NSG 5003 Chapter 1, 2, & 3 Study Guide
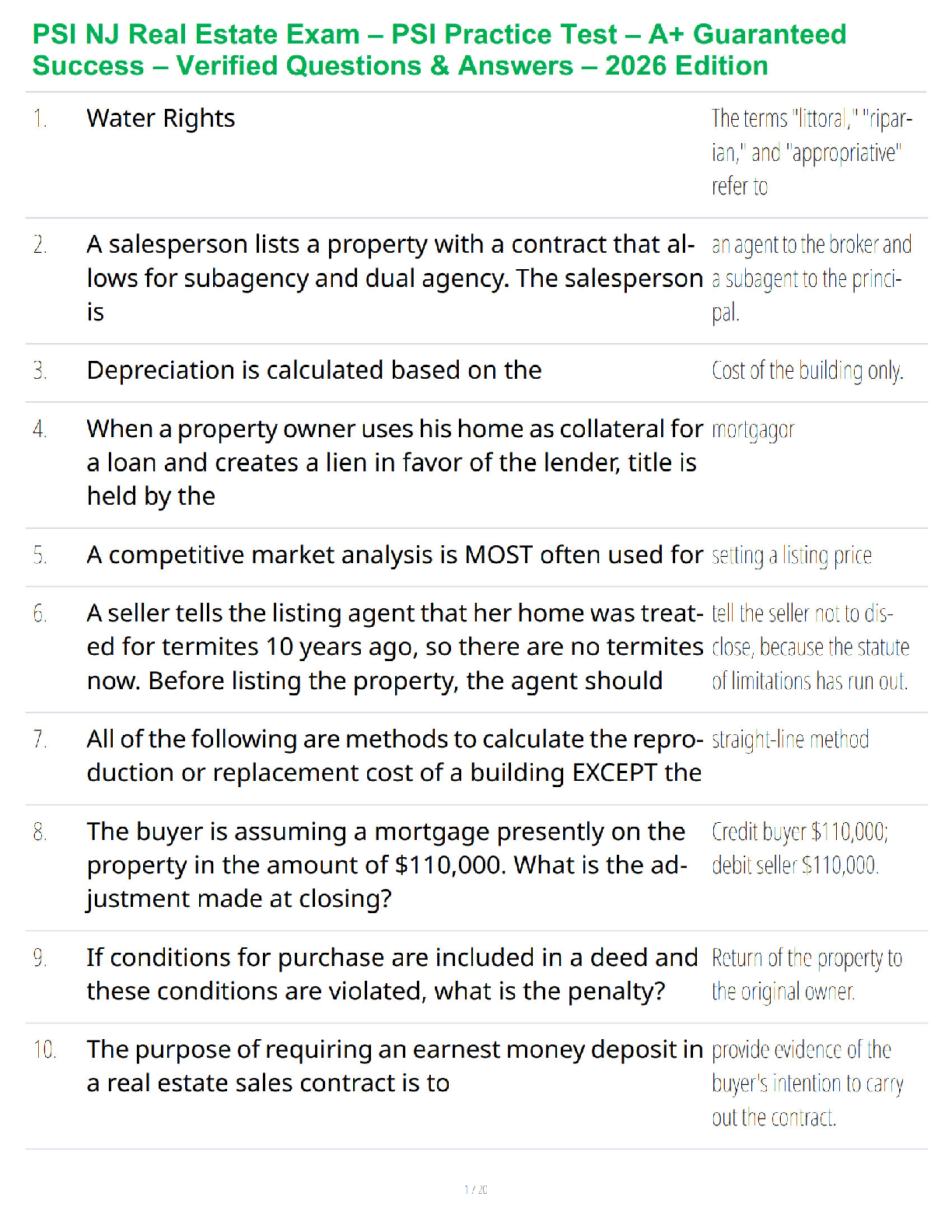
CH. 1 Cellular Biology
Match the terms
1. Generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
2. Synthesizes
3. Processes and packages proteins for delivery
4. Serves
...
NSG 5003 Chapter 1, 2, & 3 Study Guide
CH. 1 Cellular Biology
Match the terms
1. Generates ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
2. Synthesizes
3. Processes and packages proteins for delivery
4. Serves as repository of genetic information
5. Synthesizes steroid hormones
6. Synthesizes ribosomes
7. Delivers synthesized proteins to their destinations
8. Contains digestive enzymes
Describe the difference:
9. What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote?
10. What is the difference between the nucleolus and the nucleus?
11. What is the difference between microtubules and microfilaments?
12. What is the difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
13. What is the difference between a lysosome and a peroxisome?
Complete the sentence:
Write one word in each blank to complete these sentences.
14. Proteins in the nucleus that bind DNA and help regulate its activity are called
15. Cells such as neutrophils that use hydrogen peroxide as a defensive weapon synthesize it in their
16. A section of a membrane that is rich in cholesterol and helps organize membrane proteins is called a
17. The cells that secrete the extracellular matrix are called
18. The mechanical force of water pushing against cellular membranes is called ___________________ pressure.
19. An ______________solution has the same osmolality as normal body fluids.
20. In a simple epithelium, the epithelial cells are in contact with a basement membrane that provides support.
21.__________ tissue is characterized by only a few cells surrounded by a lot of extracellular matrix.
22. A myocyte is a _______________cell.
ORDER THE STEPS
Sequence the events that occur during a neuronal action potential.
23. Write the letters here in the correct order of the steps:
A. Sodium ions move into the cell.
B. Potassium ions leave the cell.
C. Sodium permeability increases.
D. Resting membrane potential is reestablished.
E. Potassium permeability increases.
Choose the correct words
24. The main difference between cells that divide rapidly and those that divide slowly is the amount of time they spend in the ___________ phase of the cell cycle.
25. Cells develop specialized functions through the process of
26.A particle that Is dissolved is called a _____________ and the medium in which it is dissolved is called the____________
27. Mitochondria need a lot of _____________ to function normally.
28. During osmosis ________________ move across the plasma membrane.
29. ____________ signals act on nearby cells by ______________through interstitial fluid.
30. A cell that has an insufficient oxygen supply will not be able to perform the chemistry of
31. _________________ can move substances against their concentration gradients.
32. Receptors are __________ that bind specific small molecules
Write your definition
33. Ligand
34. Caveolae
35. Mechanotransduction
36. Amphipathic molecule-
37. Endocytosis
choose the direction
38. If the ECF becomes hypotonic, in which direction will water move?
39. If the concentration of substance X in the ECF is higher than its concentration inside the cell, in which direction will active transport move substance X?
40. If the glucose concentration in the ECF is higher than its concentration inside the cell, in which direction will facilitated diffusion move glucose?
41. In which direction does Na1, K1-ATPase move sodium ions?
42. In which direction does Na1, K1-ATPase move potassium ions?
Provide the explanation
Use appropriate technical terms to explain these events.
43. A mutation affecting what function would cause a lysosomal storage disease?
44. How does the presence of gap junctions in cardiac muscle facilitate cardiac function?
45. Explain why intracellular receptors do not use second messengers, but many cell surface receptors do.
46. What happens during the interphase portion of the cell cycle? Why are those events important?
Ch. 2 Altered Cellular & Tissue Biology
1. Stiffening of skeletal muscles after death
2. Unintentional decrease of core body temperature below 35° C (95° F)
3. A type of cellular housekeeping in which a cell digests some of its own components –
4. Area of cell death in which dead cells disintegrate, but the debris is not digested completely by enzymes
5. Area of cell death in which denatured proteins appear firm and
6. An atom or group of atoms having an unpaired electron
7. Purple discoloration of dependent tissues after death
8. Cell death that involves orderly dismantling of cell components and packaging the remainder-
CATEGORIZE THESE CLINICAL EXAMPLES
9. Lining of uterus thickens after ovulation because of increased amounts of estrogen -
10. Man who lifts weights regularly develops larger biceps
11. Thymus gland decreases in size during childhood
12. Columnar epithelium in bronchi of cigarette smoker is replaced by stratified squamous
13. Captain of roller derby team has greater thigh diameter on left than right from skating clockwise
14. Left calf is smaller than right calf when cast is removed from it
CHOOSE THE CORRECT WORDS
16. Cell death by ___________ causes inflammation, but cell death by ____________ does not.
17. Dysplasia also is called _____________ hyperplasia.
18. Release of ______________ ions from intracellular stores into the cytoplasm during ischemia damages the cell.
19. Compared with normal aerobic metabolism, cells that use anaerobic metabolism produce ____________ ATP and __________ lactic acid.
20. The most important way to prevent medication-related poisoning deaths in children is safe ____________ of medications.
21. Reactive oxygen species, such as __________ damage cells by attacking their _______________.
22. Postmortem changes ______________ the inflammatory response.
DESCRIBE THE DIFFERENCE
23. What is the difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia?
24. What is the difference between suffocation and strangulation?
25. What is the difference between an abrasion and a laceration?
26. What is the difference between dystrophic calcification and metastatic calcification?
27. What is the difference between a penetrating gunshot wound and a perforating gunshot wound?
ORDER THE STEPS
Beginning with the acute obstruction of a coronary artery, sequence the events that occur during necrosis of a myocardial cell.
28. Write the letters here in the correct order of the steps:
COMPLETE THESE SENTENCES:
Write one word in each blank to complete these sentences.
29. Active enzymes that dismantle the cellular components during apoptosis are called _________________.
30. Acute cellular swelling during ischemia is reversible if ___________is supplied quickly.
31. Active tuberculosis disease is characterized by ______________necrosis, whereas death of brain cells is characterized by _____________ necrosis.
32. During apoptosis, cell contents are contained in vesicles called APOPTOTIC BODIES, which are removed by _____________
33. Liver enzymes metabolize most blood ethanol to _______________, which damages tissues.
34. When excessive reactive oxygen species overwhelm the endogenous antioxidant systems, _______________ occurs.
35. Death of the entire person is called _____________death.
36. Melanin is synthesized by epidermal cells called __________
RESPOND TO THESE CLINICAL SITUATIONS
37. Mr. Turin had severe crushing injuries of both lower extremities when his house collapsed on him during an earth- quake. Among other abnormal values, his laboratory tests show elevated creatine kinase in his blood. Why is his blood creatine kinase high?
38. Mrs. Montoya died peacefully in her sleep at home while lying prone. When her relatives discovered her body and rolled her over, they saw purple discoloration of half of her face and of her abdomen. They are very concerned that she might have been beaten the night before she died. What factual information do they need to relieve their concern?
39. The entire Berg family was in the hospital room when Mrs. Berg died quietly from terminal cancer. As the family is preparing to leave, Kevin Berg, age 10, says to his mother, “I don’t think grandma is really dead. She’s just sleeping. Dead people are stiff as boards. I saw that on TV. Grandma’s hands are cold, but her arms aren’t stiff.” His mother looks at the nurse for help. In addition to addressing the emotional issues, what factual information should be provided?
40. Two of your colleagues are discussing the effects of reactive oxygen species on cells. “Too many ROS cause necrosis,” says one. “But I read that too many ROS cause apoptosis,” says the other. What information should be explained to them to clarify that both are correct?
IDENTIFY THE CHARACTERISTICS
Which of the following are characteristic of apoptosis? You may select more than one answer. Choose all that apply.
43. Write the letters of your choice(s) here:
A. Cell is damaged by its own lysosomal enzymes.
B. Cell shrinks when its cytoskeleton is dismantled.
C. The cell injury is reversible if nutrients are restored in time.
D. Process causes inflammation.
E. Sections of the cell bud off into vesicles.
F. Cell swells when osmosis occurs.
G. Process occurs when caspases are inactivated.
TEACH THESE PEOPLE ABOUT PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Write your response to each situation in the space provided.
44. Kenesha Francis, age 9, broke her arm 6 weeks ago, and the cast will be removed today. Before the cast is removed, teach her about the expected appearance of her arm in words appropriate to her age.
45. “The doctor said my heart enlarged because my blood pressure is high,” says Mr. Hendricks. “Please explain that!”
46. Mr. Bax has diabetes and will have amputation of toes shown in the photograph. He says, “Why did my toes get black and hard rather than swollen and mushy like my dad’s toes did before surgery?”
Across
1. Adaptive increase in the number of cells
7. Shrunken nucleus appearing as a small dense mass
10. Adaptive replacement of one mature cell type by another normal cell type
11. Yellow-brown age pigment
down
1. Adaptive increase in cell size
2. Adaptive decrease in cell size
3. Loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength
4. Lack of oxygen to tissues caused by insufficient blood supply
5. Goes with mortis to denote postmortem reduction of body temperature
6. Abnormal change in size, shape, and organization of mature tissue cells
8. Nuclear dissolution and lysis of chromatin
9. Partial deprivation of oxygen
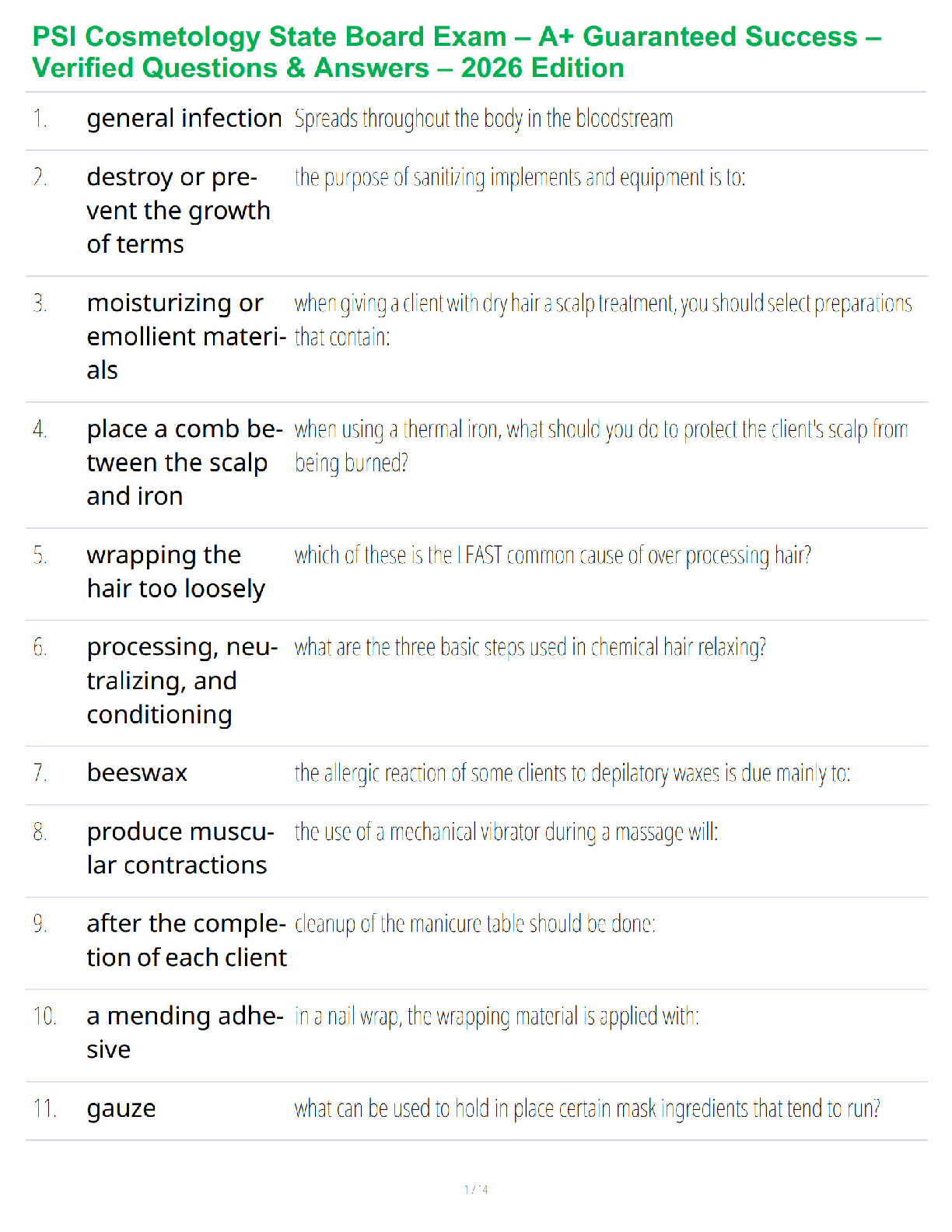
Ch. 3 The cellular Environment: Fluids and Electrolytes, Acids and Base
1. The osmolality of the intracellular fluid normally is __________the extracellular fluid because water crosses cell membranes ___________through aquaporins.
2____________ is primarily responsible for the plasma oncotic pressure.
3. Thirst prompts fluid intake through action of _______________located in the (hypothalamus).
4. Isotonic fluid excess causes ________________
5. Renal compensation for an acid-base balance is ______________ pulmonary compensation for an acid-base balance is ______________
6. Fluid moves out of capillaries by ___________ and into or out of cells by _____________
7. Hypercapnia means an excess of ______________ in the blood.
8. The most dangerous effect of hyperkalemia is its action on the __________
CATEGORIZE THESE CAUSES OF EDEMA
Write the major cause of the edema beside each clinical situation. Possible choices include: increased capillary hydrostatic pressure, decreased plasma oncotic pressure, increased capillary permeability, lymphatic obstruction.
9. Tumor grows in lymph node
10. Right heart failure
11. Infected wound
12. Clot in a vein
13. Protein malnutrition
14. Bee sting
15. End-stage kidney disease
SELECT THE GREATER
Consider the pairs and select the one that is greater.
16. Who has a greater percentage of body weight as water: _________ or an obese woman? 17. Who has a greater percentage of body weight as water: ___________ or an adolescent?
18. Who has a greater percentage of body weight as water if both persons weigh the same: a woman or a _____________?
19. Who has a greater percentage of body weight as water if both persons weigh the same: a ___________ or a 78-year-old man?
20. Where is the potassium ion concentration greater: extracellular fluid or _______________? 21. Where is the sodium ion concentration greater: ____________ fluid or intracellular fluid?
22. Which is greater: the pH of an acid solution or the _______________?
23. Which is greater: _______________ or the respiratory rate during metabolic alkalosis?
24. Compare the sodium concentration in panels A and B. ____________
25. Why did the neuron in panel A swell?
26. What cerebral clinical manifestations occur when neurons swell as in panel A?
27. Why are the cerebral clinical manifestations of the situation in panel C very similar to those in panel A?
Write one letter and one number by each hormone in the left column to indicate the stimuli that increase its secretion and its physiologic effects when secreted.
Hormone
28. Aldosterone Angiotensin II, increased plasma potassium Increases renal sodium and water reabsorption; increases renal excretion of potassium and hydrogen ions
29. Parathyroid hormone-Low plasma calcium Increases resorption of bone; stimulates renal reabsorption of calcium; inhibits renal reabsorption of phosphate
30. Atrial natriuretic peptide Increased volume in the cardiac atria Increases renal sodium and water excretion
31. Calcitonin A 5. Inhibits osteoclasts in bone
32. Antidiuretic hormone Increased plasma osmolality, substantially decreased arterial blood pressure Increases renal water reabsorption, vasoconstriction
DESCRIBE THE DIFFERENCE
Describe the difference between each pair of terms.
33. What is the difference between interstitial fluid and extracellular fluid?
34. What is the difference between a volatile acid and a nonvolatile acid?
35. What is the difference between acidemia and acidosis?
36. With regard to an acid-base imbalance, what is the difference between correction and compensation?
Write one word in each blank to complete these sentences.
37. One third of body water is in the extracellular fluid, and two thirds is in the intracellular fluid.
38. A standard 68-kg man has 40.8 liters of total body water.
39. Excessive fluid within the interstitial space is called edema
40. An isotonic fluid has the same concentration of solute as the plasma.
41. A person who has a lung disease may develop a primary respiratory acid-base imbalance, but a person who has a kidney disease may develop a primary metabolic acid-base imbalance.
42. When the blood pH is 7.40, the bicarbonate-to-carbonic acid ratio is 20:1
43. A buffer pair is a weak acid and its conjugate base.
44. Calculating the anion gap may help to distinguish between different causes of metabolic acidosis
45. Overuse of phosphate-containing over-the-counter hyperphosphatemia enemas can cause decrease the plasma calcium concentration.
46. Mrs. Singh takes glucocorticoids for a chronic disease
47. Mr. Wiggins has been sobbing and breathing deeply and rapidly for an hour since his wife die
48. Mr. Jenkins is comatose from a heroin overdose
49. Baby Thompson has repeated vomiting from pyloric stenosis
50. Mrs. Smythe has hyperparathyroidism.
51. In which direction does insulin move potassium ions?
52. In which direction does epinephrine move potassium ions?
53. In which direction does alkalosis move potassium ions?
54. In which direction does hypernatremia move water?
55. Mr. Sheehan has bilateral ankle edema from congestive heart failure. “Are my ankles inflamed?” he asks. “I know that inflammation causes swelling.”
56. Mrs. Kiley, who is taking care of her husband at home after his hospitalization for a stroke, was told to call the doc- tor if Mr. Kiley develops dependent edema. She says, “I know what edema looks like, but where is dependent edema located?”
57. Mr. Janus, who is having his first renal dialysis session, says, “I know that my failed kidneys cannot excrete acids, but I did not eat any acids, so why did I get metabolic acidosis?”
58. Ms. Winsom, age 16, has diabetic ketoacidosis. “Why is she breathing so fast?” asks her father. “Does she have pneumonia as well as diabetes ketoacidosis
59. “Tell me the most common fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base imbalances in oliguric renal failure patients,” says a nurse. “I am being sent to help on the renal unit this morning.”
Mrs. Tanaka, age 76, was brought to an urgent care facility because she fell when she stood up after sitting all afternoon in her apartment, where she lives alone. Although slow to answer questions, Mrs. Tanaka states she has muscle weakness, muscle cramping, and constipation. She has had diarrhea for 3 weeks. Physical examination with Mrs. Tanaka supine revealed flat neck veins, HR 102, pulse regular but weak, BP 90/56, respirations 20/min and deep. The on-site clinical laboratory provided these results: serum sodium 142 mEq/L, potassium 2.8 mEq/L.
60. What fluid imbalance does Mrs. Tanaka have? What data support that?
61. What imbalance is indicated by her laboratory results? What other clinical manifestations are consistent with that imbalance?
62. What additional electrolyte imbalance(s) might Mrs. Tanaka have? Provide supporting data.
63. Mrs. Tanaka may have an acid-base imbalance. Which one? What aspects of her history and clinical presentation support that?
64. Mrs. Tanaka was given intravenous isotonic sodium chloride, with appropriate electrolytes in it. What was the purpose of administering that particular fluid?
[Show More]