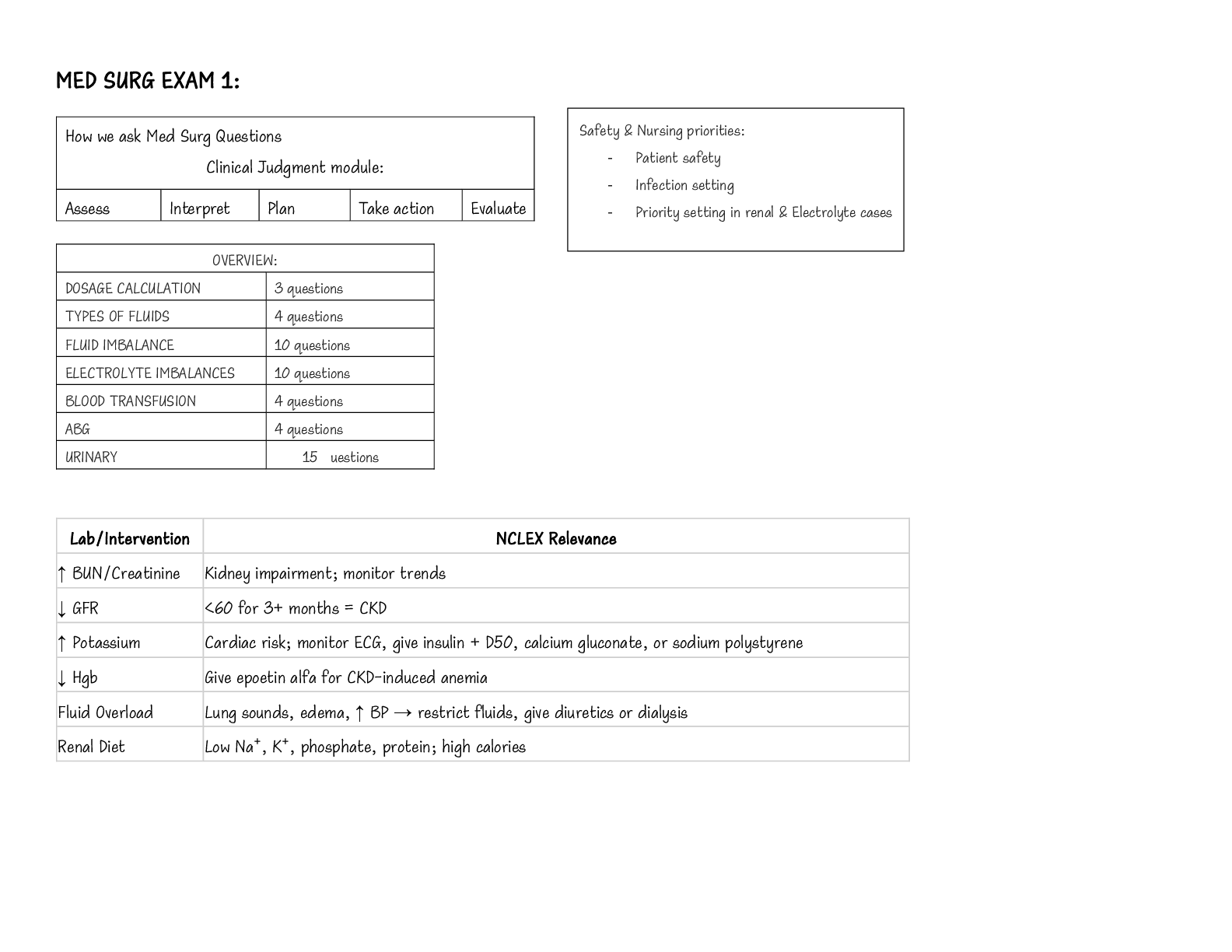
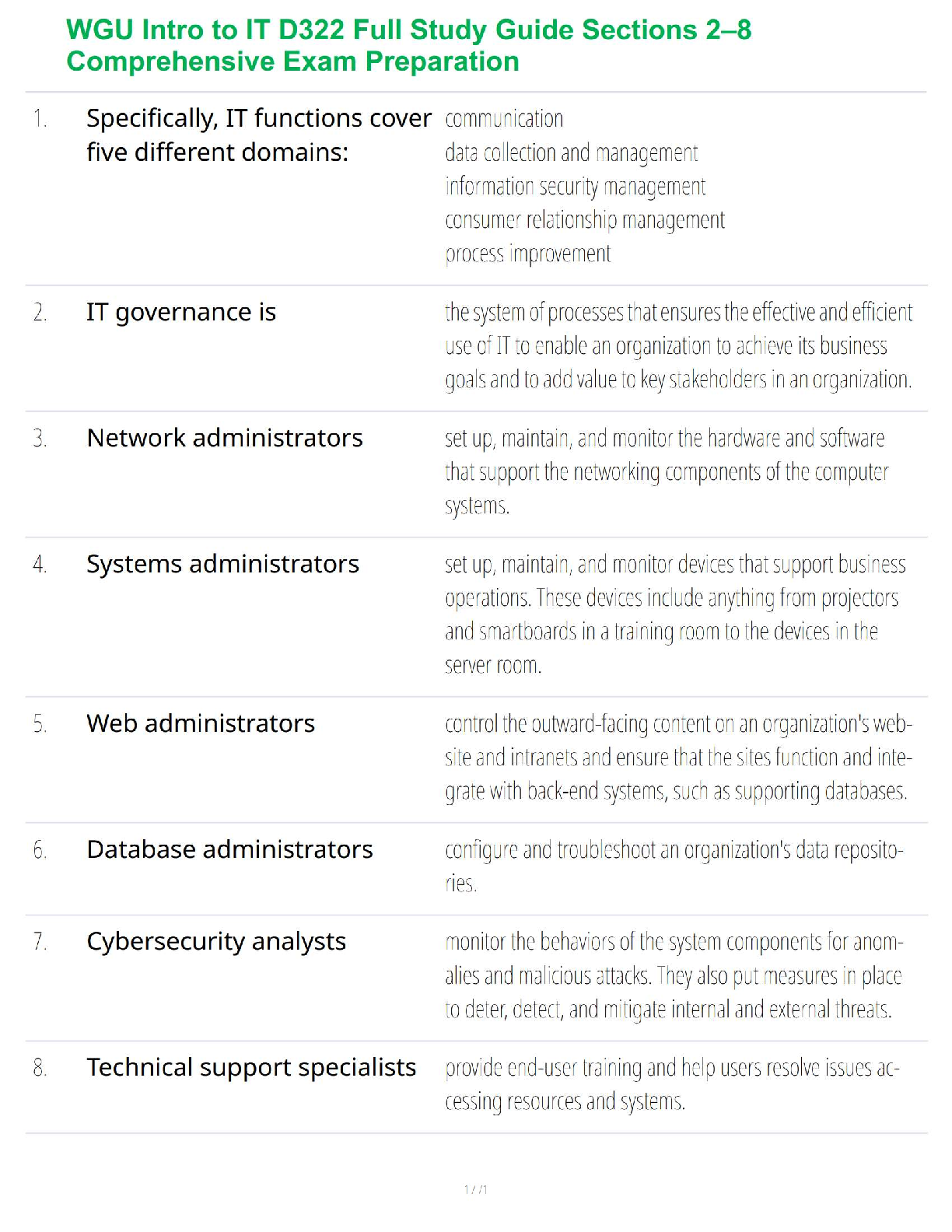
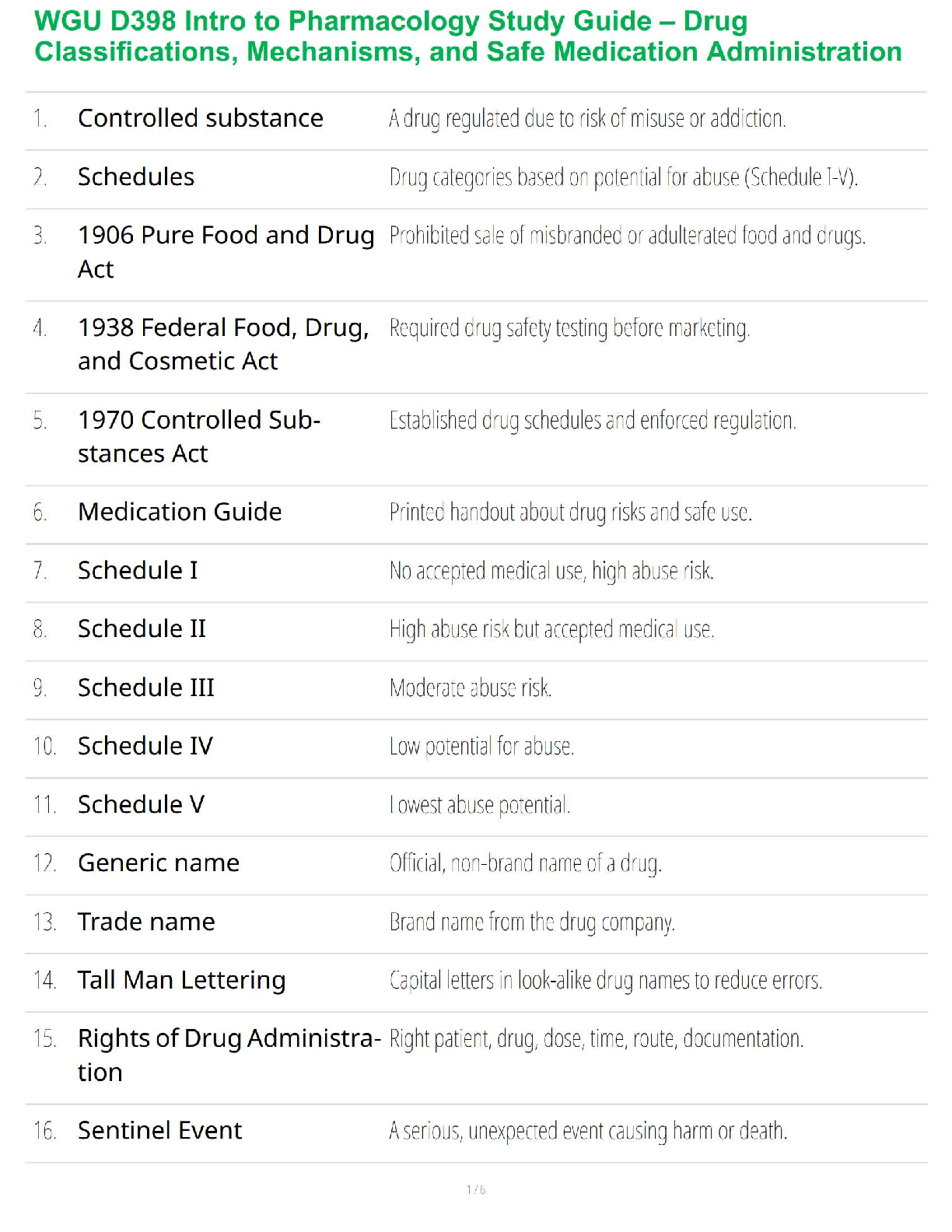
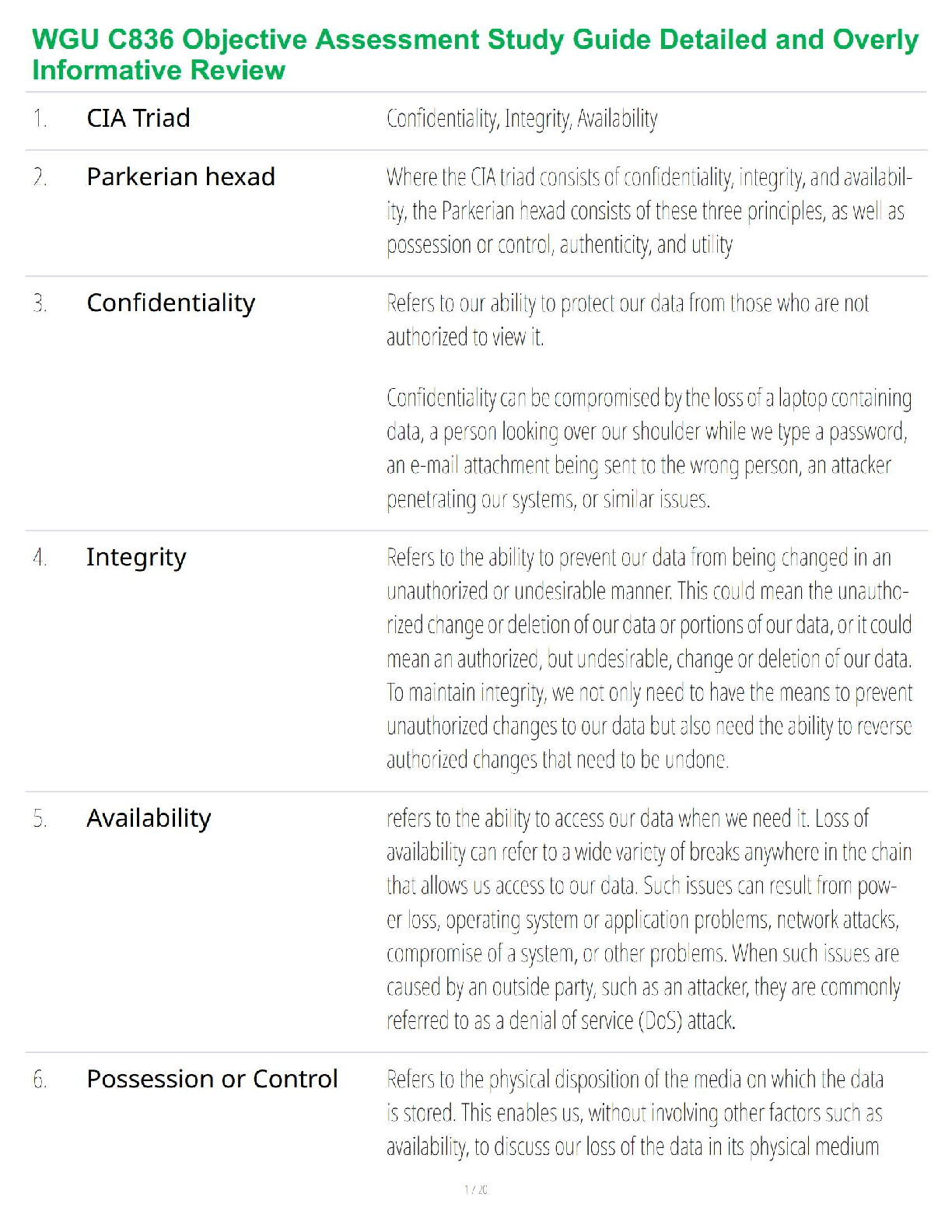
NSG 5003 Week 9 Study Guide
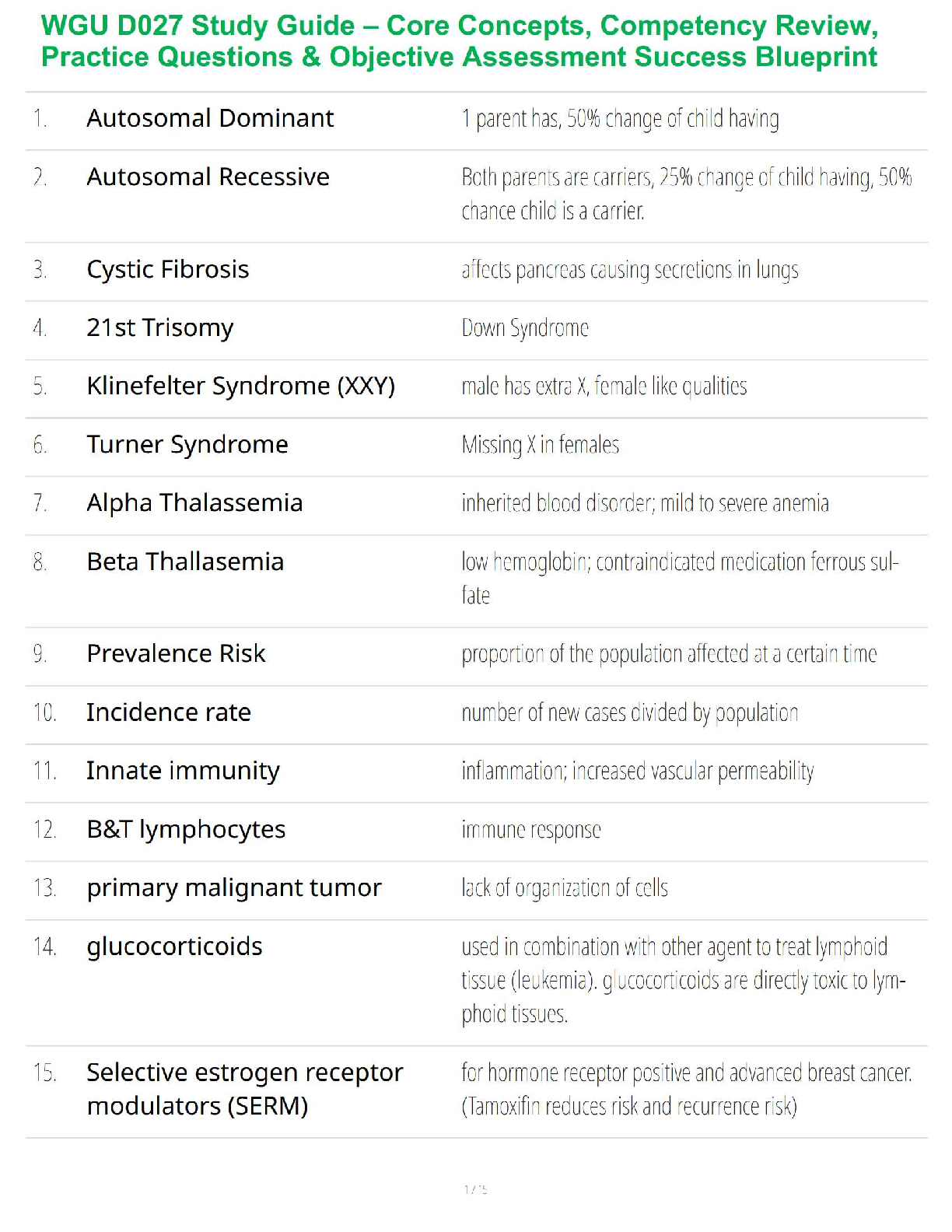
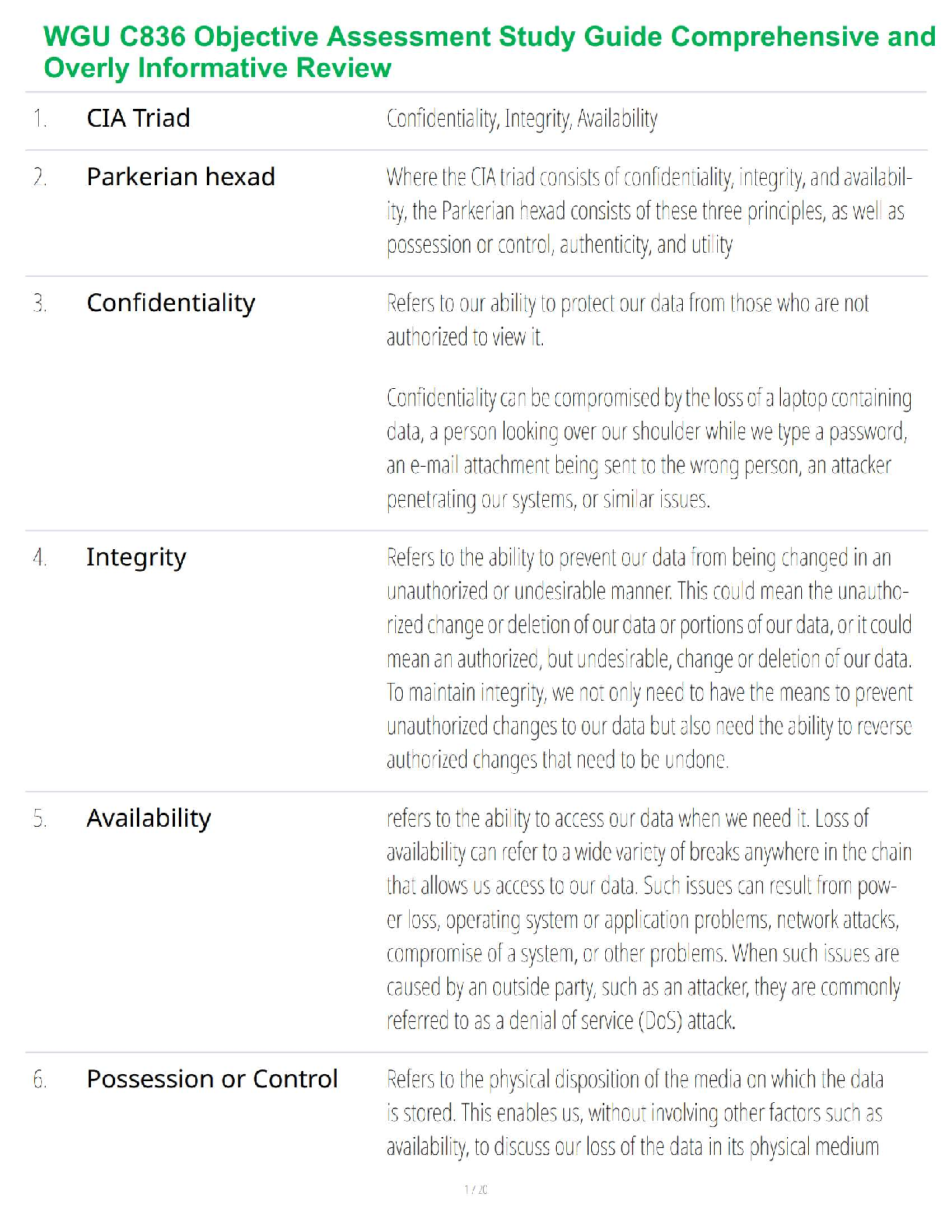
Chapter 15: Structure and Function of the Neurologic System
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which pathway carries sensory information toward the central nervous system (CNS)?
2. Which type
...
NSG 5003 Week 9 Study Guide
Chapter 15: Structure and Function of the Neurologic System
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which pathway carries sensory information toward the central nervous system (CNS)?
2. Which type of axon transmits a nerve impulse at the highest rate?
3. Which nerves are capable of regeneration?
4. The neurotransmitter, norepinephrine, is secreted in the:
5. Both oligodendroglia and Schwann cells share the ability to:
6. During a synapse, what change occurs after the neurotransmitter binds to the receptor?
7. What name is given to a large network of neurons within the brainstem that is essential for maintaining wakefulness?
8. Thought and goal-oriented behaviors are functions of which area of the brain?
9. The region responsible for the motor aspects of speech is located in the:
10. Parkinson and Huntington diseases are associated with defects in which area of the brain?
11. Maintenance of a constant internal environment and the implementation of behavioral patterns are main functions of which area of the brain?
12. The ability of the eyes to track moving objects through a visual field is primarily a function of which colliculi?
13. What parts of the brain mediate the expression of affect, both emotional and behavioral states?
14. Reflex activities concerned with heart rate, blood pressure, respirations, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing are controlled by which area of the brain?
15. From which part of the midbrain do cranial nerves V to VIII emerge?
16. From which part of the midbrain do cranial nerves IX to XII emerge?
17. Which area of the brain assumes the responsibility for conscious and unconscious muscle synergy and for maintaining balance and posture?
18. Which statement is true regarding upper motor neurons?
19. The membrane that separates the brain’s cerebellum from its cerebrum is the:
20. The function of arachnoid villi is to:
21. Where is the cerebrospinal fluid produced?
22. Which of the meninges closely adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord and follows the sulci and fissures?
23. Norepinephrine produces what primary response?
24. What is an effect of the sympathetic nervous system?
25. The brain receives approximately what percentage of the cardiac output?
26. The collateral blood flow to the brain is provided by the:
27. The nurse recognizes that a patient’s diagnosis of a viral infection of the brain’s meningeal layer is supported by which diagnostic laboratory result?
Chapter 17: Alterations in Cognitive Systems, Cerebral Hemodynamics, and Motor Function
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Cognitive operations cannot occur without the effective functioning of the brain’s:
2. Which intracerebral disease process is capable of producing diffuse dysfunction?
3. What is the most common infratentorial brain disease process that results in the direct destruction of the reticulating activation system (RAS)?
4. What stimulus causes posthyperventilation apnea (PHVA)?
5. Posthyperventilation apnea (PHVA) ceases and rhythmic breathing is resumed when levels of arterial:
6. Cheyne-Stokes respirations are described as a:
7. Vomiting is associated with central nervous system (CNS) injuries that compress which of the brain’s anatomic locations?
8. Which midbrain dysfunction causes pupils to be pinpoint size and fixed in position?
9. What characteristic is a medical criterion of brain death?
10. A clinical manifestation caused by damage to the lower pons includes an abnormal:
11. Which person is at the greatest risk for developing delirium?
12. A sudden, explosive, disorderly discharge of cerebral neurons is termed:
13. A complex partial seizure is described as:
14. Status epilepticus is considered a medical emergency because of the:
15. The most critical aspect in correctly diagnosing a seizure disorder and establishing its cause is:
16. What type of seizure starts in the fingers and progressively spreads up the arm and extends to the leg?
17. What area of the brain mediates the executive attention functions?
18. What term describes the loss of the comprehension or production of language?
19. With receptive dysphasia (fluent), the individual is able to:
20. What is the normal intracranial pressure (in mm Hg)?
21. Cerebral edema is an increase in the fluid content of the brain’s:
22. What type of cerebral edema occurs when permeability of the capillary endothelium increases after injury to the vascular structure?
23. A communicating hydrocephalus is caused by an impairment of the:
24. Which edema is most often observed with noncommunicating hydrocephalus?
ANS: B
25. Which dyskinesia involves involuntary movements of the face, trunk, and extremities?
26. Antipsychotic drugs cause tardive dyskinesia by mimicking the effects of increased:
27. The existence of regular, deep, and rapid respirations after a severe closed head injury is indicative of neurologic injury to the:
28. What type of posturing exists when a person with a severe closed head injury has all four extremities in rigid extension with the forearms in hyperpronation and the legs in plantar extension?
29. Since his cerebrovascular accident, a man has been denying his left hemiplegia. What term is used to describe this finding?
30. After a cerebrovascular accident, a man is unable to either feel or identify a comb with his eyes closed. This is an example of:
31. Most dysphasias are associated with cerebrovascular accidents involving which artery?
32. Tactile agnosia is related to injury of which area of the brain?
33. Neurofibrillary tangles characterize which neurologic disorder?
34. The body compensates for a rise in intracranial pressure by first displacing the:
35. Stage 1 intracranial hypertension is caused by the:
36. Dilated and sluggish pupils, widening pulse pressure, and bradycardia are clinical findings evident of which stage of intracranial hypertension?
37. Dilation of the ipsilateral pupil, following uncal herniation, is the result of pressure on which cranial nerve (CN)?
38. Which characteristic is the most critical index of nervous system dysfunction?
39. Diagnostic criteria for a persistent vegetative state include:
40. Uncal herniation occurs when:
41. Which assessment finding marks the end of spinal shock?
42. Characteristics of primary motor neuron atrophy include:
43. The weakness resulting from the segmental paresis and paralysis characteristic of anterior horn cell injury is difficult to recognize because:
44. Parkinson disease is a degenerative disorder of the brain’s:
45. Clinical manifestations of Parkinson disease are caused by a deficit in which of the brain’s neurotransmitters?
46. Tremors at rest, rigidity, akinesia, and postural abnormalities are a result of the atrophy of neurons in the brain’s:
Chapter 18: Disorders of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems and the Neuromuscular Junction
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Diffuse axonal injuries (DAIs) of the brain often result in:
2. What event is most likely to occur to the brain in a classic cerebral concussion?
3. Which disorder has clinical manifestations that include decreased consciousness for up to 6 hours, as well as retrograde and posttraumatic amnesia?
4. What group is most at risk of spinal cord injury from minor trauma?
5. The edema of the upper cervical cord after spinal cord injury is considered life threatening because of which possible outcome?
6. What indicates that spinal shock is terminating?
7. What term is used to describe the complication that can result from a spinal cord injury above T6 that is producing paroxysmal hypertension, as well as piloerection and sweating above the spinal cord lesion?
8. Why does a person who has a spinal cord injury experience faulty control of sweating?
9. Autonomic hyperreflexia–induced bradycardia is a result of stimulation of the:
10. A herniation of which disk will likely result in motor and sensory changes of the lateral lower legs and soles of the feet?
11. Which condition poses the highest risk for a cerebrovascular accident (CVA)?
12. A right hemisphere embolic CVA has resulted in left-sided paralysis and reduced sensation of the left foot and leg. Which cerebral artery is most likely affected by the emboli?
13. Atrial fibrillation, rheumatic heart disease, and valvular prosthetics are risk factors for which type of stroke?
14. Microinfarcts resulting in pure motor or pure sensory deficits are the result of which type of stroke?
15. Which vascular malformation is characterized by arteries that feed directly into veins through vascular tangles of abnormal vessels?
16. Which clinical finding is considered a diagnostic indicator for an arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
17. Which cerebral vascular hemorrhage causes meningeal irritation, photophobia, and positive Kernig and Brudzinski signs?
18. In adults, most intracranial tumors are located:
19. In children, most intracranial tumors are located:
20. The most common primary central nervous system (CNS) tumor is the:
21. Meningiomas characteristically compress from:
22. What is the central component of the pathogenic model of multiple sclerosis?
23. A blunt force injury to the forehead would result in a coup injury to which region of the brain?
24. A blunt force injury to the forehead would result in a contrecoup injury to which region of the brain?
25. Spinal cord injuries most likely occur in which region?
26. The most likely rationale for body temperature fluctuations after cervical spinal cord injury is that the person has:
27. A man who sustained a cervical spinal cord injury 2 days ago suddenly develops severe hypertension and bradycardia. He reports severe head pain and blurred vision. The most likely explanation for these clinical manifestations is that he is:
28. The type of vascular malformation that most often results in hemorrhage is:
29. Atheromatous plaques are most commonly found:
30. Multiple sclerosis is best described as a(an):
31. What is the most common opportunistic infection associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)?
32. It is true that Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS):
33. It is true that myasthenia gravis:
34. In which disorder are acetylcholine receptor antibodies (IgG antibodies) produced against acetylcholine receptors?
35. Multiple sclerosis and Guillain-Barré syndrome are similar in that they both:
Chapter 19: Neurobiology of Schizophrenia, Mood Disorders, and Anxiety Disorders
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which would be considered a positive symptom of schizophrenia?
2. The onset of schizophrenia can be triggered by which prenatal occurrence?
3. Which neurotransmitter is reduced in people with schizophrenia?
4. Alterations in which part of the brain are linked to hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorders associated with schizophrenia?
5. Antipsychotic drugs block which neurotransmitter receptor?
6. What data confer the link between bipolar disorders and schizophrenia?
7. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) system abnormalities exist in a large percentage of individuals with:
8. The common property among the three types of medications used to treat depression is that they:
9. The link between major depression and cortisol secretion is that individuals with depression:
10. A decrease in receptor binding for which neurotransmitter is found in individuals with depression?
11. When treating individuals with depression, the result produced by electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is believed to be an alteration in:
12. Which electrolyte imbalance contributes to lithium toxicity?
13. Which neurotransmitter is inhibited in panic disorders?
14. A criterion for a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a period of excessive worrying that lasts for at least how many months?
15. Individuals who eat aged cheese and avocado when taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) may experience:
16. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is used to treat depression:
17. A notable complication of panic disorder is:
18. Persistent symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) include:
19. Hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorders occur with alterations to which part of the brain?
Chapter 20: Alterations of Neurologic Function in Children
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. The neural groove closes dorsally during which week of gestational life?
2. Which nutritional deficiency in a pregnant woman is associated with neural tube defect (NTD)?
3. Which defect of neural tube closure is most common?
4. What is the anomaly in which the soft bony component of the skull and much of the brain is missing?
5. The most common cause of obstructive hydrocephalus in infants is:
6. What is the term for a herniation or protrusion of brain and meninges through a defect in the skull?
7. What is the result of a Chiari type II malformation associated with a myelomeningocele?
8. Prompt surgical repair of a myelomeningocele is critical to best prevent:
9. Which body system is the largest site for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in infants and children?
10. An infant diagnosed with hydrocephalus is observed to demonstrate:
11. Gait disturbances and instability are characteristic of which form of cerebral palsy?
12. Children with phenylketonuria (PKU) are unable to synthesize:
13. Benign febrile seizures are characterized by:
14. What is the most common general symptom of a localized childhood brain tumor?
15. The tonic neck reflex observed in a newborn should no longer be obtainable by:
16. What term is used to describe a hernial protrusion of a saclike cyst that contains meninges, spinal fluid, and a portion of the spinal cord through a defect in a posterior arch of a vertebra?
17. What test is performed on amniotic fluid and maternal blood to test for neural tube defect?
18. The clinical manifestations of dyskinetic cerebral palsy include:
[Show More]