PHY 91880 Midterm 3 Exam _ 2020 | PHY91880 Midterm 3 Exam _ Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
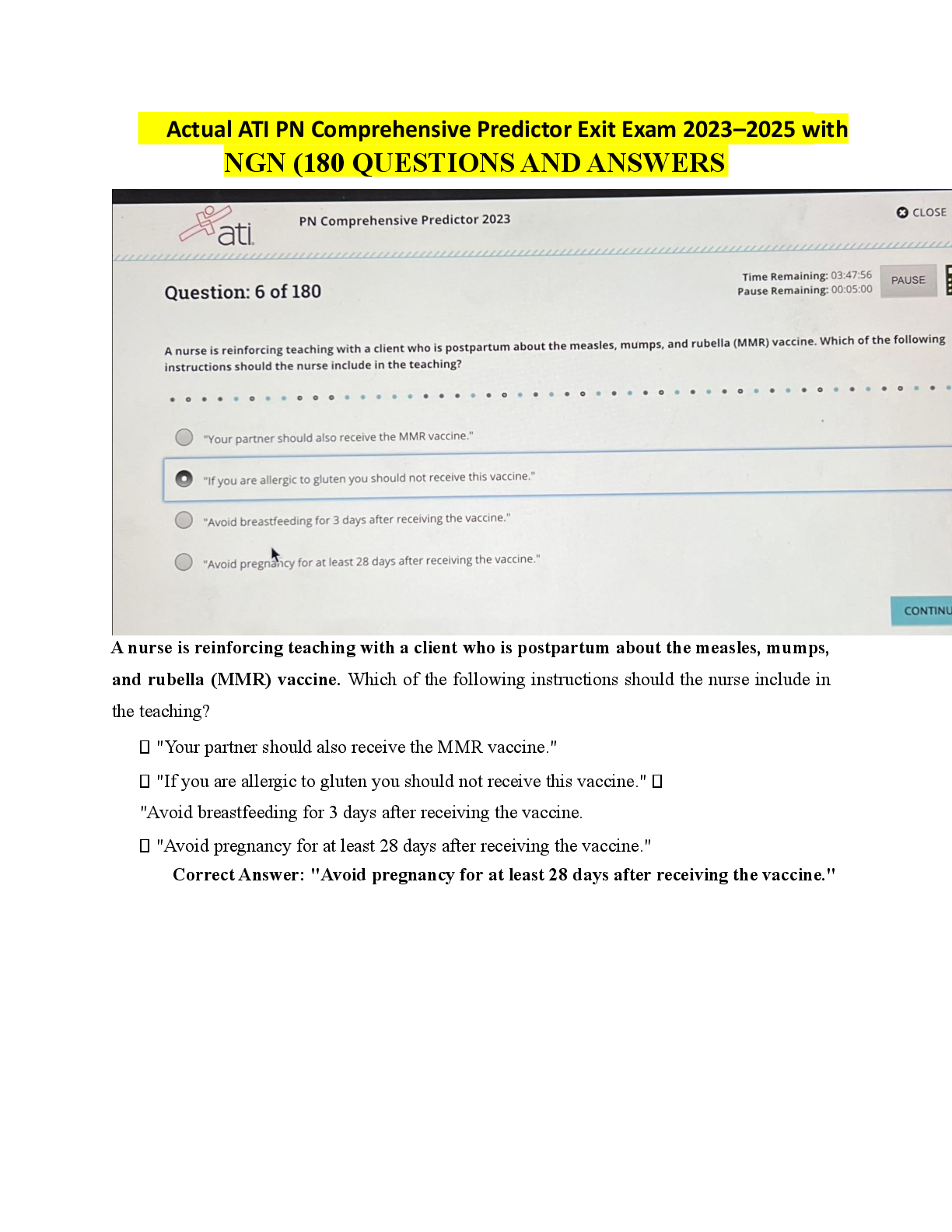
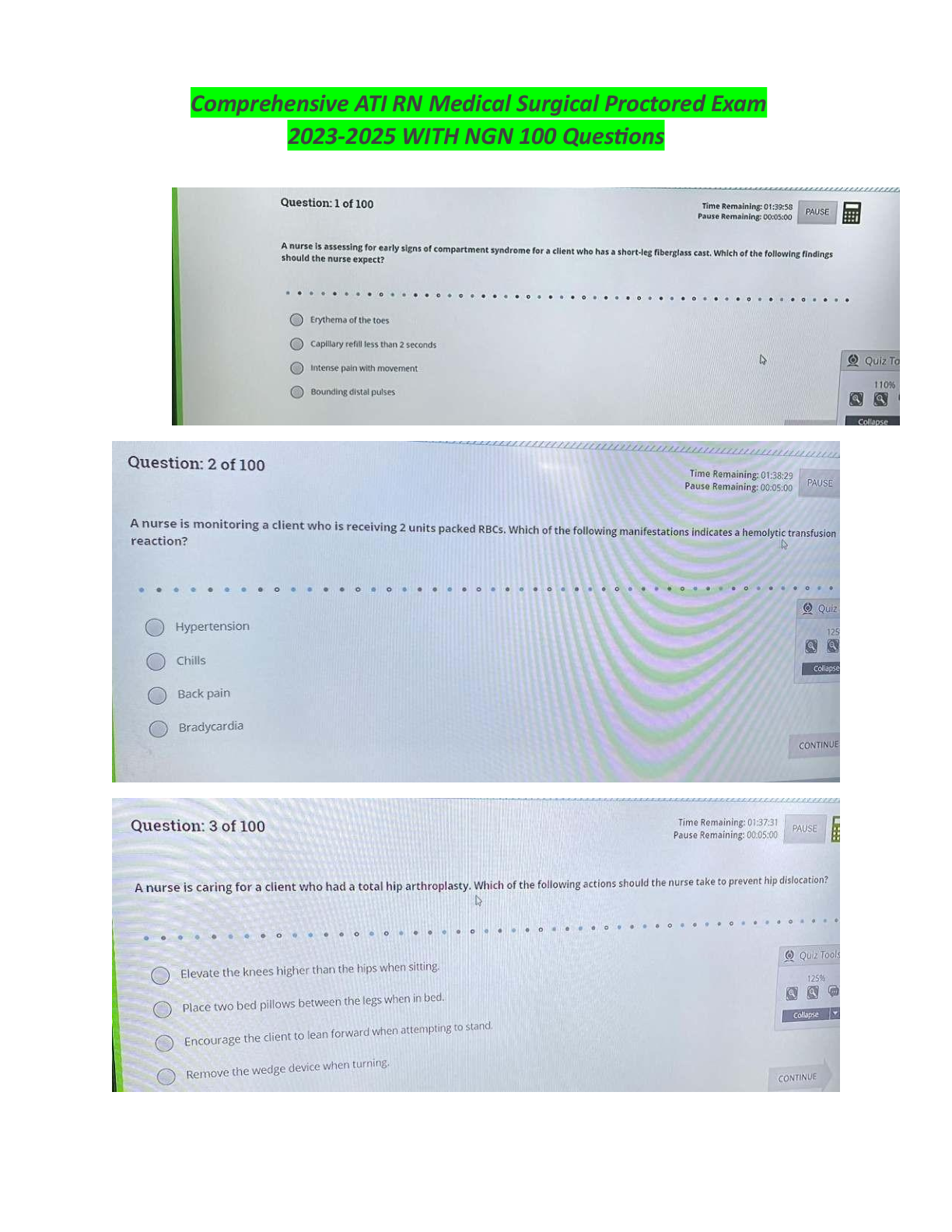
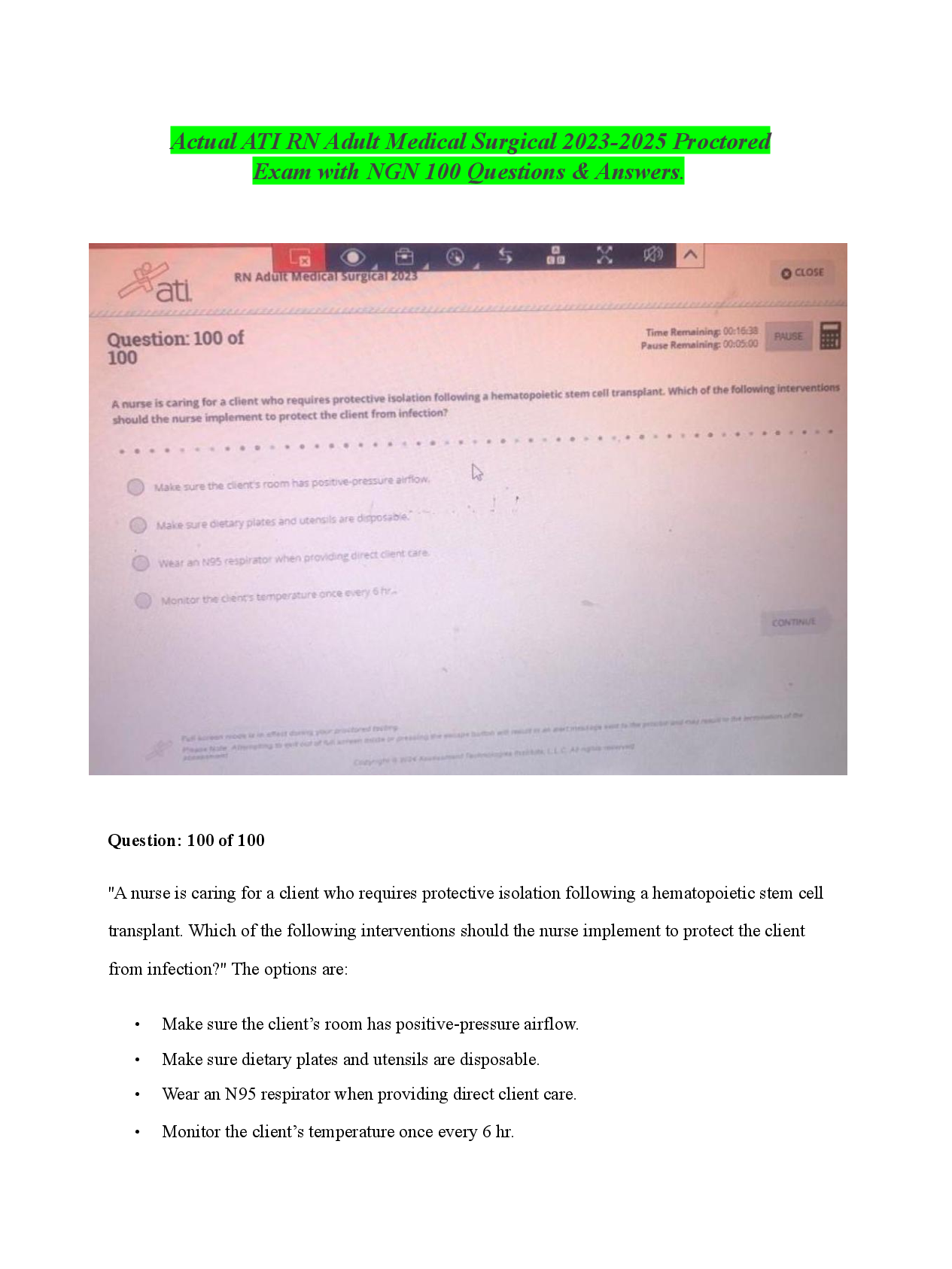
PHY 91880 Midterm 3 Exam _ 2020 | PHY91880 Midterm 3 Exam _ Graded A Version 046/AACDC – midterm 03 – turner – (93000) 1 This print-out should have 18 questions. Multiple-choice questions may ... continue on the next column or page – find all choices before answering. 001 10.0 points An infinitely long straight wire carrying a current I1 = 37 A is partially surrounded by a loop as in figure. The loop has a length L = 31.5 cm, a radius R = 11.1 cm, and carries a current I2 = 29.7 A. The axis of the loop coincides with the wire. R L I1 I2 Calculate the force exerted on the loop. 1. 311.146 2. 1247.4 3. 593.321 4. 566.24 5. 1691.62 6. 261.6 7. 509.09 8. 274.081 9. 1129.34 10. 3132.88 Correct answer: 1247.4 µN. Explanation: Let : I1 = 37 A, I2 = 29.7 A, L = 31.5 cm = 0.315 m, and R = 11.1 cm = 0.111 m. The central wire creates field B~ = µ0 I1 2 π R counterclockwise . The curved portions of the loop feels zero force since ~l × B~ = 0 there. The straight portions both feel I2~l × B~ forces to the right, amounting to F~ = I2 2 L µ0 I1 2 π R = µ0 I1 I2 L π R to the right kF~ k = µ0 (37 A) (29.7 A) (0.315 m) π (0.111 m) = 0.0012474 N = 1247.4 µN . keywords: 002 10.0 points A bar of negligible resistance and mass of 94 kg in the figure is pulled horizontally across frictionless parallel rails, also of negligible resistance, by a massless string that passes over an ideal pulley and is attached to a suspended mass of 490 g. The uniform magnetic field has a magnitude of 650 mT, and the distance between the rails is 39 cm. The rails are connected at one end by a load resistor of 46 mΩ. 650 mT 650 mT 650 mT 39 cm 490 g a 46 mΩ 94 kg What is the magnitude of the terminal velocity (i.e., the eventual steady-state speed v∞) reached by the bar? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . 1. 1.77778 2. 144.023 3. 0.127121 4. 4.6486 5. 161.262 6. 3.43735Version 046/AACDC – midterm 03 – turner – (93000) 2 7. 1.02823 8. 0.847443 9. 30.1658 10. 5.657 Correct answer: 3.43735 m/s. Explanation: Let : m = 94 kg , M = 490 g = 0.49 kg , ` = 39 cm = 0.39 m , B = 650 mT , and R = 46 mΩ = 0.046 Ω . B B B B B ` T T M Fg a R a m Fm ~Fg = M ~g ~Fm = I~` × B~ F~net = (M + m)~a = F~g − F~m E = I R = −d ΦB dt ΦB = B~ · A~ E = B ` v . It follows from Lenz’s law that the magnetic force opposes the motion of the bar. When the wire acquires steady-state speed, the gravitational force Fg is counter-balanced by the magnetic force Fm. Fg = M g = Fm = ` I B (1) I = M g ` B . (2) To find the induced current, we use Ohm’s law and substitute in the induced emf, E = −d Φ dt I = |E| R = 1 R d Φ dt . (3) Note: We have ignored the minus sign from the induced emf E because we will eventually evaluate the magnitude of the terminal velocity. The flux is Φ = B A , so |E| = d Φ dt = B dA dt = B ` v , and (4) I = B ` v R . (5) Using Eqs. 2 and 5 and noting that v is the terminal velocity v∞ M g ` B = B ` v∞ R . (6) Solving for the magnitude of the terminal velocity v∞ v∞ = M g R `2 B2 (7) = (0.49 kg) (9.8 m/s2) (0.046 Ω) (0.39 m)2(650 mT)2 = 3.43735 m/s . keywords: 003 10.0 points A uniform non-conducting ring of radius 2.37 cm and total charge 9.5 µC rotates with a constant angular speed of 3.82 rad/s around an axis perpendicular to the plane of the ring that passes through its center. What is the magnitude of the magnetic moment of the rotating ring? 1. 2.91697e-09 2. 1.10459e-08 3. 2.26777e-09 4. 1.27863e-09 5. 1.32498e-08 6. 1.95952e-09 7. 1.47807e-08 8. 1.01919e-08 9. 2.00442e-09 10. 1.39673e-09 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 06, 2021
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 06, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
55








 – University of the People.png)