Health Care > STUDY GUIDE > MED SURG 206 Exam 2 Review- Jersey College, School of Nursing (All)
MED SURG 206 Exam 2 Review- Jersey College, School of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
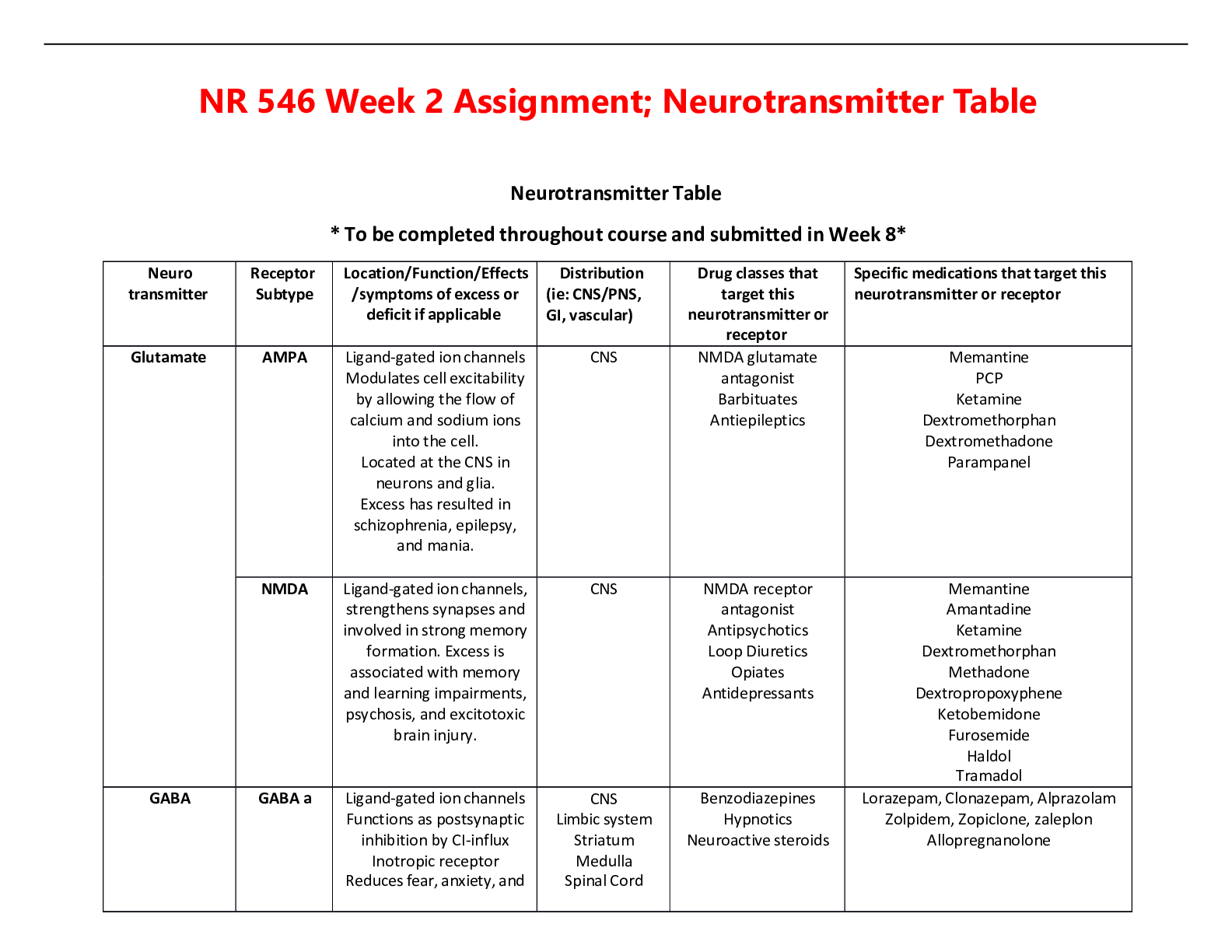
CHAPTER 41 MANAGEMENT OF PATIENT WITH MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS Low Back Pain Generally, back pain due to musculoskeletal disorders is aggravated by activity, whereas pain due to other conditions ... is not. Pathophysiology Vertebrae- rigid units intervertebral discs- flexible units Obesity, postural problems, structural problems, and overstretching of the spinal supports may result in back pain The lower lumbar discs, L4–5 and L5–S1, are subject to the greatest mechanical stress and the greatest degenerative changes. A young person’s discs are mainly fibrocartilage with a gelatinous matrix Clinical Manifestations acute back pain (lasting fewer than 3 months) chronic back pain (3 months or longer without improvement) and fatigue radiculopathy-pain radiating from a diseased spinal nerve root or radiating down the legs sciatica- pain radiating from an inflamed sciatic nerve paravertebral muscle spasm (greatly increased muscle tone of the back postural muscles) Assessment and Diagnostic Findings The presence of bruising, older age and prolonged use of glucocorticoid medications increases the risk of a fracture posttraumatic injury The diagnostic procedures are contraindicated in suspected spinal infection, severe neurologic weakness, urinary or fecal incontinence, and a new onset of back pain in a patient with cancer Diagnostic Procedures for Low Back Pain X-ray of the spine: may demonstrate a fracture, dislocation, infection, osteoarthritis, or scoliosis Bone scan and blood studies: may disclose infections, tumors, and bone marrow abnormalities Computed tomography (CT) scan: useful in identifying underlying problems, such as obscure soft tissue lesions adjacent to the vertebral column and problems of vertebral discs Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan: permits visualization of the nature and location of spinal pathology Electromyogram (EMG) and nerve conduction studies: used to evaluate spinal nerve root disorders (radiculopathies) Myelogram: permits visualization of segments of the spinal cord that may have herniated or may be compressed (infrequently performed; indicated when MRI scan is contraindicated) Ultrasound: useful in detecting tears in ligaments, muscles, tendons, and soft tissues in the back Medical Management Most back pain is self-limited and resolves within 4 to 6 weeks with analgesics, rest, and avoidance of strain Management focuses on relief of discomfort, activity modification, and patient education acute low back pain- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) short-term prescription muscle relaxants (e.g., cyclobenzaprine [Flexeril]) chronic low back pain- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline [Elavil]) serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine [Cymbalta]) radiculopathy pain - atypical anticonvulsant medications (e.g [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 93 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$19.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 14, 2023
Number of pages
93
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 14, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
118