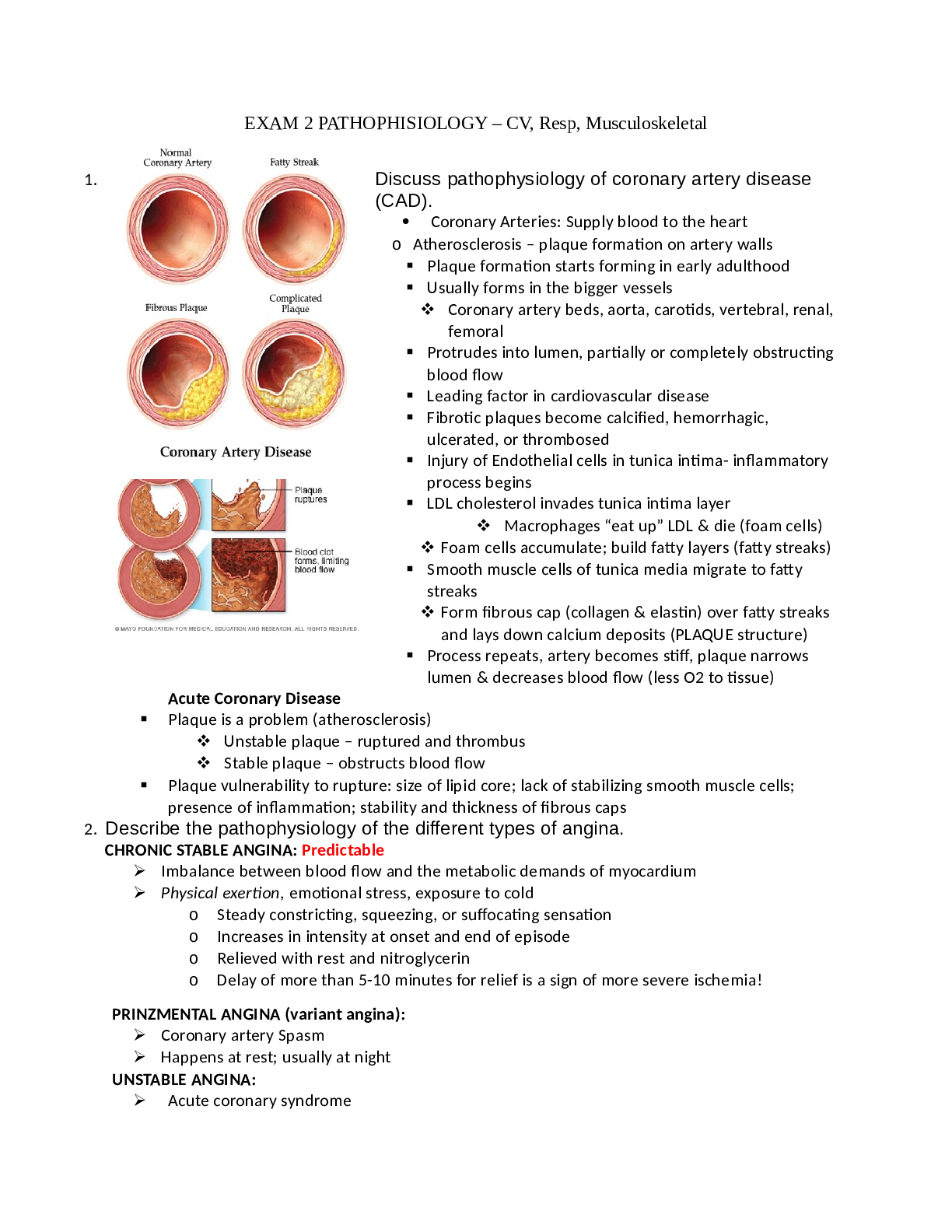
1.A nurse is caring for a patient with liver failure and is performing an assessment in the
knowledge of the patient's increased risk of bleeding. The nurse recognizes that this risk
is related to the patient's inabili
...
1.A nurse is caring for a patient with liver failure and is performing an assessment in the
knowledge of the patient's increased risk of bleeding. The nurse recognizes that this risk
is related to the patient's inability to synthesize prothrombin in the liver. What factor
most likely contributes to this loss of function?
A) Alterations in glucose metabolism
B) Retention of bile salts
C) Inadequate production of albumin by hepatocytes
D) Inability of the liver to use vitamin K
Ans: D
Feedback:
Decreased production of several clotting factors may be partially due to deficient
absorption of vitamin K from the GI tract. This probably is caused by the inability of
liver cells to use vitamin K to make prothrombin. This bleeding risk is unrelated to the
roles of glucose, bile salts, or albumin.
2.A nurse is performing an admission assessment of a patient with a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
What technique should the nurse use to palpate the patient's liver?
A) Place hand under the right lower abdominal quadrant and press down lightly with
the other hand.
B) Place the left hand over the abdomen and behind the left side at the 11th rib.
C) Place hand under right lower rib cage and press down lightly with the other hand.
D) Hold hand 90 degrees to right side of the abdomen and push down firmly.
Ans: C
Feedback:
To palpate the liver, the examiner places one hand under the right lower rib cage and
presses downward with light pressure with the other hand. The liver is not on the left
side or in the right lower abdominal quadrant.
3.A patient with portal hypertension has been admitted to the medical floor. The nurse
should prioritize which of the following assessments related to the manifestations of this
health problem?
A) Assessment of blood pressure and assessment for headaches and visual changes
B) Assessments for signs and symptoms of venous thromboembolism
C) Daily weights and abdominal girth measurement
D) Blood glucose monitoring q
[Show More]