*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > MED SURG 324 ADULT HEALTH FINAL EXAM 2 REVIEW| UPDATED (All)
MED SURG 324 ADULT HEALTH FINAL EXAM 2 REVIEW| UPDATED
Document Content and Description Below
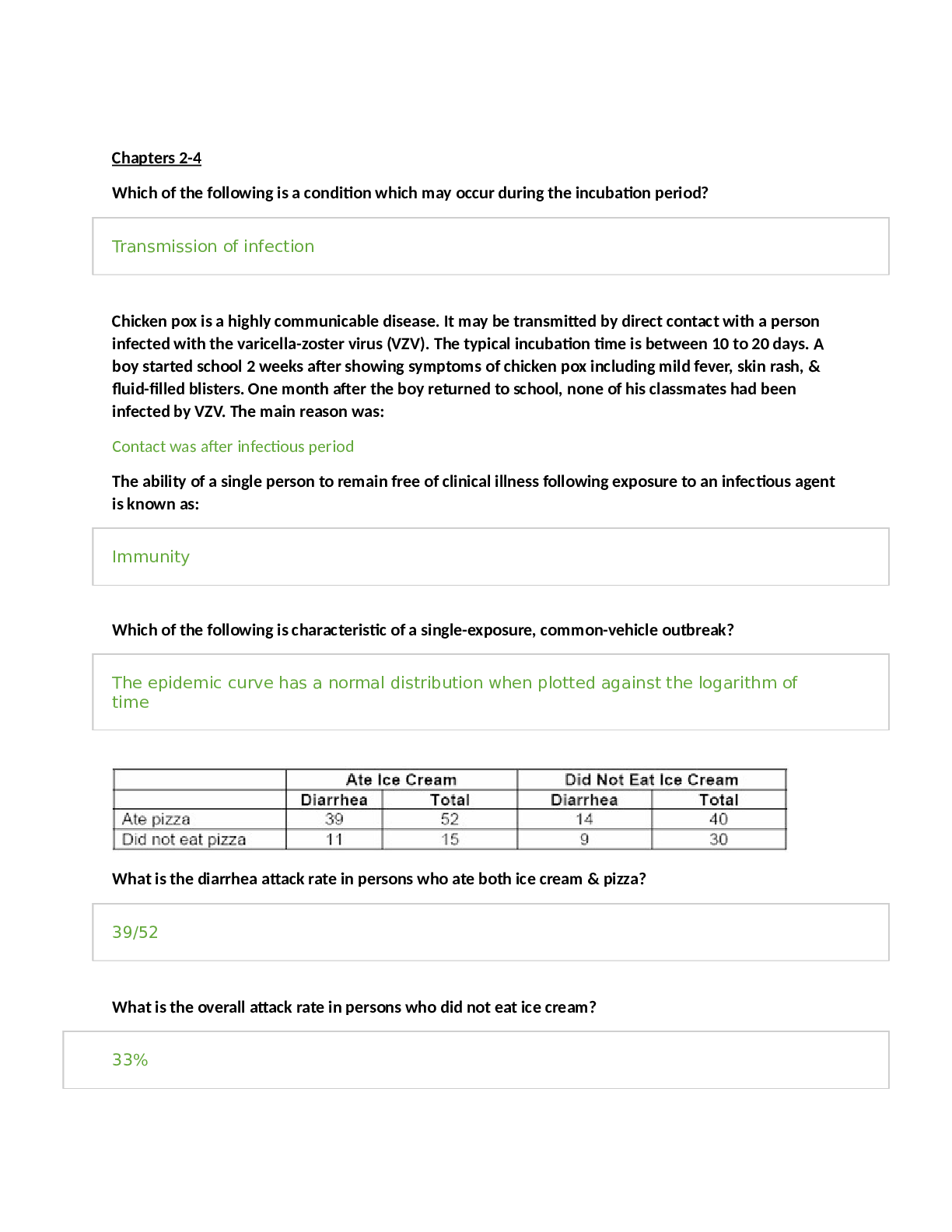
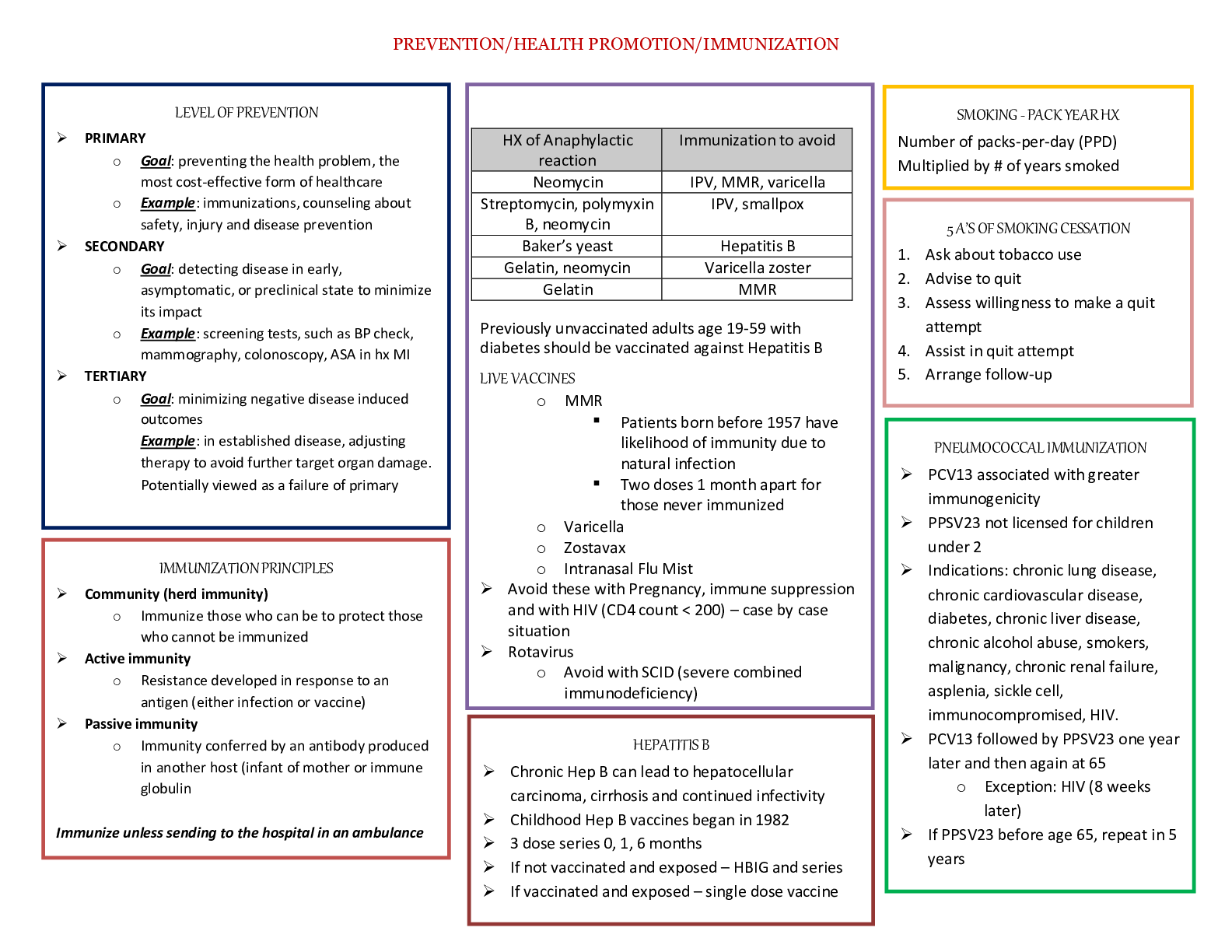
GI drugs - 3 Antacids: neutralizes acid Magnesium Hydroxide, Calcium Carbonate always give alone and allow for 1-2 hours before administering other medications Histamine-receptor blockers: decreases s... ecretion of gastric acid “Ranitidine HCL “Zantac” or Famotidine “Pepcid” Avoid giving at the same time with antacids or Carafate Proton-pump Inhibitors (PPIs): decreases stomach acid and helps esophagus heal Omeprazole “Prilosec” or Pantoprazole “Protonix” More effective than H2 receptors used in combination with abx to treat H. pylori Prokinetics: prevent delayed gastric emptying by improving pressure in LES and peristalsis of the GI tract “Bethanechol” Urecholine or Reglan “Metoclopramide” Antibiotics: used if h. pylori is causing the ulcer formation: various regime ordered by physician. They are used with PPIs or bismuth subsalicylate or H2 blockers Clarithromycin (Biaxin), Metronidazole (Flagyl), Tetracycline, Amoxicillin (Amoxil) Lab values- 1 WBC 5,000-10,000/mm3 PLT 150,000-400,000mm3 RBC 4.2-5.4million/uL (females) 4.7-6.1million/uL (males) Sodium 135-145mEq/L Potassium 3.5-5.0mEq/L Magnesium 1.5-2.5mEq/L Phosphate 2.4-4.4mg/dL Calcium 8.6-10.2mg/dL Chloride 96-106mEq/L Troponin < 0.1ng/mL Creatine kinase MB 0% of total CK (elevated in the event of an MI) BUN 10-20mg/dL Creatinine 0.6-1.2mg/dL Colostomy /colostomy care/discharge teachings- 2 Abdominal surgery- 1 Colostomy allows the intestine to rest and heal. New colostomy check stoma, should be red at first then pink/flushed if gray/black call physician. Nursing intervention/teaching Avoid foods high in fiber Raw vegetables, fried foods, strawberries, blueberries, grapes, apples, whole grains, wheat rice/bread Chew food entirely Drink plenty of water Ulcerative colitis- 2 Inflammation and ulcerations of the colon and rectum (large intestine). High dietary intake of total fats, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), omega-6 fatty acids, and meat is associated with increased risk of IBD. High vegetable intake decreased risk. Toxic megacolon CBC anemia and iron deficiency, WBC toxic megacolon or perforation, decreased serum sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarb, and magnesium, electrolyte loss from diarrhea, vomiting, hypoalbuminemia severe disease due to poor nutrition or protein loss, ESR, CRP reflect inflammation. Aminosalicylayes are more common for ulcerative colitis. A total colectomy is curative. Crohn’s disease- 1 An autoimmune disorder. Occurs anywhere in the GI tract from the mouth to the anus, most frequent site is the distal ileum and proximal colon. Healthy tissue intersected with areas of inflammation. Diarrhea and colicky pain are common symptoms. Weight loss can occur due to malabsorption. May cause peritonitis due to microscopic leaks and bowel entering to peritoneal cavity. High fruit and fiber intake decreased risk. Oral contraceptives and NSAIDs exacerbate symptoms. Diarrhea with large fluid and electrolyte losses. Nutritional problems when the terminal ileum is involved. A total proctocolectomy is curative. TPN- 4 Used when GI tract cannot be used for ingestion, digestion, and absorption of essential nutrients. Methods of administration central parental nutrition (long term support) (subclavian or jugular vein) or Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) Central PN solutions are hypertonic. 10% or 20% dextrose solution. Refeeding syndrome, fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances. Hypophosphatemia is hallmark. Cardiac dysrhythmias, respiratory arrest, and neurologic disturbances (paresthesias). Monitor electrolytes, BUN, CBC, liver enzymes. It is the nurse’s responsibility to ensure that the PN solution is discontinued and replaced with a new solution if the bag is not empty at the end of 24 hours. Hypoglycemia, check blood sugar, daily weights, check urine for glucose/ketones, nothing else should go through the line, most frequent complication is infection, needs to be on a pump. Check blood sugar every 4 to 6 hours. Gastric ulcer: 1 Peptic Ulcer (PUD) H. pylori alters gastric secretions and produces tissue damage. NSAIDs increase risk of H. pylori Gastric Ulcer Food makes pain worse (pain 1-2 hours after eating), report dull ache, weight loss, severe: vomit blood more common. More common. Perforation (small hole): severe abdominal pain bloating, vomiting, fever, increase HR and respirations (life-threatening) ridged boardlike abdominal muscles. Obstruction in pylorus: due to scarring for ulceration, cause vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating Risk factors: h. pylori, medications, alcohol and smoking, bile reflux. Projectile vomiting. Duodenal Ulcer Pain happens when stomach is empty, food makes it better (pain 3-4 hours after eating), wake in the middle of the night with pain, report of pain gnawing, weight normal, severe: tarry, black stool from GI bleeding Zollinger-Ellison syndrome rare, but severe. Cirrhosis, COPD, hyperparathyroidism, chronic kidney disease, chronic pancreatitis Endoscopy most accurate diagnostic procedure. Barium endoscopy for those who cannot do endoscopy, patient will drink barium and it coats the stomach and makes ulcer visible on x-ray. GERD- 1 Gastric contents (including enzymes) backflow into the esophagus causing pain and mucosal damage (esophagitis, Barrett’s epithelium). Most common upper GI problem. Risk factors: obesity, smoking, alcohol use, older age, pregnancy, ascites, hiatal hernia, supine position, diet high in fatty/fried/spicy foods, caffeine, citrus fruits. Symptoms: dyspepsia (indigestion), throat irritation, bitter taste, burning pain in esophagus, pain worsens when laying down, improves when sitting upright, chronic cough. Meds: antacids (1-3 hours after eating, 1 hour before/after meals), H2 receptor antagonists (ranitidine), Proton pump inhibitors (pantoprazole), prokinetics (metoclopramide: accelerates gastric emptying, watch for symptoms of EPS). Teaching: avoid spicy/fried/fatty foods, lose weight, eat small meals, remain upright after meals, sleep on right side. Priority questions- 1 Airway, breathing, circulation!! Safety always first!! Hiatal hernia: 1 Sliding hernia most common type junction in the stomach and esophagus located above the hiatus. Paraesophageal or rolling hernia occurs at the esophagogastric junction where the fundus and the greater curvature of the stomach roll up through the diaphragm. Iron deficiency anemia- 1 Most common type in children, those on poor diets and pregnant women. Blood loss is a major cause over a prolonged period before identified. Pallor is the most common, glossitis the second most common. Provide iron supplements, ferrous sulfate or iron dextran Pancytopenia (aplastic anemia) decrease in all blood cell types. Pernicious anemia- 1 Megaloblastic Most common cause of cobalamin anemia. Lack of intrinsic factor in gastric mucosa, which prevents the absorption of B12. Administer cyanocobalamin (B12) parentally or intranasally. Signs and symptoms of pernicious anemia include feeling very fatigued, tingling or burning in the hand or feet (also called paresthesia), red, smooth tongue (beefy red tongue), depression, loss of appetite etc. Treatment for pernicious anemia is supplementation of vitamin B 12 through intramuscular injections of vitamin B 12. Nursing care of a patient with pernicious anemia include administering vitamin B 12 injections, educating the patient about the condition and medication regime, good oral hygiene due to tongue changes, and safety precautions due to paresthesia in the hands and feet. GI bleed- 1 Pale skin, mucous membranes, increased HR and decreased BP, bloating or mass in abdomen, dark/tarry stool, vomiting blood that is red or dark like coffee ground, collecting occult in stool per MD order Dumping Syndrome: 20% of patients after PUD surgery stomach is not able to regulate the movement of food due to the removal of sections of the stomach so it enters the small intestine too fast before the stomach can finish digesting it. The food will act hypertonically and cause water from the blood to enter the jejunum. (early 15-30 minutes after eating) (late 3 hours after eating hypoglycemia) Assessment on all systems basics -1 Inspection, palpitation, auscultation, and percussion. Except abdomen, inspection, auscultation, palpation, and percussion. Constipation-1 Encourage fluids, high fiber diet, exercise. Difficult or infrequent stool, hard, dry and are difficult to pass. Fluid overload/deficit- 1 Fluid overload (hypervolemia): tachycardia, tachypnea, hypertension, bounding pulse, weight gain, edema, ascites, dyspnea, crackles, distended neck veins Labs: decreased Hct and Hgb, serum osmolarity, urine osmolarity, urine specific gravity, BUN (daily weight) Fluid deficit (hypovolemia): tachycardia, tachypnea, hypotension, weak pulse, fatigue, weakness, thirst, dry mucus membranes, GI upset, oliguria, decreased skin turgor, decreased cap refill, diaphoresis, flattened neck veins Labs: increased Hct, serum osmolarity, urine specific gravity, BUN, serum sodium (hypovolemic shock) EKG: 3 Electrodes, 10 minutes or less, not painful. Remove hair. P wave QRST wave. T wave elevation in hyperkalemia. U wave in hypokalemia. Echocardiogram takes 40 minutes painless. Thrombocytopenia/ITP- 2 Thrombocytopenia is manifested by a predisposition to bleeding evidenced by petechiae, ecchymosis, and epistaxis. Most common acquired. Decreased platelet production. Multiple therapys such as corticosteroids, splenectomy, immunosuppressants or thrombopoietin agonists. Platelets survive 8 to 10 days. Think BLEEDING BLEEDING BLEEDING the stopping of hemostasis (blood clotting) Abnormal destruction of circulating platelets Autoimmune disease Acute in children, Chronic in adults Manifestations: Asymptomatic Petechiae Purpura Prolonged bleeding Colonoscopy-1 Long thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the rectum in order to see the colon and to detect any abnormalities or changes. Patient will be on NPO or clear liquid diet Patient will receive laxative solution to clean out the colon. Patient will have an IV line where sedative is given must monitor VS. (ABCs) SLE: 4 Autoimmune disorder that mainly affects the cartilage. The most frequently identified drugs include procainamide (Pronestyl), hydralazine (Apresoline), and quinidine (Quinigut). Creatnine test is the best indicator for renal function (0.6-1.2). About 20% of patients have discold (round coin-shaped) lesions. The classic butterfly rash over the cheeks and bridge of the nose occurs in 55-85% of patients with SLE. Deformities such as swan neck of the fingers, ulnar deviation, subluxation with joint laxity. This disorder of coagulation that leads to clots in the arteries and veins with related risk of stroke, gangrene, and heart attack. Various psychiatric disorders are reported in SLE including depression, mood disorder, anxiety, and psychosis. Fever may indicate an underlying infection rather than lupus activity alone. SLE is marked by the presence of ANA (antinuclear antibodies) in 97% of persons with the disease. Elevated ESR and CRP are not diagnostic of SLE, but may be used to monitor disease activity and effectiveness of therapy. 24-hour urine collection for protein and creatinine clearance. Psychosis may result from CNS disease or may be the effect of corticosteroid therapy. Blood transfusion: 1 Take VS before transfusion, 15 min after transfusion, and 1 hour after transfusion Transfusion should take no less than 4 hours. If there are any reactions such as irritation, scratching, swelling. Stop the transfusion immediately! Rheumatoid Arthritis: 3 RA is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of connective tissue in the diarthrodial (synovial) joints. It can affect every system in the body. Primary goal is management of RA which is the reduction of inflammation, pain management, and minimize joint deformity. Osteoarthritis-1 Slowly progressive noninflammatory disorder of the diarthrodial joints. Risk factors include: age, decreases estrogen at menopause, obesity, anterior cruciate ligament injury, frequent kneeling and stooping. Prevention: regular moderate exercise, weight control. Heberden’s nodes. Distinction between RA and OA: systemic manifestations (fatigue, fever, and organ involvement) are not present in OA Methotrexate: 1 DMARD which is taken orally once a week. It can cause liver toxicity and bone marrow suppression and requires frequent monitoring of CBC, liver, and kidney function. It can cause fetal death and congenital abnormalities. Contraception must be used during treatment ns for 3 months after. Encourage 2 to 3L of water per day due to risk of kidney damage. Osteoporosis: 2 Risk factors: gender, age, low body weight, malabsorption problems, hx of fractures, corticosteroid use, hypothyroidism. Alendronate, GI side effects, take with a full glass of water 30 minutes before food or other medications, sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking. Adequate calcium intake, almonds, sardines, salmon, spinach, turnip greens. Weight bearing exercises, low impact (walking, hiking, dancing, weight training). HIV: 3 Transmission occurs through sexual intercourse with an infected partner, exposure with infected blood or blood products, and perinatal transmission during pregnancy, at delivery or through breastfeeding, it’s the lymphocytes that contain HIV. Genital lesions carry greater risk for transmission. Treatment with antietrovial therapy (ART) reduce the risk of perinatal transfer. Destruction of CD4+ T cells allows for opportunistic diseases to develop. Some ppl develop neurologic complications, such as aseptic meningitis, peripheral neuropathy, facial palsy, or Guillain-Barre syndrome, at this time a high viral load is noted and CD4+ T cell count fall. Oral hairy leukoplakia an Epstein-Barr virus infection on the tongue. ART can delay progression. Immune problems occurs when CD4+ T cells drop below 500 cells/uL Severe: below 200 cells/uL Normal range: 800-1200 cells. Most infectious during acute flu like symptoms. AIDS: 1 Onset of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia can be a diagnosis of AIDs for a patient with HIV. 10 years after HIV infection. Final stage of HIV. Cast/fractured tibia: 3 Open skin is broken closed skin is not broken complete break is completely through the bone incomplete partly across the bone shaft. Buck’s traction immobilization of fracture. RICE (neurovascular assessment) peripheral vascular assessment (color, temperature, capillary refill, peripheral pulses, and edema) peripheral neurologic assessment (sensation, motor function, and pain). Watch for compartment syndrome (5P’s). Call the orthopedic surgeon for compartment syndrome. Myelogram with or without CT Involves injecting a radiographic contrast medium into sac around nerve roots. CT scan may follow to show how the bone is affecting the nerve roots. Very sensitive test for nerve impingement and can detect very subtle lesions and injuries. Inform patient that headache may occur after procedure but should resolve in 1-2 days with rest and fluids but should be reported to HCP. Report a headache that is worse when sitting or standing. Furosemide: 1 Loop diuretic that helps decrease fluid in the body caused by HF and to decrease BP. Must be given slowly, no less than 2 min. If administered fast can cause ringing in the ears and hearing loss. Monitor potassium levels, renal and hepatic function levels. Partial laryngectomy: 1 Partial or total laryngectomy is a surgical procedure in which part or all of the larynx is removed. Hoarseness, check for gag reflux before allowing patient to eat or drink. DVT: 1 Clot that forms in the deep veins Chronic venous insufficiency can lead to ulcers Most occur in the lower leg or thigh Caused by: Prolonged bed rest Obesity Immobility Heart failure Elevate, compression, warmth, ambulation can help to relieve pain. Early ambulation. ABG: 2 PH 7.35-7.45 PaCO2 35-45 HCo3 22-26 Respiratory Acidosis: pH less than 7.35 and PaCO2 greater than 45 causes: respiratory depression, inadequate chest expansion, airway obstruction, PE, pulmonary edema S/S: tachycardia, tachypnea, shallow breathing, pale/cyanotic skin, confusion Respiratory Alkalosis: pH greater than 7.45 and PaCO2 less than 35 causes: hyperventilation S/S: tachypnea, deep and rapid breathing, anxiety, chest pain, dysrhythmias Metabolic Acidosis: pH less than 7.35 and HCO3 less than 22 causes: DKA, kidney failure, pancreas/liver failure S/S: bradycardia, hypotension, weak pulses, dysrhythmias, Kussmal respirations, warm/flush skin Metabolic Alkalosis: pH greater than 7.45 and HCO3 greater than 26 causes: antacid overdose, GI losses S/S: tachycardia, dysrhythmias, muscle weakness Leukemia-1 AML abrupt onset uncontrolled proliferation of myeloblasts, hyperplasia of bone marrow and spleen. ALL common in children. CLL most common in adults, infiltrate the bone marrow, spleen, and liver. Solid masses result from collections of leukemia cells. Focus on neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia, and provide psychosocial support for the patient and family. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma proliferation of abnormal giant nucleated cells, Reed-Sternberg cells. Enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma B-cell lymphomas constitute about 88% Artherosclerosis- 1 Plaque buildup in the arteries. Prevention: Diet and exercise Smoking cessation Stress management Chest tube- 1 Drains fluid, air, or blood from pleural space Collection chamber: report greater than 70ml/hr Water seal chamber: add sterile fluid up to 2cm line, check every 2hrs, must be upright and below chest tube insertion, tidaling is expected, lack of tidaling, lung re-expansion or obstruction, continuous bubbling indicates an air leak Suction control chamber: bubbling is expected, tension pneumothorax can result from a kink in the tubing or obstruction. Dislodgement use petroleum gauze taped 3 ways, place disconnected tube in sterile water. COPD-1 2types of COPD (slow progression) Emphysema loss of lung elasticity and hyperinflation of lung tissue Chronic Bronchitis inflammation of bronchi Smoking is primary risk factor S/S: dyspnea upon exertion, crackles/wheezes, barrel chest, use of accessory muscles, clubbing, hyperresonance (due to trapped air), decreased pulse ox levels, rapid and shallow respirations Labs: increased Hct (due to low O2 levels), PaO2 <80mmHg, PaCO2 >45mmHg, respiratory acidosis. Nursing Care: position patient in high fowlers. Encourage coughing, deep breathing, use of incentive spirometer. Ensure proper nutrition increase calories and protein. Education: abdominal breathing take breaths from diaphragm, lie on back w/knees bent Pursed lip breathing breathe in through nose and out through mouth Do not increase oxygen. Bronchodilators before corticosteroids. MI-1 Male gender, post-menopausal women, hypertension, smoking, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, stress, inactivity S/S: anxiety, chest pain, nausea, diaphoresis, cold/clammy skin, pallor, tachycardia Labs: elevated cardiac enzymes (CK-MB 0%, Troponin I less than 0.5, Troponin T less than 0.1, myoglobin less than 90) Troponin is most specific EKG changes: ST depression or elevation, T wave inversion, abnormal Q wave Meds: nitro, analgesics, beta blockers, thrombolytic meds (IV heparin), antiplatelet meds (asa and Plavix), anticoagulants Complications: heart failure, cardiogenic shock Primary intervention MONA (morphine, oxygen, nitro, asa) Thrombophlebitis- 1 Caused by: Prolonged bed rest History of varicose veins Trauma/infection Cancer Obesity/immobility Heart Failure Estrogen hormone Symptoms: Intense, sharp, deep muscle pain Warmth swelling redness Tender to palpation Dependent cyanosis mild or maybe absent Requires immediate attention due to high risk of pulmonary embolism Treatment: Elevate Apply heat Compression NSAIDs Blood thinners Neutropenia-1 The patient with neutropenia (low neutrophil count) is susceptible to infection and is at risk for septic shock and death. Even a low-grade temperature (>100.4o F). Barium enema- 1 X-ray taken after the insertion of a dye in the rectum using a tube. Nursing intervention would be to increase fluids, fiber, and laxatives Laryngeal cancer: 1 Hoarseness that lasts more than 2 weeks can be an early sign of laryngeal caner. Feels like a lump in their throat or voice changes. Other clinical manifestations may include a sore throat that does not get better with treatment, a unilateral sore throat or otalgia (ear pain), swelling or lumps in the neck, and coughing up blood. Unintentional weight loss and difficulty with chewing, swallowing, moving the tongue or jaw, and breathing are typically late symptoms. Asthma/Fluticasone: 2 Bronchodilators before corticosteroids. Bronchodilators before meals to relax bronchi. Post op care for Resp/Cardiac patients- 1 Respiratory system nursing dx Impaired Gas Exchange Ineffective Airway Clearance Sputum Analysis: green is infection patient will need antibiotic treatment Infection control: Room assignments, Precautions, PPE, Hand washing- 1 Airborne: TB, Measles, Varicella Private room Negative air pressure N95 mask Droplet: Pneumonia, rubella, strep, flu Private room Mask required Contact: MRSA, C.Diff, Herpes, Private room gloves , gown, mask, hand hygiene with soap and water Negative Pressure- TB Positive Pressure- compromised immune systems, must wear a mask while out of room [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$5.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 07, 2021
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 07, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
79













.png)








