Pathophysiology > STUDY GUIDE > Pathophysiology Exam 1 Study Guide | Revised and Expanded (All)
Pathophysiology Exam 1 Study Guide | Revised and Expanded
Document Content and Description Below
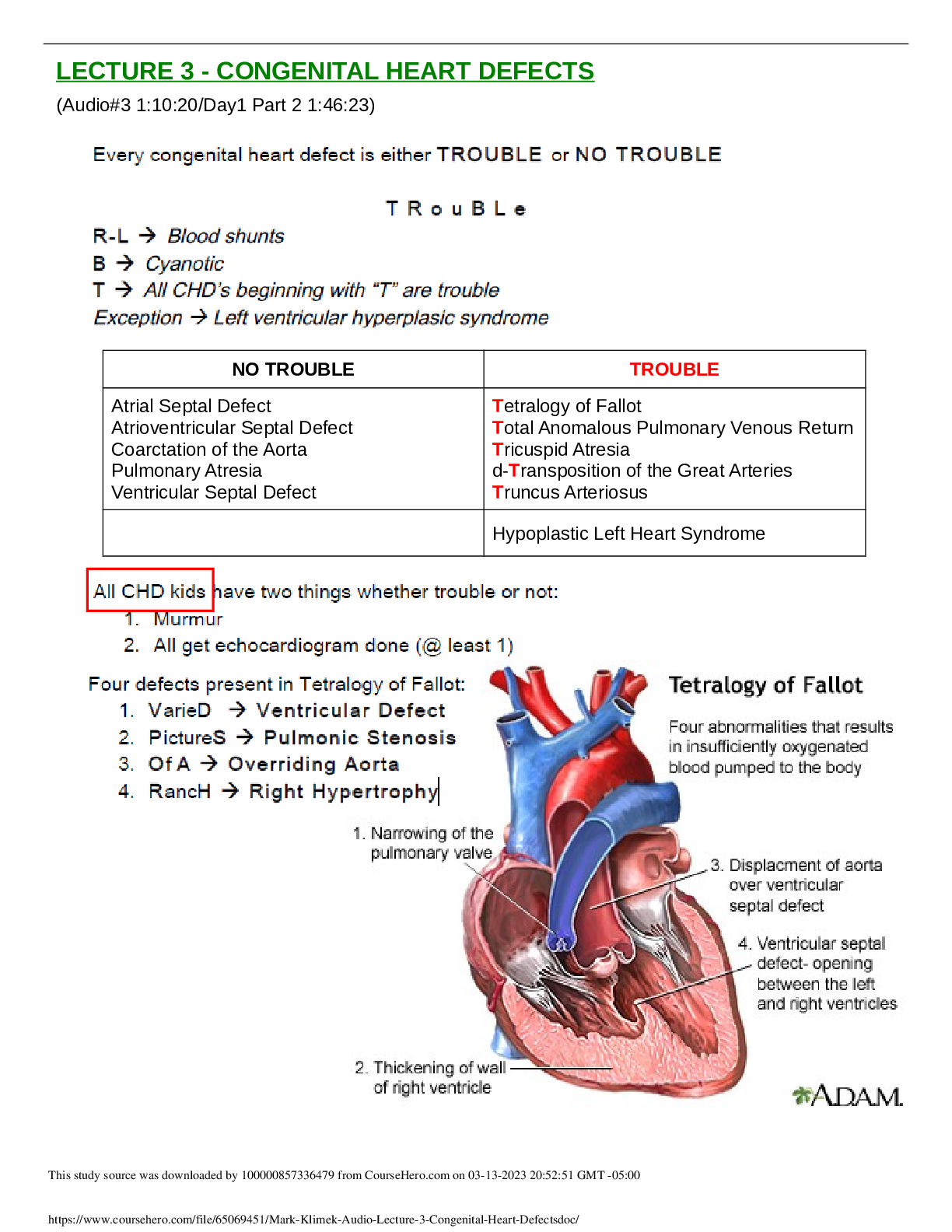
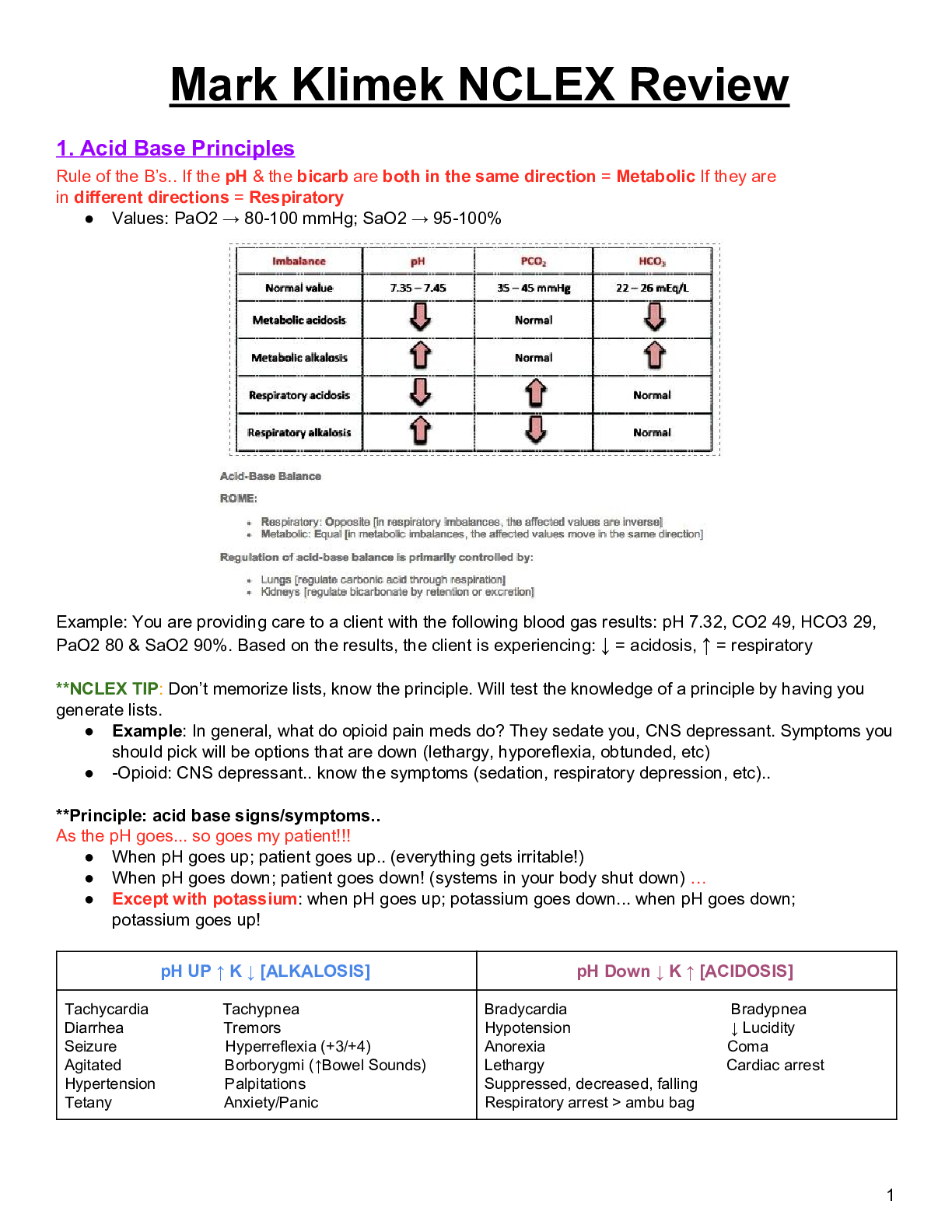
• Atrophy, Hypertrophy, Hyperplasia, Metaplasia, Dysplasia: pathophysiology, what makes them different, examples of each type of cellular adaptation • Most common cause(s) of cellular injury ... • What changes occur during cellular injury to the cell, when lack of ATP leads to ischemia and hypoxia (from class, what electrolytes move out of cell, into cell, etc.) • Types of Necrosis: Liquefactive vs. Coagulative vs. Gangrene vs. Fatty o Gangrene-large are of necrosis, Severe hypoxic injury, severe lack of oxygen, commonly occurring due to arteriosclerosis (blockage) of major arteries ESPECIALLY in the lower leg—larger area than liquefactive • Apoptosis o cell death resulting from activation of intracellular signaling cascades that course cell death. • Complications of impaired wound healing o Dysfunction during inflammatory response o Wound disruption Dehiscence o Impaired epithelialization Antiinflammatory steroids, hypoxemia, and nutritional Innate Immunity: Inflammation (Ch. 7): • Vascular response associated with inflammation & local manifestations • Main functions of the three protein systems (complement, coagulation, & kinin), not every little detail, stick to the basic and most important features • Role of “General” Mast cell in the inflammatory response • Chemotaxis and chemotactic factors: role in inflammatory response o Chemotaxis – directional movement of cells along a chemical gradient; • Role of Phagocytes & Phagocytosis (neutrophils, macrophages, eosinophils only) o Macrophages – mature monocytes #2 Monocytes produced in bone marrow, enter circulation, o Eosinophils – parasitic #3 • Chemical mediators that induce pain during an inflammatory response • Local vs. Systemic signs (clinical manifestations) of inflammation • Exudative Fluids: types and description of each o Serous exudate • Age related changes associated with immunity and wound healing o Neonates - infants • Primary characteristics that differentiate the adaptive response from the innate inflammatory response • Origins of B & T cells o B cells -from bone marrow • Clonal Diversity vs. Clonal Selection o Clonal diversity: • Passive vs. Active immunity and examples of each • Humoral vs. Cell-Mediated Immunity: major differences and roles of each o Humoral immunity • Antigens: Role and definition of antigen and immunogens, the most important determinant of an antigen being able to initiate an immune response, antigen binding • Antibody Production and protective mechanisms o produced by plasma cells. o Job is to Protect against infection. • Antibody classes: IgM, IgG, IgE (difference between these only, major points) • Age related changes in immune function o Decreased T-cell activity (leads to viral infections or cancer.) Alterations in Immunity & Inflammation (Ch. 9) & Infection (Ch. 10): • Hypersensitivity and Hypersensitivity Reactions: Type I to Type IV, major pathophysiological differences, class of antibody associated with each, and examples of each • Alloimmunity vs. Autoimmunity: definition, patho, examples of each • Transplant Rejection • Transplant rejection: Classified according to time. • HIV & AIDS: pathophysiology, diagnosis criteria, clinical manifestations o HIV: • Host lines of defense • Types of Organisms that cause infection (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites): characteristics of each [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 3 out of 13 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 21, 2020
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 21, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
223







.png)
















