Study Guide for NUR 1025 Exam 1
1. Learning Domains and Examples
a. Cognitive
i. Increases a pts knowledge about a subject
ii. Using written material, lecture and discussion
appropriate
b. Psychomotor
i. Teaches n
...
Study Guide for NUR 1025 Exam 1
1. Learning Domains and Examples
a. Cognitive
i. Increases a pts knowledge about a subject
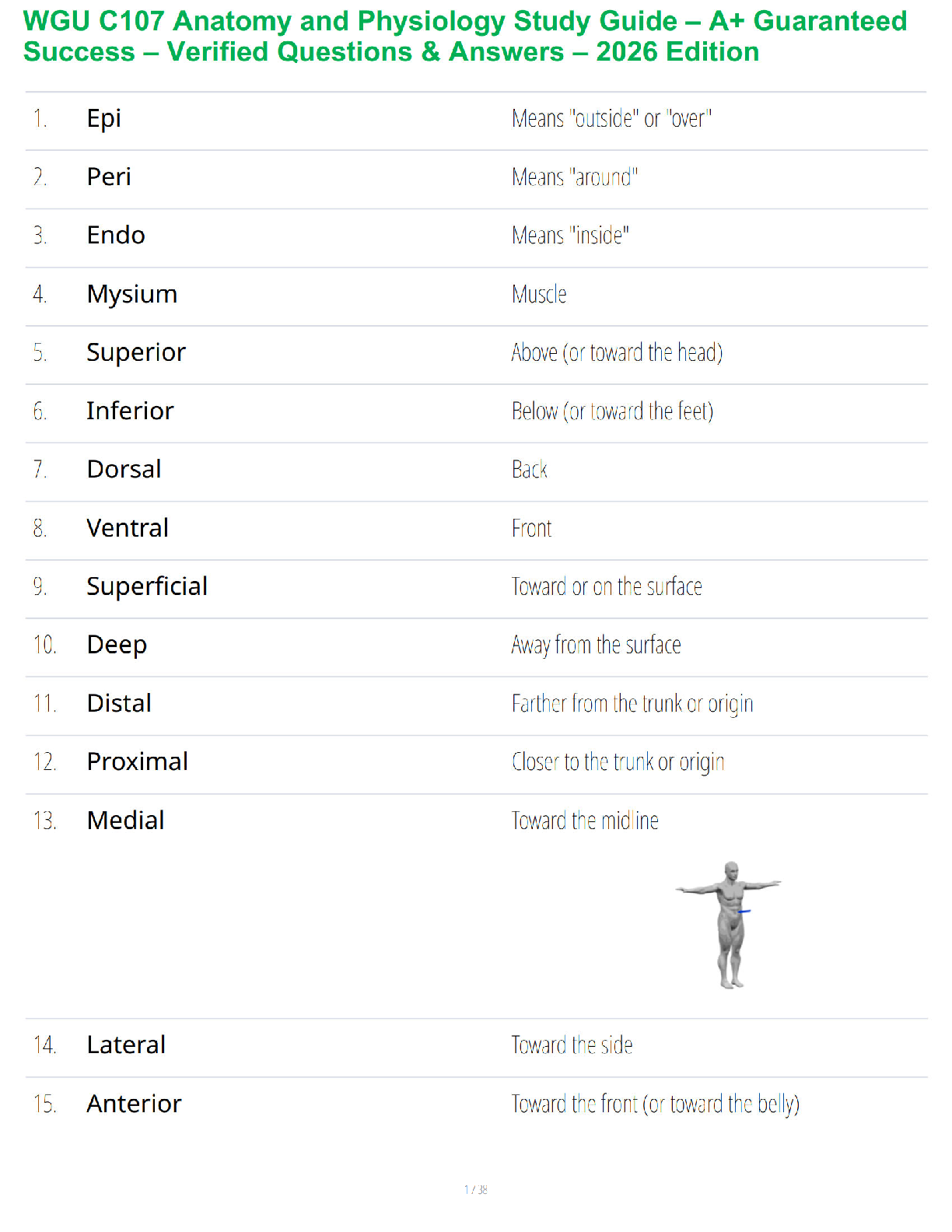
ii. Using written material, lecture and discussion
appropriate
b. Psychomotor
i. Teaches new skills to the patient
ii. Giving opportunities to touch & manipulate
equipment and practice skills
1. IE: learning to change a dressing over a wound
c. Affective
i. Education intended to change attitudes
1. IE viewing lifestyle changes for treating
coronary artery disease as a positive change vs
a burden
2. Teaching the Elderly
a. Elderly teaching should be tailored to each patient
b. Cognitive & Sensory alterations may require teaching
material to be changed
i. 81% of pts > 60 could not read or understand basic
medication labels
3. Determining patient goals
a. Incorporate patient values and beliefs
b. Primary caregivers should be actively involved in care
decisions
c. Use interpreters to facilitate inclusion of cultural beliefs and
values in care planning
d. Goals should be mutually agreed upon, prioritized to patient
needs
i. SMART: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic,
timed
e. Use Nursing Interventions Classification to help determine
goals
4. Types of families
a. Group of people who are related by
i. Heredity
ii. Marriage
iii. Living in the dame household
b. Consists of
i. Parent and children
ii. Blood relatives
c. Is who they say they are
d. Categories:
i. Nuclear Family
ii. Married Parent Family
iii. Extended Family
iv. Married blended family
v. Cohabiting parent families
vi. Single parent families
vii. No parent families
viii. Same sex families
5. Purpose of a family assessment
a. Used to measure family dynamics
i. use a model that promotes health vs an illness-care
model
ii. a high-risk family will have illness care needs that the
perinatal nurse can address while promoting the
child’s health
iii. Calgary Family Assessment Model:
1. 3 Major categories
2. structural, developmental and functional
assessments
3. focus is on interaction of individuals within the
family
b. Based on
i. the perspective of the nurse
1. personal and professional life experiences
ii. Interactions with interviewees
c. Assessment is not the truth
i. Is one perspective at one point in time
d. Used to
i. Ask family members questions to help determine or
gain an understanding of the family units with the
focus being on the interaction among the individuals
in the family
e. Determines family roles, typical family household &
structures, and dynamics in the family, especially
communication methods
f. Outlines patterns of daily living such as work and leisure
activities
g. Exposes health beliefs & practices related to disease
causation, treatment of illness, folk practices, and faith
healers
h. Outlines extended family kinship, social networks- friends,
neighbors, and significant others and their influence on
health and illness
i. Determines nutritional practices and how they relate to
cultural factors and health
6. Assessment of the structure of a family
a. Structure
i. Includes determining
1. the members of the family
2. The relationship among family members
3. Context of the family
ii. Ex questions:
1. Who is in the family
2. Does anyone else live with you?
3. Has anyone moved out recently?
4. Anyone who is family that doesn't live with you?
b. Development
i. More than concurrent development of individuals in
the family
ii. Family lifecycle and how the family grows and
changes together
c. Function
i. Addresses how individuals actually behave in relation
to each other
ii. 2 basic aspects
1. not used to define a family's emotional health
but is the family's judgement of whether they
are functioning well
2. If the family is having trouble coping with
instrumental issues, often expressive issues
exist.
3. However, the family can cope with instrumental
issues and still have expressive issues. Thus,
assessment of both is essential.
4. Instrumental
a. Routine activities of daily living
i. Eating, sleeping, laundry, etc
5. Expressive
a. Communication
b. Problem solving roles
c. Influence and power
d. Beliefs
iii. Ex questions:
1. Whose role is it to see that Granddad takes his
medicine?
2. Whose turn is it to bathe Granddad?
3. Why is Jimmy not helping to take care of
Granddad?
4. How can we get Jimmy to help with the
caretaking?
7. Negative/dysfunctional family dynamics and factors that
affect
a. Evaluation is based on changes necessary based on changes
observed in the dynamics of communication and
interactions of the family
b. Examples of factors that can affect family dynamics:
i. Cancer Diagnosis
ii. Intimate Partner Violence
iii. Death and Dying
iv. Child abuse
v. Codependency (r/t family member substance abuse)
vi. Interfering in-laws
vii. Marital infidelity
viii. Placing blame for birth of a preterm infant or for
death of a young child by SIDS
ix. Sibling rivalry
x. Adolescent pregnancy, SIDS
xi. Expanding family
xii. Caregiver role changes
xiii. Chronic illness
xiv. Marriage, divorce, & remarriage
xv. Traumatic injury/disability of a family member
xvi. Aging family members
xvii. End of life care
8. Anticipatory Guidance in Prenatal Care – Risk Related to
Behavior (drugs/smoking/alcohol)
a. Primary prevention
i. Early risk assessment and promotion of healthy
behaviors such as smoking cessation or reduction can
lead to better pregnancy outcomes
1. Smoking/second hand smoke is associated with
intrauterine growth restriction, increased
perinatal and infant morbidity and mortality
2. Increased risk of spontaneous abortion, ectopic
pregnancy, preterm birth, PROM, abruptio
placentae, placenta previa, and fetal death.
3. Decreases placental perfusion
4. Can cause low birth weight
5. Impairs fertility, lowers age of menopause
ii. Five A’s of Smoking Cessation:
1. Ask:
a. Questions assess length of time smoking,
how many smoked per day and how ready
client is to quit.
2. Advise:
a. Gives information about effects of
smoking on pregnancy and fetus as well
as household
3. Assess:
a. Support structure, reasons for
quitting/not quitting
4. Assist:
a. Give support, establish a goal to quit,
provide resources for quitting, education
about stress reduction, follow up care
5. Arrange Follow up:
a. Reassess smoking status around quit date,
all prenatal visits, positive reinforcement
and referrals if needed
iii. Alcohol is a teratogen and can lead to fetal alcohol
syndrome
1. Risks:
a. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
b. Increased perinatal & infant morbidity &
mortality
c. Neurologic developmental disabilities
d. Low birth weight
e. Behavioral problems, learning and
physical problems
f. Severe facial deformities
iv. 2
nd trimester pregnancy loss (12-20weeks gestation)
1. risk increased with alcohol and caffeine use
v. -use of illicit drugs, prescription drug abuse
increasing across all ages & socioeconomic groups
1. -addiction:
2. -biophsychosocial disease that can lead to:
a. -biogenetic predisposition
b. -lack of resilience to stressful life
experiences
c. -poor social support
3. -abuse interferes with optimal growth and
development, may lead to fetal addiction
4. -can lead to criminal charges and civil
commitment in some states
a. Marijuana risks:
i. -readily crosses placenta
ii. -increases CO levels in maternal
blood, decreasing fetal oxygen
supply
b. Cocaine:
i. Polydrug use
ii. Poor nutrition
iii. STIs, hepatitis B
iv. Poverty
v. Dysfunctional family
vi. Employment difficulties
vii. Stress/anger
viii. Cardiovascular stress, MI, stroke
ix. Liver disease
x. Seizures
xi. Increased risk of miscarriage,
preterm labor, Small gestational age
babies, abruption of placenta,
malformations or stillbirth
c. Opiate risks:
i. 6x higher risk of pregnancy
problems
ii. withdrawal symptoms:
1. fetal hyperactivity
2. preterm labor
3. fetal death
d. Methamphetamine:
i. Increased risk of STIs, pregnancy
ii. Cardiac problems, HTN, irregular
heartbeat
iii. Increased rate of pre-term birth,
Intrauterine growth restriction,
smaller head circumference
e. Phencyclidine (PCP)
i. Causes neurobehavioral effects to
the neonate
f. Hallucinogens have negative
neurobehavioral effects on fetus
9. Contraception – Risk, Benefits, Use
a. USES:
i. Intentional prevention of pregnancy
ii. Reduces risk of pregnancy
iii. reduction of STIs
iv. normalization of menstrual cycles
b. RISKS:
i. Does not always work
ii. Must be used properly
iii. Abstinence is only 100% effective method
iv. Some methods can cause amenorrhea, spotting,
increase risk of contracting HIV
v. Depo-Provera contraindicated for women over 175lbs
1. Antibiotics interfere
2. Does not provide STI protection
vi. IUD1. assess for copper allergy
2. not given to women who have never been
pregnant due to scar tissue formation
3. No STI protection
vii. Implant:
1. No STI protection
viii. Sponge must be left in for 6 hrs after intercourse
ix. Condoms can break, expire, slip off, or person could
have a latex allergy
x. Family Awareness Planning:
1. Only works for women with 26-32 day cycle
2. Woman must be aware of symptoms and track
symptoms
10. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) – Triggers/Signs and
Symptoms/
a. Assess for abuse beyond the actual partner.
i. Attempt to speak to pt alone
b. Provide phone numbers, organization names who can assist
c. Support development of a plan to leave the abusive situation
d. common elements:
i. -physical abuse
ii. -psychologic or emotional abuse
iii. -sexual assault
iv. -isolation
v. -control of all aspects of victim’s life
1. -money, shelter, food, time
e. Triggers:
i. Pregnancy can be a trigger
ii. Socioeconomic status is not a factor
iii. Biophysical relationship stressors
iv. Male jealousy of fetus
v. May be conscious or unconscious attempt to end
pregnancy
f. Signs & Symptoms of IPV:
i. -overuse of health services
ii. -vague, nonspecific complaints
[Show More]


 (5) (1).png)














.png)
.png)