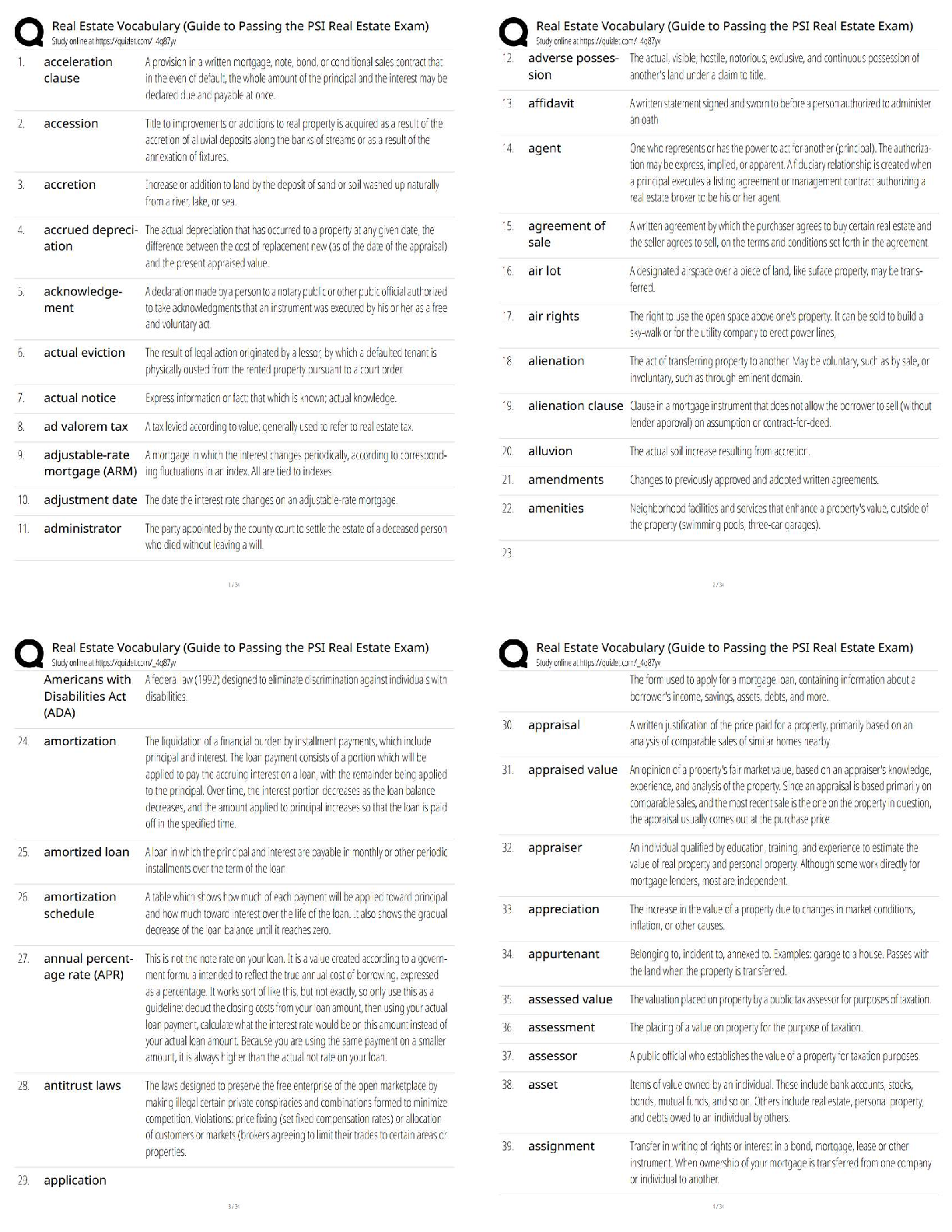
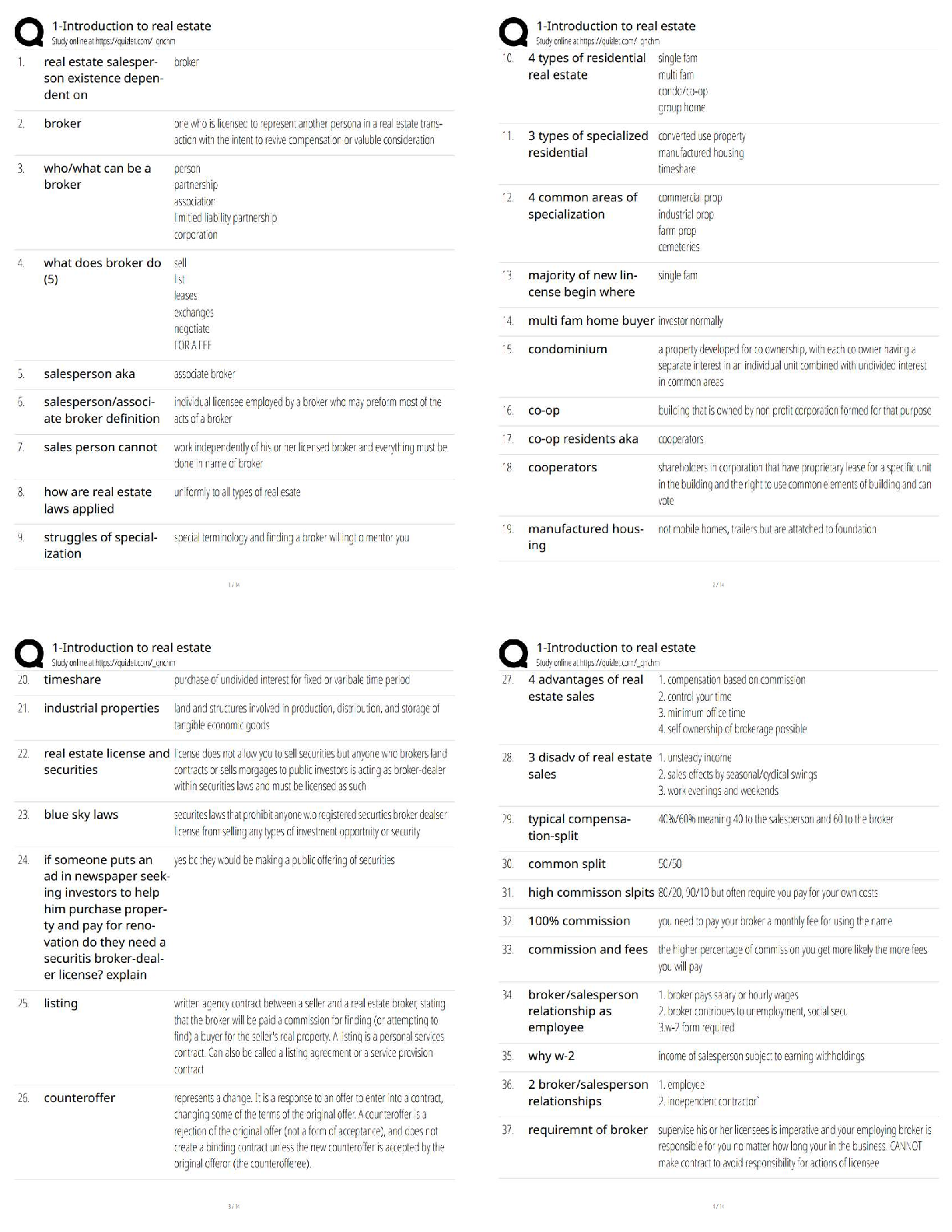
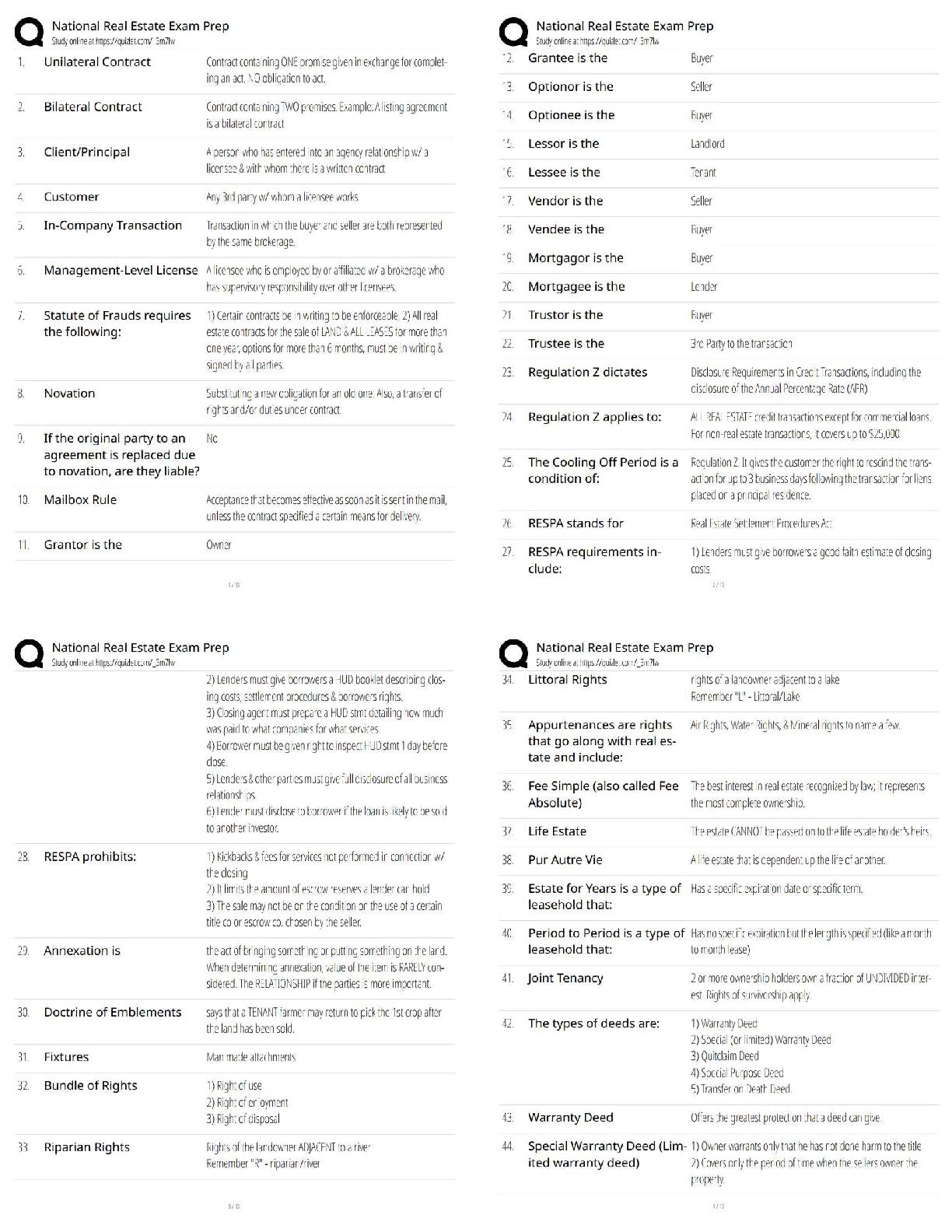
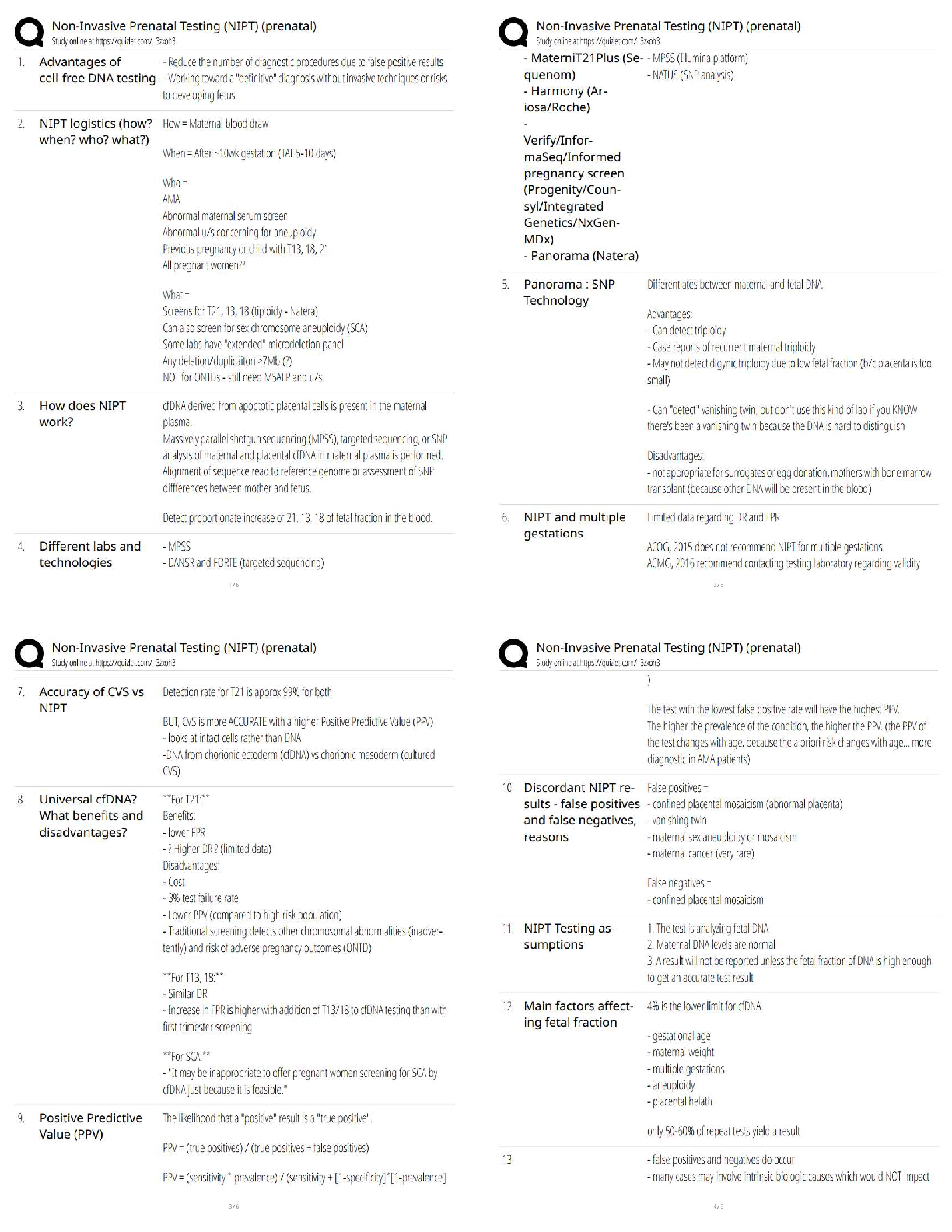
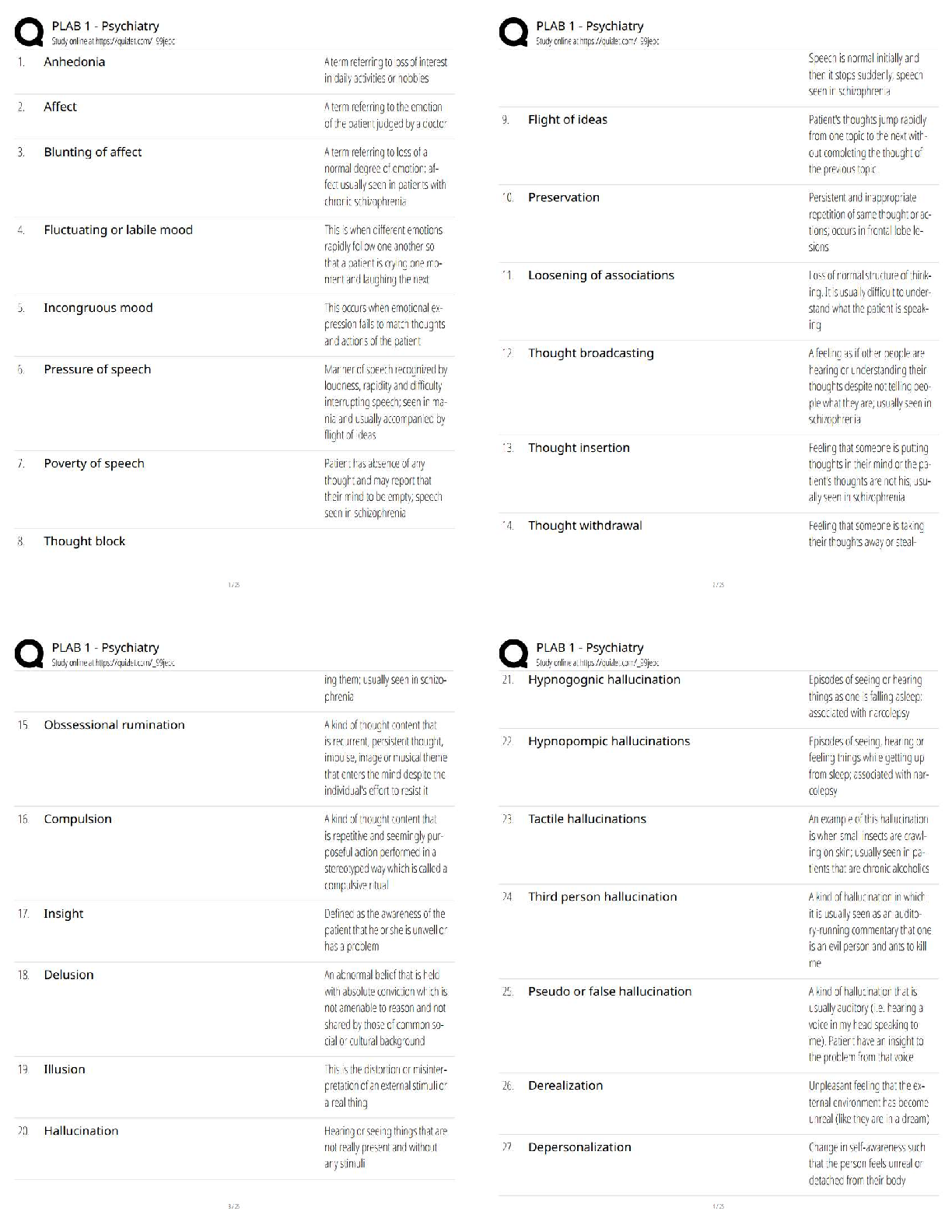
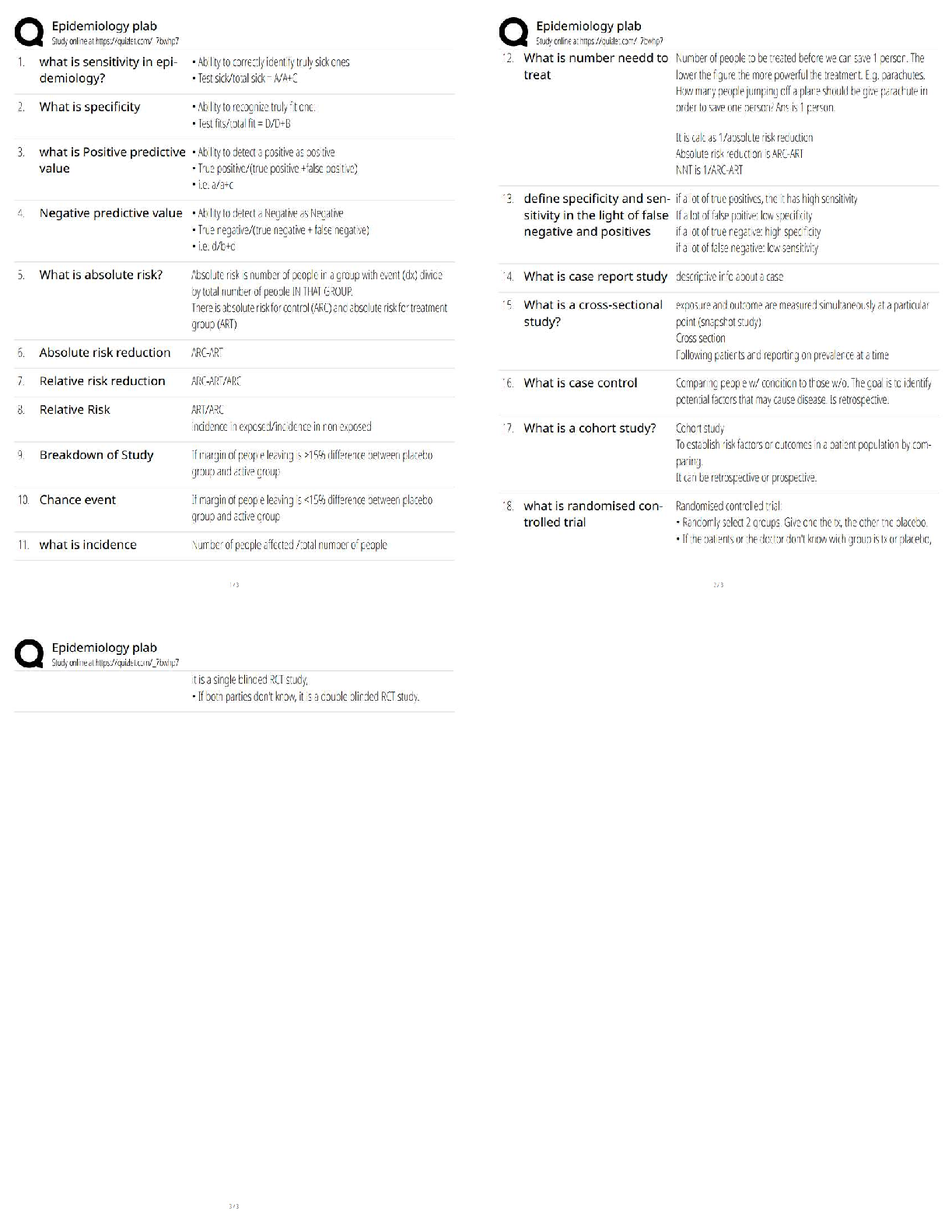
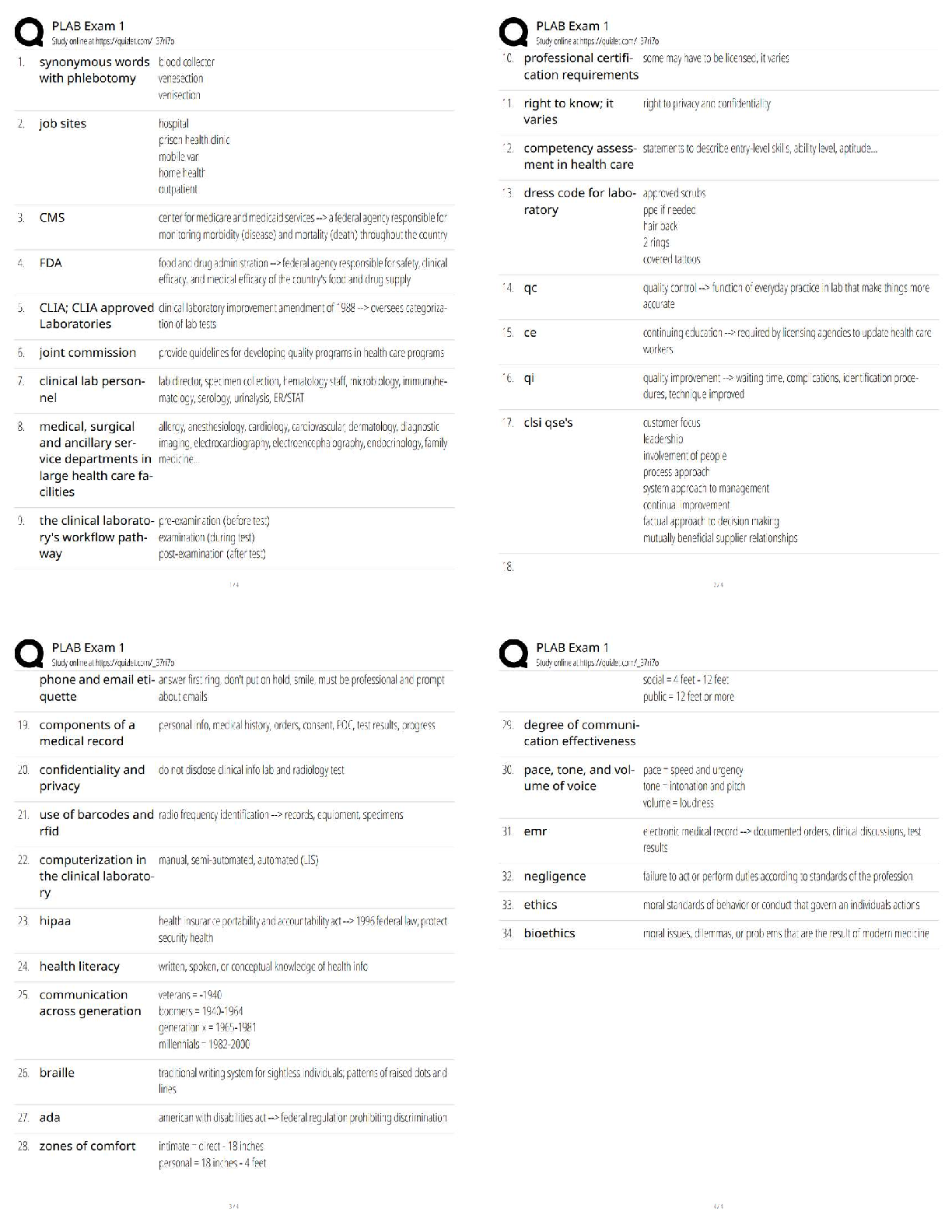
Pathophysiology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Neurosurgery Practice Questions and Answers (301-400) (All)
Neurosurgery Practice Questions and Answers (301-400)
Document Content and Description Below
301. Bicuculline is a A. glutamate agonist. B. glutamate antagonist. C. dopamine agonist. D. GABA agonist. E. GABA antagonist. 302. All of the following statements regarding Charcot–Marie–To ... oth disease are true EXCEPT: A. It may be associated with a footdrop. B. It is a condition of disordered myelination from decreased production of peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22). C. It is the most common inherited peripheral neuropathy. D. It is associated with a mutation on chromosome 17. E. It is characterized by peroneal muscle atrophy. 303. Neurons that give rise to the ventral trigeminothalamic tract arise from the A. trigeminal motor nucleus and the spinal trigeminal tract. B. dorsal aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the spinal trigeminal tract. C. ventral aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the spinal trigeminal tract. D. ventral aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the mesencephalic tract. E. dorsal aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the mesencephalic tract. 304. All of the following regarding motion perception are true EXCEPT: A. Motion is perceived by an object’s change of position on the retina. B. The sensation of movement is known as the phi phenomenon. C. Images that change positions more than 15 times per second are indistinguishable from continuous motion. D. The motion system is disabled at rates below 100 Hz. E. There is no physical process occurring on the retina that corresponds to the perceived sensation of motion. 305. Which tract decussates in the dorsal tegmental decussation? A. Rubrospinal tract B. Medial vestibulospinal tract C. Tectospinal tract D. All of the above E. None of the above 306. In paranasal sinus cancers, sphenoid sinus involvement is noteworthy because of which of the following? A. It is the major predictor of later tumor recurrence. B. It demands use of special instruments. C. It will more likely result in anosmia postoperatively. D. All of the above E. None of the above 307. Which of the following is a distinct interneuron between receptor and ganglion cell? A. Rods B. Cones C. Horizontal cells D. Amacrine cells E. Bipolar cells 308. Ependymoma is immunoreactive for A. GFAP. B. S-100. C. vimentin. D. All of the above E. None of the above 309. The caudal remnant of the median prosencephalic vein unites with the developing internal cerebral veins to form A. the straight sinus. B. the vein of Galen. C. the confluence of sinuses. D. the inferior sagittal sinus. E. None of the above 310. Which of the following statements is NOT true of Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease? A. It has been linked to severe deficiency of myelin-specific lipids. B. It is X-linked recessive in the classical form. C. The connatal form (type II) is milder than the classical form. D. It manifests as a “tigroid” pattern of perivascular myelin preservation on MRI. E. Rare instances of female cases have been described. 311. Which afferent cerebellar tract does NOT pass through the inferior cerebellar peduncle? A. Reticulocerebellar B. Vestibulocerebellar C. Trigeminocerebellar D. Pontocerebellar tract E. Olivocerebellar tract 312. All of the following statements regarding the cerebellum are true EXCEPT: A. The flocculonodular lobe receives input from the vestibular nuclei. B. The anterior lobe receives input from the spinocerebellar tracts. C. The vermis sends fibers to the VL thalamus and motor cortex. D. The intermediate zone functions with posture, tone, and ipsilateral limb movements. E. A lesion of the interposed nuclei causes intention tremor. 313. Which of the following inhibitory synaptic connections is found exclusively in the olfactory bulb? A. Dendrodendritic B. Axodendritic C. Axoaxonic D. Axosomatic E. Dendroaxonic 314. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the parvocellular system of the lateral geniculate nucleus? A. It is a small cell with a compact dendritic tree. B. It represents a minority of the total ganglion cell number. C. It projects to layer 4Cβ in the striate cortex. D. It is involved with color processing. E. It has low contrast sensitivity and high acuity. 315. All the following are true regarding venous air embolism EXCEPT: A. It manifests as a decrease in end tidal CO2. B. Air should be aspirated from the right atrium if it occurs. C. The patient should be placed in the left lateral decubitus position. D. The head should be lowered if possible. E. End tidal CO2 changes cannot precede precordial Doppler changes. 316. The stria terminalis is a fiber tract that parallels the A. caudate vein. B. septal vein. C. basal vein of Rosenthal. D. internal cerebral vein. E. thalamostriate vein. 317. What are the major contents of the proximal portion of the cubital fossa, in order from medial to lateral? A. Median nerve, brachial artery, biceps brachii tendon, radial nerve B. Median nerve, biceps brachii tendon, radial nerve, brachial artery C. Biceps brachii tendon, median nerve, radial nerve, brachial artery D. Brachial artery, biceps brachii tendon, radial nerve, median nerve E. None of the above 318. All of the following are medial rotators of the arm EXCEPT: A. Pectoralis major B. Subscapularis C. Teres major D. Teres minor E. Latissimus dorsi 319. The medial posterior choroidal artery when viewed on an angiogram occupies the same location as this structure seen on the venous phase of the angiogram. A. Vein of Galen B. Basal vein of Rosenthal C. Internal cerebral vein D. Thalamostriate vein E. Caudate vein 320. Occlusion of which of the following arteries is most likely to result in ipsilateral hypoglossal palsy? A. Basilar B. Anterior spinal C. Vertebral D. PICA E. AICA 321. The Botzinger complex is a cluster of cells that are involved in A. excitatory control of cardiac function. B. inhibitory control of cardiac function. C. excitatory control of respiratory function. D. inhibitory control of respiratory function. E. None of the above 322. The upper subscapular nerve arises from which segment of the brachial plexus? A. Superior trunk B. Medial trunk C. Lateral cord D. Posterior cord E. Medial cord 323. All of the following are true of moyamoya disease EXCEPT: A. The majority of adults with this disease present with ischemia. B. The age of onset of symptoms displays a bimodal distribution. C. It is of unknown etiology. D. It involves progressive stenosis of the supraclinoid carotid arteries with the concomitant formation of rich collaterals at the skull base. E. It is associated with Down syndrome and neurofibromatosis. 324. All of the following are true of valproic acid EXCEPT: A. It is effective in generalized tonicoclonic seizures. B. It is ~90% protein bound. C. It has a long half-life. D. It may be associated with platelet dysfunction. E. It may result in liver dysfunction. 325. Which of the following anesthetics allows patients to emerge faster from anesthesia and has the least effect on metabolism of antiepileptic drugs? A. Enflurane B. Isoflurane C. Nitrous oxide D. Halothane E. Ketamine 326. The glomus is a prominent tuft of choroid plexus found in A. the frontal horn. B. the temporal horn. C. the atrium. D. the occipital horn. E. None of the above 327. Which of the following groups of nerves is most likely to be affected by fractures of the humerus? A. Axillary, musculocutaneous B. Median, musculocutaneous C. Axillary, radial, ulnar D. Median, radial, ulnar E. Median, radial 328. Apraxia usually results from a lesion of the A. precentral gyrus. B. postcentral gyrus. C. premotor cortex. D. prefrontal cortex. E. cingulated gyrus. 329. On an angiogram, the colliculocentral point is halfway between tuberculum sellae and the sinus confluence. This point is closest to which structure? A. Vein of Galen B. Basal vein of Rosenthal C. Internal cerebral vein D. Straight sinus E. Precentral cerebellar vein 330. Theta activity can be described for which of the following frequencies? A. 5 Hz B. 10 Hz C. 15 Hz D. 20 Hz E. 25 Hz 331. Cells of which area have true unipolar neurons? A. Motor nucleus of V (trigeminal) B. Mesencephalic nucleus of V C. Sensory nucleus of V D. Red nucleus E. Locus ceruleus 332. The spinal border cells found in the ventral horns at L1–S2 give rise to A. first-order neurons of the ventral spinocerebellar tract. B. second-order neurons of the ventral spinocerebellar tract. C. first-order neurons of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. D. second-order neurons of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. E. None of the above 333. Chromophobe pituitary cells A. represent corticotrope cells. B. stain purple after periodic acid-Schiff(PAS) staining. C. represent somatotrope cells. D. lack cytoplasmic granules. E. can only be acidophils or basophils. 334. Both retrospective and prospective studies of anterior temporal lobectomy have shown that seizure control in medial temporal lobe epilepsy is related to the extent of A. anterior resection. B. posterior resection. C. lateral resection. D. medial resection. E. None of the above 335. Overall, the most common type of chorea is A. Huntington’s chorea. B. chorea gravidarum. C. senile chorea. D. hysterical chorea. E. Sydenham’s chorea. 336. Side effects of the medication shown here include A. myopathy. B. susceptibility to infection. C. posterior subcapsular cataracts. D. All of the above E. None of the above 337. Which of the following is true concerning relationships to the flexor retinaculum? A. The ulnar artery is superficial to it. B. The median nerve is deep to it. C. The ulnar nerve is superficial to it. D. All of the above E. None of the above 338. If a patient has already had a thalamotomy for tremor and now seeks treatment for tremor of the other hand, which deep brain stimulation (DBS) procedure should be done? A. Thalamotomy B. Ventralis intermedius stimulation C. GPi stimulation D. Any of the above E. None of the above 339. Temozolomide is a chemotherapeutic agent approved for use in treating A. meningioma. B. arteriovenous malformations. C. anaplastic astrocytoma. D. ependymomas. E. None of the above 340. The H-reflex is most useful to assess A. polyneuropathy. B. cervical radiculopathy. C. myopathy. D. S1 radiculopathy. E. median nerve compression. 341. Which of the following is NOT a normal phenomenon in the aging neuron? A. Lipofuscin accumulation B. Lewy bodies C. Marinesco bodies D. Alzheimer changes E. Colloid inclusions 342. A patient is asked to close his eyes during the neurological exam and the doctor places a key in the patient’s hand. The ability of the patient to tell what the object is depends on the integrity of which pathway? A. Dorsal column B. Spinospinal C. Ventral spinocerebellar D. Dorsal spinocerebellar E. Spinothalamic 343. All of the following are true regarding intracranial pressure monitoring EXCEPT: A. Pressure gradients between left and right sides of the brain and supra- and infratentorial compartments may be present. B. The incidence of hemorrhage after insertion is about 1%. C. Irrigating the tubing decreases the contamination rate of ventricular catheters. D. Decreased intracranial compliance is suggested when the “b wavelet” is greater than the “a wavelet.” E. There is no clear consensus as to whether to use prophylactic antibiotics. 344. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the corticospinal tract? A. In the pyramidal decussation, arm areas of cortex cross rostral to those that arise from leg areas. B. It receives contribution from somatomotor cortex, prefrontal regions, and parietal areas. C. Glutamate is present in cortical efferent fibers that project to the spinal cord. D. Leg fibers are lateral to arm fibers at most levels of this particular tract. E. Area 4 and postcentral gyrus fibers terminate in the same spinal cord lamina. 345. The middle cerebral artery supplies all of the following structures EXCEPT: A. The inferior parietal lobule B. Broca’s area C. Wernicke’s area D. The primary auditory cortex E. The paracentral lobule 346. During a transcallosal approach to a tumor, the risk of left hemialexia is minimized by preserving A. the genu of the corpus callosum. B. the cingulate gyrus. C. the pericallosal artery. D. the splenium of the corpus callosum. E. None of the above 347. The clivoaxial angle is normally about A. 13 degrees. B. 30 degrees. C. 100 degrees. D. 130 degrees. E. 180 degrees. 348. The sensorimotor region is located in which part of the GPi? A. Anteromedial B. Anterolateral C. Posteromedial D. Posterolateral E. None of the above 349. This lesion is resected from the lumbar spine (see intraoperative picture). Which of the following statements is FALSE? A. The majority of these lesions arise from a ventral nerve root. B. 10 to 15% extend through the dural root sleeve. C. The fourth through sixth decades represent the peak incidence of occurrence. D. These masses are typically described as smooth globoid and do not produce enlargement of the nerve. E. They are suspended eccentrically from the nerve root with a discrete attachment. 350. Which of the following is particular to type I muscle fibers? A. Anaerobic B. Fast C. Stain dark with ATPase at pH 9.4 D. Are found in red muscle E. Have few mitochondria 351. Which of the following pathological inclusions is intranuclear? A. Pick bodies B. Lewy bodies C. Cowdry type B bodies D. Bunina bodies E. Lafora bodies 352. All of the following tracts decussate EXCEPT: A. Lateral spinothalamic B. Ventral spinocerebellar C. Ventral corticospinal D. Dorsal spinocerebellar E. Ventral spinothalamic 353. Which of the following is most accurate of Ménière’s disease? A. Nystagmus is horizontal and ipsilateral to the affected side. B. Nystagmus is vertical. C. Falling and past-pointing are contralateral. D. Nystagmus is contralateral to the affected side. E. None of the above 354. Which of the following thalamic nuclei has reciprocal connections with the inferior parietal lobule? A. Pulvinar B. Anterior nucleus C. Centromedian nucleus D. VA nucleus E. VL nucleus 355. Visual–verbal disconnection syndrome is most likely to be seen with sectioning of the A. anterior commissure. B. hippocampal commissure. C. body of the corpus callosum. D. genu of the corpus callosum. E. splenium of the corpus callosum. 356. Pineal tumors usually displace the precentral cerebellar vein A. anterosuperiorly. B. posterosuperiorly. C. anteroinferiorly. D. posteroinferiorly. E. None of the above 357. Which of the following structures can be found two-thirds of the way from the vomer to the foramen magnum? A. Occipital condyle B. Inion C. Pharyngeal tubercle D. Pituitary gland E. Sphenoid sinus 358. Which of the following arteries supply the choroid plexus? A. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery B. Posterior cerebral artery C. Anterior choroidal artery D. All of the above E. None of the above 359. Which one of the following neurological manifestations is NOT associated with hepatic encephalopathy? A. Asterixis B. Slowing of the EEG waves C. Increased levels of ammonia D. Increased levels of GABA neurotransmitter E. Decreased levels of glutamate 360. Which statement regarding hepatolenticular degeneration disease is FALSE? A. Serum ceruloplasmin is low. B. Urinary copper is increased. C. The gene locus is on chromosome 13. D. Inheritance is autosomal dominant. E. Early in the course of the disease, liver biopsy shows a high copper content. 361. Which of the following is FALSE regarding Bergmann glia? A. They serve as guides for migrating granular cell neurons during development. B. They have cell bodies located in the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex. C. They undergo reactive gliosis adjacent to infarcts. D. They extend long cytoplasmic processes through the molecular layer to the subpial surface. E. They are inconspicuous until stimulated by local damage. 362. A 62-year-old man presents with cauda equina syndrome from a herniated disk. All of the following statements are true EXCEPT: A. The signs are frequently unilateral. B. It classically involves spinal roots inferior to L3. C. It may result in profound motor defects. D. It may result in urinary or fecal incontinence. E. It usually results in a Babinski sign. 363. The vestibule contains A. the kinetic labyrinth. B. the ampullae. C. the static labyrinth. D. the cochlear duct. E. None of the above 364. The ipsilateral central tegmental tract gives projections to which nucleus of the thalamus? A. VA B. VL C. VPL D. VPM E. None of the above 365. A meningioma located at the lateral tentorial notch with major extension infratentorially would be best managed with A. a lateral suboccipital retrosigmoid approach. B. a combined subtemporal presigmoid approach. C. an infratentorial supracerebellar approach. D. a suboccipital transtentorial approach. E. a pterional approach 366. Pineal calcifications are considered abnormal if encountered in patients younger than A. 6 years. B. 12 years. C. 18 years. D. 26 years. E. 30 years. 367. Which of the following ligaments is found between the anterior tubercle of the atlas and the dens? A. Anterior longitudinal ligament B. Posterior longitudinal ligament C. Alar ligament D. Transverse ligament E. None of the above 368. The most frequent site for a subependymoma is the A. third ventricle. B. fourth ventricle. C. left lateral ventricle. D. right lateral ventricle. E. septum pellucidum. 369. The lamina terminalis is continuous with A. the anterior commissure. B. the fornix. C. the rostrum of the corpus callosum. D. the mammillary body. E. None of the above 370. Damage to Brodmann area 8 on the right results in A. both eyes being deviated to the right at rest. B. both eyes being deviated to the left at rest. C. the right eye being “down-and-out.” D. the patient being unable to look upward. E. both eyes being deviated upward. 371. Immunoreactivity to transthyretin and S-100 would most likely be seen in A. oligodendroglioma. B. low-grade astrocytoma. C. pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. D. choroid plexus papilloma. E. schwannoma. 372. Electroencephalographic (EG) activity becomes isoelectric at a cerebral blood flow of A. 7 mL/100 g/min. B. 16 mL/100 g/min. C. 30 mL/100 g/min. D. 35 mL/100 g/min. E. 45 mL/100 g/min. 373. All of the following are true regarding the lateral vestibulospinal tract EXCEPT: A. It arises from the ipsilateral Deiter’s nucleus. B. It is located in the lateral pontine tegmentum. C. It crosses the midline with MLF fibers. D. It facilitates extensor muscle tone in the antigravity muscles. E. It is found at all spinal cord levels. 374. Lesions of this thalamic nucleus are found in patients with the Korsakoff amnestic state. A. Anterior nucleus B. Centromedian nucleus C. Pulvinar D. VA E. Mediodorsal nucleus 375. Before one transects the tentorium, which cranial nerve must be identified? A. III B. IV C. V D. VI E. VII 376. All the following statements regarding germ cell tumors are true EXCEPT: A. They are the most common parapineal neoplasm. B. They occur predominantly in males. C. They commonly occur at around age 30 and above. D. They are five to ten times more likely in Japan. E. They are infiltrated by T cell lymphocytes. 377. All of the following regarding CNS sarcoid are true EXCEPT: A. It is sensitive to steroids. B. It may mimic multiple sclerosis. C. It can involve cranial nerves. D. It is characterized pathologically by caseating granulomas. E. Leptomeningeal involvement is common. 378. Which of the following is the most frequent brain tumor in the first year of life? A. Choroid plexus tumor B. Gliosarcoma C. Cystic astrocytoma D. Oligodendroglioma E. Glioblastoma multiforme 379. A “square” anterior cerebral artery (ACA) shift on a cerebral angiogram suggests that there may be a mass in which area? A. Frontal lobe B. Temporal lobe C. Parietal lobe D. Occipital lobe E. Basal ganglia 380. The motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is located in the A. upper midbrain. B. lower midbrain. C. upper pons. D. middle pons. E. lower pons. 381. Circumventricular organs include all of the following EXCEPT: A. Obex B. Subcommissural organ C. Median eminence D. Organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis E. Area postrema 382. Hyponatremia may be a direct cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) from rupture of which of the following aneurysms? A. Pericallosal B. Anterior communicating C. Posterior communicating D. Middle cerebral E. Superior hypophyseal 383. All of the following are true statements of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) EXCEPT: A. It is a branch of the vertebral artery. B. It supplies the vestibular nuclei in the medulla. C. It supplies the medial lemniscus in the medulla. D. It supplies the inferior cerebellar peduncle. E. It supplies the lateral spinothalamic tract. 384. The optic disc A. is located lateral to the fovea. B. contains myelinated axons from the retinal ganglion cell layer of the retina. C. contains only cones. D. All of the above E. None of the above 385. Which muscle is the border of the superior and inferior suboccipital triangles? A. Rectus capitis posterior major B. Superior obliquus capitis C. Inferior obliquus capitis D. Longissimus capitis E. None of the above 386. The key to translabyrinthine dissection is anatomical identification of A. the trigeminal nerve. B. the abducens nerve. C. the facial nerve. D. All of the above E. None of the above 387. All of the following are true of thoracic spine meningiomas EXCEPT: A. The great majority of spinal meningiomas occur in females. B. The most common presenting symptom is pain. C. Plain film calcification is often seen. D. Inversion recovery sequences and use of gadolinium increase detection sensitivity. E. Calcospheres may be seen. 388. Damage to the posterior cord of the brachial plexus results in paralysis of all of the following muscles EXCEPT: A. Teres minor B. Teres major C. Latissimus dorsi D. Subscapularis E. Infraspinatus 389. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding radiation injury after stereotactic radiosurgery? A. Time of development is directly related to the rate of turnover of the cells. B. Cell loss after radiation occurs in connection with the cell division. C. Time of development is directly dependent on the radiation dose. D. Slowly proliferating tissue like CNS may take years to show the effects. E. All of the above statements are true. 390. Inherited mitochondrial disorders include all of the following EXCEPT: A. Leigh’s disease B. MERFF C. MELAS D. Kearns–Sayre’s syndrome E. Kawasaki’s disease 391. Chromosomal alterations that are known to occur in tumors include all of the following EXCEPT: A. Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at 1p and 19q in oligodendrogliomas B. LOH at 22 in ependymomas C. LOH at 17 in astrocytomas D. Monosomy of 22 in ATRT E. Amplification of N-myc in glioblastoma 392. During routine preoperative screening for meningioma excision, the single greatest contraindication to surgery would be A. myocardial infarction within the last 6 months. B. age greater than 75. C. more than five ventricular ectopic beats per minute. D. smoking more than one pack of cigarettes a day. E. being hepatitis C positive. 393. All of the following tracts pass through the inferior cerebellar peduncle EXCEPT: A. Dorsal spinocerebellar B. Cuneocerebellar C. Fastigiovestibular D. Olivocerebellar E. Vestibulocerebellar 394. A lower altitudinal hemianopia is the results of A. unilateral destruction of the cuneus. B. bilateral destruction of both cunei. C. unilateral destruction of the lingual gyrus. D. bilateral destruction of both lingual gyri. E. None of the above 395. During clipping of the unruptured aneurysm shown here, what is the best maneuver to minimize rupture? A. Temporary clipping of the carotid in the neck B. Lumbar drainage C. Preoperative use of steroids D. Keeping the patient intubated until surgery E. Minimal retraction 396. The reasons for monitoring wave 5 during acoustic neuroma surgery include which of the following? A. It is an indication of the activity peripheral to the tumor. B. It is easier to detect than the other waves. C. Wave 5 is an accurate predictor of hearing postoperatively regardless of N1. D. All of the above E. None of the above 397. All of the following are true of multiple sclerosis EXCEPT: A. Axons are intact. B. Unidentified bright objects (UBOs) may be seen on MRI. C. Active lesions show contrast enhancement. D. Initial symptoms are referable to motor function. E. About 10 percent have a positive family history. 398. All of the following are structures of the circuit of Papez EXCEPT: A. Anterior thalamus B. Cingulated gyrus C. Fornix D. Hippocampus E. Dorsomedial thalamus 399. Leigh’s disease is a disease of the mitochondria that has an autosomal recessive inheritance. Which one of the following is not a manifestation of this metabolic disease? A. White matter degeneration affecting mostly subcortical U-fibers B. Bilateral spongiform degeneration of the thalamus and basal ganglia C. Degeneration of the peripheral nerves D. Degeneration of the spinal cord E. Degeneration of the brainstem 400. A nonfluent, expressive aphasia can result from damage to A. Brodmann area 40. B. Brodmann area 41. C. Brodmann area 42. D. Brodmann area 43. E. Brodmann area 44. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 08, 2020
Number of pages
26
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 08, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
137








.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)