healthcare > STUDY GUIDE > CCRP Physical Activity Counseling Study Guide (Already GRADED A) (All)
CCRP Physical Activity Counseling Study Guide (Already GRADED A)
Document Content and Description Below
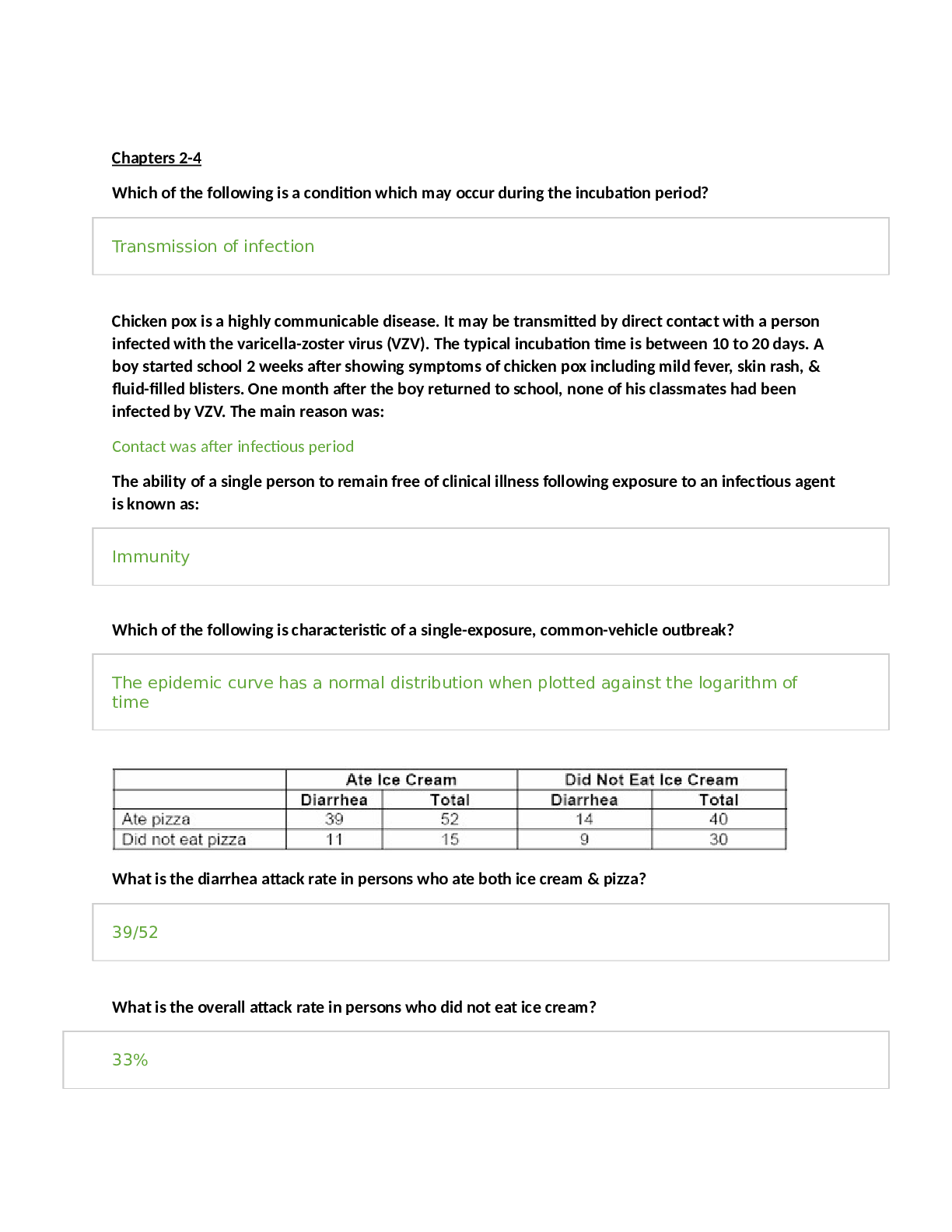
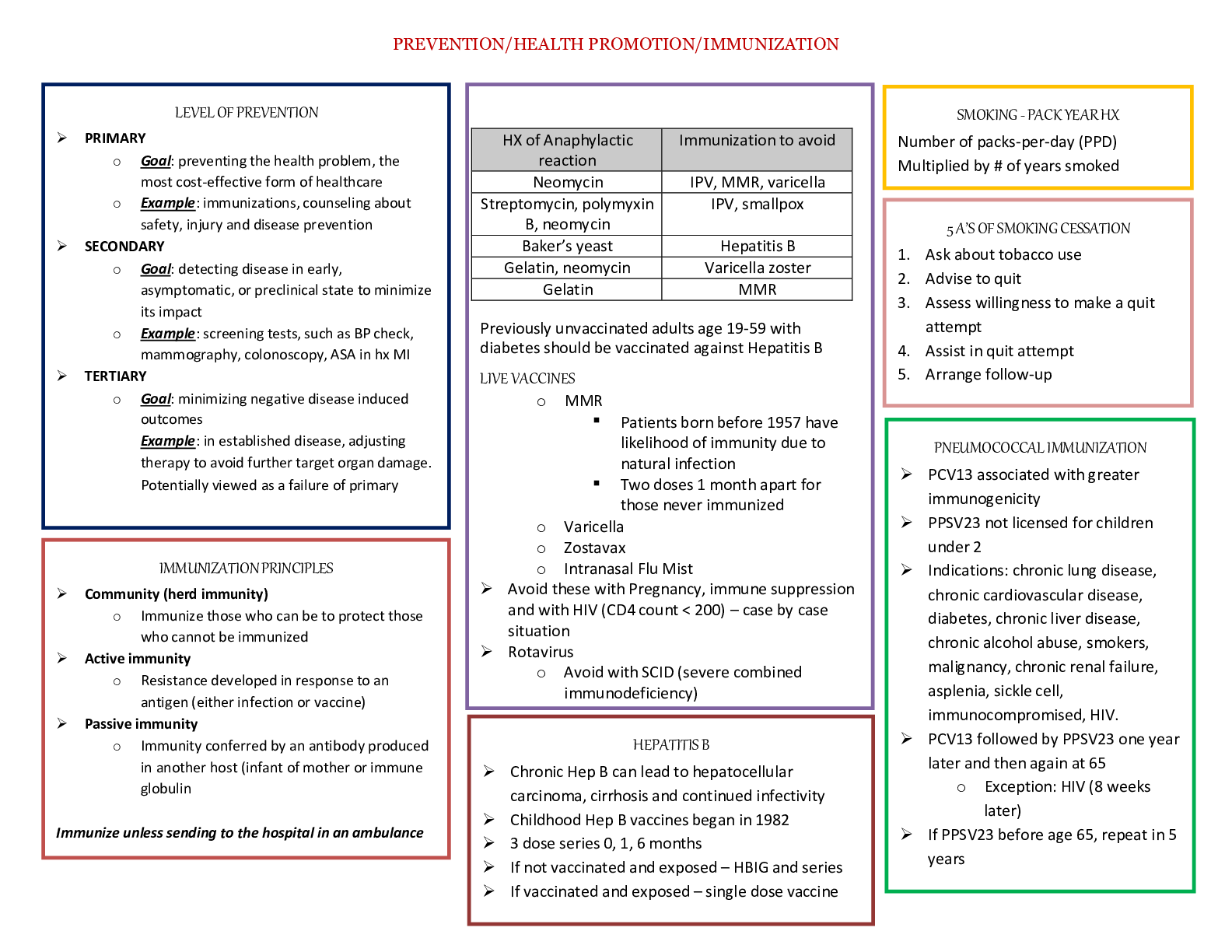
Name the 4 Components of Physical Activity FITT and Progress is the ITP fifth Physical activity is defined as bodily movement that is produced by the contraction of skeletal muscle and that su ... bstantially increases energy expenditure. Exercise is defined as planned, structured, and repetitive bodily movement done specifically to improve one or more of the components of physical fitness. Name the 4 general categories of physical activity: 1. Occupational or work-related activity 2. Housework or activities of daily living 3. Transportation or activities done with the intent of getting from one place to another 4. Leisure time pursuits including recreational activities, hobbies and exercise Guidelines for exercise from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology Foundation recommend for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease: "For all patients, the clinician should encourage 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity at least 5 days and preferably 7 days per week...". Exercise recommendations from 2008 Physical Activity Guidelines • Inactivity should be avoided. Some physical activity is better than none, and adults who participate in any amount of physical activity gain some health benefits. • For substantial health benefits, adults should do at least 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) a week of moderate-intensity, or 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes) a week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic activity. Aerobic activity should be performed in episodes of at least 10 minutes, and preferably, it should be spread throughout the week. • For additional and more extensive health benefits, adults should increase their aerobic physical activity to 300 minutes (5 hours) a week of moderate intensity, or 150 minutes a week of vigorous intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity activity. Additional health benefits are gained by engaging in physical activity beyond this amount. • When older adults cannot do 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity a week because of chronic conditions, they should be as physically active as their abilities and conditions allow. • Older adults should determine their level of effort for physical activity relative to their level of fitness. • Older adults with chronic conditions should understand whether and how their conditions affect their ability to do regular physical activity safely One MET represents the approximate energy requirements expended while an individual is quietly sitting. The metabolic demands and an individual's oxygen consumption increase as the intensity of the activity increases. The MET system allows for comparing the energy demands of disparate activities. The MET system is useful for CR professionals because it can be used to provide advice and counsel to CR participants about returning to physical activities. It is possible to determine an estimated MET level for the exercise that an individual is able to do at CR. An exercise MET levels can then be compared to estimates for recreational, occupational, or domestic-related physical activities. What is a downfall of only considering METS when deciding when a patient is able to return to work? the MET system does not take into consideration job stress or environmental factors such as air quality, temperature and wind. Obviously, a number of factors should be considered when counseling an individual's return to work. Compendium of Physical activity provides the most extensive resource for the energy requirements for a wide-range of activities in all 4 categories of physical activity. The Compendium assigns a measure of energy expenditure to a given activity. It is then possible to compare the metabolic requirements of different activities. What kinds of assessments are the following: 30-Second Chair Stand, the Timed Up and Go, Continuous Scale Physical Functional Performance-10, and the Short Battery Physical Performance. Integrated assessment tests that attempt to assess an individual's capacity to do everyday activities are available. During maximal efforts, individuals are able to achieve total _______ work rates with leg activity as compared to arm activity During maximal efforts, individuals are able to achieve total higher work rates with leg activity as compared to arm activity Arm activity is mechanically inefficient. This stresses the musculoskeletal and the cardiopulmonary system more than leg activity. What should be considered when writing an exercise prescription for arm exercises when the pre-rehab ETT is done walking. Prescribing intensity for arm-related activity based on the heart rate derived from leg testing may result in an inappropriately high target heart rate for arm activities. The arm versus leg work discrepancy is exacerbated because of upper-body weight restrictions during the period of convalescence after valve or coronary artery bypass surgeries. Cardiac rehabilitation participants should be advised to gradually return to arm-dominated activity as tolerated At submax fixed levels of work what is higher with arm exercises compared to leg? At fixed sub-maximal levels of work, heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rates, oxygen consumption, and blood lactate levels are all higher with arm versus leg activity. What theory of change is the following describing? "process involving progress through a series of stages." Studies have suggested that to most effectively influence behavior change, the intervention should match where a person reports to be in their willingness to take action. Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change: Pre-contemplation Not ready to take action (individual may or may not be aware that physical inactivity is problematic). Encourage the individual to become more aware of the negative health consequences of sedentary behavior and the benefits of being physically active. Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change: Contemplation Getting ready to consider taking action and individuals considering the consequences of being physically inactive. Provide education regarding the benefits of being physically active. Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change: Preparation People are ready to take action presently and may have begun to increase their physical activity. Support should be provided for the individual as they start to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine. Encourage the person to seek an environment to support their behavior change. Prepare the individual that the challenge of being physically active on a near-daily basis is difficult. Help support the person from reverting to sedentary behavior. Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change: Action action - Individuals have modified their behavior and Participants are incorporating physical activity into their near-daily routine. People in this stage need to be taught techniques for reinforcing their commitment to being physically active and avoiding sedentary behavior. Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change: Maintenance Individuals have been successful at incorporating physical activity into their daily routine and are working to prevent a relapse of sedentary behavior. Individuals should be provided with support for continuing their commitments to being physically active. Utilizing positive reinforcements and rewards for continuing to pursue an active lifestyle may be helpful. Self-monitoring regarding physical activity refers to keeping track or recording activities performed. Describe SMART goal setting in terms of cardiac rehab exercise goals • Specific: The physical activity should be clearly defined incorporating the FITT principle of frequency, intensity, time, and type. • Measurable: Record the activity performed. • adjustable: Make adjustments to FITT components as indicated. • Realistic: In establishing a goal it is important to balance putting forth a challenge with making the goal attainable. • time Specific: There is a saying, "a goal without a plan is a wish" or less likely to be achieved. It is important to establish a timeframe within which the goal will be completed. Name some other important elements for encouraging physical activity: (hint: R&R, PS, CB, SS, AD) Rewards & Reinforcement, Problem Solving, Confidence Building, Social Support, Avoid Drugery Name the 10 most Common Barriers to Physical Activity • Perceived lack of time • Physical activity is "inconvenient" • Lack of self-motivation • Exercise is not enjoyable • Find exercise boring • Lack confidence in their ability to be physically active (low self-efficacy) • Fear injury • Lack self-management skills, such as the ability to set personal goals, monitor progress, or reward progress toward such goals • Lack encouragement, support, or companionship from family and friends • Do not have parks, sidewalks, bicycle trails, or safe and pleasant walking paths convenient to their homes or offices. Describe some Special Considerations for Physical Activity: Extreme Heat or Cold, High Altitude, Poor Air Quality, Comorbid Medical Considerations (how to exercise patients with disabilities or high risk/multiple diseases in a safe environment outside of CR) Accelerometer sensors are the next level of sophistication for activity monitors and can often transfer data to computer or cell phone. Can track upper and lower body actvities, sleep, and multiple measures [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

CCRP AACVPR TESTS COMPILATION PACKAGE DEAL (100% Correct Solutions)
CCRP AACVPR TESTS COMPILATION PACKAGE DEAL (100% Correct Solutions)
By Prof. Goodluck 2 years ago
$20.5
13
Reviews( 0 )
$9.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 05, 2023
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 05, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
95