BSC 1011 Midterm Study Guide - Florida Gulf coast University
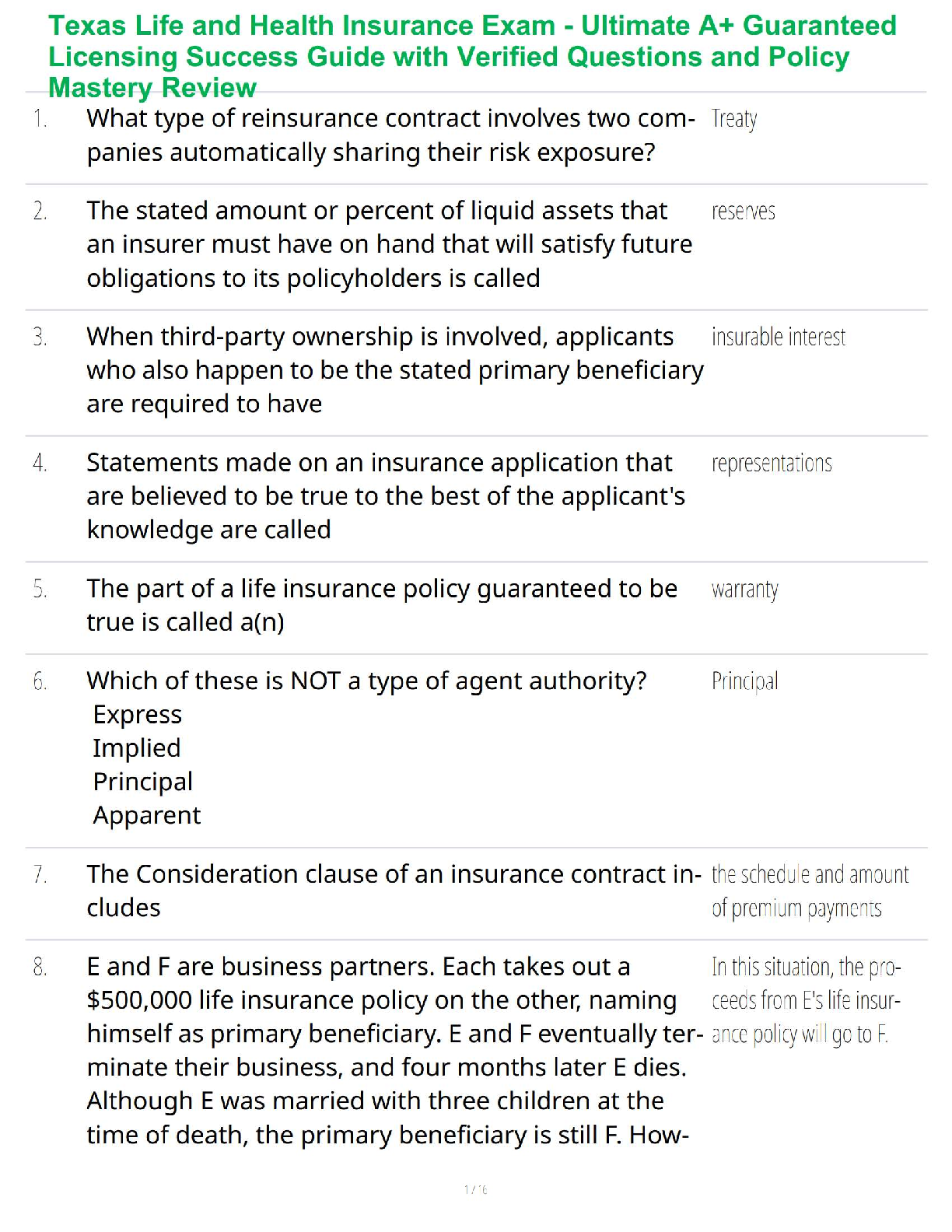
BSC 1011 Midterm Study Guide
General Biology II Lab
Midterm Practical Study Guide
Lab 1: Genetics and Microevolution
Vocabulary
...
BSC 1011 Midterm Study Guide - Florida Gulf coast University
BSC 1011 Midterm Study Guide
General Biology II Lab
Midterm Practical Study Guide
Lab 1: Genetics and Microevolution
Vocabulary
________________________ A heritable feature that varies among individuals
________________________ Over many generations will produce only the same
variety as the parent plant
________________________ Mating of two individuals.
________________________ An organism’s genetic make-up
________________________ An organism’s appearance or observable traits
________________________ An organism with an identical pair of alleles (ex. AA,
aa)
________________________ An organism that has two different alleles for a gene
(Aa)
________________________ An allele that is fully expressed in an organism’s
phenotype.
________________________ An allele that is not observed in an organism’s
phenotype.
________________________ A unit of hereditary information.
________________________ Any of the alternative versions of genes that account for
variation.
________________________ A specific place on a chromosome where a gene is
located.
Mendel’s Laws
● Law of Segregation (**1 gene**)
o Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters.
o For each character, an organism inherits 2 alleles for a gene, one from each
parent.
o If the 2 alleles differ, the dominant allele determines the organism’s
appearance; the recessive allele has no effect on appearance.
o Two alleles for a heritable character segregate during gamete formation and
end up in different gametes.
● Law of Independent Assortment (**2 or more genes**)o Two or more genes assort independently – each pair of alleles segregates
independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation.
Punnett Squares
● Diagrams used to solve genetics problems. Allow you to predict the probability of
allele composition of off-spring when 2 individuals of known genetic composition
mate.
● Solve the following examples and answer the subsequent questions:
1. In pea plants, green seeds (G) are dominant to yellow seeds (g). Draw a Punnett Square
for a mating between 2 heterozygotes.
a. What genotypes are present? ___________________________________________
b. What phenotypes are present? __________________________________________
c. What is the proportion of green seeds? ___________________________________
d. What is the proportion of yellow seeds? __________________________________
2. In pea plants, being tall (T) is dominant to short (t). Draw a Punnett Square for a mating
between an individual that is heterozygous for height and the other homozygous recessive.
a. What is the proportion of individuals that will be tall? _______________________
b. What genotypes are present? ___________________________________________
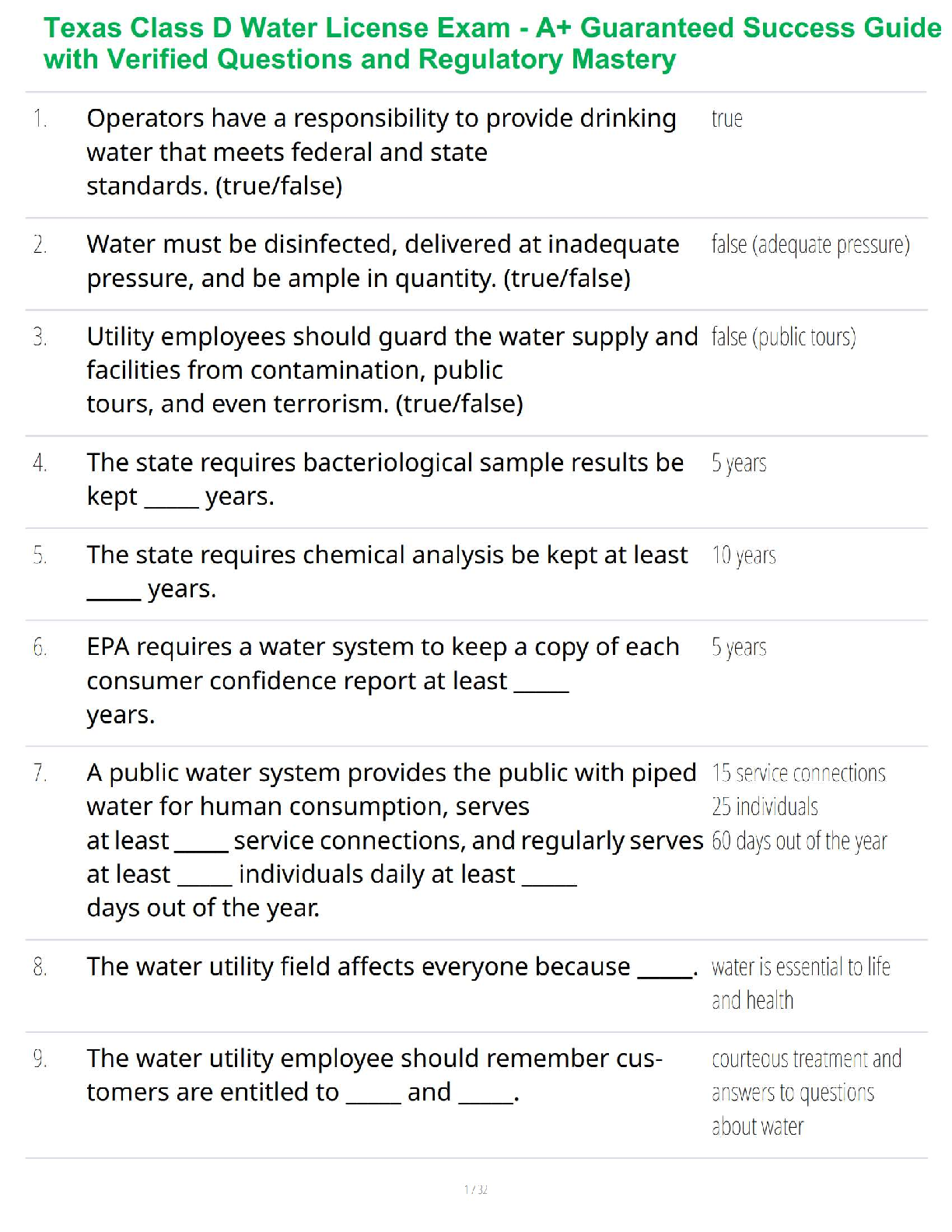
Genotype and Phenotype Frequencies
Microevolution or “descent with modification” is the change in genetic make-up of a
population from one generation to the next.The population in the sample table has 8 individuals; each individual has 2 alleles for their
genotype. Identify the frequencies of the genotypes, phenotypes and alleles. Assume D is the
dominant allele, and if present, the organism will be Dark in color. The phenotype for the d
allele is light color. Only organisms that show the homozygous recessive genotype dd will be
light in color.
Individual Genotype Phenotype
1 DD Dark
2 DD Dark
3 Dd Dark
4 Dd Dark
5 Dd Dark
6 dd Light
7 dd Light
8 dd Light
The population has 3 genotypes: ____________ _____________ _______________
Calculate the genotype frequency for this population:
Genotype Number of Individuals with Genotype Genotype Frequency
Calculate the phenotype frequency for this population:
Phenotype Genotypes with this Phenotype Phenotype Frequency
The alleles D and d are also found in a specific frequency within the population. Remember
that individuals have 2 alleles, so a population of 8 individuals has 8 x 2 = 16 alleles.
Calculate the frequency of the alleles within this population.
Allele Total Number of Allele Allele Frequency
Forces of Change to Allele Frequencies and Natural Selection
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Lab 6: Plant Diversity II (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms)
Vocabulary
1. ___________________________ An embryo and its food supply, surrounded by a
protective coat.
2. ___________________________ Consists of the megasporangium, megaspore and
the integument(s).
3. ___________________________ Consists of a male gametophyte enclosed within a
pollen wall.
4. ___________________________ Plants that are cone-bearing; thrive in drier
climates; leaves have thick cuticles and are
needle-shaped.
5. ___________________________ Seed plants with reproductive structures known as
fruits and flowers.
Gymnosperms
Name the three groups of Gymnosperms and be able to identify a type of plant from each
group.
1.
2.
3.
Which is the dominant life form of a pine tree?
**Review the life cycle of Gymnosperms (Lab 6 handout)
Angiosperm Vocabulary
1. ___________________________ Attract insects and other animals and use them
as specialized pollinators; unique structure for
sexual reproduction.
2. ___________________________ Mature ovary with a thickened wall; protects the
ovule and provides nutrients for the embryo.
3. ___________________________ Base of the flower; usually green in color,
enclosesthe flower before it opens.
4. ___________________________ Brightly colored and aid in attracting pollinators.
5. ___________________________ Male reproductive parts of the flower; also known
as stamen.
6. ___________________________ Female reproductive parts of the flower; also
known as the pistil or carpel.
7. ___________________________ Stalk portion of the stamen, bearing the anthers.
8. ___________________________ Terminal sac where the pollen is produced.
9. ___________________________ Sticky structure at the top of the flower; pollen is
deposited here, where it then germinates.
10. __________________________ The stalk that supports the stigma.
Seeds
Seeds have three critical parts. Name them and be able to define their purpose:
1.
2.
3.
Name three advantages of seeds:
1.
2.
3.
_____________________________ are seeds with one cotyledon; _____________________
have two cotyledons.
1. ____________________________ Small opening on the surface of the seed, through
which the pollen tubule grew.
2. ____________________________ Place on the seed where the ovule was attached tothe ovary.
3. ____________________________ Special “seed leaves” found only in the embryo.
Angiosperm Roots, Stems and Leaves
Monocots have ________________________ root systems, which consists of a bundle of roots
where individual roots are roughly the same size.
Eudicots have_______________________ root systems, with a long central primary root and
many smaller lateral roots branching off the main root.
Two types of above ground roots are ________________ and ____________________.
Be able to name species that exhibit above ground root systems:
1.
2.
Three types of stems, which store food are: _____________________, __________________,
and ___________________________.
Stems that grow horizontally underground, like roots, are _____________________________.
______________________ are stems that support the plant by attaching to other structures.
Write the equation for Photosynthesis:
____________________ + Chlorophyll + Sunlight → ________________________
[Show More]