Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics. Midterm Exam. 50 Q&A | Ryerson University (All)
ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics. Midterm Exam. 50 Q&A | Ryerson University
Document Content and Description Below
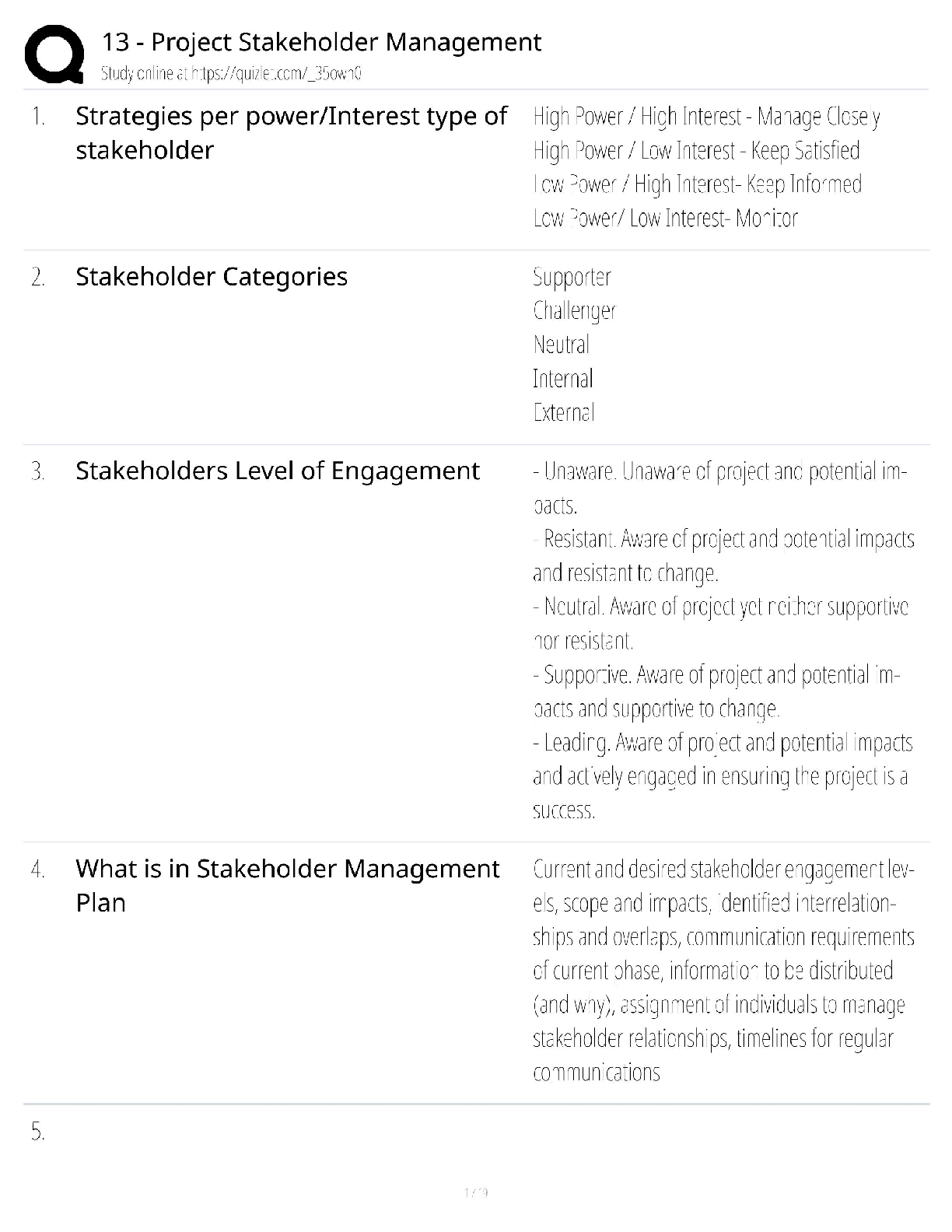
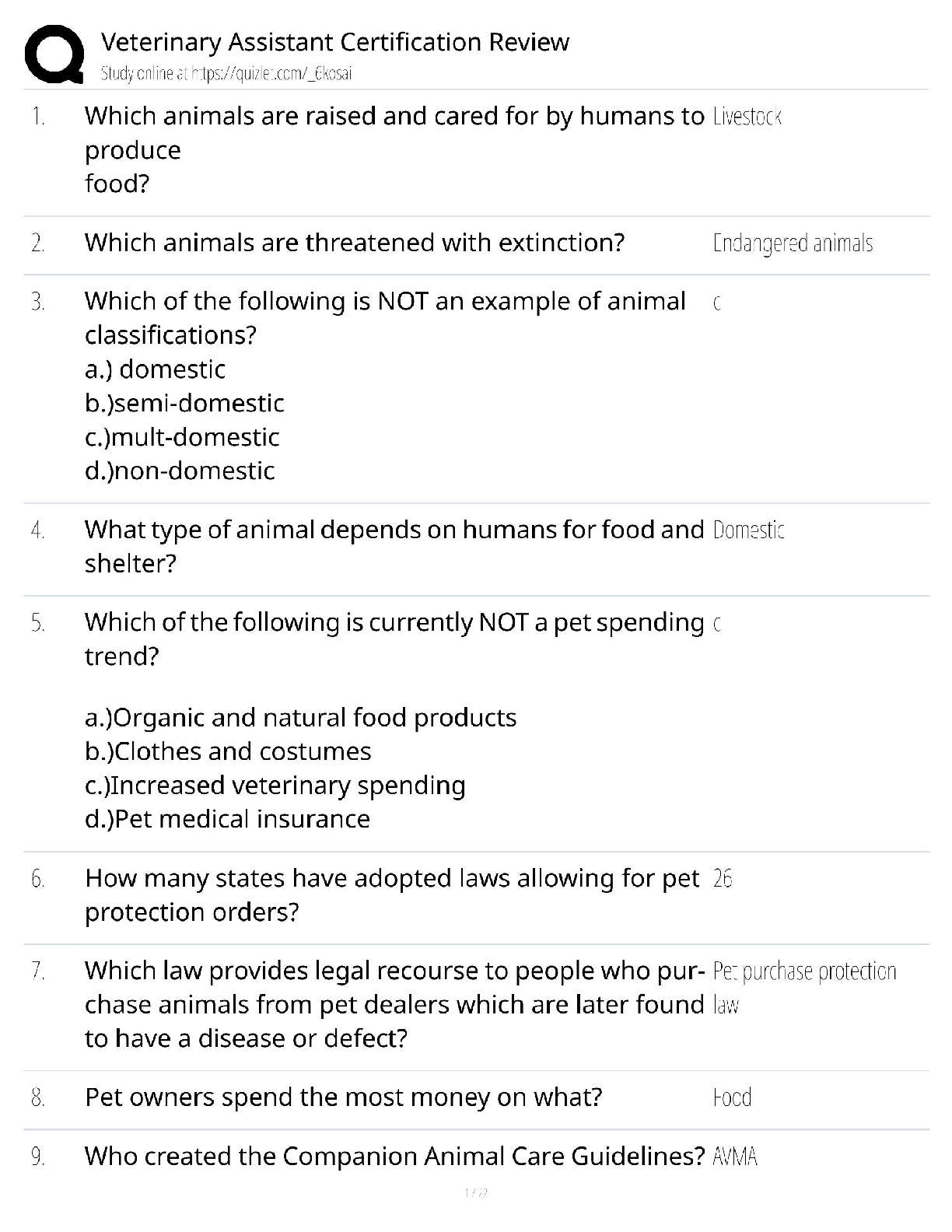
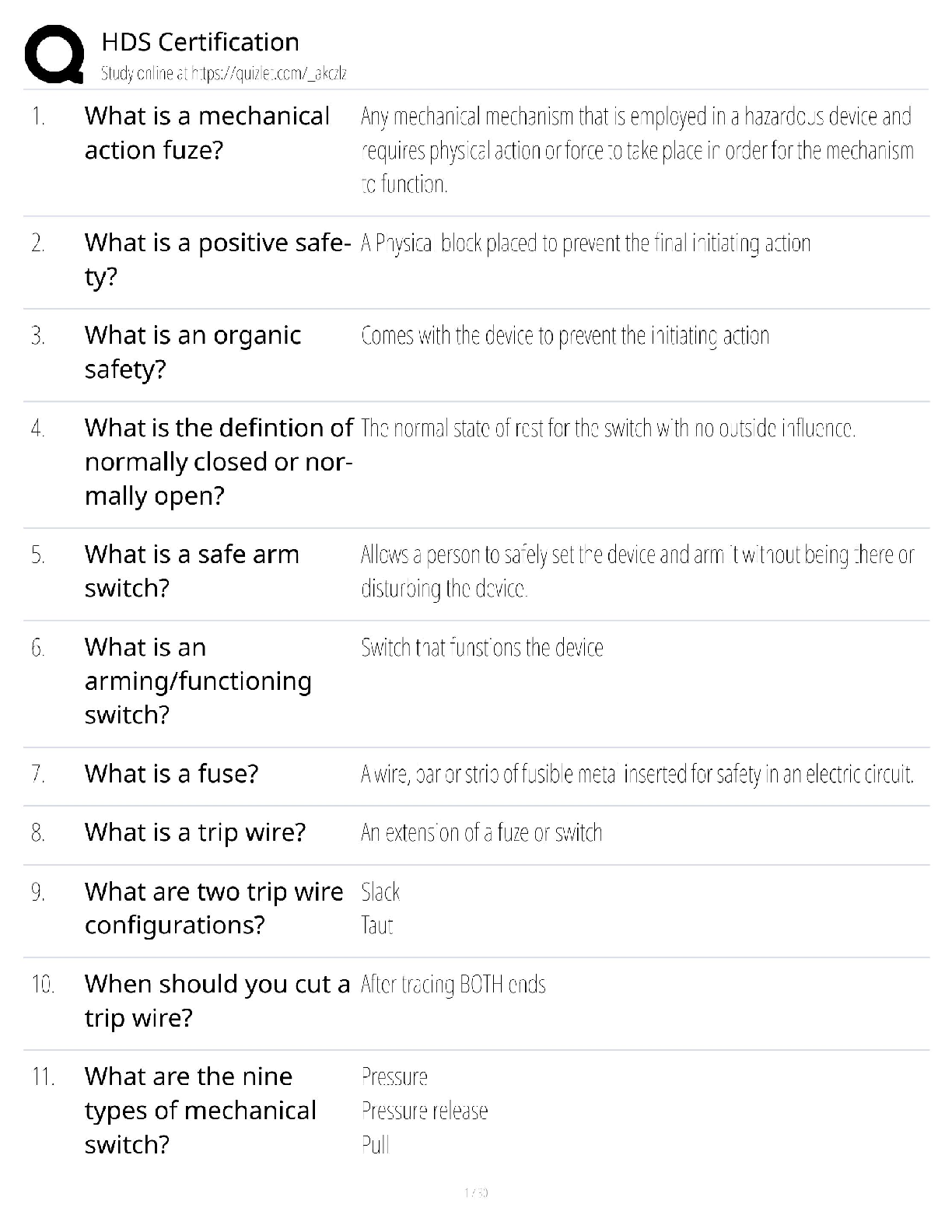
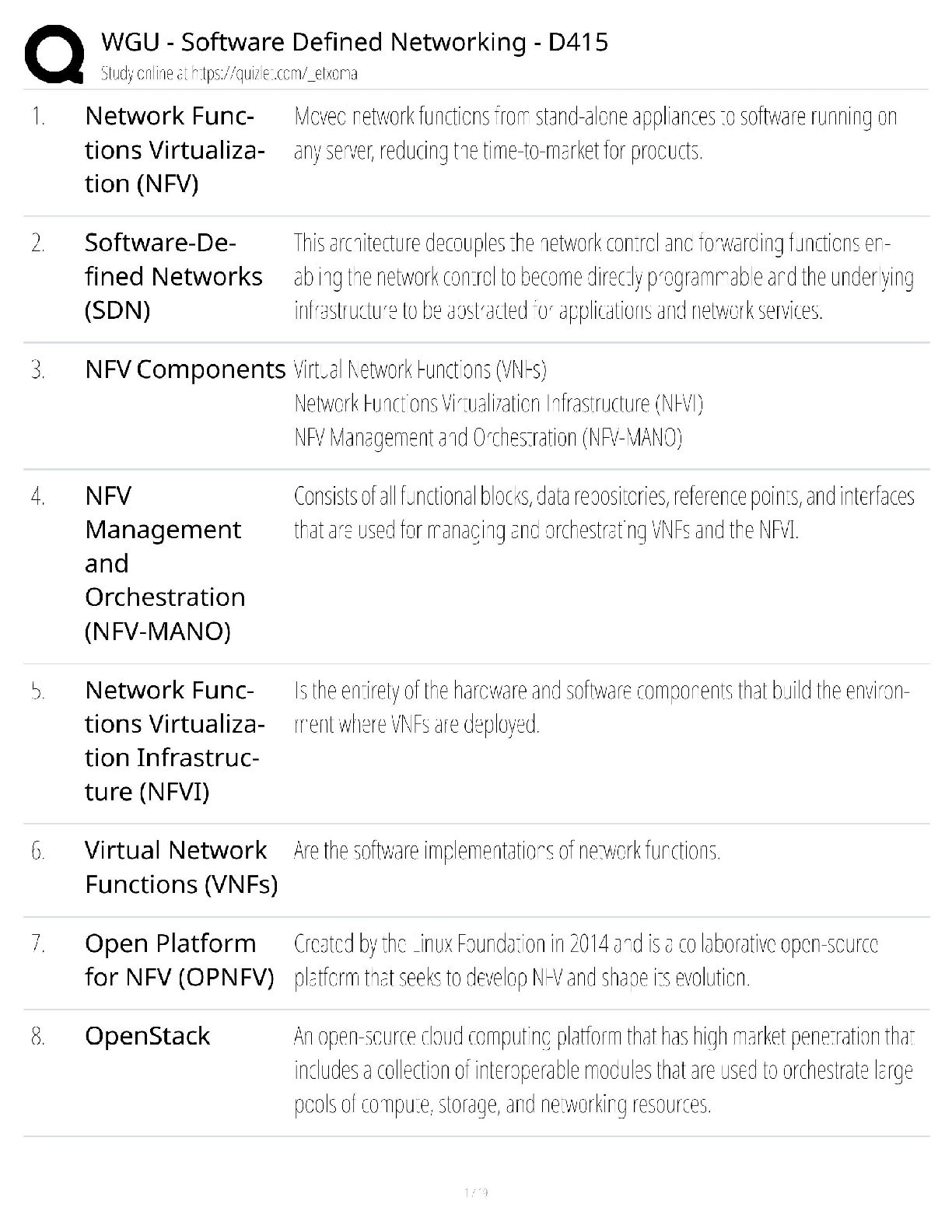
Ryerson University Department of Economics ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Midterm Exam Name__________________________ Student #________________________________ Select the BEST answer and ... record it both on the test and the scanner sheet. 1. Real GDP was $9,950 billion in Year 1 and $10,270 billion in Year 2. The population rose from 270 million in Year 1 to 275 million in Year 2. What was the approximate increase in real GDP per capita rate from Year 1 to Year 2? A. 4.2 percent B. 2.1 percent C. 3.3 percent D. 1.3 percent. 2. Working as an elevator operator used to be a common job in the workforce four decades ago, but today few jobs remain. The unemployment created by introduction of automatic elevators would be considered: A. structural. B. cyclical. C. wait. D. frictional. 3. If the multiplier in an economy is 5, a $20 billion increase in net exports will: A. decrease GDP by $100 billion. B. increase GDP by $100 billion. C. increase GDP by $20 billion. D. reduce GDP by $20 billion.4. Knowing that in the real world, the demand for goods and services could change unexpectedly, firms would attempt to deal with it by: A. producing different levels of goods and services according to the changes in demand. B. closing down the production in the short-run with the hope that the situation would change in the future. C. switching to the production of another product in the short-run. D. maintaining an inventory. 5. Because prices change too slowly in the short-run and as a result, they do not quickly equalize the quantity demanded and quantity supplied of goods and services, the short-run response of the economy to a demand shock is through: A. changes in output but not in the employment. B. changes in employment but not in output. C. changes in prices rather than through changes in employment. D. changes in output and employment levels rather than through changes in prices. 6. If Smith's disposable income increases from $1,200 to $1,700 and her level of saving increases from minus $100 to a plus $100, it may be concluded that her marginal propensity to: A. consume is three-fifths. B. consume is one-half. C. consume is one-sixth. D. save is three-fifths. 7. If government expenditures increase by $20 billion and equilibrium GDP increases by $50 billion as a result, we can conclude that: A. the MPS for this economy is .6. B. the MPC for this economy is .6. C. the expenditures multiplier is 2. D. inflation is occurring. 8. Which would be considered an investment according to economists? A. the purchase of a laptop by a university student to prepare her class projects B. the construction of a new factory by Intel C. the purchase of government bonds by the nation's central bank D. the purchase of shares of stock by Manulife, a mutual fund company.9. Real GDP was $9,950 billion in Year 1 and $10,270 billion in Year 2. What was the approximate rate of economic growth from Year 1 to Year 2? A. 1.6 percent B. 4.3 percent C. 2.4 percent D. 3.2 percent. 10. If a nation's real GDP is growing by 3 percent per year, its real domestic output will double in approximately: A. 29 years. B. 42 years. C. 23 years. D. 21 years. 11. To be officially unemployed a person must be in the labour force and must: A. have just lost a job. B. be 21 years of age or older. C. be waiting to be called back from a layoff. D. be actively seeking work. 12. The multiplier effect means that: A. a small change in consumption demand can cause a much larger increase in investment. B. a small decline in the MPC can cause equilibrium GDP to rise by several times that amount. C. consumption is typically several times as large as saving. D. a small increase in investment can cause national income to change by a larger amount. 13. An example of a final good in national income accounts would be new: A. chemicals purchased by Green Grass Lawn Care. B. trees purchased by Wendy Lee's Garden Center. C. lawn mowers purchased by Cut-rite Mowers. D. flowers purchased by homeowner Lenny Davis. 14. Setup Corporation buys $100,000 of sand, rock, and cement to produce ready-mix concrete. It sells 10,000 cubic yards of concrete at $30 a cubic yard. The value added by Setup Corporation is: A. $200,000 B. $300,000 C. zero dollars. D. $100,000.15. Refer to the above information. If government now spends $80 billion at each level of GDP and taxes remain at zero, the equilibrium GDP: A. will rise to $700. B. may either rise or fall. C. will rise to $500. D. will rise to $600. 16. Anne Kasperson works in her own home as a full-time caretaker and homemaker. Officially, she is: A. not in the labour force. B. in the labour force. C. employed. D. unemployed. 17. A nation's capital stock was valued at $300 billion at the start of the year and $350 billion at the end. Consumption of private fixed capital in the year was $25 billion. Assuming stable prices, gross investment was: A. $90 billion. B. $75 billion. C. $25 billion. D. $50 billion. 18. The following are national income account data for a hypothetical economy in billions of dollars: government purchases ($940); personal consumption expenditures ($4,920); imports ($170); exports ($133); gross investment ($640). What is GDP in this economy? A. $6,633 billion B. $6,500 billion C. $6,537 billion D. $6,463 billion.19. GDP data are criticized as being inaccurate measures of economic welfare because: A. they do not take into account changes in the amount of leisure. B. they do not take into account changes in product quality. C. they do not take into account the adverse effects of economic activity on the environment. D. of all of the above considerations. 20. When the public sector is added to the aggregate expenditures model: A. we add a new leakage in the form of taxes and a new injection in the form of government spending. B. the equilibrium condition becomes G + T = S + Ig + X. C. the equilibrium condition becomes Ca + Ig + Xn + G + T = GDP. D. the equilibrium condition becomes G + S = T + Ig + X. 21. ________ shocks are unexpected changes in the demand for goods and services While, _________ shocks are unexpected changes in the supply of goods and services. A. Demand; supply. B. Investment; savings. C. Internal; external. D. Supply; demand. 22. In which of the following industries or sectors of the economy is output likely to be most strongly affected by the business cycle? A. durable goods (machinery, equipment, etc.) B. textile products (clothing) C. military goods D. agricultural commodities (wheat, corn, etc.) 23. In response to an unexpected change in demand, if the prices are free to adjust quickly: A. a firm would not be able to change its employment accordingly. B. a firm would experience a decline in its output and employment. C. a firm could always operate at its optimal output level. D. a firm would not be able to adjust its output according to the plan. 24. There are several institutional structures that promote and sustain economic growth. These factors include: A. efficient financial institutions, education, free trade, patent and copyrights, property rights and competitive market system. B. restricted trade, property rights and, monopoly power. C. monopoly power, education and strong market incentives. D. both A and B. 25.Refer to the above diagrams, one can conclude that if expectations are always fulfilled, Fancy Auto Company: A. has to adjust the optimal output level but not the employment. B. will never have to adjust the optimal output and employment levels accordingly. C. has to adjust the employment level but not the optimal output. D. has to adjust both optimal output level and employment accordingly. 26. If the natural rate of unemployment is 6 percent and the actual unemployment rate is 9 percent, then Okun's law indicates that the GDP gap is: A. 3 percent. B. 4 percent. C. 6 percent. D. 2 percent. 27. In an economy nominal GDP is $4,000 billion. The actual unemployment rate is 8 percent and the natural rate of unemployment is 6 percent. According to Okun's law there will be: A. $80 billion lost in potential output. B. $300 billion lost in potential output. C. $100 billion lost in potential output. D. $160 billion lost in potential output. 28. Money spent on the purchase of a new house is included in the GDP as a part of: A. personal saving. B. personal consumption expenditures. C. the consumption of private fixed capital. D. investment.29. Assuming inflexible prices, if the demand for many goods and services falls across the entire economy and for an extended period of time: A. many firms will face a constant reduction in their inventories and will be forced to hire more workers. B. many firms will face a constant reduction in their inventories. C. many firms will face with an inventory pile up and will be forced to cut production. D. many firms will face with an inventory pile up and will be forced to hire more workers. 30. Assume an economy which is producing only one product. Output and price data for a threeyear period are as follows. Refer to the above data. If year 2 is chosen as the base year, the price index for year one is: A. 100 B. 20 C. 80 D. 120. 31. At the point where the consumption schedule intersects the 45-degree line: A. the economy is in equilibrium. B. the APC is 1.00. C. saving is equal to consumption. D. the MPC is 1.00. 32. The financial institutions play an important role in transferring the savings of the individuals to the investments by businesses. Which of the following correctly states this transfer? A. banks collect the savings and invest it in the stock market. B. financial institutions do not have a major role in this process. C. banks collect the savings and lend the funds to the government who in turn redistribute it through different kinds of subsidies. D. banks collect the savings, rewarding the savings by interest and dividend payments and, lend the funds to businesses who in turn buy equipment, factories and capital goods. 33. The higher is the current level of saving: A. the higher is the current level of investment and higher the future level of consumption. B. the lower is the current level of investment and lower the future level of consumption. C. the lower is the current level of investment and higher the future level of consumption. D. the higher is the current level of investment and lower the future level of consumption.34. Which is a demand factor in economic growth? A. an increase in total spending in the economy B. more human and natural resources C. an increase in the economy's stock of capital goods D. technological progress and innovation. 35. The simple multiplier is: A. 1/MPC. B. 1/MPS. C. 1/APS. D. 1/APC. 36. Which is best considered an efficiency factor in economic growth? A. the quality of human resources B. the full employment of resources C. the quantity of human resources D. the quantity of natural resources. 37. If the real interest rate in the economy is i and the expected rate of return from additional investment is r, then more investment will be forthcoming when: A. i is greater than r. B. r falls. C. r is greater than i. D. i rises. 38. he investment-demand curve will shift to the right as the result of: A. the availability of excess productive capacity. B. an increase in the real interest rate. C. an increase in business taxes. D. businesses becoming more optimistic with respect to future business conditions. 39. Economic growth is best defined as an increase in: A. total consumption expenditures. B. wealth in the economy. C. either real GDP or real GDP per capita. D. nominal GDP.40. Refer to the information below. GDP is: All figures are in billions of dollars. A. $467 B. $422 C. $417 D. $402. 41. Real GDP was $4,719 billion in Year 1 and $4,848 billion in Year 2. In contrast, real GDP per capita in Year 1 was $19,261, but in Year 2 it was only $19,162. Why did one measure increase while the other measure decreased? A. Inflation occurred during this period; therefore the two measures are not comparable. B. Real GDP per capita measures changes in labour productivity that are not captured by a simple measure like real GDP. C. Real GDP indicates the level of industrial production and provides a measure of the economic strength of the nation; it is the only valid measure of economic growth. D. Population increased during this time period so real GDP per capita data reflect this change. 42. The relationship between the real interest rate and investment is shown by the: A. consumption of fixed capital schedule. B. aggregate supply curve. C. investment-demand schedule. D. saving schedule.43. Refer to the above diagram. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to: A. AE/0E. B. CF/CD. C. CD/CF. D. CB/AB. 44. The table below indicates the price and output data over a five year period for an economy that produces only one good. Refer to the above data. If year 2 is the base year, real GDP in year 5 is: A. $60 B. $90 C. $120 D. $30.45. Answer the question(s) based on the following data, using year 1 as the base year. All dollars are in billions. Refer to the above data. From year 1 to year 4, prices rose by: A. 12 percent. B. 4 percent. C. 8 percent. D. 10 percent. 46. If the marginal propensity to consume is .80 and both taxes and government purchases increase by $50 billion, GDP will: A. increase by $10 billion. B. increase by $50 billion. C. decrease by $50 billion. D. decrease by $10 billion. 47. The investment-demand curve will shift to the right as a result of: A. technological progress. B. an increase in the excess productive capacity available in industry. C. an increase in business taxes. D. an increase in the acquisition and maintenance cost of capital goods. 49. The following are national income account data for a hypothetical economy in billions of dollars: government purchases ($1,050); personal consumption expenditures ($4,800); imports ($370); exports ($240); gross investment ($1,130). Personal consumption expenditures are approximately what percentage of this economy? A. 60 percent B. 70 percent C. 75 percent D. 65 percent49. Waiting for employment and "searching for employment" are both types of: A. hidden unemployment. B. structural unemployment. C. cyclical unemployment. D. frictional unemployment. 50. A trough in the business cycle occurs when: A. cyclical unemployment is at a minimum point. B. the natural rate of unemployment is at a minimum point. C. structural and frictional unemployment are at their highest levels. D. employment and output reach their lowest levels. 51. Refer to the above diagram. If net exports are X n2, the GDP in the open economy will exceed GDP in the closed economy by: A. FG. B. AB. C. AD. D. BD. 52. If the dollar appreciates relative to foreign currencies, we would expect: A. a country's exports and imports to both fall. B. the multiplier to decrease. C. a country's net exports to rise. D. a country's net exports to fall.53. If Ben's MPC is .80, this means that he will: A. spend eight-tenths of any increase in his disposable income. B. break even when his disposable income is $8,000. C. save eight-tenths of any level of disposable income. D. spend eight-tenths of any level of disposable income. 54. Gross domestic product (GDP) is equal to personal consumption expenditures: A. plus gross investment, plus government spending, and minus net exports. B. plus gross investment, plus government spending, and plus net exports. C. minus gross investment, plus government spending, and plus net exports. D. plus gross investment, minus government spending, and plus net exports. 55. Refer to the above graph. If the production possibilities curve for an economy is at CD but the economy is operating at point X, the reasons are most likely to be: A. lack of full employment and inefficient allocation of resources. B. technological progress and industrial change. C. improvement in labour productivity and the number of worker-hours. D. increases in the quantity and the quality of resources. 56. Assume that the size of the underground economy increases both absolutely and relatively over time. As a result: A. GDP will tend to increasingly overstate the level of output through time. B. real GDP will rise more rapidly than nominal GDP. C. the accuracy of GDP will be unaffected through time. D. GDP will tend to increasingly understate the level of output through time.57. If government increases its purchases by $15 billion and the MPC is 2/3, then we would expect the equilibrium GDP to: A. decrease by $35 billion. B. increase by $45 billion. C. increase by $50 billion. D. increase by $30 billion. 58. Assume that an economy has 1500 workers, each working 2000 hours per year. If the average real output per worker-hour is $20, then total output or real GDP will be: A. $3 million. B. $60 million. C. $45 million. D. $30 million. 59. The labour force includes: A. permanent employees, but excludes temporary employees. B. employed workers and persons who are officially unemployed. C. employed workers, but excludes persons who are officially unemployed. D. full-time workers, but excludes part-time workers. 60. What are the two prominent schools of thought in Macroeconomics: A. Classical and Communism B. Classical and Neo Classical C. Classical and Keynesian D. Keynesian and Neo Keynesian [Show More]
Last updated: 5 months ago
Preview 3 out of 14 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 04, 2022
Number of pages
14
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 04, 2022
Downloads
1
Views
259






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)