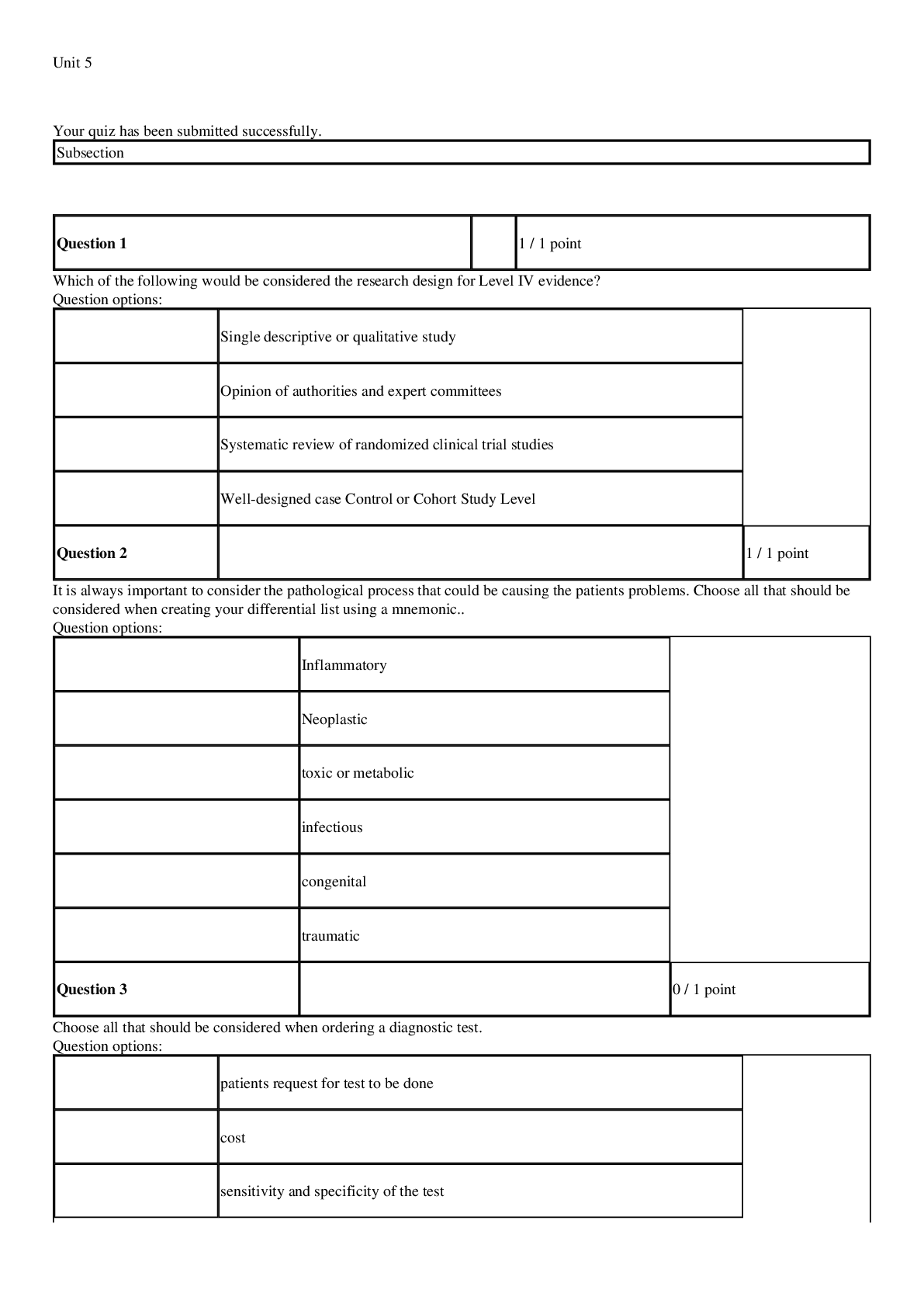
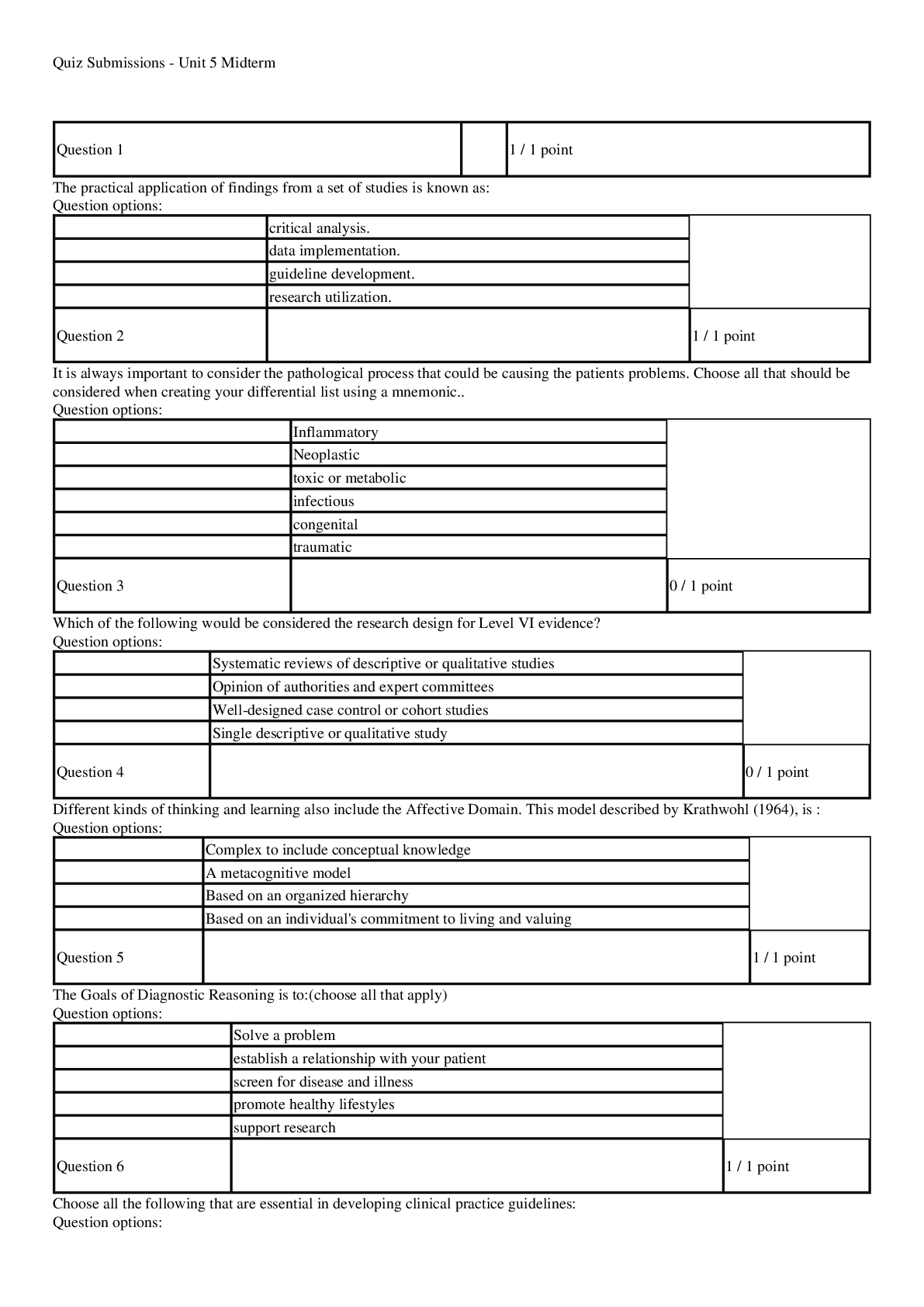
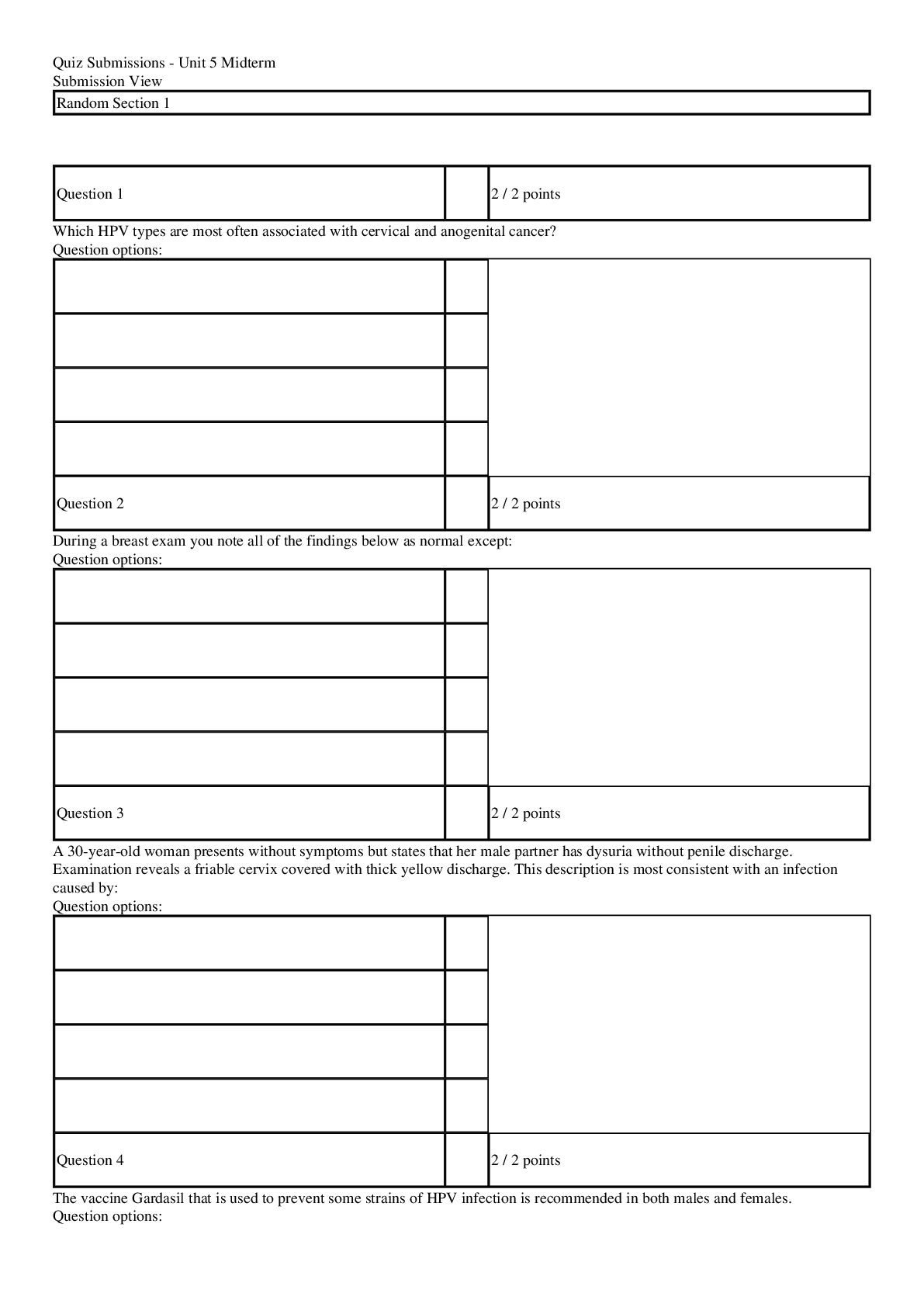
*NURSING > EXAM > NUR2488 Mental Health Nursing Final Exam Question Bank (Latest 2020/2021): Rasmussen College |(Verif (All)
NUR2488 Mental Health Nursing Final Exam Question Bank (Latest 2020/2021): Rasmussen College |(Verified Answers, Already graded A)
Document Content and Description Below
NUR2488 Mental Health Nursing Final Exam Question Bank (Latest): Rasmussen College NUR2488 Final Exam / NUR 2488 Final Exam (Practice Questions) (Latest): Mental Health Nursing: Rasmussen College 1. B... esides antianxiety agents, which classification of drugs is also commonly given to treat anxiety and anxiety disorders? a. Antipsychotics b. Mood stabilizers c. Antidepressants d. Cholinesterase inhibitors 2. What assessment question will provide the nurse with information regarding the effects of a woman’s circadian rhythms on her quality of life? a. “How much sleep do you usually get each night?” b. “Does your heart ever seem to skip a beat?” c. “When was the last time you had a fever?” d. “Do you have problems urinating?” 3. You realize that your patient who is being treated for a major depressive disorder requires more teaching when she makes the following statement: a. “I have been on this antidepressant for 3 days. I realize that the full effect may not happen for a period of weeks.” b. “I am going to ask my nurse practitioner to discontinue my Prozac today and let me start taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor tomorrow.” c. “I may ask to have my medication changed to Wellbutrin due to the problems I am having being romantic with my wife.” d. “I realize that there are many antidepressants and it might take a while until we find the one that works best for me.” 4. A patient being treated for insomnia is prescribed ramel-teon (Rozerem). Which comorbid mental health condition would make this medication the hypnotic of choice for this particular patient? a. Obsessive-compulsive disorder b. Generalized anxiety disorder c. Persistent depressive disorder d. Substance use disorder 5. Which statement made by a patient prescribed bupropion (Wellbutrin) demonstrates that the medication education the patient received was effective? Select all that apply. a. “I hope Wellbutrin will help my depression and also help me to finally quit smoking.” b. “I’m happy to hear that I won’t need to worry too much about weight gain.” c. “It’s okay to take Wellbutrin since I haven’t had a seizure in 6 months.” d. “I need to be careful about driving since the medication could make me drowsy.” e. “My partner and I have discussed the possible effects this medication could have on our sex life.” 6. Which drug group calls for nursing assessment for development of abnormal movement disorders among individuals who take therapeutic dosages? a. SSRIs b. antipsychotics c. benzodiazepines d. tricyclic antidepressants 9. The nurse administers each of the following drugs to various patients. The patient who should be most carefully assessed for fluid and electrolyte imbalance is the one receiving: a. lithium (Eskalith) b. clozapine (Clozaril) c. diazepam (Valium) d. amitriptyline 10. A psychiatric nurse is reviewing prescriptions for a patient with major depression at the county clinic. Since the patient has a mild intellectual disability, the nurse would question which classification of antidepressant drugs: a. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors b. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors c. Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors d. All of the above 4. The mental health team is determining treatment options for a male patient who is experiencing psychotic symptoms. Which question(s) should the team answer to determine whether a community outpatient or inpatient setting is most appropriate? Select all that apply. a. “Is the patient expressing suicidal thoughts?” b. “Does the patient have intact judgment and insight into his situation?” c. “Does the patient have experiences with either community or inpatient mental healthcare facilities?” d. “Does the patient require a therapeutic environment to support the management of psychotic symptoms?” e. “Does the patient require the regular involvement of their family/significant other in planning and executing the plan of care?” 10. Pablo is a homeless adult who has no family connection. Pablo passed out on the street and emergency medical services took him to the hospital where he expresses a wish to die. The physician recognizes evidence of substance use problems and mental health issues and recommends inpatient treatment for Pablo. What is the rationale for this treatment choice? Select all that apply. a. Intermittent supervision is available in inpatient settings. b. He requires stabilization of multiple symptoms. c. He has nutritional and self-care needs. d. Medication adherence will be mandated. e. He is in imminent danger of harming himself. 1. Which statement made by the nurse demonstrates the best understanding of nonverbal communication? a. “The patient’s verbal and nonverbal communication is often different.” b. “When my patient responds to my question, I check for congruence between verbal and nonverbal communication to help validate the response.” c. “If a patient is slumped in the chair, I can be sure he’s angry or depressed.” d. “It’s easier to understand verbal communication that nonverbal communication.” 2. Which nursing statement is an example of reflection? a. “I think this feeling will pass.” b. “So you are saying that life has no meaning.” c. “I’m not sure I understand what you mean.” d. “You look sad.” 3. When should a nurse be most alert to the possibility of communication errors resulting in harm to the patient? a. Change of shift report b. Admission interviews c. One-to-one conversations with patients d. Conversations with patient families 4. During an admission assessment and interview, which channels of information communication should the nurse be monitoring? Select all that apply. a. Auditory b. Visual c. Written d. Tactile e. Olfactory 5. What principle about nurse-patient communication should guide a nurse’s fear about “saying the wrong thing” to a patient? a. Patients tend to appreciate a well-meaning person who conveys genuine acceptance, respect, and concern for their situation. b. The patient is more interested in talking to you than listening to what you have to say and so is not likely to be offended. c. Considering the patient’s history, there is little chance that the comment will do any actual harm. d. Most people with a mentally illness have by necessity developed a high tolerance of forgiveness. 6. You have been working closely with a patient for the past month. Today he tells you he is looking forward to meeting with his new psychiatrist but frowns and avoids eye contact while reporting this to you. Which of the following responses would most likely be therapeutic? a. “A new psychiatrist is a chance to start fresh; I’m sure it will go well for you.” b. “You say you look forward to the meeting, but you appear anxious or unhappy.” c. “I notice that you frowned and avoided eye contact just now. Don’t you feel well?” d. “I get the impression you don’t really want to see your psychiatrist—can you tell me why?” 7. Which student behavior is consistent with therapeutic communication? a. Offering your opinion when asked to convey support. b. Summarizing the essence of the patient’s comments in your own words. c. Interrupting periods of silence before they become awkward for the patient. d. Telling the patient he did well when you approve of his statements or actions. 8. James is a 42-year-old patient with schizophrenia. He approaches you as you arrive for day shift and anxiously reports, “Last night, demons came to my room and tried to rape me.” Which response would be most therapeutic? a. “There are no such things as demons. What you saw were hallucinations.” b. “It is not possible for anyone to enter your room at night. You are safe here.” c. “You seem very upset. Please tell me more about what you experienced last night.” d. “That must have been very frightening, but we’ll check on you at night and you’ll be safe.” 9. Therapeutic communication is the foundation of a patient- centered interview. Which of the following techniques is not considered therapeutic? a. Restating b. Encouraging description of perception c. Summarizing d. Asking “why” questions 10. Carolina is surprised when her patient does not show for a regularly scheduled appointment. When contacted, the patient states, “I don’t need to come see you anymore. I have found a therapy app on my phone that I love.” How should Carolina respond to this news? a. “That sounds exciting, would you be willing to visit and show me the app?” b. “At this time, there is no real evidence that the app can replace our therapy.” c. “I am not sure that is a good idea right now, we are so close to progress.” d. “Why would you think that is a better option than meeting with me?” 11. A nursing student new to psychiatric-mental health nursing asks a peer what resources he can use to figure out which symptoms are present in a specific psychiatric disorder. The best answer would be: a. Nursing Interventions Classification (NIC) b. Nursing Outcomes Classification (NOC) c. NANDA-I nursing diagnoses d. DSM-5 12. Epidemiological studies contribute to improvements in care for individuals with mental disorders by: a. Providing information about effective nursing techniques. b. Identifying risk factors that contribute to the development of a disorder. c. Identifying individuals in the general population who will develop a specific disorder. d. Identifying which individuals will respond favorably to a specific treatment. 1. Which statement demonstrates a well-structured attempt at limit setting? a. “Hitting me when you are angry is unacceptable.” b. “I expect you to behave yourself during dinner.” c. “Come here, right now!” d. “Good boys don’t bite.” 2. Which activity is most appropriate for a child with ADHD? a. Reading an adventure novel b. Monopoly c. Checkers d. Tennis 3. Cognitive-behavioral therapy is going well when a 12-year- old patient in therapy reports to the nurse practitioner: a. “I was so mad I wanted to hit my mother.” b. “I thought that everyone at school hated me. That’s not true. Most people like me and I have a friend named Todd.” c. “I forgot that you told me to breathe when I become angry.” d. “I scream as loud as I can when the train goes by the house.” 4. What assessment question should the nurse ask when attempting to determine a teenager’s mental health resilience? Select all that apply. a. “How did you cope when your father deployed with the Army for a year in Iraq?” b. “Who did you go to for advice while your father was away for a year in Iraq?” c. “How do you feel about talking to a mental health counselor?” d. “Where do you see yourself in 10 years?” e. “Do you like the school you go to?” 5. Which factors tend to increase the difficulty of diagnosing young children who demonstrate behaviors associated with mental illness? Select all that apply. a. Limited language skills b. Level of cognitive development c. Level of emotional development d. Parental denial that a problem exists e. Severity of the typical mental illnesses observed in young children 7. In pediatric mental health there is a lack of sufficient numbers of community-based resources and providers, and there are long waiting lists for services. This has resulted in: Select all that apply. a. Children of color and poor economic conditions being underserved b. Increased stress in the family unit c. Markedly increased funding d. Premature termination of services 8. Child protective services have removed 10-year-old Christopher from his parents’ home due to neglect. Christopher reveals to the nurse that he considers the woman next door his “nice” mom, that he loves school, and gets above average grades. The strongest explanation of this response is: a. Temperament b. Genetic factors c. Resilience d. Paradoxical effects of neglect 9. April, a 10-year-old admitted to inpatient pediatric care, has been getting more and more wound up and is losing self-control in the day room. Time-out does not appear to be an effective tool for April to engage in self-reflection. April’s mother admits to putting her in time-out up to 20 times a day. The nurse recognizes that: a. Time-out is an important part of April’s baseline discipline. b. Time-out is no longer an effective therapeutic measure. c. April enjoys time-out, and acts out to get some alone time. d. Time-out will need to be replaced with seclusion and restraint. 10. Adolescents often display fluctuations in mood along with undeveloped emotional regulation and poor tolerance for frustration. Emotional and behavioral control usually increases over the course of adolescence due to: a. Limited executive function b. Cerebellum maturation c. Cerebral stasis and hormonal changes d. A slight reduction in brain volume 1. Which characteristic in an adolescent female is sometimes associated with the prodromal phase of schizophrenia? a. Always afraid another student will steal her belongings. b. An unusual interest in numbers and specific topics. c. Demonstrates no interest in athletics or organized sports. d. Appears more comfortable among males. 2. Which nursing intervention is particularly well chosen for addressing a population at high risk for developing schizophrenia? a. Screening a group of males between the ages of 15 and 25 for early symptoms. b. Forming a support group for females aged 25 to 35 who are diagnosed with substance use issues. c. Providing a group for patients between the ages of 45 and 55 with information on coping skills that have proven to be effective. d. Educating the parents of a group of developmentally delayed 5- to 6-year-olds on the importance of early intervention. 3. To provide effective care for the patient diagnosed with schizophrenia, the nurse should frequently assess for which associated condition? Select all that apply. a. Alcohol use disorder b. Major depressive disorder c. Stomach cancer d. Polydipsia e. Metabolic syndrome 4. A female patient diagnosed with schizophrenia has been prescribed a first-generation antipsychotic medication. What information should the nurse provide to the patient regarding her signs and symptoms? a. Her memory problems will likely decrease. b. Depressive episodes should be less severe. c. She will probably enjoy social interactions more. d. She should experience a reduction in hallucinations. 5. Which characteristic presents the greatest risk for injury to others by the patient diagnosed with schizophrenia? a. Depersonalization b. Pressured speech c. Negative symptoms d. Paranoia 6. Gilbert, age 19, is described by his parents as a “moody child” with an onset of odd behavior about at age 14, which caused Gilbert to suffer academically and socially. Gilbert has lost the ability to complete household chores, is reluctant to leave the house, and is obsessed with the locks on the windows and doors. Due to Gilbert’s early and slow onset of what is now recognized as schizophrenia, his prognosis is considered: a. Favorable with medication b. In the relapse stage c. Improvable with psychosocial interventions d. To have a less positive outcome 7. Which therapeutic communication statement might a psychiatric-mental health registered nurse use when a patient’s nursing diagnosis is altered thought processes? a. “I know you say you hear voices, but I cannot hear them.” b. “Stop listening to the voices, they are NOT real.” c. “You say you hear voices, what are they telling you?” d. “Please tell the voices to leave you alone for now.” 8. When patients diagnosed with schizophrenia suffer from anosognosia, they often refuse medication, believing that: a. Medications provided are ineffective. b. Nurses are trying to control their minds. c. The medications will make them sick. d. They are not actually ill. 9. Kyle, a patient with schizophrenia, began to take the first-generation antipsychotic haloperidol (Haldol) last week. One day you find him sitting very stiffly and not moving. He is diaphoretic, and when you ask if he is okay he seems unable to respond verbally. His vital signs are: BP 170/100, P 110, T 104.2°F. What is the priority nursing intervention? Select all that apply. a. Hold his medication and contact his prescriber. b. Wipe him with a washcloth wet with cold water or alcohol. c. Administer a medication such as benztropine IM to correct this dystonic reaction. d. Reassure him that although there is no treatment for his tardive dyskinesia, it will pass. e. Hold his medication for now and consult his prescriber when he comes to the unit later today. 10. Tomas is a 21-year-old male with a recent diagnosis of schizophrenia. Tomas’s nurse recognizes that self-medicating with excessive alcohol is common in this disease and can co-occur along with: a. Generally good health despite the mental illness. b. An aversion to drinking fluids. c. Anxiety and depression. d. The ability to express his needs. 1. Which nursing response demonstrates accurate information that should be discussed with the female patient diagnosed with bipolar and her support system? Select all that apply. a. “Remember that alcohol and caffeine can trigger a relapse of your symptoms.” b. “Due to the risk of a manic episode, antidepressant therapy is never used with bipolar disorder. c. “It’s critical to let your healthcare provider know immediately if you aren’t sleeping well.” d. “Is your family prepared to be actively involved in helping manage this disorder?” e. “The symptoms tend to come and go and so you need to be able to recognize the early signs.” 2. Which statement made by the patient demonstrates an understanding of the effective use of newly prescribed lithium to manage bipolar mania? Select all that apply. a. “I have to keep reminding myself to consistently drink six 12-ounce glasses of fluid every day.” b. “I discussed the diuretic my cardiologist prescribed with my psychiatric care provider.” c. “Lithium may help me lose the few extra pounds I tend to carry around.” d. “I take my lithium on an empty stomach to help with absorption.” e. “I’ve already made arrangements for my monthly lab work.” 3. The nurse is providing medication education to a patient who has been prescribed lithium to stabilize mood. Which early signs and symptoms of toxicity should the nurse stress to the patient? Select all that apply. a. Increased attentiveness b. Getting up at night to urinate c. Improved vision d. An upset stomach for no apparent reason e. Shaky hands that make holding a cup difficult 4. A male patient calls to tell the nurse that his monthly lithium level is 1.7 mEq/L. Which nursing intervention will the nurse implement initially? a. Reinforce that the level is considered therapeutic. b. Instruct the patient to hold the next dose of medication and contact the prescriber. c. Have the patient go to the hospital emergency room immediately. d. Alert the patient to the possibility of seizures and appropriate precautions. 5. Which intervention should the nurse implement when caring for a patient demonstrating manic behavior? Select all that apply. a. Monitor the patient’s vital signs frequently. b. Keep the patient distracted with group-oriented activities. c. Provide the patient with frequent milkshakes and protein drinks. d. Reduce the volume on the television and dim bright lights in the environment. e. Use a firm but calm voice to give specific concise directions to the patient. 6. Substance abuse is often present in people diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Laura, a 28-year-old with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, drinks alcohol instead of taking her prescribed medications. The nurse caring for this patient recognizes that: a. Anxiety may be present. b. Alcohol ingestion is a form of self-medication. c. The patient is lacking a sufficient number of neurotransmitters. d. The patient is using alcohol because she is depressed. 7. Ted, a former executive, is now unemployed due to manic episodes at work. He was diagnosed with bipolar I 8 years ago. Ted has a history of IV drug abuse, which resulted in hepatitis C. He is taking his lithium exactly as scheduled, a fact that both Ted’s wife and his blood tests confirm. To reduce Ted’s mania the psychiatric nurse practitioner recommends: a. Clonazepam (Klonopin) b. Fluoxetine (Prozac) c. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) d. Lurasidone (Latuda) 8. A 33-year-old female diagnosed with bipolar I disorder has been functioning well on lithium for 11 months. At her most recent checkup, the psychiatric nurse practitioner states, “You are ready to enter the maintenance therapy stage, so at this time I am going to adjust your dosage by prescribing”: a. A higher dosage b. Once a week dosing c. A lower dosage d. A different drug 9. Tatiana has been hospitalized for an acute manic episode. On admission the nurse suspects lithium toxicity. What assessment findings would indicate the nurse’s suspicion as correct? a. Shortness of breath, gastrointestinal distress, chronic cough b. Ataxia, severe hypotension, large volume of dilute urine c. Gastrointestinal distress, thirst, nystagmus d. Electroencephalographic changes, chest pain, dizziness 10. Luc’s family comes home one evening to find him extremely agitated and they suspect in a full manic episode. The family calls emergency medical services. While one medic is talking with Luc and his family, the other medic is counting something on his desk. What is the medic most likely counting? a. Hypodermic needles b. Fast food wrappers c. Empty soda cans d. Energy drink containers 1. Which response by a 15-year-old demonstrates a common symptom observed in patients diagnosed with major depressive disorder? a. “I’m so restless. I can’t seem to sit still.” b. “I spend most of my time studying. I have to get into a good college.” c. “I’m not trying to diet, but I’ve lost about 5 pounds in the past 5 months.” d. “I go to sleep around 11 p.m. but I’m always up by 3 a.m. and can’t go back to sleep.” 2. Which assessment question asked by the nurse demonstrates an understanding of comorbid mental health conditions associated with major depressive disorder? Select all that apply. a. “Do rules apply to you?” b. “What do you do to manage anxiety?” c. “Do you have a history of disordered eating?” d. “Do you think that you drink too much?” e. “Have you ever been arrested for committing a crime?” 3. Which nursing intervention focuses on managing a common characteristic of major depressive disorder associated with the older population? a. Conducting routine suicide screenings at a senior center. b. Identifying depression as a natural, but treatable result of aging. c. Identifying males as being at a greater risk for developing depression. d. Stressing that most individuals experience just a single episode of major depression in a lifetime. 4. Which characteristic identified during an assessment serves to support a diagnosis of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder? Select all that apply. a. Female b. 7 years old c. Comorbid autism diagnosis d. Outbursts occur at least once a week e. Temper tantrums occur at home and in school 5. Which chronic medical condition is a common trigger for major depressive disorder? a. Pain b. Hypertension c. Hypothyroidism d. Crohn’s disease 6. Tammy, a 28-year-old with major depressive disorder and bulimia nervosa, is ready for discharge from the county hospital after 2 weeks of inpatient therapy. Tammy is taking citalopram (Celexa) and reports that it has made her feel more hopeful. With a secondary diagnosis of bulimia nervosa, what is an alternative antidepressant to consider? a. Fluoxetine (Prozac) b. Isocarboxazid (Marplan) c. Amitriptyline d. Duloxetine (Cymbalta) 7. Cabot has multiple symptoms of depression including mood reactivity, social phobia, anxiety, and overeating. With a history of mild hypertension, which classification of antidepressants dispensed as a transdermal patch would be a safe medication? a. Tricyclic antidepressants b. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors c. Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors d. Monoamine oxidase inhibitor 8. When a nurse uses therapeutic communication with a withdrawn patient who has major depression, an effective method of managing the silence is to: a. Meditate in the quiet environment b. Ask simple questions even if the patient will not answer c. Use the technique of making observations d. Simply sit quietly and leave when the patient falls asleep 9. The biological approach to treating depression with electrodes surgically implanted into specific areas of the brain to stimulate the regions identified to be underactive in depression is: a. Transcranial magnetic stimulation b. Deep brain stimulation c. Vagus nerve stimulation d. Electroconvulsive therapy 10. Two months ago, Natasha’s husband died suddenly and she has been overwhelmed with grief. When Natasha is subsequently diagnosed with major depressive disorder, her daughter, Nadia, makes which true statement? a. “Depression often begins after a major loss. Losing dad was a major loss.” b. “Bereavement and depression are the same problem.” c. “Mourning is pathological and not normal behavior.” d. “Antidepressant medications will not help this type of depression.” 1. Which statement made by the patient demonstrates an understanding of the treatment of choice for patients managing the effects of traumatic events? a. “I attend my therapy sessions regularly.” b. “Those intrusive memories are hidden for a reason and should stay hidden.” c. “Keeping busy is the key to getting mentally healthy.” d. “I’ve agreed to move in with my parents so I’ll get the support I need.” 2. Which goal should be addressed initially when providing care for 10-year-old Harper who is diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)? a. Harper will be able to identify feelings through the use of play therapy. b. Harper and her parents will have access to protective resources available through social services. c. Harper will demonstrate the effective use of relaxation techniques to restore a sense of control over disturbing thoughts. d. Harper and her parents will demonstrate an understanding of the personal human response to traumatic events. 3. The care plan of a male patient diagnosed with a dissociative disorder includes the nursing diagnosis ineffective coping. Which behavior demonstrated by the patient supports this nursing diagnosis? a. Has no memory of the physical abuse he endured. b. Using both alcohol and marijuana. c. Often reports being unaware of surroundings. d. Reports feelings of “not really being here.” 4. Which statement accurately describes the effects of emotional trauma on the individual physically? a. Emotional trauma is a distinct category and unrelated to physical problems b. The physical manifestations of emotional trauma are usually temporary c. Emotional trauma is often manifested as physical symptoms d. Patients are more aware of the physical problems caused by trauma 5. The school nurse has been alerted to the fact that an 8-year-old boy routinely playacts as a police officer “locking up” other children on the playground to the point where the children get scared. The nurse recognizes that this behavior is most likely an indication of: a. The need to dominate others b. Inventing traumatic events c. A need to develop close relationships d. A potential symptom of traumatization 6. A pregnant woman is in a relationship with a male who routinely abuses her. Her unborn child may engage in high-risk behavior as a teen as a result of: a. Maternal stress b. Parental nurturing c. Appropriate stress responses in the brain d. Memories of the abuse 7. Maggie, a child in protective custody, is found to have an imaginary friend, Holly. Her foster family shares this information with the nurse. The nurse teaches the family members about children who have suffered trauma and knows her teaching was effective when the foster mother states: a. “I understand that imaginary friends are abnormal.” b. “I understand that imaginary friends are a maladaptive behavior.” c. “I understand that imaginary friends are a coping mechanism.” d. “I understand that we should tell the child that imaginary friends are unacceptable.” 8. An incest survivor undergoing treatment at the mental health clinic is relieved when she learns that her anxiety and depression are: a. Going to be eradicated with treatment b. Normal and will soon pass c. Abnormal but will pass d. A normal reaction to posttraumatic events 9. During a routine health screening, a grieving widow whose husband died 15 months ago reports emptiness, a loss of self, difficulty thinking of the future, and anger at her dead husband. The nurse suggests bereavement counseling. The widow is most likely suffering from: a. Major depression b. Normal grieving c. Adjustment disorder d. Posttraumatic stress disorder 10. A young child is found wandering alone at a mall. A male store employee approaches and asks where her parents are. She responds, “I don’t know. Maybe you will take me home with you?” This sort of response in children may be due to: a. A lack of bonding as an infant b. A healthy confidence in the child c. Adequate parental bonding d. Normal parenting 1. Which patient statement acknowledges the characteristic behavior associated with a diagnosis of pica? a. “Nothing could make me drink milk.” b. “I’m ashamed of it, but I eat my hair.” c. “I haven’t eaten a green vegetable since I was 3 years old.” d. “I regurgitate and re-chew my food after almost every meal.” 2. When considering an eating disorder, what is a physical criterion for hospital admission? a. A daytime heart rate of less than 50 beats per minute b. An oral temperature of 100°F or more c. 90% of ideal body weight d. Systolic blood pressure greater than 130 mm Hg 3. When considering the need for monitoring, which intervention should the nurse implement for a patient with anorexia nervosa? Select all that apply. a. Provide scheduled portion-controlled meals and snacks. b. Congratulate patients for weight gain and behaviors that promote weight gain. c. Limit time spent in bathroom during periods when not under direct supervision. d. Promote exercise as a method to increase appetite. e. Observe patient during and after meals/snacks to ensure that adequate intake is achieved and maintained. 4. Which intervention will promote independence in a patient being treated for bulimia nervosa? a. Have the patient monitor daily caloric intake and intake and output of fluids. b. Encourage the patient to use behavior modification techniques to promote weight gain behaviors. c. Ask the patient to use a daily log to record feelings and circumstances related to urges to purge. d. Allow the patient to make limited choices about eating and exercise as weight gain progresses. 5. Which patient statement supports the diagnosis of anorexia nervosa? a. “I’m terrified of gaining weight.” b. “I wish I had a good friend to talk to.” c. “I’ve been told I drink way too much alcohol.” d. “I don’t get much pleasure out of life anymore.” 6. Obesity can be the end result of a binge-eating disorder. The nurse understands that the best treatment option in persons with a binge-eating disorder promotes: a. Bariatric surgery b. Coping strategies c. Avoidance of public eating d. Appetite suppression medications 7. Taylor, a psychiatric registered nurse, orients Regina, a patient with anorexia nervosa, to the room where she will be assigned during her stay. After getting Regina settled, the nurse informs Regina: a. “I need to go through the belongings you have brought with you.” b. “You can use the scale in the back room when you need to.” c. “You will be eating five times a day here.” d. “The daily structure is based around your desire to eat.” 8. Safety measures are of concern in eating-disorder treatments. Patients with anorexia nervosa are supervised closely to monitor: Select all that apply. a. Foods that are eaten b. Attempts at self-induced vomiting c. Relationships with other patients d. Weight 9. Malika has been overweight all of her life. Now an adult, she has health problems related to her excessive weight. Seeking weight loss assistance at a primary care facility Malika is surprised when the nurse practitioner suggests: a. A trial of SSRI antidepressant therapy b. Mild exercise to start, increasing in intensity over time c. Removing snack foods from the home d. Medication treatment for hypertension 10. Malika agrees to try losing weight according to the nurse practitioner’s outlined plan. Additional teaching is warranted when Malika states: a. “I am willing to admit I am depressed.” b. “Psychotherapy will be a part of my treatment.” c. “I prefer to have a gastric bypass rather than use this plan.” d. “My comorbid conditions may improve with weight loss.” 6. Which patient has the greatest risk for suicide? a. A patient who expresses the inability to stop searching the internet for child pornography. b. A patient who reports having lost interest in having a sexual relationship with his wife. c. A patient with a history of exposing himself to female strangers on the bus. d. A patient whose attraction to prepubescent girls has increased. 7. When Melissa was a small child, she insisted that she was a boy, refused to wear dresses, and wanted to be called Mitch. As Melissa reached puberty, she no longer displayed a desire to be male. This change in identity is considered: a. Gender dysphoria b. Reaction formation c. Normal d. Early transgender syndrome 8. Phillip, a 63-year-old male, has exposed his genitals in public for all of his adult life, but the act has lost some of the former thrill. A rationale for this change in his experience may be: a. An increasing sense of shame b. Disgust over his lack of control c. Desire waning with age d. Progression into actual assault 9. A male arrested for inappropriate sexual contact in a subway car denies the allegation. Upon interviewing the man, the nurse suspects frotteuristic disorder due to his: a. Lack of relationships b. Overall aggressive nature c. Criminal history including robbery d. Intense hatred of women 10. Pedophilic disorder is the most common paraphilic disorder where adults who have a primary or exclusive sexual preference for prepubescent children. A subset of this disorder is termed hebephilia and is defined as attraction to: a. Infants b. Pubescent individuals c. Teens between the ages of 15 and 19 d. Males only 1. Which statement made by the psychiatric nurse demonstrates an accurate understanding of the factors that affect an individual’s personality? a. “Therapy will help her identify that her problems are personality related.” b. “I’ll need to learn more about this patient’s cultural beliefs.” c. “It’s encouraging to know that personality disorders respond well to treatment.” d. “A person’s personality is fluid and adjusts to current social situations.” 2. When assessing a patient diagnosed with a borderline personality disorder, which statement by the patient warrants immediate attention? a. “My mother died ten years ago.” b. “I haven’t needed medication in weeks.” c. “My dad never loved me.” d. “I’d really like to hurt her for hurting me.” 3. What is the current accepted professional view of the effect of culture on the development of a personality disorder? a. There aren’t sufficient studies to confirm the role that ethnicity and race have on the prevalence of personality disorders. b. The North American and Australian cultures produce higher incidences of personality disorders among their populations. c. Neither culture nor ethnic background is generally considered in the development of personality disorders. d. Personality disorders have been found to be primarily the products of genetic factors, not cultural factors. 4. Which personality disorders are generally associated with behaviors described as “odd or eccentric”? Select all that apply. a. Paranoid b. Schizoid c. Histrionic d. Obsessive-compulsive e. Avoidant 5. Which behaviors are examples of a primitive defense mechanism often relied upon by those diagnosed with a personality disorder? Select all that apply. a. Regularly attempts to split the staff b. Attempts to undo feelings of anger by offering to do favors c. Regresses to rocking and humming to sooth themselves when fearful d. Lashes out verbally when confronted with criticism e. Destroys another person’s belongings when angry 6. Personality disorders often co-occur with mood and eating disorders. A young woman is undergoing treatment at an eating disorders clinic and her nurse suspects the patient may also have a Cluster B personality disorder due to the young woman’s: a. Desire to avoid eating b. Dramatic response to frustration c. Excessive exercise routine d. Morose personality traits 7. Larry is from a small town and began displaying aggressive and manipulative traits while still a teenager. Now at 40 years old, Larry is serving a life sentence for the murders of his wife and her brother. John, the prison psychiatric nurse practitioner, recognizes that Larry’s treatment will most likely: a. Transform Larry to a model prisoner b. Not improve Larry’s coping skills c. Reaffirm Larry’s high-risk behaviors d. Manifest as small incremental changes 8. Connor is a 28-year-old student, referred by his university for a psychiatric evaluation. He reports that he has no friends at the university and people call him a loner. Recently, Connor has been giving lectures to pigeons at the university fountains. Connor is diagnosed as schizotypal, which differs from schizophrenia in that persons diagnosed as schizotypal: a. Can be made aware of their delusions b. Are far more delusional than schizophrenics c. Have a greater need for socialization d. Do not usually respond to antipsychotic medications 9. Garret’s wife of 8 years is divorcing him because the marriage never developed a warm or loving atmosphere. Garrett states in therapy, “I have always been a loner,” and was never concerned about what others think. The nurse practitioner suggests that Garrett try a trial of bupropion (Wellbutrin) to: a. Improve his flat emotions b. Assist in getting a good night’s sleep c. Increase the pleasure of living d. Prepare Garrett for group therapy 10. Josie, a 27-year-old patient, complains that most of the staff do not like her. She says she can tell that you are a caring person. Josie is unsure of what she wants to do with her life and her “mixed-up feelings” about relationships. When you tell her that you will be on vacation next week, she becomes very angry. Two hours later, she is found using a curling iron to burn her underarms and explains that it “makes the numbness stop.” Given this presentation, which personality disorder would you suspect? a. Obsessive-compulsive b. Borderline c. Antisocial d. Schizotypal 1. Which statement made by the primary caregiver of a patient diagnosed with dementia demonstrates accurate understanding of providing the patient with a safe environment? a. “The local police know that he has wandered off before.” b. “I keep the noise level low in the house.” c. “We’ve installed locks on all the outside doors.” d. “Our telephone number is always attached to the inside of his shirt pocket.” 2. Which statement made by a family member tends to support a diagnosis of delirium rather than dementia? a. “She was fine last night but this morning she was confused.” b. “Dad doesn’t seem to recognize us anymore.” c. “She’s convinced that snakes come into her room at night.” d. “He can’t remember when to take his pills or whether he’s bathed.” 3. When considering the pathophysiology responsible for both delirium and dementia, which intervention is appropriate for delirium specifically? a. Assist with needs related to nutrition, elimination, hydration, and personal hygiene. b. Monitor neurological status on an ongoing basis. c. Place identification bracelet on patient. d. Give one simple direction at a time in a respectful tone of voice. 4. What side effects should the nurse monitor for when caring for a patient prescribed donepezil (Aricept)? Select all that apply. a. Insomnia b. Constipation c. Bradycardia d. Signs of dizziness e. Reports of headache 5. What is the rationale for providing a patient diagnosed with dementia easily accessible finger foods thorough the day? a. Increases input throughout the day b. The person may be anorexic c. Assists with monitoring food intake d. Helps prevent constipation 6. Ophelia, a 69-year-old retired nurse, attends a reunion of her former coworkers. Ophelia is concerned because she usually knows everyone, and she cannot recognize faces today. A registered nurse colleague recognizes Ophelia’s distress and “introduces” Ophelia to those attending. The nurse practitioner recognizes that Ophelia seems to have a deficit in: a. Lower-level cognitive domain b. Delirium threshold c. Executive function d. Social cognition 7. Nancy is a nurse. After talking with her mother, she became concerned enough to drive over and check on her. Her mother’s appearance is disheveled, words are nonsensical, smells strongly of urine, and there is a stain on her dressing gown. Nancy recognizes that her mother’s condition is likely temporary due to: a. Early onset dementia b. A mild cognitive disorder c. A urinary tract infection d. Skipping breakfast 8. Darnell is an 84-year-old widower who has lived alone since his wife died 6 years ago. A neighbor called Darnell’s son to tell him that Darnell was trying to start his car from the passenger’s side. He became angry and aggressive when the car would not start. After a medical assessment, Darnell was diagnosed with a major neurocognitive disorder. The nurse realized additional family teaching is necessary when Darnell’s son states: a. “My father’s diagnosis is interfering with his daily functioning.” b. “This neurocognitive disorder will probably progress.” c. “Advancing age is a risk factor in my father’s diagnosis.” d. “With person-centered care, my father will be able to remain in his home.” 9. In the 2 months after his wife’s death, Aaron, aged 90 and in good health, has begun to pay less attention to his hygiene and seems less alert to his surroundings. He complains of difficulty concentrating and sleeping and reports that he lacks energy. His family sometimes has to remind and encourage him to shower, take his medications, and eat, all of which he then does. Which response is most appropriate? a. Reorient Mr. Smith by pointing out the day and date each time you have occasion to interact with him. b. Meet with family and support them to accept, anticipate, and prepare for the progression of his stage 2 dementia. c. Avoid touch and proximity; these are likely to be uncomfortable for Mr. Smith and may provoke aggression when he is disoriented. d. Arrange for an appointment with a therapist for evaluation and treatment of suspected depression. 10. Nurses caring for patients who have neurocognitive disorders are exposed to stress on many levels. Specialized skills training and continuing education are helpful to diffuse nursing stress, as well as: Select all that apply. a. Expressing emotions by journaling b. Describing stressful events on Facebook c. Engage in exercise and relaxation activities d. Having realistic patient expectations e. Happy hour after work to blow off steam 1. Which statement made by a 9-year-old child after hitting a classmate is a typical comment associated with childhood conduct disorder? a. “I’m sorry, I won’t hit him again.” b. “He deserved it for being a sissy.” c. “I didn’t think I hit him very hard.” d. “He hit me first. You just didn’t see it.” 2. What assessment data would support a diagnosis of conduct disorder? Select all that apply. a. Evidence of social isolation b. Arrested twice for disorderly conduct c. Expresses difficulty in keeping employment d. Demonstrates objective signs of phobia e. Exhibits signs of chronic self-mutilation 3. Which event experienced in the patient’s childhood increases the risk of the development of behaviors associated with intermittent explosive disorder? a. Orphaned at age 4 b. Physically abused from ages 3 to 10 c. Born with a chronic congenital disorder d. One parent was diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder 4. What is a common behavior observed in a patient diagnosed with intermittent explosive disorder? Select all that apply. a. Short attention span b. Threatens suicide c. Often purges after eating d. Uses alcohol to excess e. States, “Everyone is out to get me.” 5. When discussing oppositional defiant disorder with a group of parents, what information should the nurse include about the disorder? Select all that apply a. Classic symptoms include anger, irritation, and defiant behavior. b. Children generally outgrow the behaviors without formal treatment. c. Severity is considered mild when symptoms are present in only one setting. d. Disorder is diagnosed equally in both males and females. e. Argumentative and defiant are terms often used to describe the patient. 6. Tommy, a 12-year-old boy admitted to the pediatric psychiatric unit, has recently been diagnosed with conduct disorder. In the activity room, the games he wanted to play were already in use. He responded by threatening to throw furniture and to hurt his peers who had the game he wanted. Nancy, a registered nurse, recognizes that Tommy’s therapy must include: a. Consistency in implementing the consequences of breaking rules b. Empathetic reasoning when Tommy acts out in the activity room c. Teaching Tommy the benefits of socializing d. Solitary time so that Tommy can think about his actions 7. Some cultures have lower rates of diagnosed conduct disorders than observed in Western societies. The lower rate of incidence may be contributed to: a. Strict parenting with corporal punishment b. Cultural expression of anger as normal behavior c. Parents’ limited tolerance for externalizing behavior d. Widespread acceptance of conduct disorders 8. Larry, a middle-aged male in a treatment facility, is loudly displaying anger in the day room with a visiting family member. It is obvious to the nurse this pattern has played out before. Violence is often escalated when family members or authority figures: a. Use a soft tone of voice to gain control of the situation b. Move away from the agitated person in fear c. Use simple words to communicate d. Engage in a power struggle 9. The impulse control spectrum can begin in childhood and continue on into adulthood, often morphing into criminal behaviors. Working with patients diagnosed with these disorders, the best examples of expressed emotion by the nursing staff are: a. Low to prevent emotional reactions b. Matched to the patient’s level of emotion c. Flat without evidence of any emotional output d. High expression to improve therapeutic patient emotions 10. Claude is a new nurse on the psychiatric unit. He asks a senior nurse on staff for the “best advice” when working with oppositional defiant disorder. Which statement reflects advice on solid therapeutic communication? a. “When correcting behavior, use a loud firm tone.” b. “Use language beyond the patient’s education level.” c. “When setting limits, be specific and outline consequences.” d. “An aggressive body language will make the patients respect your position.” . A patient with a history of alcohol use disorder has been prescribed disulfiram (Antabuse). Which physical effects support the suspicion that the patient has relapsed? Select all that apply. a. Intense nausea b. Diaphoresis c. Acute paranoia d. Confusion e. Dyspnea 2. Which assessment data confirm the suspicion that a patient is experiencing opioid withdrawal? Select all that apply. a. Pupils are dilated b. Pulse rate is 62 beats/min c. Slow movements d. Extreme anxiety e. Sleepy 3. The nursing diagnosis ineffective denial is especially useful when working with substance use disorders and gambling. Which statements describe this diagnosis? Select all that apply. a. Reports inability to cope b. Does not perceive danger of substance use or gambling c. Minimizes symptoms d. Refuses healthcare attention e. Unable to admit impact of disease on life pattern 4. What action should you take when a female staff member is demonstrating behaviors associated with a substance use disorder? a. Accompany the staff member when she is giving patient care. b. Offer to attend rehabilitation counseling with her. c. Refer her to a peer assistance program. d. Confront her about your concerns and/or report your concerns to a supervisor immediately. 5. A patient diagnosed with opioid use disorder has expressed a desire to enter into a rehabilitation program. What initial nursing intervention during the early days after admission will help ensure the patient’s success? a. Restrict visitors to family members only. b. Manage the patient’s withdrawal symptoms well. c. Provide the patient a low stimulus environment. d. Advocate for at least 3 months of treatment. 6. Lester and Eileen have always enjoyed gambling. Lately, Eileen has discovered that their savings account is down by $50,000. Eileen insists that Lester undergo therapy for his gambling behavior. The nurse recognizes that Lester is making progress when he states: a. “I understand that I am a bad person for depleting our savings.” b. “Gambling activates the reward pathways in my brain.” c. “Gambling is the only thing that makes me feel alive.” d. “We have always enjoyed gaming. I do not know why Eileen is so upset.” 7. Opioid use disorder is characterized by: a. Lack of withdrawal symptoms b. Intoxication symptoms of pupillary dilation, agitation, and insomnia c. Tolerance d. Requiring smaller amounts of the drug to achieve a high over time 8. Terry is a young male in a chemical dependency program. Recently he has become increasingly distracted and disengaged. The nurse concludes that Terry is: a. Bored b. Depressed c. Bipolar d. Not ready to change 9. Maxwell is a 30-year-old male who arrives at the emergency department stating, “I feel like I am having a stroke.” During the intake assessment, the nurse discovers that Maxwell has been working for 36 hours straight without eating and has consumed eight double espresso drinks and 12 caffeinated sodas. The nurse suspects: a. Fluid overload b. Dehydration and caffeine overdose c. Benzodiazepine overdose d. Sleep deprivation syndrome 10. Donald, a 49-year-old male, is admitted for inpatient alcohol detoxification. He is cachexic, has multiple scabs on his arms and legs, and has lower extremity edema. An appropriate nursing diagnosis for Donald along with an expected outcome is: a. Risk for injury/Remains free from injury b. Ineffective denial/Accepts responsibility for behavior c. Nutrition: Less than body requirements/Maintains nutrient intake for metabolic needs d. Risk for suicide/Expresses feelings, plans for the future 2. Madelyn, a 29-year-old patient recently diagnosed with depression, comes to the mental health clinic complaining of continued difficulty sleeping. One week ago she was started on a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRRI), fluoxetine (Prozac), for her depressive symptoms. When educating Madelyn your response is guided by the knowledge that: a. SSRIs such as fluoxetine more commonly cause hypersomnolence as opposed to difficulty sleeping. b. The sleep problem is caused by the depression and is unrelated to the medication. c. The neurotransmitters involved in sleep and wakefulness are the same neurotransmitters targeted by many psychiatric medications and the problem may be temporary. d. The medication should be discontinued since sleep is the most important element to her recovery. 3. Which behaviors will the nurse encourage a patient diagnosed with insomnia disorder to adopt? Select all that apply. a. Avoiding exercising at bedtime b. Avoiding napping during the day c. Eating a hearty snack at bedtime d. Getting up at the same time each day e. Moving the clock so it is not visible from the bed 4. Which treatment is typically prescribed for primary insomnia? Select all that apply. a. Cognitive-behavioral therapy-insomnia (CBT-I) b. Intravenous medication for sedation c. Stimulus control d. Sleep restriction e. Sleep hygiene measures 5. Light projected into the retina is believed to trigger changes in sleep patterns and quality of sleep. Therefore the nurse should suggest: a. Not reading within an hour of bedtime b. Exercising before bedtime in a darkened environment c. Limiting use of electronic devices in the hour before bedtime d. Dimming the screen on cellphones and computers in the evening 6. Sleep disturbances are often overlooked or undiagnosed due to: a. A lack of formal nurse and physician training in sleep disturbances b. Patients not often accurately describing sleep disturbance patterns c. The belief that sleep disturbance is a necessary part of hospitalization d. Patients hiding the fact that they have issues with sleep 7. Many people allow life circumstances to dictate their amount of sleep instead of recognizing sleep as a priority. Which statement will the nurse recognize as progress in the patient’s sleep hygiene program? a. “I go to bed even if I am not sleepy, hoping I will fall asleep.” b. “I have one glass of red wine at bedtime each night.” c. “I take a nap each day to ‘catch up’ on my sleep deficit.” d. “I have removed the television from my bedroom.” 8. Larry is a 50-year-old man who works about 60 hours per week. He arrives at the clinic seeking assistance with a weight gain of 50 pounds over the past year. Larry admits to sleeping 4 to 5 hours a night. The nurse recognizes that the weight gain may be related to: a. A new onset of diabetes b. Suspected cardiovascular disease c. Dysregulation of hormones that influence appetite d. Comorbidity of depression with obesity 9. Sleep deprivation is considered a safety issue that results in loss of life and property. Psychomotor impairments of sleep deprivation are similar to symptoms caused by: a. Sleeping in excess of 10 hours b. Misuse of caffeine products c. Alcohol consumption d. Working more than 40 hours per week 10. The stage of sleep known as rapid eye movement or REM sleep is characterized by atonia and myoclonic twitches in addition to the actual rapid movement of the eyes. Atonia is thought to be a protective mechanism as it: a. Limits physical movements b. Prevents nightmares c. Enhances the dream state d. Regulates the autonomic nervous system 1. Which patient statement does not demonstrate an understanding of a suicide safety plan? a. “I know that when I start thinking about my dad, I’m going to start thinking about killing myself.” b. “Going for a really long, hard run helps clear my mind and stops the suicidal thoughts.” c. “My sister is always there for me when I start getting suicidal.” d. “I keep the suicide prevention phone number in my wallet.” 2. Which interventions will help make the environment on the unit safer for suicidal patients? Select all that apply. a. All windows are kept locked. b. Every shower has a breakaway shower rod. c. Eating utensils are counted when trays are collected. d. Patient doors are kept open. e. Staying within listening distance of the patient. 3. What are the nursing responsibilities to a patient expressing suicidal thoughts? Select all that apply. a. Instituting one-to-one observation. b. Documenting the patient’s whereabouts and mood every 15 to 30 minutes. c. Ensuring that the patient has no contact with glass or metal utensils. d. Ensuring that patient has swallowed each individual dose of medication. e. Discussing triggers of depression. 4. When considering community suicide prevention programs, what population should the nurse plan to service with regular suicide screenings? Select all that apply. a. 10- to 34-year-olds b. Males c. College-educated adults d. Rural population e. Native American 5. Research supports which intervention implemented on a long-term basis significantly reduces the incidence of suicide and suicide attempts in a patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder? a. A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) b. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) c. One-on-one observation d. Lithium 6. Gladys is seeing a therapist because her husband committed suicide 6 months ago. Gladys tells her therapist, “I know he was in pain, but why didn’t he leave me a note?” The therapist’s best response would be: a. “He probably acted quickly on his impulse to kill himself.” b. “He did not want to think about the pain he would cause you.” c. “He was not able to think clearly due to his emotional pain.” d. “He thought you may think it was an accident if there was no note.” 7. Martin is a 23-year-old male with a new diagnosis of schizophrenia, and his family is receiving information from a home health nurse. The topic of education is suicide prevention, and the nurse recognizes effective teaching when the mother says: a. “Persons with schizophrenia rarely commit suicide.” b. “Suicide risk is greatest in the first few years after diagnosis.” c. “Suicide is not common in schizophrenia due to confusion.” d. “Most persons diagnosed with schizophrenia die of suicide.” 8. Sigmund Freud, Karl Menninger, and Aaron Beck theorized that hopelessness was an integral part of why a person commits suicide. A more recent theory suggest suicide results from: a. Elevated serotonin levels b. The diathesis-stress model c. Outward aggression turned inward d. A lack of perfectionism 9. Which person is at the highest risk for suicide? a. A 50-year-old married white male with depression who has a plan to overdose if circumstances at work do not improve. b. A 45-year-old married white female who recently lost her parents, suffers from bipolar disorder, and attempted suicide once as a teenager. c. A young single white male who is alcohol dependent, hopeless, impulsive, has just been rejected by his girlfriend, and has ready access to a gun he has hidden. d. An older Hispanic male who is Catholic, is living with a debilitating chronic illness, is recently widowed, and who states, “I wish that God would take me too.” 10. Kara is a 23-year-old patient admitted with depression and suicidal ideation. Which intervention(s) would be therapeutic for Kara? Select all that apply. a. Focus primarily on developing solutions to the problems leading the patient to feel suicidal. b. Assess the patient thoroughly and reassess the patient at regular intervals as levels of risk fluctuate. c. Avoid talking about the suicidal ideation as this may increase the patient’s risk for suicidal behavior. d. Meet regularly with the patient to provide opportunities for the patient to express and explore feelings. e. Administer antidepressant medications cautiously and conservatively because of their potential to increase the suicide risk in Kara’s age group. f. Help the patient to identify positive self-attributes and to question negative self-perceptions that are unrealistic. 1. Which patient statement indicates the helpfulness of the nurse-patient relationship? a. “I appreciate the time you spent with me. I have a better understanding of what I can do to manage my problem.” b. “I really need to talk with you. You always give me good advice about how to address my anger issues.” c. “If it wasn’t for you and the hours we’ve spent talking, I don’t think I would be on my way to getting my anxiety under control.” d. “You always showed me sympathy when I was at my lowest point after the sexual assault. Knowing you had been there too was such a help.” 2. A female nurse had been sexually assaulted as a teenager. She finds it difficult to work with patients who have undergone the same trauma. What is the most helpful response? a. Discussing these feelings with the nurse supervisor. b. Requesting that these patients not be a part of her patient assignment. c. Discussing these feelings with a mental health professional. d. Accepting her role in providing unbiased, respectful, and professional care to all patients. 3. A patient whose history includes experiences with abusive partners is being treated for major depressive disorder. The patient’s care plan includes rape-trauma syndrome among its nursing diagnoses. What goal is directly associated with this diagnosis? a. Remains free from self-harm b. Wears appropriate clothing c. Reports feeling stronger and having a sense of hopefulness d. Demonstrates appropriate affect for both positive and negative emotions 4. The nurse is engaged in crisis intervention with a patient reporting, “I have no reason to keep on living.” What is the nurse’s initial intervention? a. Advise the patient about the services available to help them. b. Ask the patient, “Have you ever been this depressed before?” c. Ask the patient, “Do you have any plan to hurt yourself or anyone else?” d. Assure the patient that he or she is in a safe place and will be well cared for. 5. Which statement concerning a crisis experience is true and should be used as a guideline for crisis management care? Select all that apply. a. A crisis is self-limiting and usually resolves within 4 to 6 weeks. b. The earlier interventions are implemented, the better the expected prognosis. c. The nurse should maintain a nondirective role. d. The patient in crisis is assumed to be mentally unhealthy and in an extreme state of disequilibrium. e. The goal of crisis management is to return the patient to at least the precrisis level of functioning. 6. Which statement about crisis theory will provide a basis for nursing intervention? a. A crisis is an acute time-limited phenomenon experienced as an overwhelming emotional reaction to a problem perceived as unsolvable. b. A person in crisis has always had adjustment problems and has coped inadequately in the usual life situations. c. Crisis is precipitated by an event that enhances a person’s self-concept and self-esteem. d. Nursing intervention in crisis situations rarely has the effect of stopping the crisis. 7. Lilly, a single mother of four, comes to the crisis center 24 hours after a fire in which all the houses within a one-block area were wiped out. All of Lilly’s household goods and clothing were lost. Lilly has no other family in the area. Her efforts to mobilize assistance have been disorganized, and she is still without shelter. She is distraught and confused. You assess the situation as: a. A maturational crisis. b. An adventitious crisis. c. A crisis of confidence. d. An existential crisis. 8. When responding to the patient in question 7, the intervention that takes priority is to: a. Reduce anxiety. b. Arrange shelter. c. Contact out-of-area family. d. Hospitalize and place the patient on suicide precautions. 9. Which belief would be least helpful for a nurse working in crisis intervention? a. A person in crisis is incapable of responding to instruction. b. The crisis counseling relationship is one between partners. c. Crisis counseling helps the patient refocus to gain new perspectives on the situation. d. Anxiety-reduction techniques are used so the patient’s inner resources can be accessed. 10. The highest-priority goal of crisis intervention is: a. Anxiety reduction. b. Identification of situational supports. c. Teaching specific coping skills that are lacking. d. Patient safety. 1. Which statement made by a new mother should be explored further by the nurse? a. “I have three children, that’s enough.” b. “I think the baby cries just to make me angry.” c. “I wish my husband could help more with the baby.” d. “Babies are a blessing, but they are a lot of work.” 2. Which problem is observed in children who regularly witness acts of violence in their family? Select all that apply. a. Phobias b. Low self-esteem c. Major depressive disorder d. Narcissistic personality disorder e. Posttraumatic stress disorder 3. What situation associat [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 60 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$14.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 05, 2021
Number of pages
60
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 05, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
185





 Questions and Answers 100% VERIFIED.png)
 Questions and Answers 100% correct Solutions.png)