*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Care Plan 1 Epidural Pain management Pathophysiology of Labor Pain/ Epidural pain management (All)
Care Plan 1 Epidural Pain management Pathophysiology of Labor Pain/ Epidural pain management
Document Content and Description Below
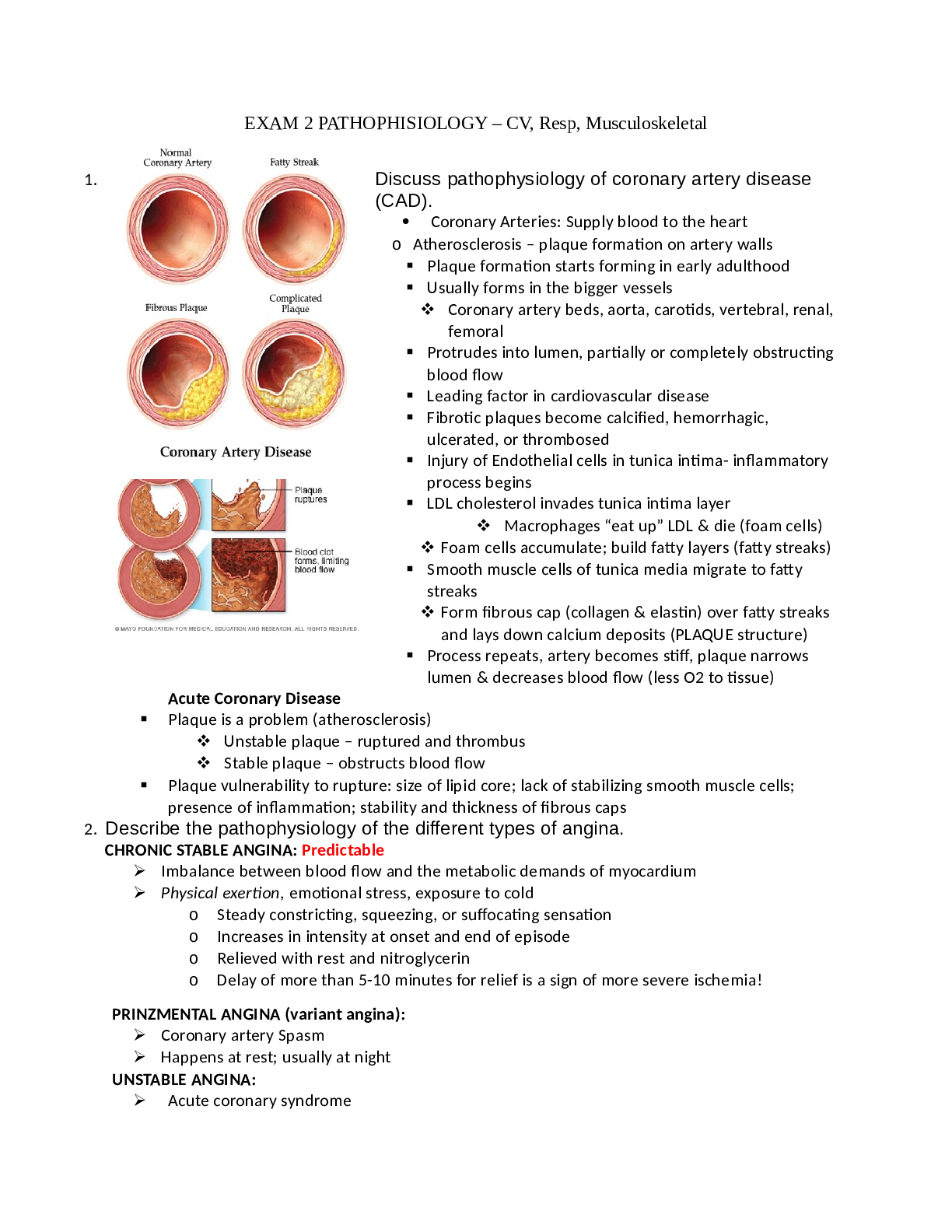
Care Plan 1: Epidural Pain Management (Graded) Pathophysiology of Labor Pain/ Epidural pain management: The severe pain that accompanies labor originates with the spread of sensory input to the cen... tral nervous system (CNS). “The neurophysiology of pain can be summarized as follows: (a) Noxious impulses originate in nociceptive receptors distributed throughout the skin, subcutaneous tissue, periosteum, joints, muscles, and viscera; (b) nociceptive stimuli are transmitted via primary afferent neurons that almost always are myelinated A delta or unmyelinated C fibers to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord; (c) the stimuli are processed primarily in the substantia gelatinosa (laminae II) of the dorsal horn and transmitted by interneurons of the spinothalamic tract to the thalamus and cerebral cortex, where spatial and temporal analysis occurs, and to the hypothalamic and limbic systems, where emotional and autonomic responses originate; (d) transmission by the spinoreticular tract to the reticular formation of the brain mediates motor, autonomic, and sensory functions associated with pain perception and discrimination and triggers arousal and the affective dimension of pain; and (e) at the level of the substantia gelatinosa, modulation of nociceptive impulse transmission occurs through several complex inhibitory systems that are activated at many supraspinal levels of the CNS [ CITATION Bon90 \l 1033 ].” Mechanical and chemical nociceptors are found in the ovaries, uterus and broad ligaments. These nociceptors are triggerd by concentrated pressure as with labor contractions. The perception of increasing intensity of pain as a labor progresses can be attributed to a lowerthreshold response in the mechanical nociceptors after repeated contractions. The subjective interpretation of pain that exists within accepted cultural and social norms also play a role in the observable behaviors associated with labor pain and thus can be widely variable with each pregnancy. It is important to note that generally multipara’s report having less early labor pain than their nullipara counterparts but both groups consistently report increased pain during second stage labor. Research suggests that having psychosocial support that is focused on supporting the laboring mother through the birthing process can significantly reduce the need for pharmacological interventions. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 39 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 01, 2021
Number of pages
39
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 01, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
38