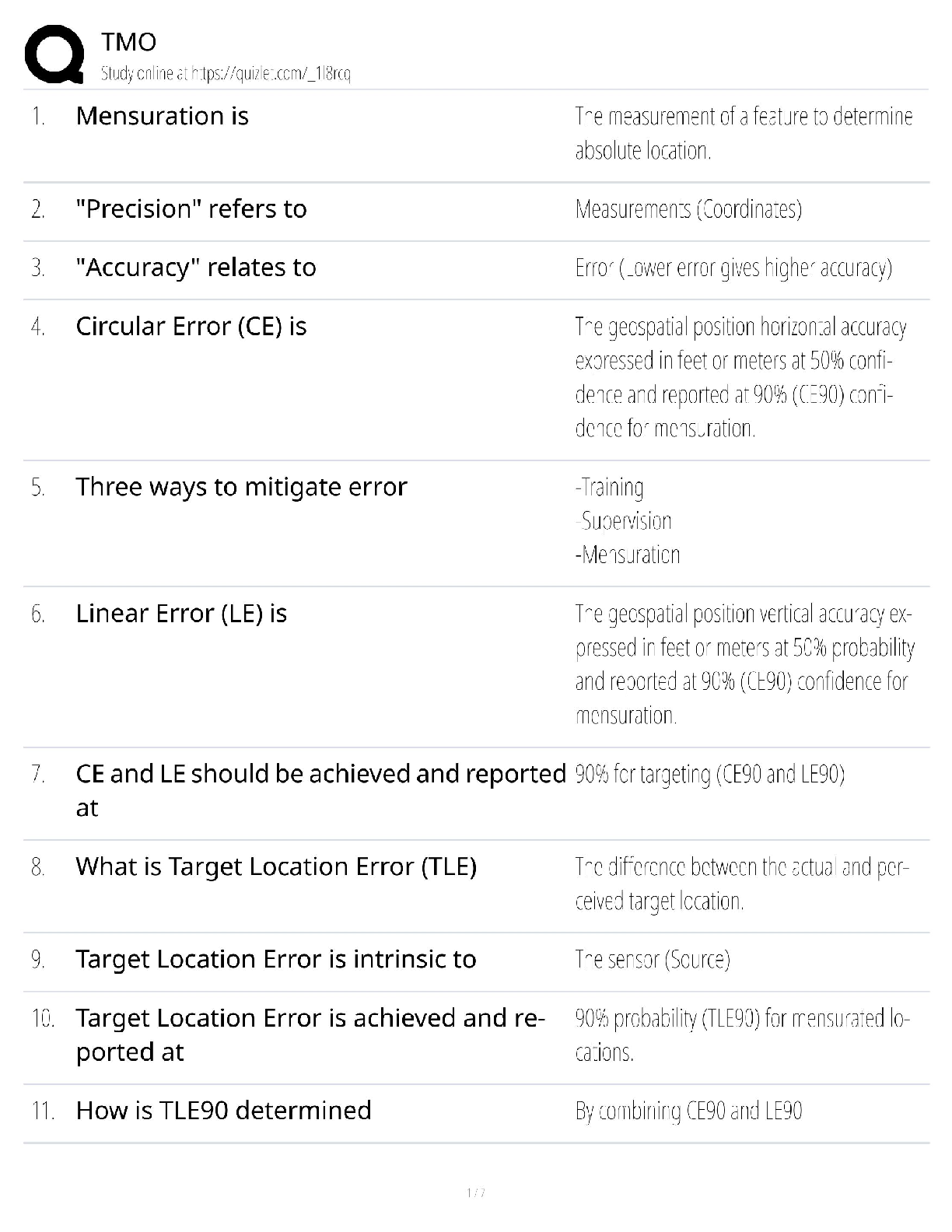
1. Questions
When planning an assessment of the urethra, what does the nurse do first?
A. Examine the meatus.
B. Note any unusual discharge.
C. Record the presence of abnormalities.
D.
...
NURSING 101 Exam 1 Med
1. Questions
When planning an assessment of the urethra, what does the nurse do first?
A. Examine the meatus.
B. Note any unusual discharge.
C. Record the presence of abnormalities.
D. Don gloves.
2.
When caring for a client with uremia, the nurse assesses for which symptom?
A. Tenderness at the costovertebral angle (CVA)
B. Cyanosis of the skin
C. Nausea and vomiting
D. Insomnia
3. 3.ID: 4615547591
Which laboratory test is the best indicator of kidney function?
A. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
B. Creatinine
C. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
D. Alkaline phosphatase
4. When performing bladder scanning to detect residual urine in a female client, the nurse must first assess which factor?
A. Abdominal girth
B. Presence of urinary infection
C. History of hysterectomy
D. Hematuria
5.
The nurse is reviewing the medical record for a client with polycystic kidney disease who is scheduled for computed tomographic angiography with contrast:
History and Physical Assessment Medications Diagnostic Findings
Polycystic kidney disease
Diabetes
Hysterectomy
Abdomen distended
Negative edema Glyburide
Metformin
Synthroid BUN 26 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
HbA1c 6.9%
Glucose 132 mg/dL
Which intervention is essential for the nurse to perform?
A. Obtain a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level.
B. Report the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine.
C. Hold the metformin 24 hours before and on the day of the procedure.
D. Notify the provider regarding blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) values.
6.
A client has returned from a captopril renal scan. Which teaching does the nurse provide when the client returns?
A. “Arise slowly and call for assistance when ambulating.”
B. “I must measure your intake and output.”
C. “We must save your urine because it is radioactive.”
D. “I must attach you to this cardiac monitor.”
7.
Which assessment finding alarms the nurse immediately after a client returns from the operating room for cystoscopy performed under conscious sedation?
A. Pink-tinged urine
B. Urinary frequency
C. Temperature of 100.8° F
D. Lethargy
8. 8.ID: 4615547599
Which instruction does the nurse give a client who needs a clean-catch urine specimen?
A. “Save all urine for 24 hours.”
B. “Use the sponges to cleanse the urethra, and then initiate voiding directly into the cup.”
C. “Do not touch the inside of the container.”
D. “You will receive an isotope injection, then I will collect your urine.”
9. 9.ID: 4615549926
The nurse has these client assignments. Which client does the nurse encourage to consume 2 to 3 liters of fluid each day?
A. Client with chronic kidney disease
B. Client with heart failure
C. Client with complete bowel obstruction
D. Client with hyperparathyroidism
10. 10.ID: 4615549936
A client with these assessment data is preparing to undergo a computed tomography scan with contrast:
Physical Assessment Diagnostic Findings Medications
Flank pain BUN 54 mg/dL Captopril
Dysuria Creatinine 2.4 mg/dL Metformin
Bilateral knee pain Calcium 8.5 mg/dL Acetylcysteine
Which medication does the nurse plan to administer before the procedure?
A. Acetylcysteine (Mucosil)
B. Metformin (Glucophage)
C. Captopril (Capoten)
D. Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
11. 11.ID: 4615547585
The nurse visualizes blood clots in a client’s urinary catheter after a cystoscopy. What nursing intervention does the nurse perform first?
A. Administer heparin intravenously.
B. Remove the urinary catheter.
C. Notify the health care provider.
D. Irrigate the catheter with sterile saline.
12. 12.ID: 4615549909
A client is scheduled for a cystoscopy later this morning. The consent form is not signed, and the client has not had any preoperative medication. The nurse notes that the provider visited the client the day before. What action does the nurse take?
A. Asks the client to sign the informed consent
B. Cancels the procedure
C. Asks the client’s spouse to sign the form
D. Notifies the department and the provider
13. 13.ID: 4615549924
An older adult woman who reports a change in bladder function says, “I feel like a child who sometimes pees her pants.” What is the nurse’s best response?
A. “Have you tried using the toilet at least every couple of hours?”
B. “How does that make you feel?”
C. “We can fix that.”
D. “That happens when we get older.”
14. 14.ID: 4615549905
A client is in the emergency department for an inability to void and for bladder distention. What is most important for the nurse to provide to the client?
A. Increased oral fluids
B. IV fluids
C. Privacy
D. Health history forms
15. 15.ID: 4615549920
The nurse is teaching a client how to provide a clean-catch urine specimen. Which statement by the client indicates that teaching was effective?
A. “I must clean with the wipes and then urinate directly into the cup.”
B. “I will have to drink 2 liters of fluid before providing the sample.”
C. “I’ll start to urinate in the toilet, stop, and then urinate into the cup.”
D. “It is best to provide the sample while I am bathing.”
16. 16.ID: 4615549916
Which age-related change can cause nocturia?
A. Decreased ability to concentrate urine
B. Decreased production of antidiuretic hormone
C. Increased production of erythropoietin
D. Increased secretion of aldosterone
17. 17.ID: 4615547589
Which percussion technique does the nurse use to assess a client who reports flank pain?
A. Place outstretched fingers over the flank area and percuss with the fingertips.
B. Place one hand with the palm down flat over the flank area and use the other fisted hand to thump the hand on the flank.
C. Place one hand with the palm up over the flank area and cup the other hand to percuss the hand on the flank.
D. Quickly tap the flank area with cupped hands.
18. 18.ID: 4615547595
Which urinary assessment information for a client indicates the potential need for increased fluids?
A. Increased blood urea nitrogen
B. Increased creatinine
C. Pale-colored urine
D. Decreased sodium
19. 19.ID: 4615549901
Which technique does the nurse use to obtain a sterile urine specimen from a client with a Foley catheter?
A. Disconnect the Foley catheter from the drainage tube and collect urine directly from the Foley.
B. Remove the existing catheter and obtain a sample during the process of inserting a new Foley.
C. Use a sterile syringe to withdraw urine from the urine collection bag.
D. Clamp the tubing, attach a syringe to the specimen, and withdraw at least 5 mL of urine.
20. 20.ID: 4615549932
A client had a computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast dye 8 hours ago. Which nursing intervention is the priority for this client?
A. Maintaining bedrest
B. Medicating for pain
C. Monitoring for hematuria
D. Promoting fluid intake
21. 21.ID: 4615549907
The charge nurse is making client assignments for the day shift. Which client is best to assign to an LPN/LVN?
A. Client who has just returned from having a kidney artery angioplasty
B. Client with polycystic kidney disease who is having a kidney ultrasound
C. Client who is going for a cystoscopy and cystourethroscopy
D. Client with glomerulonephritis who is having a kidney biopsy
22. 22.ID: 4615549914
The RN is caring for a client who has just had a kidney biopsy. Which action does the nurse perform first?
A. Obtain blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine.
B. Position the client supine.
C. Administer pain medications.
D. Check urine for hematuria.
23. 23.ID: 4615547597
When a client with diabetes returns to the medical unit after a computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast dye, all of these interventions are prescribed. Which intervention does the nurse implement first?
A. Give lispro (Humalog) insulin, 12 units subcutaneously.
B. Request a breakfast tray for the client.
C. Infuse 0.45% normal saline at 125 mL/hr.
D. Administer captopril (Capoten).
24. 24.ID: 4615547593
One of the nurse’s roles is talking to adult clients about urinary and sexual hygiene. Which words does the nurse use when referring to the client’s reproductive body parts?
A. Children’s terms that are easily understood
B. Slang words and terms that are heard “socially”
C. Technical and medical terminology
D. Words that the client uses
25. 25.ID: 4615547587
For which clients scheduled for a computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast does the nurse communicate safety concerns to the health care provider? (Select all that apply.)
A. Client with an allergy to shrimp
B. Client with a history of asthma
C. Client who requests morphine sulfate every 3 hours
D. Client with a blood urea nitrogen of 62 mg/dL and a creatinine of 2.0 mg/dL
E. Client who took metformin (Glucophage) 4 hours ago
1. Questions
1. 1.ID: 4615438045
Which nursing activity illustrates proper aseptic technique during catheter care?
A. Applying Betadine ointment to the perineal area after catheterization
B. Irrigating the catheter daily
C. Positioning the collection bag below the height of the bladder
D. Sending a urine specimen to the laboratory for testing
2. 2.ID: 4615438067
The nurse is instructing an older adult female client about interventions to decrease the risk for cystitis. Which client comment indicates that the teaching was effective?
A. “I must avoid drinking carbonated beverages.”
B. “I need to douche vaginally once a week.”
C. “I should drink 2½ liters of fluid every day.”
D. “I will not drink fluids after 8 PM each evening.”
3. 3.ID: 4615438073
The nurse is educating a female client about hygiene measures to reduce her risk for urinary tract infection. What does the nurse instruct the client to do?
A. “Douche—but only once a month.”
B. “Use only white toilet paper.”
C. “Wipe from front to back.”
D. “Wipe with the softest toilet paper available.”
4. 4.ID: 4615438025
The nurse is teaching a client about pelvic muscle exercises. What information does the nurse include?
A. “For the best effect, perform all of your exercises while you are seated on the toilet.”
B. “Limit your exercises to 5 minutes twice a day, or you will injure yourself.”
C. “Results should be visible to you within 72 hours.”
D. “You know that you are exercising muscles if you can stop urine flow in midstream.”
5. 5.ID: 4615438083
The nurse is teaching the importance of a low purine diet to a client admitted with urolithiasis consisting of uric acid. Which statement by the client indicates that teaching was effective?
A. “I am so relieved that I can continue eating my fried fish meals every week.”
B. “I will quit growing rhubarb in my garden since I’m not supposed to eat it anymore.”
C. “My wife will be happy to know that I can keep enjoying her liver and onions recipe.”
D. “I will no longer be able to have red wine with my dinner.”
6. 6.ID: 4615438023
An older adult woman confides to the nurse, “I am so embarrassed about buying adult diapers for myself.” How does the nurse respond?
A. “Don’t worry about it. You need them.”
B. “Shop at night, when stores are less crowded.”
C. “Tell everyone that they are for your husband.”
D. “That is tough. What do you think might help?”
7. 7.ID: 4615438089
The nurse is teaching a client who is scheduled for a neobladder and a Kock pouch. Which client statement indicates a understanding of these procedures?
A. “If I restrict my oral intake of fluids, the adjustment will be easier.”
B. “I must go to the restroom more often because my urine will be excreted through my anus.”
C. “I need to wear loose-fitting pants so the urine can flow into my ostomy bag.”
D. “I will have to drain my pouch with a catheter.”
8. 8.ID: 4615438037
Which nursing intervention or practice is most effective in helping to prevent urinary tract infection (UTI) in hospitalized clients?
A. Encouraging them to drink fluids
B. Irrigating all catheters daily with sterile saline
C. Recommending that catheters be placed in all clients
D. Periodically re-evaluating the need for indwelling catheters
9. Which type of incontinence benefits from pelvic floor muscle (Kegel) exercise?
A. Functional
B. Overflow
C. Stress
D. Urge
10.
The certified Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurse or enterostomal therapist teaches a client who has had a cystectomy about which care principles for the client’s post-discharge activities?
A. Nutritional and dietary care
B. Respiratory care
C. Stoma and pouch care
D. Wiping from front to back (asepsis)
11.
The nurse educates a group of women who have had frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs) about how to avoid recurrences. Which client statement shows a understanding of what the nurse has taught?
A. “I should be drinking at least 1.5 to 2.5 liters of fluids every day.”
B. “It is a good idea for me to reduce germs by taking a tub bath daily.”
C. “Trying to get to the bathroom to urinate every 6 hours is important for me.”
D. “Urinating 1000 mL on a daily basis is a good amount for me.”
12. The nurse is teaching a client with a neurogenic bladder to use intermittent self-catheterization for bladder emptying. Which client statement indicates a need for further clarification?
A. “A small-lumen catheter will help prevent injury to my urethra.”
B. “I will use a new, sterile catheter each time I do the procedure.”
C. “My family members can be taught to help me if I need it.”
D. “Proper handwashing before I start the procedure is very important.”
13.
A male client being treated for bladder cancer has a live virus compound instilled into his bladder as a treatment. What instruction does the nurse provide for postprocedure home care?
A. “After 12 hours, your toilet should be cleaned with a 10% solution of bleach.”
B. “Do not share your toilet with family members for the next 24 hours.”
C. “Please be sure to stand when you are urinating.”
D. “Your underwear worn during the procedure and for the first 12 hours afterward should be bagged and discarded.”
14.
Which client does the nurse manager on the medical unit assign to an experienced LPN/LVN?
A. A 42-year-old with painless hematuria who needs an admission assessment
B. A 46-year-old scheduled for cystectomy who needs help in selecting a stoma site
C. A 48-year-old receiving intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer
D. A 55-year-old with incontinence who has intermittent catheterization prescribed
15.
A client is referred to a home health agency after being hospitalized with overflow incontinence and a urinary tract infection. Which nursing action can the home health RN delegate to the home health aide (unlicensed assistive personnel [UAP])?
A. Assisting the client in developing a schedule for when to take prescribed antibiotics
B. Inserting a straight catheter as necessary if the client is unable to empty the bladder
C. Teaching the client how to use the Credé maneuver to empty the bladder more fully
D. Using a bladder scanner (with training) to check residual bladder volume after the client voids
16. A client who is admitted with urolithiasis reports “spasms of intense flank pain, nausea, and severe dizziness.” Which intervention does the nurse implement first?
A. Administer morphine sulfate 4 mg IV.
B. Begin an infusion of metoclopramide (Reglan) 10 mg IV.
C. Obtain a urine specimen for urinalysis.
D. Start an infusion of 0.9% normal saline at 100 mL/hr.
17.
The nurse receives the change-of-shift report on four clients. Which client does the nurse decide to assess first?
A. A 26-year-old admitted 2 days ago with urosepsis with an oral temperature of 99.4° F (37.4° C)
B. A 28-year-old with urolithiasis who has been receiving morphine sulfate and has not voided for 8 hours
C. A 32-year-old admitted with hematuria and possible bladder cancer who is scheduled for cystoscopy
D. A 40-year-old with noninfectious urethritis who is reporting “burning” and has estrogen cream prescribed
18.
A cognitively impaired client has urge incontinence. Which method for achieving continence does the nurse include in the client’s care plan?
A. Bladder training
B. Credé method
C. Habit training
D. Kegel exercises
19.
A client is admitted for extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). What information obtained on admission is most critical for a nurse to report to the health care provider before the ESWL procedure begins?
A. “Blood in my urine has become less noticeable, so maybe I don’t need this procedure.”
B. “I have been taking cephalexin (Keflex) for an infection.”
C. “I previously had several ESWL procedures performed.”
D. “I take over-the-counter naproxen (Aleve) twice a day for joint pain.”
20.
A client who is 6 months pregnant comes to the prenatal clinic with a suspected urinary tract infection (UTI). What action does the nurse take with this client?
A. Discharges the client to her home for strict bedrest for the duration of the pregnancy
B. Instructs the client to drink a minimum of 3 liters of fluids, especially water, every day to “flush out” bacteria
C. Recommends that the client refrain from having sexual intercourse until after she has delivered her baby
D. Refers the client to the clinic nurse practitioner for immediate follow-up
21.
A 53-year-old postmenopausal woman reports “leaking urine” when she laughs, and is diagnosed with stress incontinence. What does the nurse tell the client about how certain drugs may be able to help with her stress incontinence?
A. “They can relieve your anxiety associated with incontinence.”
B. “They help your bladder to empty.”
C. “They may be used to improve urethral resistance.”
D. “They decrease your bladder’s tone.”
22.
A 32-year-old female with a urinary tract infection (UTI) reports urinary frequency, urgency, and some discomfort upon urination. Her vital signs are stable except for a temperature of 100° F. Which drug does the health care provider prescribe?
A. Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin) after intercourse
B. Estrogen (Premarin)
C. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
D. Phenazopyridine (Pyridium) with intercourse
23.
A client who was previously diagnosed with a urinary tract infection (UTI) and started on antibiotics returns to the clinic 3 days later with the same symptoms. When asked about the previous UTI and medication regimen, the client states, “I only took the first dose because after that, I felt better.” How does the nurse respond?
A. “Not completing your medication can lead to return of your infection.”
B. “That means your treatment will be prolonged with this new infection.”
C. “This means you will now have to take two drugs instead of one.”
D. “What you did was okay; however, let’s get you started on something else.”
24.
The nurse is caring for clients on a renal/kidney medical-surgical unit. Which drug, requested by the health care provider for a client with a urinary tract infection (UTI), does the nurse question?
A. Bactrim
B. Cipro
C. Noroxin
D. Tegretol
25.
The health care provider requests phenazopyridine (Pyridium) for a client with cystitis. What does the nurse tell the client about the drug?
A. “It will act as an antibacterial drug.”
B. “This drug will treat your infection, not the symptoms of it.”
C. “You need to take the drug on an empty stomach.”
D. “Your urine will turn red or orange while on the drug.”
26.
What does the nurse teach a client to do to decrease the risk for urinary tract infection (UTI)?
A. Limit fluid intake.
B. Increase caffeine consumption.
C. Limit sugar intake.
D. Drink about 3 liters of fluid daily.
27. The nurse is questioning a female client with a urinary tract infection (UTI) about her antibiotic drug regimen. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further instruction?
A. “I take my medication only when I have symptoms.”
B. “I always wipe front to back.”
C. “I don’t use bubble baths and other scented bath products.”
D. “I try to drink 3 liters of fluid a day.”
28.
Which clients with an indwelling urinary catheter does the nurse reassess to determine whether the catheterization needs to be continued or can be discontinued? (Select all that apply.)
A. Three-day postoperative client
B. Client in the stepdown unit
C. Comatose client with careful monitoring of intake and output (I&O)
D. Incontinent client with perineal skin breakdown
E. Incontinent older adult in long-term care
29.
Which interventions are helpful in preventing bladder cancer? (Select all that apply.)
A. Drinking 2½ liters of fluid a day
B. Showering after working with or around chemicals
C. Stopping the use of tobacco
D. Using pelvic floor muscle exercises
E. Wearing a lead apron when working with chemicals
F. Wearing gloves and a mask when working around chemicals and fumes
30.
Which clients with long-term urinary problems does the nurse refer to community resources and support groups? (Select all that apply.)
A. A 32-year-old with a cystectomy
B. A 44-year-old with a Kock pouch
C. A 48-year-old with urinary calculi
D. A 78-year-old with urinary incontinence
E. An 80-year-old with dementia
31.
The nurse is teaching a group of older adult women about the signs and symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI). Which concepts does the nurse explain in the presentation? (Select all that apply.)
A. Dysuria
B. Enuresis
C. Frequency
D. Nocturia
E. Urgency
F. Polyuria
32.
An older adult client diagnosed with stress incontinence is prescribed the medication oxybutynin (Ditropan). Which side effects does the nurse tell the client to expect? (Select all that apply.)
A. Dry mouth
B. Increased blood pressure
C. Increased intraocular pressure
D. Constipation
E. Reddish-orange urine color
33.
A client diagnosed with stress incontinence is started on propantheline (Pro-Banthine). What interventions does the nurse suggest to alleviate the side effects of this anticholinergic drug? (Select all that apply.)
A. Take the drug at bedtime.
B. Encourage increased fluids.
C. Increase fiber intake.
D. Limit the intake of dairy products.
E. Use hard candy for dry mouth.
34.
A client with a urinary tract infection is prescribed trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim). What information does the nurse provide to this client about taking this drug? (Select all that apply.)
A. “Be certain to wear sunscreen and protective clothing.”
B. “Drink at least 3 liters of fluids every day.”
C. “Take this drug with 8 ounces of water.”
D. “Try to urinate frequently to keep your bladder empty.”
E. “You will need to take all of this drug to get the benefits.”
35.
The nurse in the urology clinic is providing teaching for a female client with cystitis. Which instructions does the nurse include in the teaching plan? (Select all that apply.)
A. Cleanse the perineum from back to front after using the bathroom.
B. Try to take in 64 ounces of fluid each day.
C. Be sure to complete the full course of antibiotics.
D. If urine remains cloudy, call the clinic.
E. Expect some flank discomfort until the antibiotic has worked.
36.
What information will the nurse provide to a client who is scheduled for extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy? (Select all that apply.)
A. “Your urine will be strained after the procedure.”
B. “Be sure to finish all of your antibiotics.”
C. “Immediately call the health care provider if you notice bruising.”
D. “Remember to drink at least 3 liters of fluid a day to promote urine flow.”
E. “You will need to change the incisional dressing once a day.”
1. Questions
1. A client admitted with a non–life-threatening illness says, “I was asked to fill out an advance directive when I was admitted, but I was too stressed. What was it all about?” How does the nurse respond?
A. “Advance directives are only for those individuals who are severely ill.”
B. “Advance directives allow a client to convey his or her wishes about health care ahead of time.”
C. “Most Americans have an advance directive in place; you will need to see a lawyer.”
D. “You should have completed the paperwork before you were admitted.”
.
2.
A dying client is having difficulty swallowing oral medications. Which intervention does the nurse implement for this client?
A. Asks the pharmacy to substitute intramuscular (IM) equivalents for the medications
B. Asks the provider if the medications can be discontinued or substituted
C. Crushes the pills, opens the sustained-release capsules, and mixes them with a spoonful of applesauce
D. Does not give the medications and documents: “Unable to swallow”
3.
The family of an unconscious dying client realizes that their mother will die soon. The client’s children are having a difficult time letting go. How does the nurse respond to the needs of this family?
A. “Don’t be upset; she wouldn’t want it that way.”
B. “She will soon be in a better place.”
C. “Things will be fine, try not to worry so much.”
D. “This must be difficult for you.”
4.
A dying client says to the nurse, “I am afraid to die. I did a lot of wrong things in my life.” How does the nurse respond?
A. “Don’t worry, God will forgive you.”
B. “I’m sure it is nothing to worry about.”
C. “Tell me more about that.”
D. “Why? What did you do wrong?”
5.
A hospitalized client of the Islamic (Muslim) religion is dying. What concept does the nurse share with the health care team about this client’s beliefs about death?
A. Death is seen as the transition to the other side, with Islam as the vehicle.
B. Life experiences do not affect the individual’s preparation for “everlasting life.”
C. The timing of death is under the power of the person who is facing death.
D. Plans for burial will take days, maybe even weeks, after the death.
6.
The daughter of a dying client says, “I don’t want my father to be uncomfortable.” How does the nurse respond?
A. “Do you want to talk to the bereavement nurse?”
B. “Your father will be closely monitored and cared for.”
C. “Your father will be kept sedated.”
D. “We will send him to hospice when the time comes.”
7.
A dying client becomes increasingly withdrawn and begins to refuse to eat and drink. What intervention does the nurse implement?
A. Brings in the client’s favorite Chinese takeout food
B. Calls the family to come in right away
C. Gives intravenous hydration
D. Offers ice chips
8.
Which condition, when assessed in a dying client, requires that the nurse take action?
A. Alternating apnea and rapid breathing
B. Anorexia
C. Cool extremities
D. Moaning
9.
A dying client exhibits signs of agitation. The Foley catheter has drained 100 mL in the last 3 hours, and the client’s last bowel movement was yesterday evening. What does the nurse do first?
A. Administers an analgesic
B. Arranges for a consultation with a bereavement counselor
C. Assesses the client for impaction
D. Changes the Foley catheter to ensure adequate drainage
10.
A nurse who is skilled in complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) therapies works on a cancer unit with clients who are terminally ill. For which client symptom does the nurse use these therapies?
A. Constipation
B. Cool extremities
C. Increased pain
D. Memory loss
11.
A client dying of cancer is receiving high doses of opioids. In addition, which intervention is the most effective for this client?
A. Classical music
B. Deep muscle massage
C. More pain medication
D. Short, light massage
12.
The nurse is coordinating interdisciplinary palliative care interventions for the dying client. Which goal is the nurse seeking to meet?
A. Avoiding symptoms of client distress
B. Ensuring an expedited death
C. Meeting all of the client’s needs
D. Facilitating a peaceful death for the client
13.
A client has died after a long hospital stay. The family was present at the time of the client’s death. Which postmortem action does the nurse implement?
A. Asks the family if they wish to help wash the client
B. Asks the family to leave
C. Raises the head of the bed and opens the client’s eyes
D. Removes dentures and any prosthetics
14.
A client diagnosed with lung cancer 6 months ago is now ventilator-dependent and unresponsive. The family wants to remove the ventilator and stop antibiotics and IV fluids. What does the nurse do next?
A. Facilitates a meeting with the family and health care team
B. Removes the interventions, per the family’s wishes
C. Tells the family that removing the interventions is illegal
D. Waits to obtain information on the client’s wishes
15. The nurse recognizes signs and symptoms of depression in an 80-year-old client who is dying from metastatic breast cancer. What does the nurse do initially for this client?
A. Assesses these behaviors as normal steps or stages in the grief process for the client
B. Collaborates with the end-of-life (EOL) care team to manage these feelings in the client
C. Documents these findings and continues to monitor the client
D. Reduces the quantity of depression-causing opioids that are being administered to the client
16. The nurse is performing a spiritual assessment on a dying client. Which question provides the most accurate data on this aspect of the client’s life?
A. “Do you believe in God?”
B. “Tell me about the history of religion in your life.”
C. “What gives you purpose and meaning in your life?”
D. “Where have you been attending church for the past several years?”
17.
In a comatose dying client’s hospital room, the nurse overhears family discussing the memorial service. What action does the nurse take?
A. Asks the family to speak in low tones or whispers so as not to disturb the client
B. Offers to call and have a hospital chaplain come and discuss plans with them
C. Shares some personal insights and experiences on planning a meaningful memorial service
D. Suggests that the family leave the room to carry on their discussion
18.
A client with terminal lung cancer is receiving hospice care at home. Which nursing action does the RN manager ask the LPN/LVN to do?
A. Administer prescribed medications to relieve the client’s pain, shortness of breath, and nausea.
B. Clarify family members’ feelings about the meaning of client behaviors and symptoms.
C. Develop a plan for care after assessing the needs and feelings of both the client and the family.
D. Teach the family to recognize signs of client discomfort such as restlessness or grimacing.
19.
A client with terminal pancreatic cancer is near death and reports increasing shortness of breath with associated anxiety. Which hospice protocol order does the nurse implement first?
A. Albuterol (Proventil) 0.5% solution per nebulizer
B. Morphine sulfate (Roxanol) 5 to 10 mg sublingually as needed
C. Oxygen 2 to 6 L/min per nasal cannula
D. Prednisone (Deltasone) elixir 10 mg orally
.
20.
A hospice client has just died. Which of these postmortem nursing tasks is most appropriate to delegate to a nursing assistant?
A. Assessing the client for cessation of respiratory effort and lack of pulse
B. Documenting the time of death and required assessment data on the chart
C. Notifying the spouse and other family members about the client’s death
D. Removing or cutting all IV lines or tubes according to the hospice policy
21.
The nurse manager for home health and hospice is scheduling daily client visits. Which client is appropriate for the nursing assistant to visit?
A. Advanced cirrhosis of the liver; called the hospice agency reporting nausea
B. Aggressive brain tumor; needs daily assistance with ambulation and bathing
C. Inoperable lung cancer; considering whether to have radiation and chemotherapy
D. Prostate cancer and bone metastases; has new-onset leg weakness and tingling
22.
The nurse working on an inpatient hospice unit has received the change-of-shift report. Which client does the nurse assess first?
A. A 26-year-old with metastatic breast cancer who is experiencing pain rated at 10 (0-to-10 scale) and anxiety
B. A 30-year-old with AIDS-associated dementia and agitation who is asking for assistance with calling family members
C. A 62-year-old with lung cancer who has cool, clammy, dusky skin and blood pressure of 64/20 mm Hg
D. A 70-year-old with cancer of the colon who has a respiratory rate of 8 with loud, wet-sounding respirations
23. A hospice client becomes too weak to swallow. What does the nurse do initially to increase the client’s comfort?
A. Administers nutrition and fluids through a nasogastric tube
B. Explains to the family that aspiration may be a concern
C. Obtains a physician order to initiate an IV line
D. Teaches the family how to provide oral care
24.
A dying client cannot swallow and is accumulating audible mucus in the upper airway (death rattles). The nursing assistant reports that these noises are upsetting to family members. What does the nurse tell the assistant to do?
A. Assist the family in leaving the room so that they can compose themselves.
B. Place the client in a side-lying position so secretions can drain.
C. Position the client in a high-Fowler’s position to minimize secretions.
D. Use a Yankauer suction tip to remove secretions from the client’s upper airway.
25. A Christian client is struggling with a diagnosis of cancer and says, “Why is life so unfair?” What health care team member does the nurse ask to provide support?
A. Client’s family
B. Physician
C. Hospital chaplain
D. Psychiatrist
26.
In which newly admitted client situations does the nurse initiate a conversation about advance directives? (Select all that apply.)
A. A client with a non–life-threatening illness
B. A person who currently has advance directives
C. The client with end-stage kidney disease
D. The comatose client who was injured in an automobile crash
E. The laboring mother expecting her first child
1. Questions
1.
In the role of client advocate, what does the nurse do first for a client who reports pain?
A. Administers pain medication
B. Assesses the level of pain
C. Believes the client’s report of pain
D. Calls the provider for a medication order
.
2.
The nurse is preparing a client for home care pain management following discharge. Which intervention does the nurse implement?
A. Discuss pain-relieving strategies on the day of discharge.
B. Discuss home care with only the client’s family, not with the client.
C. Offer flexibility in home management of the client’s current regimen.
D. Offer information about end-of-life pain control management.
3.
A client being discharged after hip replacement says, “I am going to use hypnosis instead of medication to manage my pain. I believe in mind over body.” How does the nurse respond?
A. “I will cancel your medication order.”
B. “That sounds like a great plan; can you tell me more about it?”
C. “That sounds like a wonderful idea; and I think it will definitely work!”
D. “Your plan will not work; people with your type of pain need narcotics.”
4.
When assessing a client for pain, acute or chronic, what question does the nurse ask the client to obtain the most data?
A. “Did someone do this to you?”
B. “Does it hurt badly?”
C. “Is the pain really that bad?”
D. “When does it hurt?”
5.
A postoperative client is requesting medication for pain every 4 hours. In planning effective pain management, what assessment question does the nurse ask the client before administering the medication?
A. “Are you bleeding?”
B. “Are you really hurting every 4 hours?”
C. “Is your pain controlled between doses?”
D. “What do you do for pain when you’re at home?”
6.
A client with extensive burn injuries is to be weaned from long-term opioid use. What type of opioid dependence does the nurse expect this client to have?
A. Addiction
B. Equianalgesia
C. Physical dependence
D. Pseudoaddiction
7.
A client with cancer who is taking pain medication states, “I am still having pain.” During the assessment, the client does not exhibit any physical manifestations of pain. What does the nurse do next?
A. Decreases the client’s standard pain medication dose
B. Gives the client a placebo and monitors the outcome
C. Gives the pain medication as requested
D. Withholds the pain medication
8.
A postoperative client reports, “I have pain from a mild headache.” Which PRN medication does the nurse administer?
A. Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
B. Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
C. Midazolam (Versed)
D. Oxycodone hydrochloride/acetaminophen (Tylox)
9.
A client had a hip replacement 2 days ago and reports having a moderate amount of pain, stating that it is “a 7 on a 0-to-10 scale” of intensity. What intervention has the highest priority in the client’s nursing care plan?
A. Encouraging diversional activities
B. Incorporating activities of daily living as soon as possible
C. Teaching key points of the relaxation response
D. Using pre-emptive analgesia
10. 10.ID: 4615498571
A client with cancer is receiving low-dose oral morphine but is reporting both “breakthrough” pain and constipation. What intervention does the nurse implement first?
A. Administers ordered docusate sodium (Colace) and gabapentin (Neurontin)
B. Decreases the morphine (morphine sulfate) dosage for the client
C. Gives the client a Fleet’s (sodium biphosphate) enema
D. Records the client’s bowel movements
11. 11.ID: 4615500201
A postoperative client is vomiting and states, “I am having a lot of pain—about a 7 on a scale of 0 to 10.” Which route of administration does the nurse choose to administer an analgesic to the client?
A. Intravenous
B. Oral
C. Rectal
D. Transdermal
12. 12.ID: 4615500203
A client with chronic pain feels no relief with high-dose opioids and says, “I just can’t manage living right now.” What intervention does the nurse anticipate the health care provider will order for this client?
A. Adding acetaminophen (Tylenol)
B. Adding duloxetine (Cymbalta) as adjuvant therapy
C. Increasing the opioid dose to control the pain
D. Replacing the opioid with duloxetine (Cymbalta) for depression
13. 13.ID: 4615498553
A client who is using patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is asleep. The nurse observes a family member pushing the PCA button for the sleeping client. What does the nurse say to the visitor?
A. “Please allow the client to push the button when needed.”
B. “Please don’t touch any equipment in the client’s room.”
C. “Thank you. I am sure the client appreciated that.”
D. “The client is asleep and is not in pain.”
14. 14.ID: 4615498577
A postoperative client is receiving epidural analgesia and reports itching. What does the nurse do next?
A. Reduces the analgesic dose
B. Gives diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
C. Gives an antiemetic
D. Calls the surgeon
15. 15.ID: 4615498569
Which statement is true about assessing pain in an older adult client?
A. The nurse should assess for present and past pain.
B. Older adults typically believe that expressing pain is acceptable.
C. Older adults are at great risk for undertreated pain.
D. Older adults usually believe that pain signifies a minor illness.
16. 16.ID: 4615498557
A client with osteoarthritis pain tells the nurse, “I take two arthritis-strength Tylenol (650 mg) every 8 hours.” How does the nurse respond?
A. “Aspirin would be a better, more effective choice for your pain relief.”
B. “More Tylenol is needed to provide effective pain relief for you.”
C. “That is the appropriate dose of Tylenol for your pain.”
D. “You will need to have routine liver and kidney function laboratory tests.”
17. The nurse is planning a dressing change on a postoperative mastectomy client. The client is receiving acetaminophen and oxycodone (Percocet) orally for pain every 4 hours and is due to receive them at 4:00 p.m. When will the nurse change the dressing?
A. 3:30 p.m.
B. 4:00 p.m.
C. 4:30 p.m.
D. 7:00 p.m.
.
18. The nurse is caring for a client who had a fractured ankle repaired. Twenty minutes after receiving 1.5 mg of hydromorphone (Dilaudid) IV push, the client is slow to respond and has constricted pupils and a respiratory rate of 6 breaths/min. What action does the nurse take initially?
A. Calls the care provider for a change in the medication order
B. Changes the order to every 6 hours rather than every 4 hours
C. Gives the client a dose of naloxone (Narcan) 0.4 mg IV
D. Performs a cognitive assessment on the client
19.
The family of a client with chronic cancer pain says to the nurse, “Can you please reduce Dad’s pain medication so that we can spend more quality time with him?” How does the nurse respond?
A. “I will ask his oncologist about your question.”
B. “Let’s ask your father about your request.”
C. “No, his pain relief is more important than your concerns.”
D. “Yes, this is a valuable way for all of you to make needed adjustments.”
20.
A newly admitted client who was in an automobile accident has a concussion and is reporting pain from a fractured femur and broken fingers. Which staff member does the charge nurse on the orthopedic unit assign to care for this client?
A. An experienced RN travel nurse who arrived on the unit this morning
B. An LPN/LVN who has worked on the orthopedic unit for 6 years
C. The neurology unit RN who has floated to the orthopedic unit
D. The RN orthopedic case manager who is responsible for discharge planning
21.
During change-of-shift report, the day shift staff learns that a client who had back surgery has been reporting increasing lower back pain during the night. It is most appropriate for which day staff member to assess the client’s pain?
A. LPN/LVN who is responsible for administering medications to the client
B. RN nurse manager who is in charge of coordinating care for several units
C. RN team leader who is responsible for updating the care plan for the client
D. RN who has floated to the unit from the emergency department
22. Which activity does the RN team leader on a large medical-surgical unit assign to the LPN/LVN?
A. Assessment of a client scheduled for surgery who is crying and expressing fear that the pain will be intolerable
B. Assessment of a client using a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation unit to relieve chronic pain
C. Complex dressing changes for a sacral wound for a client with type 2 diabetes who was given prescriptions for pain medication before wound care
D. Instructions to a postoperative hip replacement client who has just been placed on patient-controlled analgesia for pain relief
23.
The nurse is establishing a plan of care for a hospitalized client with chronic pain caused by fibromyalgia. Which nursing action does the nurse delegate to a nursing assistant?
A. Application of a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) device
B. Education about nonpharmacologic interventions for pain control
C. Referral to available community resources for pain management
D. Engagement in conversation about the client’s family to distract the client
24. 24.ID: 4615498573
Which client does the RN arriving for duty assess first?
A. A 27-year-old who has chronic severe back pain with movement
B. A 51-year-old with lung cancer who reports pain “whenever I cough”
C. A 56-year-old with acute pancreatitis who reports increasing abdominal pain
D. A 63-year-old who reports ongoing pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis
25. 25.ID: 4615498597
The nurse manager for an oncology unit is evaluating a newly hired staff nurse. Which action by the nurse is of greatest concern to the nurse manager?
A. Asking a client with chest pain if the pain is sharp and stabbing
B. Instructing a confused postoperative client about how to use patient-controlled analgesia
C. Preparing to administer a placebo to a client with chronic back pain
D. Requesting that a client with chronic pain describe the specific location of the pain
26. 26.ID: 4615498581
The nurse manager on the surgical unit is making assignments for the day. Who is assigned to check and program the patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pumps on the unit?
A. A pharmacy technician
B. One registered nurse (RN)
C. One registered nurse (RN) and a certified nursing assistant (CNA)
D. Two registered nurses (RNs)
.
27. 27.ID: 4615498599
A hospitalized client anticipates a daily painful dressing change. Which complementary and alternative medicine therapy might the nurse offer before the procedure?
A. Animal-assisted therapy
B. Hydrotherapy
C. Imagery
D. Acupuncture
28. 28.ID: 4615498587
A hospitalized client expresses satisfaction after using a recommended complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) therapy, saying that pain was diminished and anxiety reduced. Which CAM did the client most likely use?
A. Herbs
B. Homeopathy
C. Imagery
D. Tai chi
29. 29.ID: 4615498567
A client reports increasing pain during dressing changes. Which interventions are recommended for the client? (Select all that apply.)
A. Assistance by the client with the dressing change
B. Distraction
C. Epidural analgesic
D. Music therapy
E. Premedication
F. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
[Show More]