The Resiliency Model of Family Stress, Adjustment, and Adaptation is based on 4 assumptions
(Ans-
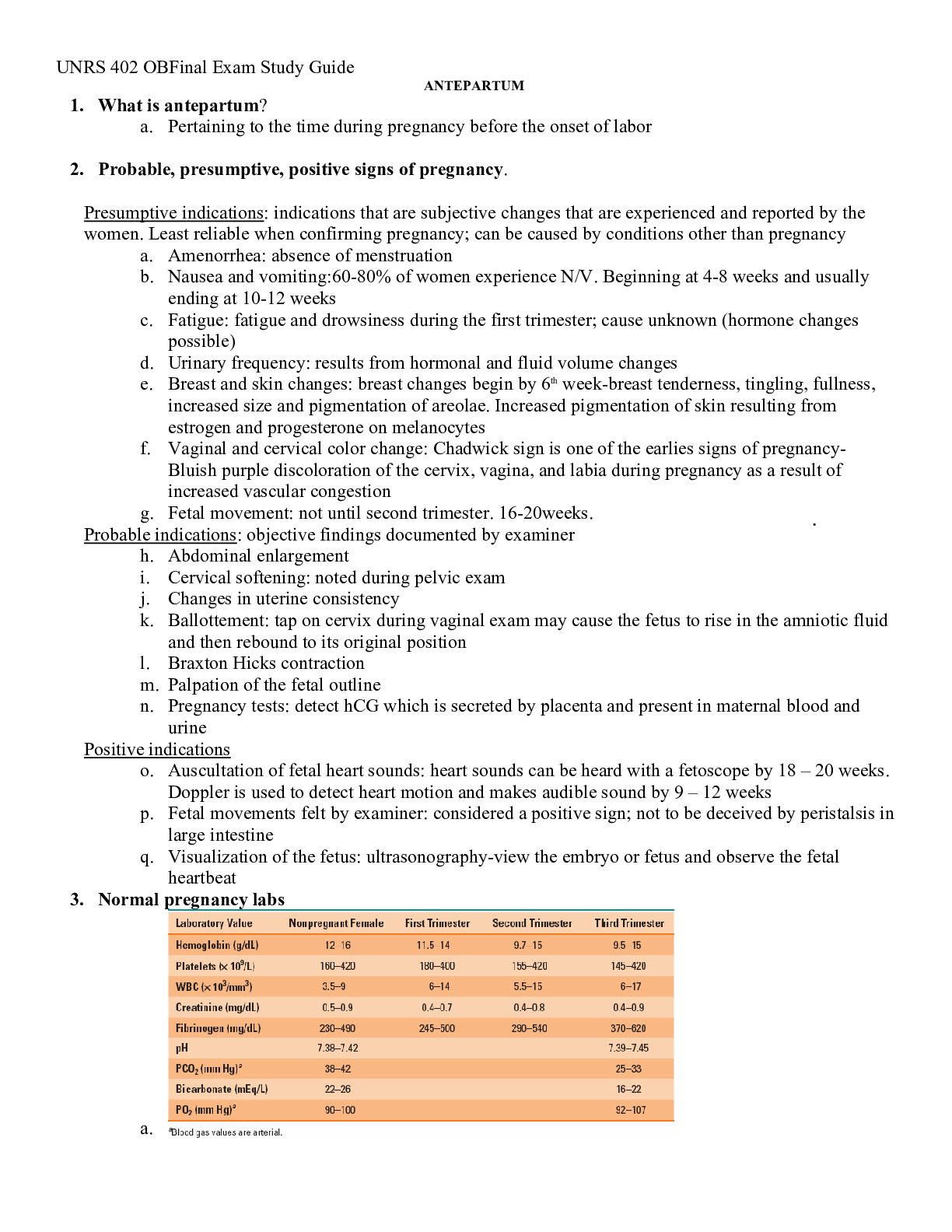
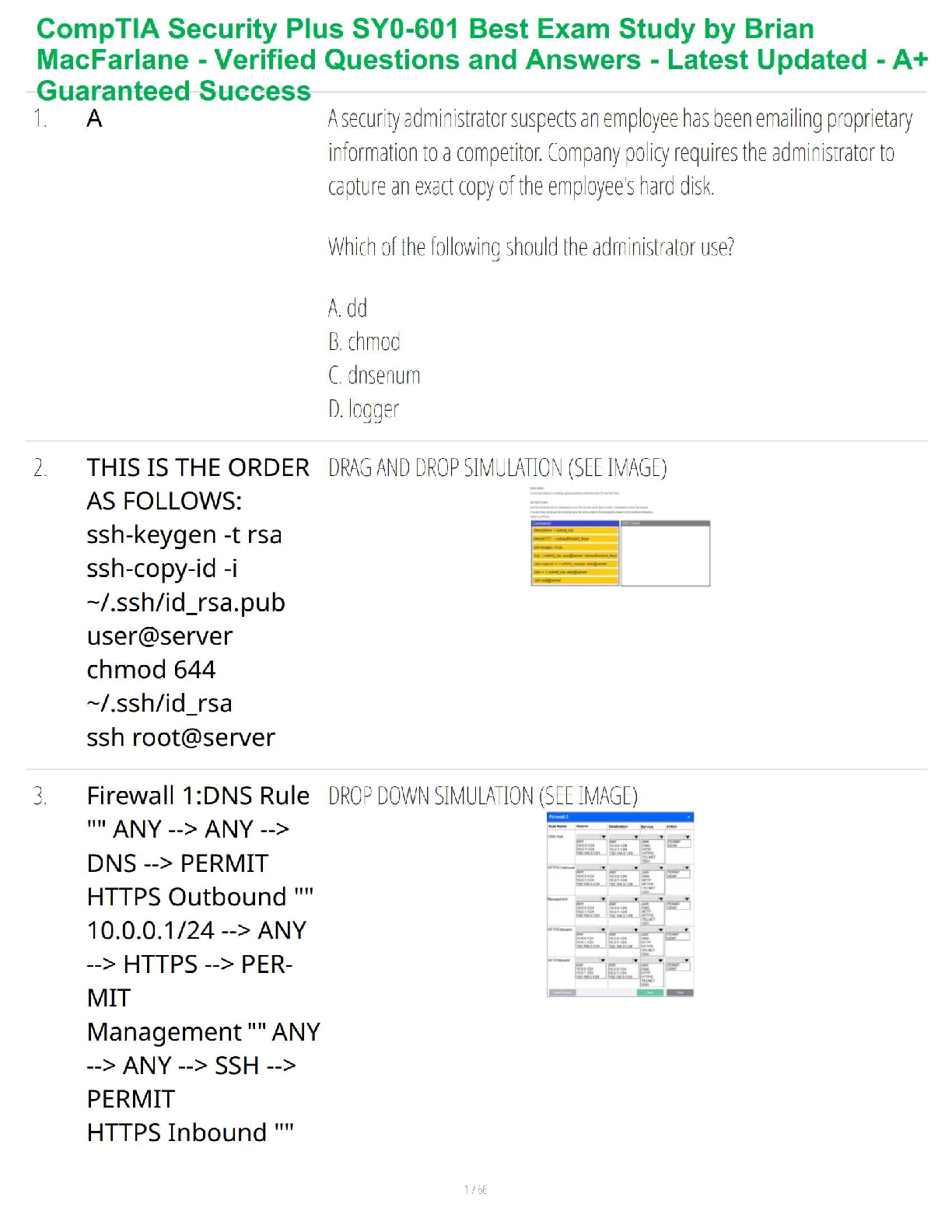
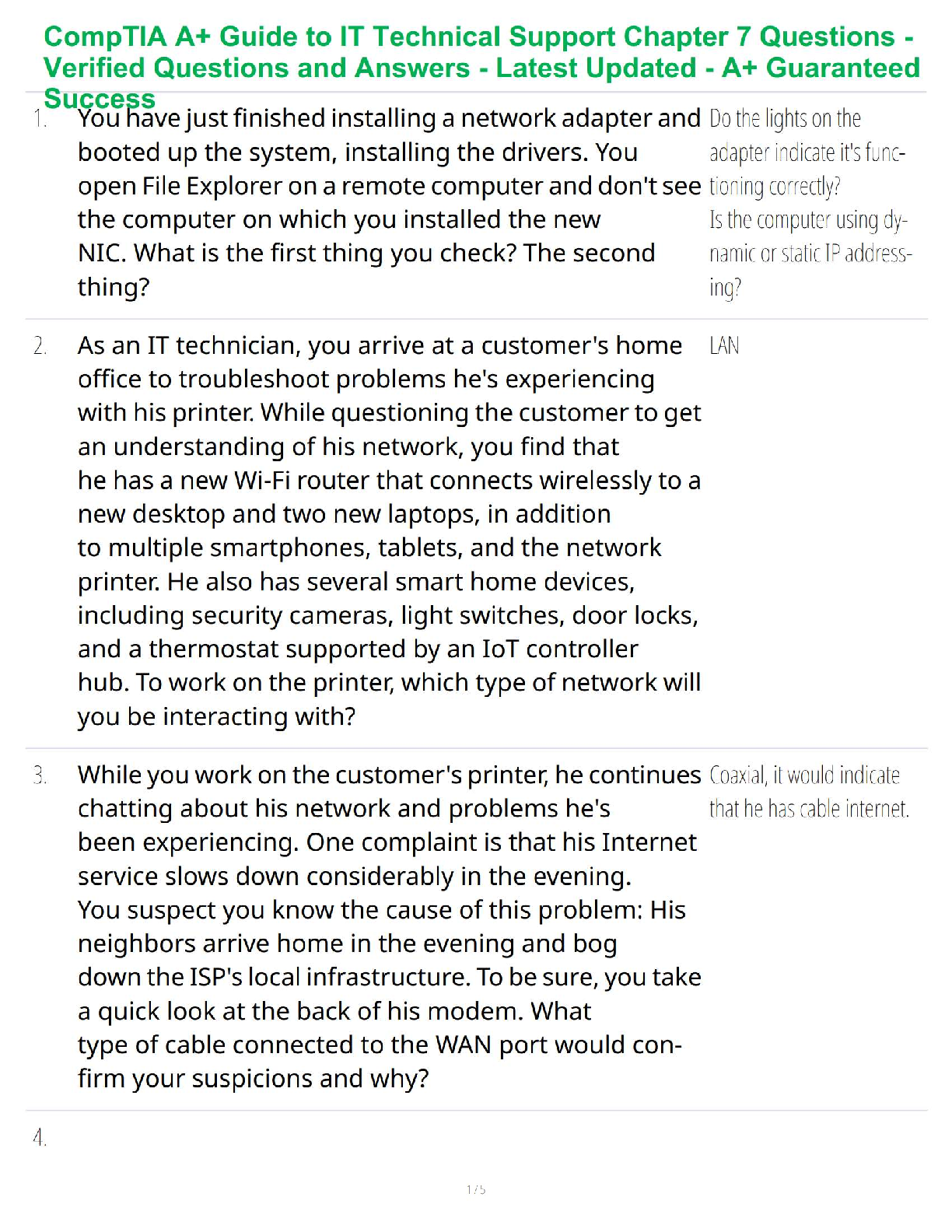
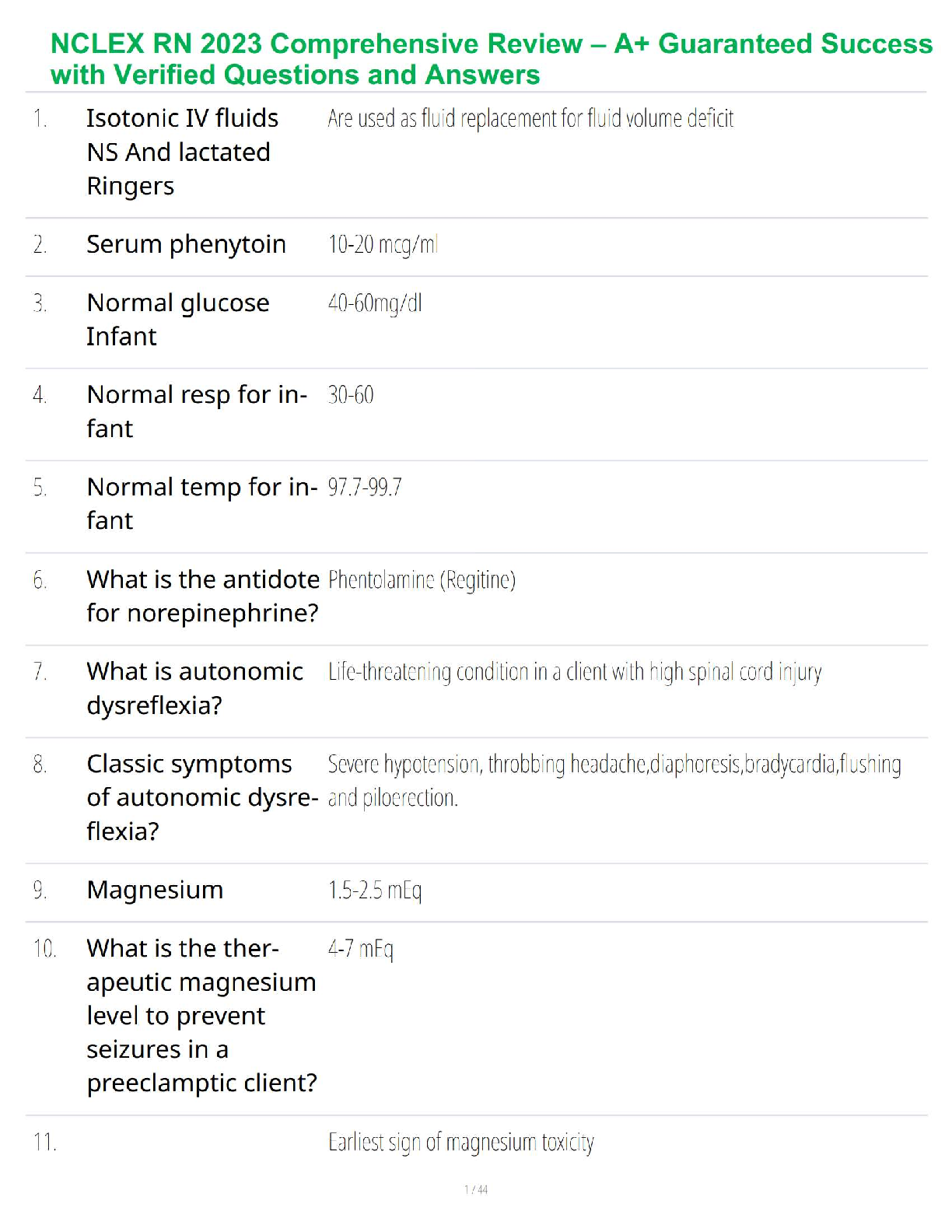
It is normal for families to face hardships and make changes to adapt.
Families develop strengths to protect members
...
The Resiliency Model of Family Stress, Adjustment, and Adaptation is based on 4 assumptions
(Ans-
It is normal for families to face hardships and make changes to adapt.
Families develop strengths to protect members from major disruptions.
Families develop coping mechanisms and defense strategies with change.
Families benefit and contribute to communities at times of stress and crisis.
Interacting variables in Hill's Family Stress Theory
(Ans-
A: Event and related hardships B: Crises in meeting the hardships. C: How the family defines the event: The crises or noncrisis2.The adjustment phase post-crisis Disorganizations, recovery, reorganization
Hill's Family Stress Theory (ABCX Model)
(Ans-
Focus is on the precrisis stage
Landmark family stress theory
Developed by Hill and named the ABCX Model
A, B, C, X are variables that interact and lead to family crisis or noncrisis
Antistress Period
(Ans- Occurs prior to confronting the stressor; anticipation; if the stressor is identified early coping strategies can be identified to lessen the impact.
Actual Stress Period
(Ans- Increased energy required by family members to cope with stressor(s); basic survival methods can be used at this time which may include intrafamilial and spiritual resources.
Post stress Period
(Ans- Focus is on attaining homeostasis of the family unit; families are challenged at this time and can regress in dynamics; families need to focus intensely on affective function at this time.
The three phases of stress include
(Ans-
Antistress Period
Actual Stress Period
Post stress Period
6 behavior-specific cognitions in the Health promotion model
(Ans-
Perceived benefits of action
perceived barriers to action
Perceived self-efficacy
Activity-related affect
Interpersonal influences (family, peers, providers); norms, support, models
Situational influences; options demand characteristics aesthetics
Information communication
(Ans- information is the content of what is said
[Show More]