Business > EXAM > Threat, Attacks, & Vulnerabilities: Comitias Security+ SY0-501 FedVTE Course 142 Questions with Answ (All)
Threat, Attacks, & Vulnerabilities: Comitias Security+ SY0-501 FedVTE Course 142 Questions with Answers,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
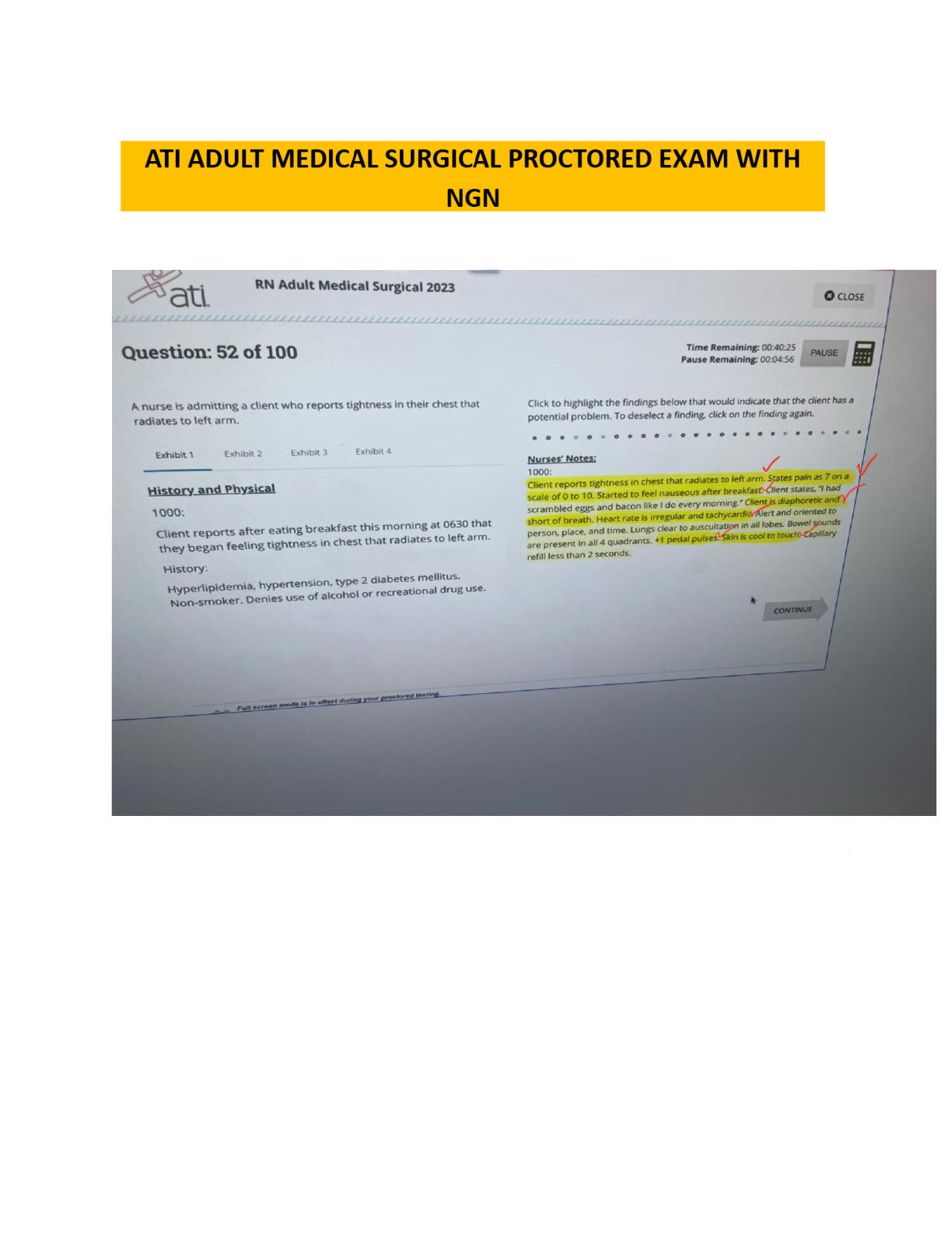
Threat, Attacks, & Vulnerabilities: Comitias Security+ SY0-501 FedVTE Course 142 Questions with Answers Rootkits - CORRECT ANSWER Programs that have the ability to hide themselves and cover trace ... s of a hacker's activities from the user and potentially the operating system. Primary purpose of Rootkits - CORRECT ANSWER To provide repeated, undetected access to a system. Allows hackers to continually use a system without the adminstrator's knowledge. User Mode Rootkit - CORRECT ANSWER Runs with same permissions as user: - If the user is administrator, rootkit is now running in a privileged mode - If regular user, rootkit is limited in scope in what it can do Kernel Mode Rootkit - CORRECT ANSWER Typically installs as a device driver...kernel-mode rootkits are usually more powerful and harder to detect and eradicate Trojan Horse - CORRECT ANSWER A destructive program that presents itself to the user as a benign application (usually in conjunction with Social Engineering attack( Unlike viruses/worms, Trojan Horses do not manually replicate themselves RAT - CORRECT ANSWER Remote Administration Trojan Remote Administration Trojan - CORRECT ANSWER - Allows an attacker to remotely control the victim host via GUI interface - Victim host acts as the server - Attacker accesses multiple victims via the "client" app Botnets - CORRECT ANSWER networks of computers that have been appropriated by hackers without the knowledge of their owners Bot - CORRECT ANSWER Zombie - Code that infects a host and forces it to act as a remote-controlled roBOT Botherder / Botmaster - CORRECT ANSWER One who controls a botnet to perform malicious activities such as: -Sending Spam -Distributed Denial of Service -Information Harvesting -Bogus Advertising Calls Spyware - CORRECT ANSWER Type of malware that collects personal information about users without their knowledge Adware - CORRECT ANSWER Malware that generates "pop-ups" usually with advertising for sites or products Scareware - CORRECT ANSWER Overarching class of scam software that uses malicious payloads to cause excessive "pop-ups" on a system replicating a virus and warns the user their system is infected, requiring them to pay for protection /cleaning. Ransomware - CORRECT ANSWER Overt malware that restricts access to your data and demands a ransom be paid before the malware creator releases the restrictions on your data. Hoaxes - CORRECT ANSWER Fraudulent threats/promises users receive via email asking them to perform a task to avoid consequence (i.e logic bomb, virus) or received reward (i.e. sweepstakes) Can cause panic/damage if user is convinced they should install an application or delete file Backdoors - CORRECT ANSWER Access mechanism deliberately planted in an application or system by the developer (or attacker) allowing them to circumvent security controls and lessen the burden on themselves during development. Logic Bomb - CORRECT ANSWER Malicious code inserted into a legitimate application that will launch when specific conditions are met (i.e. event, date). May be used to grant access, execute destructive code, disable functionality, or send alert back to code originator confirming execution. Mobile Code - CORRECT ANSWER Generic Term Code from one system that executes on another - Active Web Content -ActiveX, Javascript, Flash Man in the middle attack (MITM) - CORRECT ANSWER Attacker intercepts traffic and has both originating parties believe they are communicating with each other. May be software between client/server. Common in Telnet, Wireless MITM Tools - CORRECT ANSWER Juggernaut, T-Sight, Hunt Denial of Service/Distributed Denial of Service (DoS/DDoS) - CORRECT ANSWER Disrupts legitimate use of services Commonly accomplished by causing buffer overflow overwhelming the target system May also block communications with TCP session overloads DDoS intensifies the DoS activity by using multiple systems to launch attack. Buffer Overflow - CORRECT ANSWER Sending more data than the buffer can handle Ping Flood - CORRECT ANSWER Sending more ping requests than a target can manage Ping of Death - CORRECT ANSWER Sending packets larger than a target can manage SYN Flood - CORRECT ANSWER Takes advantage of 3-Way handshake Teardrop - CORRECT ANSWER Attacks with fragmented UDP packets that cannot be reassembled Smurf Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Ping request using victim's source address causing a flood with replies Denial of Service (DoS) - CORRECT ANSWER An attack on the availability of a service - Attempt to deny, degrade, disrupt, or otherwise interfere with the ability of a provider to keep services available DoS Chokepoints - CORRECT ANSWER Bandwidth - by generating more traffic than routes can handle Servers - either directly (e.g. OS) or indirectly through a supporting function (e.g. the power, A/C, etc) Applications - attack the application's ability to process requests End Users - attack the users to prevent them from accessing services DoS Classifications - CORRECT ANSWER DoS - an attack that originates from a central point Distributed DoS (DDoS) - attack originates from multiple points, usually geographically seperated DoS Packet Flooding - CORRECT ANSWER Uses the network protocols against themselves and either saturates all the available bandwidth or overwhelms the operating system, device, or app that process all the incoming packets Packet Flooding attack Vectors - CORRECT ANSWER Buffer Overflows Ping of Death Teardrop DoS SYN-Flooding - CORRECT ANSWER Attacker generates SYN packets (the first part of the three way handshake) but never responds to the SYN-ACK sent by the recipient - leaving the victim with many "half-open" connections and unable to respond to new connections. RST Injection - CORRECT ANSWER Sends RST packet to a client or server to reset connection XMas Scan/Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Scan that uses Christmas Tree (XMas) Packets, or TCP packets with FIN, PSH, and URG flags set in the TCP header, to scan a fire wall for open ports while eluding detection. Smurf Attack - CORRECT ANSWER generates a large amount of spoofed ICMP messages (appear to have come from victim), which the recipients to issue a ICMP echo reply to the victim Fraggle Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Similar to the Smurf attack, uses UDP echo packets. Generates spoofed packets to a host's chargen service, which in turn generates packets to the victim's ECHO service, which duplicates the packets and further amplifies the attack. Amplification Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Attack that uses its unwitting hosts and victims to generate much more traffic than the original packets used to initiate the attack. Back Door Attack Tools - CORRECT ANSWER Back Orifice, NetBus, SubSeven - allows an infected server to be remotely controlled by a client from the Internet Privileged user creates "back door" user account with elevated privileges Spoofing Attacks - CORRECT ANSWER Masquerading to appear to be something other than the true source by falsifying packet header information - IP Address - DNS - User - Data - Mac Address - Website DNS Spoofing - CORRECT ANSWER the DNS server is given information about a name server that it thinks is legit when it isn't Replay Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Info is extracted from packets captured over the network by attackers and "replayed" later. Login information, banking transactions, Kerberos certs, and other sensitive data is susceptible. Transitive Attack - CORRECT ANSWER An attack on the trust chain between machines: A trusts B, which trusts C, so C can attack A. Client-Side Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Web-based attack that targets the user's browser such as cross-site scripting. Brute Force Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Attacker uses every possible combination of characters for the password Dictionary Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Attacker uses files containing common passwords (a "dictionary") and tries one password after the next until they find the password. Faster than brute force, but still slow compared to other methods Hybrid Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Combines dictionary and brute force attacks. Takes dictionary words and add brute force elements onto them Birthday Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Uses brute force attack with a hash function If user's key is hashed, it is probable that another value can be created returning the same hash. Tries to find two of the same cryptographic hash values Defense: choose strong hashing algorithms (AES, SHA-256) Rainbow Table - CORRECT ANSWER - An attacker uses a table that contains all possible passwords already in a hash format -Sort by hash value to make searching by hash value incredibly fast -Designed to crack hashed passwords files almost instantly -Rainbow tables can be downloaded/generated -Tables are specific to the cryptographic hash used on the password file (MD5, SHA-256) -Processor and hard drive intensive -Tools used: rcrack, Ophcrack Crypto Attacks - CORRECT ANSWER Attack the Key Attack the Algorithm Gather in Transit Weak Key Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Algorithm attack on weak choice in number of combinations during encryption When used with a specific cypher, cypher may perform in an undesirable way Typically in block cipher using 40 and 56 bit encryption Mathematical Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Algorithm attack using the properties of that algorithm to run sophisticated computations in an attempt to break cryptographic scheme. Brute force-like attack working through all possible keys to decrypt message. Database Exploitation - CORRECT ANSWER Performed through advanced queries -Attacker hijacks legitimate client to database server session Application Exploit - CORRECT ANSWER An exploit that is designed to target an application as opposed to an operating system or hardware. Application exploits have become increasingly popular, as client-side systems typically run a large number of applications, which makes them a potentially attractive target. Macro is programming instructions (script) directing the app to perform some undesired action (used in Word, Excel, etc..) Email Exploit - CORRECT ANSWER - Virus sent via email - User features in email clients are what is usually exploited: 1) Access to users' address book 2) Ability to readily open attachments -Once infected, virus will use users' address book to propagate to others Typo Squatting - CORRECT ANSWER aka URL Hijacking -Targets users by registering one-off domain names of recognized organizations -Users who fat-finger entries will reach an unintended destination Defense: - Typo squatting is illegal - Purchase common misspellings of your domain Water Hole Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Attacker knows websites an organization visits often Precision attack and not meant to infect as many people as possible (quality, not quantity) Process: - attack gains intel about your web patterns - attacker infects common website victim visits often - victim visits site, attacker attempts to exploit Social engineering - CORRECT ANSWER techniques that trick a person into disclosing confidential information Low cost, effective method of obtaining info from unsuspecting users Principles of Social Engineering - CORRECT ANSWER Authority - perceived legitimacy, justification, right to exercise power Intimidation - using implied authority and force of personality to gain access or achieve another outcome Consensus/Social Proof - mirroring popular behavior in a social setting Scarcity - sense of urgency is implied when people feel something is limited Urgency - using time as a basis for performing an action Familiarity/Liking - people draw closer to things they are familiar with and like Trust - uniting principle of Social Engineering as the victim trusts what you are saying/conveying is accurate Shoulder Surfing - CORRECT ANSWER Gaining compromising information through observation (as in looking over someone's shoulder). Eavesdropping - CORRECT ANSWER listening secretly to a conversation, reading messages, or other info by audio, video, or read/written means Dumpster Diving - CORRECT ANSWER Searching for sensitive information carelessly thrown out by the target. Third Party Authorization - CORRECT ANSWER Using the name of a trusted third person, usually someone in authority, to add credibility to the social engineering attempt Tailgating - CORRECT ANSWER Physically entering a secure area by following someone through a secure door Piggybacking - CORRECT ANSWER Requesting an authorized person to provide access to a secure area Reverse Social Engineering - CORRECT ANSWER Attacker appears to be in a position of authority, relying on his victims to give him the info he seeks instead of asking for it Phishing - CORRECT ANSWER An attack that sends an email or displays a Web announcement that falsely claims to be from a legitimate enterprise in an attempt to trick the user into surrendering private information Spear Phishing - CORRECT ANSWER Gathers detailed personal info to craft convincing emails that can trick people into opening tainted email attachments or visiting fake websites -Narrowly focused variant of phishing Whaling - CORRECT ANSWER Phishing attacks targeted towards senior executives Pharming - CORRECT ANSWER Reroutes requests for legitimate websites to false websites Vishing - CORRECT ANSWER Phishing attacks committed using telephone calls or VoIP systems. Insider Threat - CORRECT ANSWER A malicious danger to an organization that comes from people within the organization, such as employees, former employees, contractors or business associates, who have inside information concerning the organization's security practices, data and computer systems. Wireless Attack Methodology - CORRECT ANSWER 1) Find Networks to Attack 2) Choose Network to Attack 3) Analyze the Network 4) Crack the Security Key 5) Sniff the Network War Walking - CORRECT ANSWER locating wireless networks by walking War Driving - CORRECT ANSWER locating networks by driving War Flying - CORRECT ANSWER locating wireless networks by airplane/helicopter War Chalking - CORRECT ANSWER identifies location of wireless networks with chalk Blue Jacking - CORRECT ANSWER The sending of unwanted messages to others over Bluetooth connections. Blue Snarfing - CORRECT ANSWER of an attack against Bluetooth enabled devices where an unauthorized user can connect to an unprotected device and access any data stored on the device. Rogue Access Point - CORRECT ANSWER unauthorized access point that allows easy access to underlying wired network Default SSID - CORRECT ANSWER good indication that AP is not securely configured MAC Spoofing - CORRECT ANSWER An attack that changes the source MAC address. Replay Attack - CORRECT ANSWER A type of network attack where an attacker captures network traffic and stores it for retransmission at a later time to gain unauthorized access to a network. - Client A associates to a Server, however Client B is sniffing the communication - Client B then sends the recorded association to the Server and obtains the same authentication as Client A Evil Twin - CORRECT ANSWER A wireless network with the same name as another wireless access point. Users unknowingly connect to the evil twin; hackers monitor the traffic looking for useful information. Eavesdropping Wireless Attack - CORRECT ANSWER attacker sniffs wireless network traffic looking for insecure protocols like HTTP, POP, IMAP, FTP, TELNET and compromises usernames and passwords that are sent in the clear Manipulation Wireless Attack - CORRECT ANSWER attacker intercepts and modifies a victim's packets and replaces them for transmission DoS Attacks (wireless) - CORRECT ANSWER Physical - use radio signals in the same frequency band as the AP to disrupt traffic Data-Link - use disassociation frames and spoofed access points to disrupt traffic on the wireless network Network - use regular network traffic to saturate the bandwidth of the AP, including its upstream bandwidth, to preclude normal network traffic NFC Attack - CORRECT ANSWER Data Corruption - using antenna, attacker can inject packets into the transmission, corrupting the transfer Spoofing - attacker makes malicious NFC tag appear legitimate and entices person to place phone near it Cross Site Scripting (XSS) - CORRECT ANSWER An attack that leverages scripts, served by a malicious or compromised server or web application, to access the site visitor's computer Javascript - CORRECT ANSWER Self-contained program that can be downloaded and executed to control or manipulate browser settings Vulnerabilities include unauthorized file access, cache access, uploads, and potential for email exposure ActiveX - CORRECT ANSWER Pre-compiled executables implemented by Microsoft to customize client usability -Executes w/ permissions of logged user Auto-accepting ActiveX components may cause malicious code to be executed or other system vulnerability exploitation SQL Injection - CORRECT ANSWER Server side attack in which SQL statements are used to map out the entire database and possibly modify entries XML Injection - CORRECT ANSWER An attack that injects XLM tags and data into a database. LDAP Vulnerabilites - CORRECT ANSWER Buffer overflows may make LDAP server vulnerable to execution of malicious code Unauthorized access may be achieved by exploiting format string vulnerabilities DoS attacks may be initiated by illicitly formatted requests Directory Traversal Attacks - CORRECT ANSWER Occurs when an attacker is able to browse directories and files outside the web application itself. Attacks of this nature often expose the directory structure of the application, web server, and underlying operating system, providing the attacker access to potentially secure or restricted pages, files, source code, and information. Arbitrary / Remote Code Execution - CORRECT ANSWER weakness in program or service allows the running of code not intended by the programmer Allows the attacker to run their code locally or remotely, often with same permission as the exploited program - Privilege escalation Buffer Overflow - CORRECT ANSWER Causes system to crash by sending more data than memory buffer can handle Integer Overflow - CORRECT ANSWER errors that occur when a number is too large to be stored in a variable Zero Day Exploit - CORRECT ANSWER Target vulnerabilities in applications or OS for which the developer does not yet know about Cookies - CORRECT ANSWER Tex file sent to a web browser from a server, and sent back to the server each time it is accessed - "maintains state" Used for tracking client history, authentication, tracking, and other user information Allowing cookies may reveal personal info Cookie Poisoning - CORRECT ANSWER An attack where an attacker modifies the contents of a cookie to exploit web app vulnerabilities. Local Shared Object (LSO) - CORRECT ANSWER Flash Cookies Similar to http cookies but associated with Adobe Flash Associated with games, stores more than user info: -Large amounts of data -Applications -User Files Session Hijacking - CORRECT ANSWER An attack in which an attacker attempts to impersonate the user by using his session token. Intruder takes control of a legitimate TCP/IP session by spoofing the source address SMTP Relay - CORRECT ANSWER Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Relay Feature that allows email servers to forward email to other email servers Protects actual email servers from direct attacks May be target of DoS caused by Spam Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) - CORRECT ANSWER a sophisticated, possibly long-running computer hack that is perpetrated by large, well-funded organizations such as governments. APT adversaries have both ______ and ______, are skilled, organized and well funded. - CORRECT ANSWER Capability and Intent Examples of APT adversaries - CORRECT ANSWER -Competitors, Hacktivsts -State Sponsored/Commercial Espionage -Organized Crime -State Sponsored Entities Hackers - CORRECT ANSWER People who try to get access to your computer without your permission in order to steal information which they could use for malicious or criminal purposes. white hat hackers - CORRECT ANSWER ethical hackers that break into the systems for non malicious reasons such as to test the system security vulnerabilities or to expose undisclosed weaknesses. Gray Hat Hackers - CORRECT ANSWER Use their skills for both offensive and defensive purposes that are not illegal or malicious and have approval to operate Types of Gray Hat Hackers - CORRECT ANSWER Penetration Tester - Take a holistic look at an organization in identifying vulnerabilities to a network and systems Red Teams - Team of experts acting as an adversary (hacker) to penetrate an organization just as a Black Hat would but with the intention of stressing and/or training the organizations security programs and processes. Black Hat Hackers - CORRECT ANSWER use their technical skills to break into computer systems, without the owner's permission, to steal information or cause damage. Types of Black Hats - CORRECT ANSWER Script Kiddies - individuals who download and use scripts/exploit tools with no real understanding of the concepts being employed Hacktivissts - Non-violent use of illegal/legally ambiquous digital tools in pursuit of political ends. Crackers - Reference for hackers who use their skills for malicious purposes. Vulnerability Assessment - CORRECT ANSWER Scanning of a network/domain to identify and report on known vulnerabilities Penetration Test - CORRECT ANSWER Scanning of a network/domain to identify and verify known vulnerabilities by actively exploiting each identified vulnerability Risk Assessment - CORRECT ANSWER Analyzing the potential impact to an organization if a threat were to exploit a vulnerability to an Information System 3 Types of Assessment Approaches - CORRECT ANSWER Black Box White Box Grey Box Black Box Assessment - CORRECT ANSWER No prior knowledge of the system or network to be assessed White Box Assessment - CORRECT ANSWER Full knowledge of the system or network to be assessed Grey Box Assessment - CORRECT ANSWER Assessment performed by the system or network administrator Banner Grabbing - CORRECT ANSWER Connecting to an open port on a host, emulating the service to receive header information. Port Scanner - CORRECT ANSWER Tool that probes system for open ports and reports back which ports are closed, filtered, and/or open. Vulnerability Scanners - CORRECT ANSWER Program that probes hosts for weaknesses, misconfigurations, patch versions, etc. intrusive vulnerability scan - CORRECT ANSWER Cause network/service disruptions -Agressive port scans -Non-credentialed -Attempt to exploit a system -Attemp to DoS a system non-intrusive vulnerability scan - CORRECT ANSWER Do not cause service diruptions -Slow/Non-aggressive port scans -Credentialed - Uses privileged accounts to access and scan for missing patches (NESSUS) Code Scanning Tools - CORRECT ANSWER Security Tools designed to find SECURITY bugs in the source code Protocol Analyzer - CORRECT ANSWER Hardware or software that captures packets to decode and analyze their contents. Network Enumerator - CORRECT ANSWER Tool that scans the network collecting information on users, groups, shares and services that are visible. Useful for discovering how much network information is available to outsiders, and which systems and services need to be secured. Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) - CORRECT ANSWER Cost due to the occurrence of a risk on an asset SLE = AV x EF Asset Value (AV) - CORRECT ANSWER Value of the asset in dollars Exposure Factor (EF) - CORRECT ANSWER Percentage of asset lost due to the occurrence of a risk on an asset. Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) - CORRECT ANSWER An estimate of how often a threat will be successful in exploiting a vulnerability over the period of a year. Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE) - CORRECT ANSWER Expected annual loss due to the occurrence of risk on an asset SLE x ARO = ALE Passive Reconnaissance - CORRECT ANSWER Gathering information on a target without their knowledge of your actions Active Reconnaissance - CORRECT ANSWER Gathering information on a target where the potential exists that your actions will be seen by the target. Information Gathering - CORRECT ANSWER Open-source intelligence the action of searching for publicly available information via the Internet to build a map/understanding of the organization, its people/employees, and relationships to other organizations. Footprinting - CORRECT ANSWER Process of gathering information to create a blueprint or map of an organization's network and systems Security Testing - CORRECT ANSWER Process of exercising specific security objectives under specified conditions to compare actual and expected behavious Internal Security Testing - CORRECT ANSWER Security testing conducted from inside the organization's security perimeter. Conducted from the internal network and assumes the identity of a trusted insider or an attacker who has penetrated the perimeter defenses. External Security Testing - CORRECT ANSWER Conducted from outside the organization's security perimeter. Overt Security Testing - CORRECT ANSWER White hat testing involves testing with the knowledge and consent of the organization's IT staff. Covert Security Testing - CORRECT ANSWER Black hat testing Testing without the knowledge of the organization's IT staff but with the full knowledge and permission of upper management. Test technical security controls, IT staff response to perceived security incidents, and staff knowledge and implementation of the organization's security policies. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

ALL FedVTE Exam (21 Sets) Questions with Verified Answers,100% CORRECT
FedVTE Cyber Risk Management for Technicians Questions with Answers,Cyber security Analyst Quiz FedVTE 40 Questions with Verified Answers,FedVTE Windows Operating System Security 50 Questions with Ver...
By securegrades 2 years ago
$0.5
21
Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 08, 2023
Number of pages
20
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 08, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
170