Business Law > EXAM > Fayetteville State University Leg 100 Unit 2 Milestone Questions And Answers( Rated A) (All)
Fayetteville State University Leg 100 Unit 2 Milestone Questions And Answers( Rated A)
Document Content and Description Below
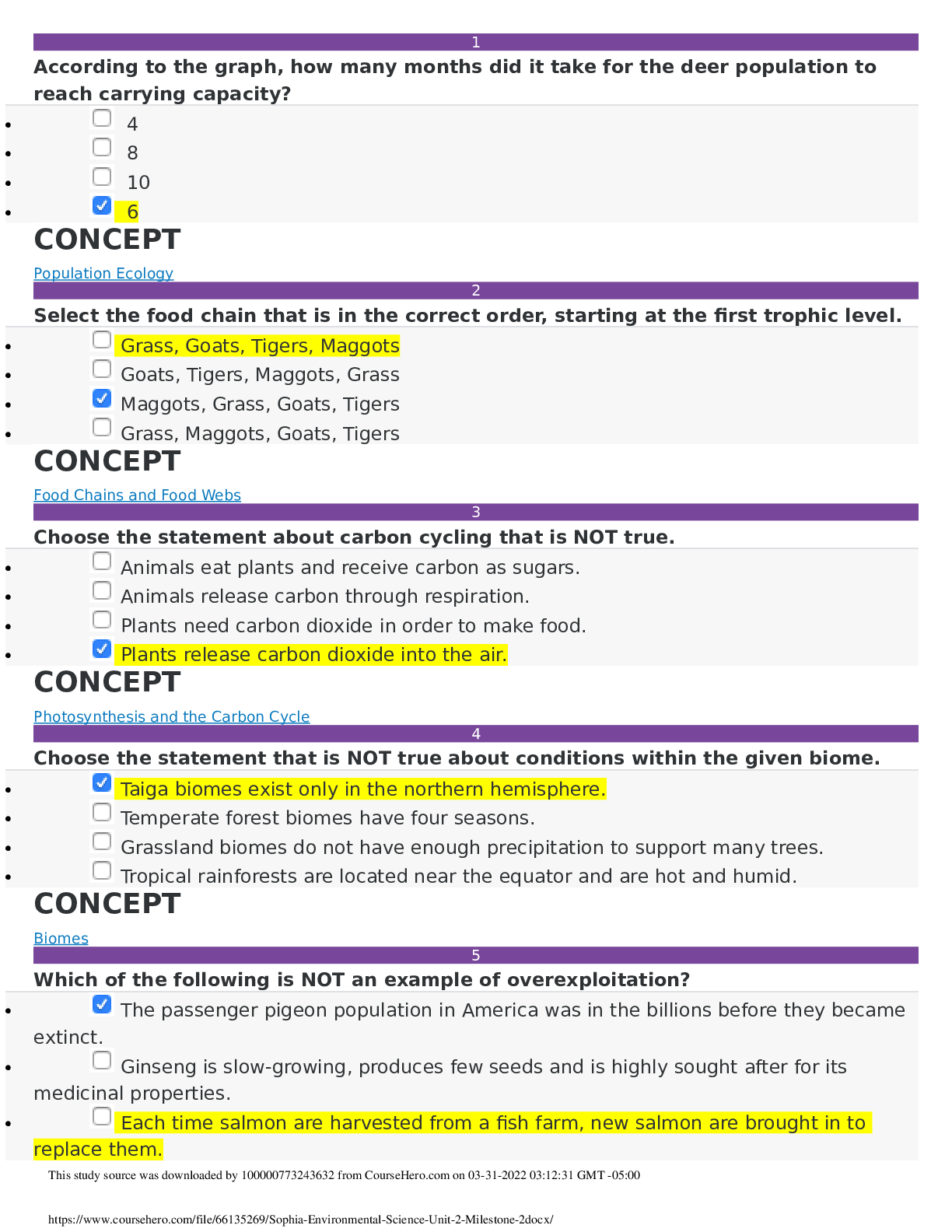
Leg 100 Unit 2 Milestone 1 In which scenario would strict liability most likely apply? • A dishwasher fails to fully clean the dishes. • A car's radio sometimes stops working. • A ... lightbulb burns out prematurely. • An airplane's brakes fail in freezing weather. CONCEPT Strict Liability 2 Which contract generally must be in writing under the Statute of Frauds? • Harlow agrees to pay $50 to anyone who can help her find her lost dog. • Finn agrees to buy a watch from a friend for $300. • Miguel agrees to replace his neighbor's roof in three months for $15,000. • Neesa agrees to co-sign a loan for her daughter to pay for college tuition. CONCEPT Statute of Frauds 3 Which of the following scenarios would likely result in an order for specific performance or an injunction, rather than a monetary award? • Martina pays Omar $250 to deliver a cord of firewood to her home. Omar never delivers the wood, and Martina eventually sues him for breach of contract. • Uma buys a copy of a photograph she loves from a local home decor shop. When she has the photograph framed, the framing company damages it and refuses to pay for its restoration. Uma sues the framing company for breach of contract. • Darien buys a new car from a dealership that is supposed to come with leather seating. When he takes possession of the car, it has regular fabric seating. Darien sues the car dealership for breach of contract. • Cheryl has all of her employees sign non-compete agreements that extend for two years after their employment ends. Cheryl's former employee, Jen, starts working for a competitor three months after she stops working for Cheryl. Cheryl files a suit against Jen for breach of contract. CONCEPT Equitable Remedies: Specific Performance and Injunction 4 Tort law is similar to criminal law in that __________. • they both require specific intent on the part of the defendant • they both require specific intent on the part of the plaintiff • they both require a wrongful act by a defendant for the plaintiff to recover • they both have primarily developed in common law courts CONCEPT Introduction to Tort Law 5 A manufacturer of a portable circular saw is sued by Dennis, who, while using the saw, put it down on the ground in front of him after it was shut off but while the blade was still turning. The still-circulating saw creeped across the floor, causing significant personal injury to Dennis' foot. Dennis sued the manufacturer for defective design of the circular saw based on it not having a brake mechanism or a retractable cover for the blade once the saw was turned off. How strong of a case does Dennis have in his strict liability lawsuit against the manufacturer based on the defective design of the circular saw? • Weak, because Dennis assumed the risk of injury when he chose to use a circular saw, which is known to be dangerous. • Strong, but only if Dennis can prove that the saw was less safe when turned off than other saws on the market. • Strong, because the saw was unreasonably dangerous under circumstances that would be foreseeable as normal use by a consumer. • Weak, because there is no evidence that the saw was unreasonably dangerous in normal use. CONCEPT Strict Products Liability 6 The purpose of contracts is __________. • to eliminate any disagreement in economic exchanges • to facilitate economic transactions between individuals • to bring order to medieval societies • to limit personal freedom CONCEPT General Perspectives on Contracts 7 Cynthia orders 100 blue shirts for her screenprinting business from Juan, a shirt supplier. When Cynthia receives the shirts, she discovers that Juan has sent her a batch of pink shirts. She rightfully rejects delivery, and the shirts are shipped back to Juan. Because of the delay in receiving the blue shirts, Cynthia is unable to fill a large order and loses $500 in sales. What remedy does Cynthia have in this scenario? • Cynthia must fulfill the contract by paying for the blue shirts when they finally arrive, but she is entitled to recover damages relating to her business losses in the meantime. • Cynthia can cancel the contract with Juan and recover in full what she paid for the shirts, as well as sue for damages since she suffered a loss directly related to the non-delivery. • Since she rejected the delivery, Cynthia has no recourse in this scenario except for a refund of the price she paid for the shirts. • Cynthia may either replevy the shirts or sue Juan for specific performance. CONCEPT Buyer's Remedies Under the Uniform Commercial Code 8 Andy is driving a 20-year-old boat that he borrowed from a friend. While he's on the water, the steering system fails and the boat crashes. Subsequent investigation shows that the steering system failed as a result of corrosion. Andy sues the boat manufacturer for negligence. How strong is his negligence case against the product manufacturer? • Strong, because there is no evidence that Andy's own actions contributed to the damages. • Weak, unless he can show that the corrosion was the result of a design defect rather than normal wear and tear on a 20-year-old boat. • Strong, because proximate cause between the corroded steering system and the crash is easy to establish. • Weak, because he does not have privity of contract, since he was borrowing his friend's boat. CONCEPT Negligent Products Liability 9 Select the statement that is true of consumer law prior to the 20th century. • It relied primarily on the threat of litigation to ensure product safety. • Its central tenet was "seller beware." • It was rooted in the fact that consumers had much more direct contact with producers than they do now. • It essentially functioned in the same way as current products liability law. CONCEPT Products Liability 10 A laundry detergent company advertises that its new product can remove any stain from clothes in just one wash, although company testing has shown that it oftentimes takes two or three washes for a stain to disappear. Which type of intentional tort does this represent? • Tortious interference with contract • This action does not rise to the level of an intentional tort. • Misrepresentation • Defamation CONCEPT Intentional Torts 11 Which of the following is an example of a voidable contract? • A 21-year-old forms a contract with an able-bodied and competent 30-year-old neighbor to drive her to work all year in exchange for gas money. • A 52-year-old forms an oral contract with an able-bodied and competent adult neighbor to paint his deck for $1,000. • A 21-year-old adult forms a written contract with an able-bodied and competent adult neighbor to clean his house for $1 per month. • A 28-year-old adult forms a written contract with an able-bodied and competent 17-year-old neighbor to cut her lawn for $200 per week. CONCEPT Different Types of Contracts 12 Select the true statement about the Restatement of the Law of Contracts. • It must be renewed by Congress every ten years. • It is a valuable resource for judges to consult, but it is not formal law. • It completely overturned the contract law that had developed in the common law courtroom. • It is the primary source of law for contract cases involving the sale of goods. CONCEPT Sources of Contract Law 13 A store employee drops a box of oranges while stocking the produce section, and oranges roll all over the floor. A customer steps on an orange and falls, injuring her arm. The customer sues the store employee for negligence. Assuming it is true, which of the following would represent a strong defense against the negligence claim? • The employee had already partially cleaned up the oranges when the customer fell. • The customer has mounting debts and needs money to pay them off. • The customer ignored a barrier that the employee had set up around the produce section of the store. • The customer was talking to her friend when the accident happened. CONCEPT Negligent Torts: Damages and Defenses 14 Select the example that is inconsistent with the provisions of the UCC for contract remedies for a seller's breach of contract. • An auto manufacturer's sales contract reduces the statute of limitations for breach of contract claims to nine months. • In its sales contract, a jewelry maker gives buyers a maximum of 18 months to raise any concerns relating to breach of contract. • The sales contract for a company that sells rare antiques includes a liquidated damages clause in the event of a breach of contract that the courts have deemed reasonable. • The sales contract for machine parts excludes responsibility for any loss of business that may result from a delivery delay. CONCEPT Remedies in General Under the Uniform Commercial Code 15 Which of the following conditions always renders a contract unenforceable? • If a party to the contract is deemed incapacitated by intoxication or mental state • If a party to the contract is unable to fulfill the terms of the contract • If the contract is deemed to be unfair to one party • If the contract is informal (i.e., verbal rather than written) CONCEPT Unenforceable Contracts 16 Zahra and Joseph sign a contract worth $1,000. When Zahra breaks the contract, Joseph loses the $1,000. Which type of monetary award does Joseph receive if he is later awarded $1,000? • Compensatory damages • Restitution • Nominal damages • Incidental damages CONCEPT Monetary Awards 17 An example of foreseeable damages from a faulty repair of your car that led to an accident would be __________. • your loss of one year's wages from a job, since you were fired that day for being late after the accident • the cost to repair your vehicle, as well as all damage to other vehicles involved in the accident • your loss of a winning lottery ticket that blew away in the wind during the accident • additional hotel and travel charges that you incurred, because you missed your flight that day as a result of the accident CONCEPT Limitations on Contract Remedies 18 To be enforceable, a contract typically must __________. • have assent and consideration from at least one party, and have legal capacity and purpose from both parties • have mutual assent and legal capacity of both parties, and be in written form • have mutual assent, legal value exchanged by both parties, and be entered into in good faith • have mutual assent, legal value exchanged by both parties, legal capacity of both parties, and be for a legal purpose CONCEPT Contract Formation 19 A driver is texting and runs into a pedestrian crossing the road at a crosswalk. The pedestrian suffers a broken leg and is rushed to the hospital. Is the driver liable for negligence if the pedestrian sues? • Yes, because the driver had a duty of care which was breached by texting while driving, and the pedestrian had legally recognizable injuries directly resulting from that breach. • No, because it would be difficult to prove that the driver's texting was the proximate cause of the pedestrian's broken leg. • No, because even though the driver was texting while driving, the pedestrian had a duty to look out for possible dangers before entering the crosswalk. • Yes, because the driver broke the law by texting while driving. CONCEPT Negligent Torts: Liability 20 Cynthia orders 100 shirts in a variety of colors for her screenprinting business from Juan, a shirt supplier. Before Juan ships the shirts, Cynthia calls him to inform him that she is going out of business and no longer needs the shirts. Juan decides to resell the 100 shirts at public auction. What further remedy does Juan have in this scenario? • If Juan sells the shirts at auction for more that the original contract price, he is obligated to share the profits, less any incidental costs, with Cynthia. • Juan may sell the shirts at public auction without notifying Cynthia, since she is in breach of contract. • If Cynthia becomes aware of the public auction, Juan may refuse to allow Cynthia to bid on the shirts since she is in breach of contract. • Since Juan is reselling the shirts at public auction and they are not a perishable good, he must notify Cynthia of the public sale and allow her to bid if she wishes. CONCEPT Seller's Remedies Under the Uniform Commercial Code 21 A manufacturer of kitchen knives is sued for strict product liability by Jack, who cut himself with one of the knives and suffered permanent nerve damage and paralysis in three fingers on his left hand. Jack argues that the knives were overly sharp and, thus, defective in their manufacturing. The manufacturer defends against the claim by arguing that the risk to the consumer is outweighed by the utility of the knives. How does Jack's claim stand up to the manufacturer's defense? • Jack is likely to win, unless the manufacturer can prove that Jack was misusing or abusing the knife in some way. • Jack is likely to win, because the risk-utility test is only applicable to strict product liability claims involving pharmaceuticals. • Jack is likely to lose, because the knife is clearly safe for its intended use. • Jack is likely to lose, because the knife cannot function for its intended purpose unless it is sharp, and the risk to consumers is more than outweighed by the utility of a sharp kitchen knife. CONCEPT Problems with Strict Products Liability [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 08, 2021
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
193

.png)