ATI Teas 6 A & P
TEAS Test Study Guide: Science
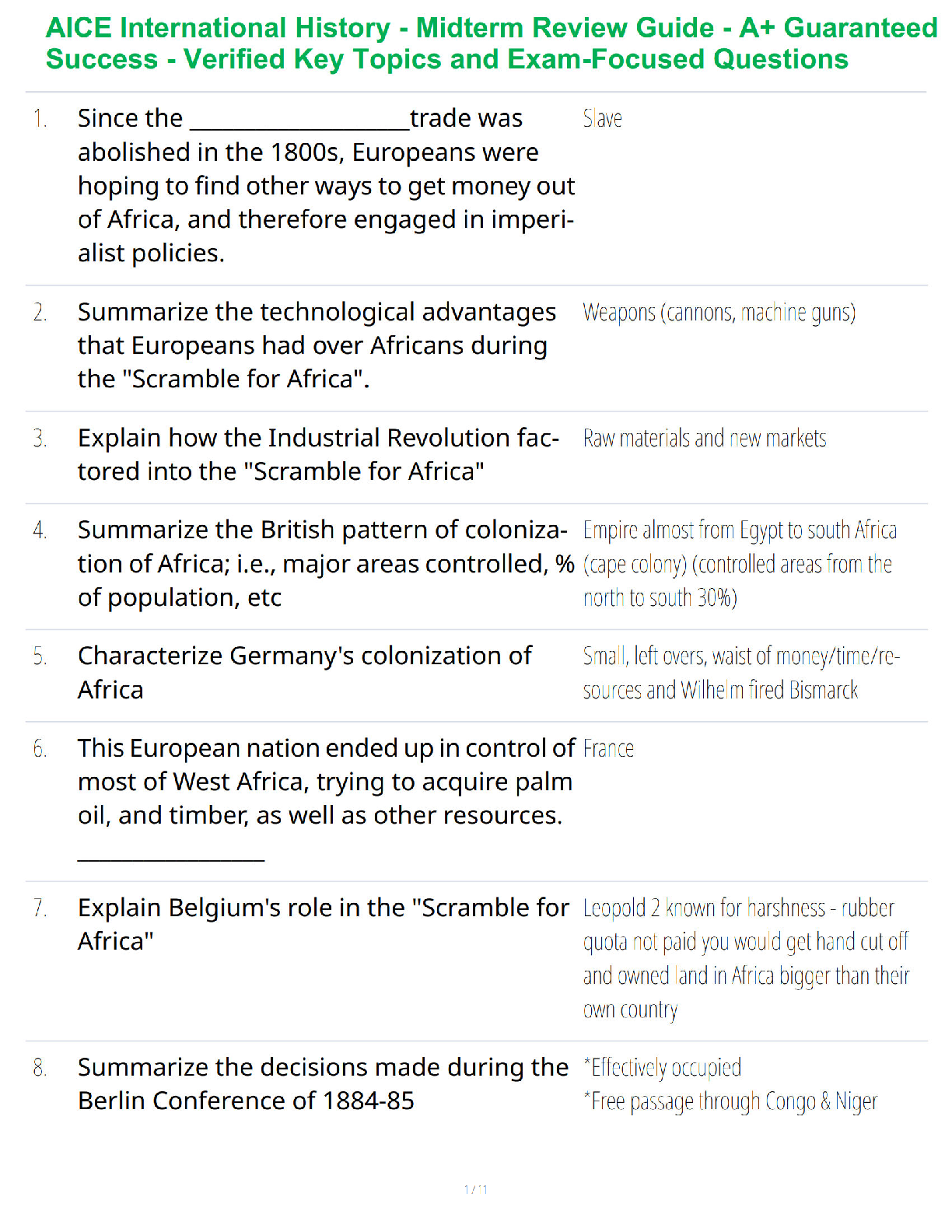
Cell Cycle
• ⦁ Mitosis = “daughter cell” exact replica
• ⦁ Interphase (G1, S, G2)
• 1 Prophase
• 2 Metaphase
• 3 Anaphase
• 4 Telophase
• 5 Cytokinesis
• ⦁ Mei
...
ATI Teas 6 A & P
TEAS Test Study Guide: Science
Cell Cycle
• ⦁ Mitosis = “daughter cell” exact replica
• ⦁ Interphase (G1, S, G2)
• 1 Prophase
• 2 Metaphase
• 3 Anaphase
• 4 Telophase
• 5 Cytokinesis
• ⦁ Meiosis = “daughter cells” different genetic coding
• ⦁ Only happens in gametes*
• 1 1st phase
• ⦁ chromosomes cross over
• 1 genetic material exchanged
• 2 tetrads of 4 chromatids formed
◊ Homologous pairs of chromatids are separated and go to different poles
◊2 cells go through 2nd cell division
◊ 4 daughter cells with different sets of chromosomes
• ⦁ Haploid : contains half genetic material of parent cell
Zygote- controls cell differentiation
Tissues
◊ groups of cells
◊ Muscle, nerve, epithelial, connective
Epithelial: (joined together tightly) ex. Skin
Connective: (dense, loose, or fatty) ex. Bone tissue, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, fat, blood, lymph
◊Protects & binds body parts
a. a. Cartilage: cushions & provides structural support
i. i. Fibrous
b. b. Blood: transports oxygen to cells & removes waste / ALSO carries hormones & defends against disease
c. c. Bone: (hard) produces red blood cells
d. 1. Muscle: Support & move body
e. a. Smooth
f. b. Cardiac
g. c. Skeletal
h. 2. Nervous: ex. Brain, spinal cord, & nerves
i. a. Neurons- control responses to changes in environment
Organs
◊ groups of tissues
ex. Heart = muscle tissue in myocardium; connective tissue in blood; nervous tissue for heart rate; epithelial tissue in membranes
Organ Systems
◊ groups of organs
a. 1. Integumentary (Exocrine system)
b. a. Skin
i. i. Sebaceous glands sweat glands
ii. ii. Hair
iii. iii. Nails
c. b. Protection
i. i. Protects body from pathogens
d. c. Secretion
i. i. Secrete oil
e. d. Communication
i. i. Sensory receptors send info. about pain, touch, pressure, and temperature
LAYERS OF THE SKIN
1. 1. Epidermis
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Female
• ⦁ Produce ova (oocytes, egg cells), transfer the ova to fallopian tubes for fertilization, receive sperm, & provide a protective, nourishing environment for embryo
• 1 External structure
• ⦁ Labia major
• 1 Labia minor
• ⦁ Protect vagina
• ⦁ Bartholin’s glands
• ⦁ Secrete lubricating fluid
• ⦁ Clitoris
• ⦁ contains erectile tissue and nerve endings
• ⦁ Internal structure
• ⦁ Ovaries
• ⦁ Female gonads
• 1 Produce ova
• 2 Secrete estrogen and progesterone
• ⦁ Fallopian tubes
• ⦁ Carry mature egg toward uterus
• 1 Fertilization occurs here
• ⦁ Uterus
• ⦁ Fertilized egg travels here & implants in uterine wall
• 1 Protects embryo
• ⦁ Vagina
• ⦁ Provide birth canal
Body Planes
Transverse = horizontal (superior/inferior)
Sagittal = vertically right & left; parallel to midline
Coronal = frontal; vertically front & back (anterior/ posterior)
Direction
Medial: near midline (EX. Little finger is medial to thumb)
Lateral: away from midline (EX. Thumb is lateral to little finger)
Proximal: center of body (EX. Hip is proximal to knee)
Distal: away from center (EX. Knee is distal to hip)
Anterior: front
Posterior: behind
Cephalad: towards head
Caudad: towards posterior
Superior: above (closer to head)
Inferior: below (closer to feet)
***specific heat of water is 1 calorie/gram °C = 4.186 joule/gram °C
Calculating population change
(# births/time period) / population size *1000
P.E. = mgh
m = mass in kilograms
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m / s2 at the surface of the earth)
h is the height in meters.
kinetic energy, kg m2 / s2
**periodic table Khan Academy
1. Alkanes - Are saturated hydrocarbons that therefore contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms bonded to each other, and typically follow the chemical formula CnH2n+2. A common example is paraffin.
2. Alkenes - These unsaturated hydrocarbons are molecules that contain at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond. With the chemical formula consisting of molecules of CnH2n, alkenes are very common in the petrochemical industry; the simplest alkene is ethylene, or ethane.
3. Alkynes - This category of hydrocarbons are unsaturated, and contain at least one carbon-to-carbon triple bond. The hydrophobic acetylenes are common examples of alkynes.
4. Cycloalkanes - The saturated hydrocarbons not only form only carbon-to-hydrogen bonds, rather than the carbon-to-carbon bonds that have to then have added hydrogen atoms. These alkanes have to prefix "cyclo" due to the configuration of rings of carbon atoms in their structure.
5. Aromatic hydrocarbons - These unsaturated hydrocarbons have alternating carbon-to-carbon single or double bonds in their molecules. The term aromatic was applied to this category of hydrocarbons before the chemical nature of aromaticity was discovered, and they were therefore called aromatic simply because these compounds had a pleasant smell.
[Show More]