MED SURG 211 EXAM 2 PRACTICE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (LATEST 2021)
Document Content and Description Below
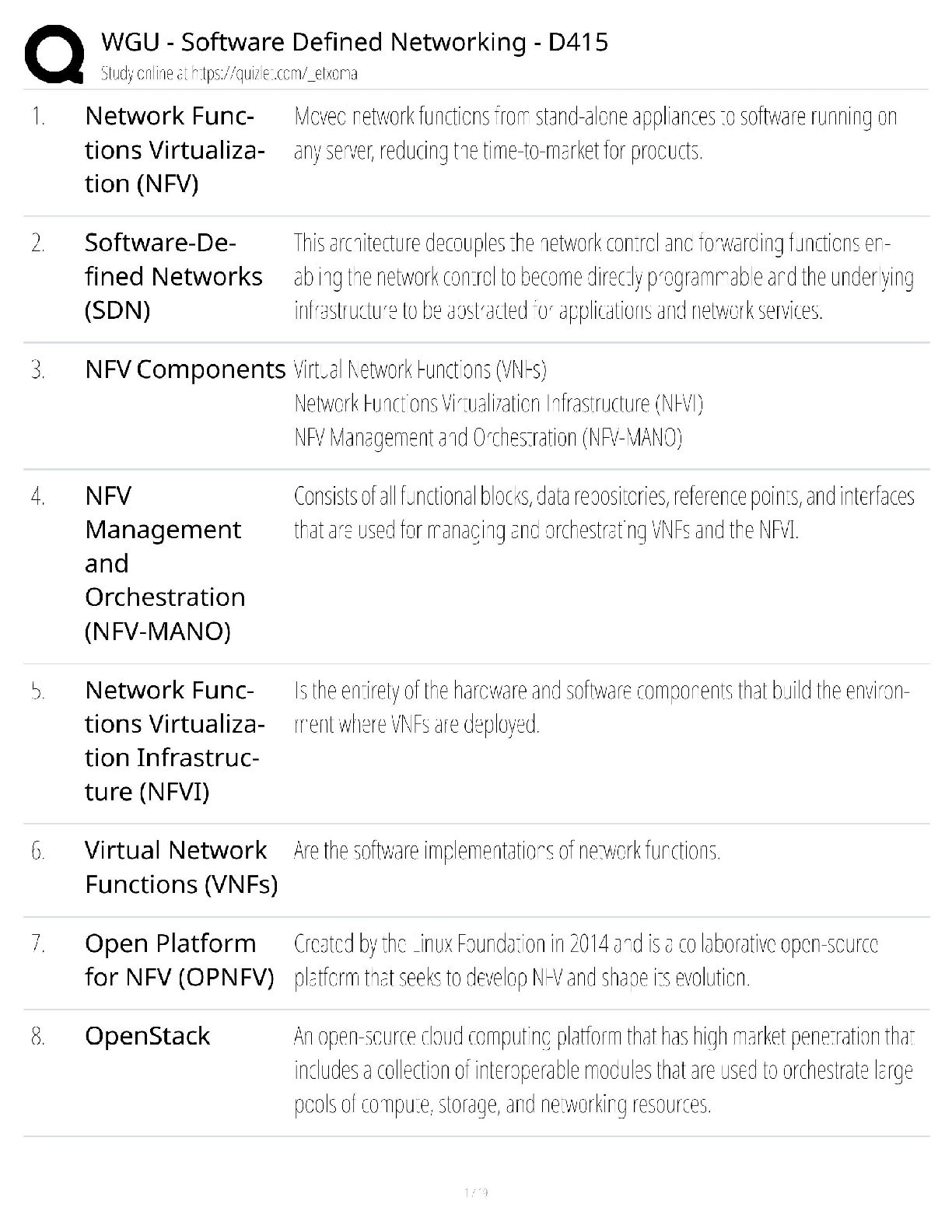
1. The nurse is caring for a woman recently diagnosed with viral hepatitis A. Which individual should the nurse refer for an immunoglobulin (IG) injection?
A. A caregiver who lives in the same househ
...
old with the patient Correct
B. A friend who delivers meals to the patient and family each week
C. A relative with a history of hepatitis A who visits the patient daily
D. A child living in the home who received the hepatitis A vaccine 3 months ago
IG is recommended for persons who do not have anti-HAV antibodies and are exposed as a result of close contact with persons who have HAV or foodborne exposure. Persons who have received a dose of HAV vaccine more than 1 mw3onth previously or who have a history of HAV infection do not require IG.
2. 2.ID: 14478179959
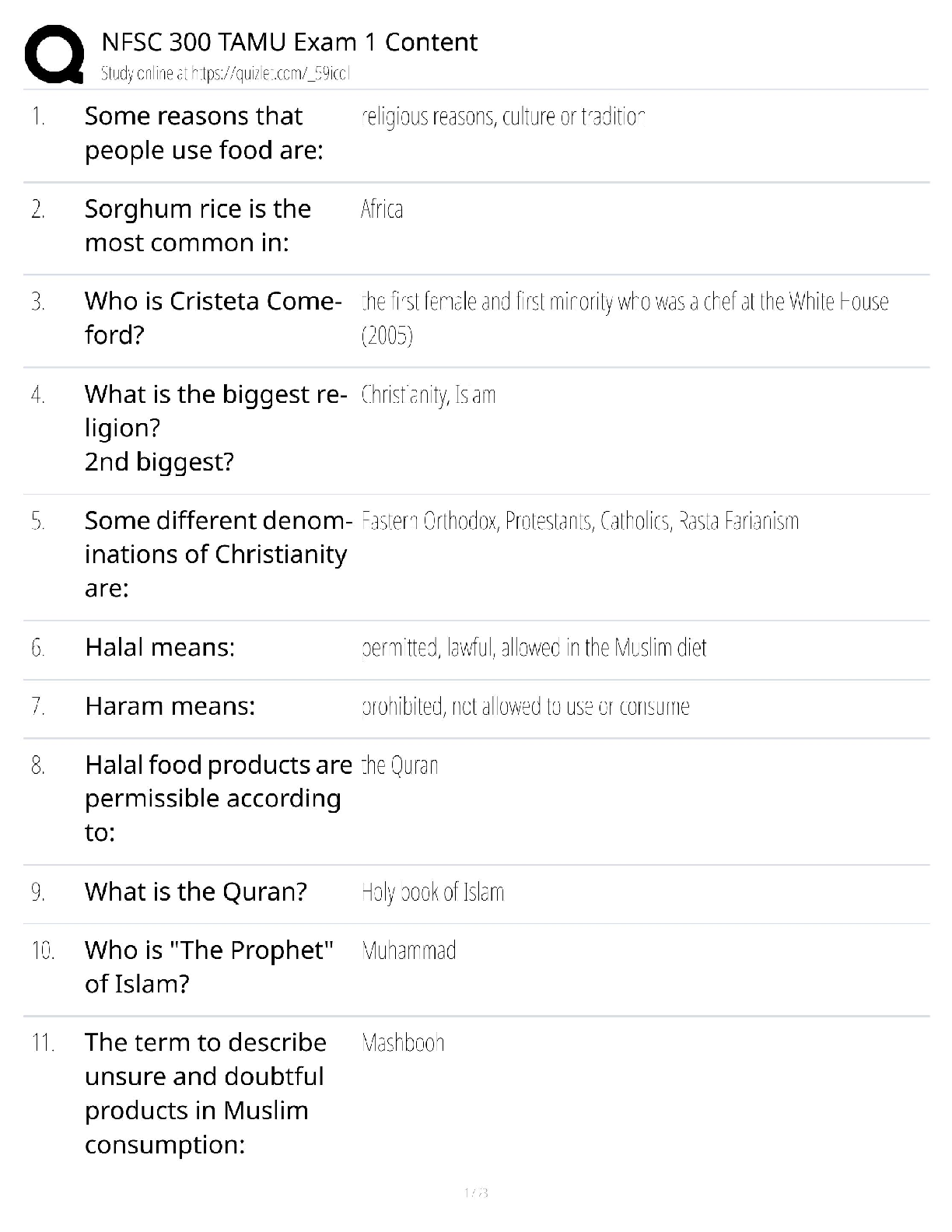
The nurse provides discharge instructions for a 64-yr-old woman with ascites and peripheral edema related to cirrhosis. Which patient statement indicates teaching was effective?
A. “Lactulose should be taken every day to prevent constipation.”
B. “It is safe to take acetaminophen up to four times a day for pain.”
C. “Herbs and other spices should be used to season my foods instead of salt.” Correct
D. “I will eat foods high in potassium while taking spironolactone (Aldactone).”
A low-sodium diet is indicated for patients with ascites and edema related to cirrhosis. Table salt is a well-known source of sodium and should be avoided. Alternatives to salt to season foods include the use of seasonings such as garlic, parsley, onion, lemon juice, and spices. Pain medications such as acetaminophen, aspirin, and ibuprofen should be avoided because these medications may be toxic to the liver. The patient should avoid potentially hepatotoxic over-the-counter drugs (e.g., acetaminophen) because the diseased liver is unable to metabolize these drugs. Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic. Lactulose results in the acidification of feces in bowel and trapping of ammonia, causing its elimination in feces.
3. 3.ID: 14478179967
The nurse is caring for a 55-yr-old man patient with acute pancreatitis resulting from gallstones. Which clinical manifestation would the nurse expect?
A. Hematochezia
B. Left upper abdominal pain Correct
C. Ascites and peripheral edema
D. Temperature over 102o F (38.9o C)
Abdominal pain (usually in the left upper quadrant) is the predominant manifestation of acute pancreatitis. Other manifestations of acute pancreatitis include nausea and vomiting, low-grade fever, leukocytosis, hypotension, tachycardia, and jaundice. Abdominal tenderness with muscle guarding is common. Bowel sounds may be decreased or absent. Ileus may occur and causes marked abdominal distention. Areas of cyanosis or greenish to yellow-brown discoloration of the abdominal wall may occur. Other areas of ecchymoses are the flanks (Grey Turner’s spots or sign, a bluish flank discoloration) and the periumbilical area (Cullen’s sign, a bluish periumbilical discoloration).
4. 4.ID: 14478179963
The nurse is caring for a group of patients. Which patient has the highest risk for developing pancreatic cancer?
A. A 38-yr-old Hispanic woman who is obese and has hyperinsulinemia
B. A 72-yr-old African American man who has smoked cigarettes for 50 years Correct
C. A 23-yr-old man who has cystic fibrosis–related pancreatic enzyme insufficiency
D. A 19-yr-old patient who has a 5-year history of uncontrolled type 1 diabetes mellitus
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer include chronic pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, age, cigarette smoking, family history of pancreatic cancer, high-fat diet, and exposure to chemicals such as benzidine. African Americans have a higher incidence of pancreatic cancer than whites. The most firmly established environmental risk factor is cigarette smoking. Smokers are two or three times more likely to develop pancreatic cancer compared with nonsmokers. The risk is related to duration and number of cigarettes smoked.
5. 5.ID: 14478179961
The nurse instructs a 50-yr-old woman about cholestyramine to reduce pruritus caused by gallbladder disease. Which patient statement indicates understanding of the instructions?
A. “This medication will help me digest fats and fat-soluble vitamins.”
B. “I will apply the medicated lotion sparingly to the areas where I itch.”
C. “The medication is a powder and needs to be mixed with milk or juice.” Correct
D. “I should take this medication on an empty stomach at the same time each day.”
For treatment of pruritus, cholestyramine may provide relief. This is a resin that binds bile salts in the intestine, increasing their excretion in the feces. Cholestyramine is in powder form and should be mixed with milk or juice before oral administration.
6. 6.ID: 14478179991
A 54-yr-old patient admitted with diabetes mellitus, malnutrition, osteomyelitis, and alcohol abuse has a serum amylase level of 280 U/L and a serum lipase level of 310 U/L. Which diagnosis does the nurse expect?
A. Starvation
B. Pancreatitis Correct
C. Systemic sepsis
D. Diabetic ketoacidosis
The patient with alcohol abuse could develop pancreatitis as a complication, which would increase the serum amylase (normal, 30-122 U/L) and serum lipase (normal, 31- 186 U/L) levels as shown.
7. 7.ID: 14478179983
The health care provider orders lactulose for a patient with hepatic encephalopathy. Which finding indicates the medication has been effective?
A. Relief of constipation
B. Relief of abdominal pain
C. Decreased liver enzymes
D. Decreased ammonia levels Correct
Hepatic encephalopathy is a complication of liver disease and is associated with elevated serum ammonia levels. Lactulose traps ammonia in the intestinal tract. Its laxative effect then expels the ammonia from the colon, resulting in decreased serum ammonia levels and correction of hepatic encephalopathy. An additional finding may be an improvement in level of consciousness.
8. 8.ID: 14478181003
The family of a patient newly diagnosed with hepatitis A asks the nurse what they can do to prevent becoming ill. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
A. “You will need to be tested first; then treatment can be determined.”
B. “The hepatitis vaccine will provide immunity from this and future exposures.”
C. “There is nothing you can do since the patient was infectious before admission.”
D. “An immunoglobulin injection will be given to prevent infection or limit symptoms.” Correct
Immunoglobulin provides temporary (1-2 months) passive immunity and is effective for preventing hepatitis A if given within 2 weeks after exposure. It may not prevent infection in all persons, but it will at least modify the illness to a subclinical infection. The hepatitis vaccine is only used for preexposure prophylaxis.
9. 9.ID: 14478179987
When planning care for a patient with cirrhosis, the nurse will give highest priority to which nursing diagnosis?
A. Impaired skin integrity related to edema, ascites, and pruritus
B. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to anorexia
C. Excess fluid volume related to portal hypertension and hyperaldosteronism
D. Ineffective breathing pattern related to pressure on diaphragm and reduced lung volume Correct
Although all of these nursing diagnoses are appropriate and important in the care of a patient with cirrhosis, airway and breathing are always the highest priorities.
10. 10.ID: 14478179993
A patient with type 2 diabetes and cirrhosis asks the nurse if it would be acceptable to take silymarin (milk thistle) to help minimize liver damage. The nurse responds based on what knowledge?
A. Milk thistle may affect liver enzymes and thus alter drug metabolism. Correct
B. Milk thistle is generally safe in recommended doses for up to 10 years.
C. There is unclear scientific evidence for the use of milk thistle in treating cirrhosis.
D. Milk thistle may elevate the serum glucose levels and is thus contraindicated in diabetes.
Scientific evidence indicates there is no real benefit from milk thistle to protect liver cells from toxic damage in the treatment of cirrhosis. Milk thistle does affect liver enzymes and thus could alter drug metabolism. Therefore, patients will need to be monitored for drug interactions. It is noted to be safe for up to 6 years, not 10 years, and it may lower, not elevate, blood glucose levels.
11. 11.ID: 14478179989
A patient with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) present in the serum is being discharged with pain medication after knee surgery. Which medication order should the nurse question?
A. Tramadol
B. Hydromorphone (Dilaudid)
C. Oxycodone with aspirin (Percodan)
D. Hydrocodone with acetaminophen Correct
The analgesic with acetaminophen should be questioned because this patient is a chronic carrier of hepatitis B and is likely to have impaired liver function. Acetaminophen is not suitable for this patient because it is converted to a toxic metabolite in the liver after absorption, increasing the risk of hepatocellular damage.
12. 12.ID: 14478179999
The condition of a patient who has cirrhosis of the liver has deteriorated. Which diagnostic study would help determine if the patient has developed liver cancer?
A. Serum α-fetoprotein level
B. Ventilation/perfusion scan
C. Hepatic structure ultrasound
Correct
D. Abdominal girth measurement
Hepatic structure ultrasonography, CT scan, and MRI are used to screen for and diagnose liver cancer. Serum α-fetoprotein level may be elevated with liver cancer or other liver problems. Ventilation/perfusion scans are used to diagnose pulmonary emboli. Abdominal girth measurement would not differentiate between cirrhosis and liver cancer.
13. 13.ID: 14478181005
The patient with right upper quadrant abdominal pain has an abdominal ultrasound that reveals cholelithiasis. What is the nurse’s priority?
A. Prevent all oral intake.
B. Control abdominal pain. Correct
C. Provide enteral feedings.
D. Avoid dietary cholesterol.
Patients with cholelithiasis can have severe pain, so controlling pain is important until the problem can be treated. NPO status may be needed if the patient will have surgery but will not be used for all patients with cholelithiasis. Patients with pancreatitis may be NPO. Enteral feedings should not be needed, and avoiding dietary cholesterol is not used to treat cholelithiasis.
14. 14.ID: 14478181007
A patient with cholelithiasis is being prepared for surgery. Which patient assessment represents a contraindication for a cholecystectomy?
A. Low-grade fever of 100°F and dehydration
B. Abscess in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen
C. Multiple obstructions in the cystic and common bile duct
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 103 pages
.png)





 NRS428V week 5 Benchmark – Community Teaching Plan Community Presentation, Latest Summer 2021.png)
 NRS429 Week 3 amily Assessment Part II, complete latest 2021.png)

.png)

.png)