*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NURSING 28_HAP Midterm Exam Study Guide | complete (2021) | Santa Monica College (All)
NURSING 28_HAP Midterm Exam Study Guide | complete (2021) | Santa Monica College
Document Content and Description Below
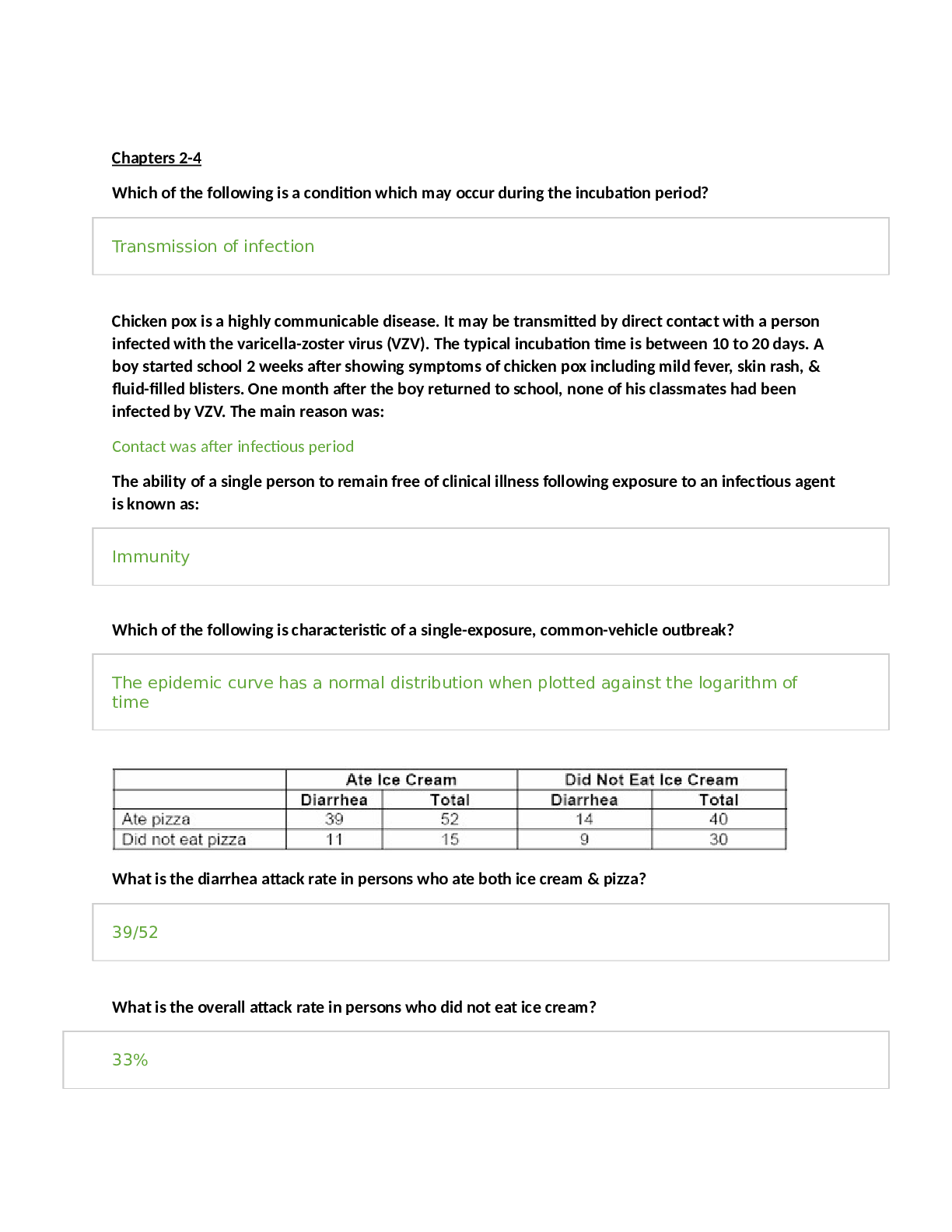
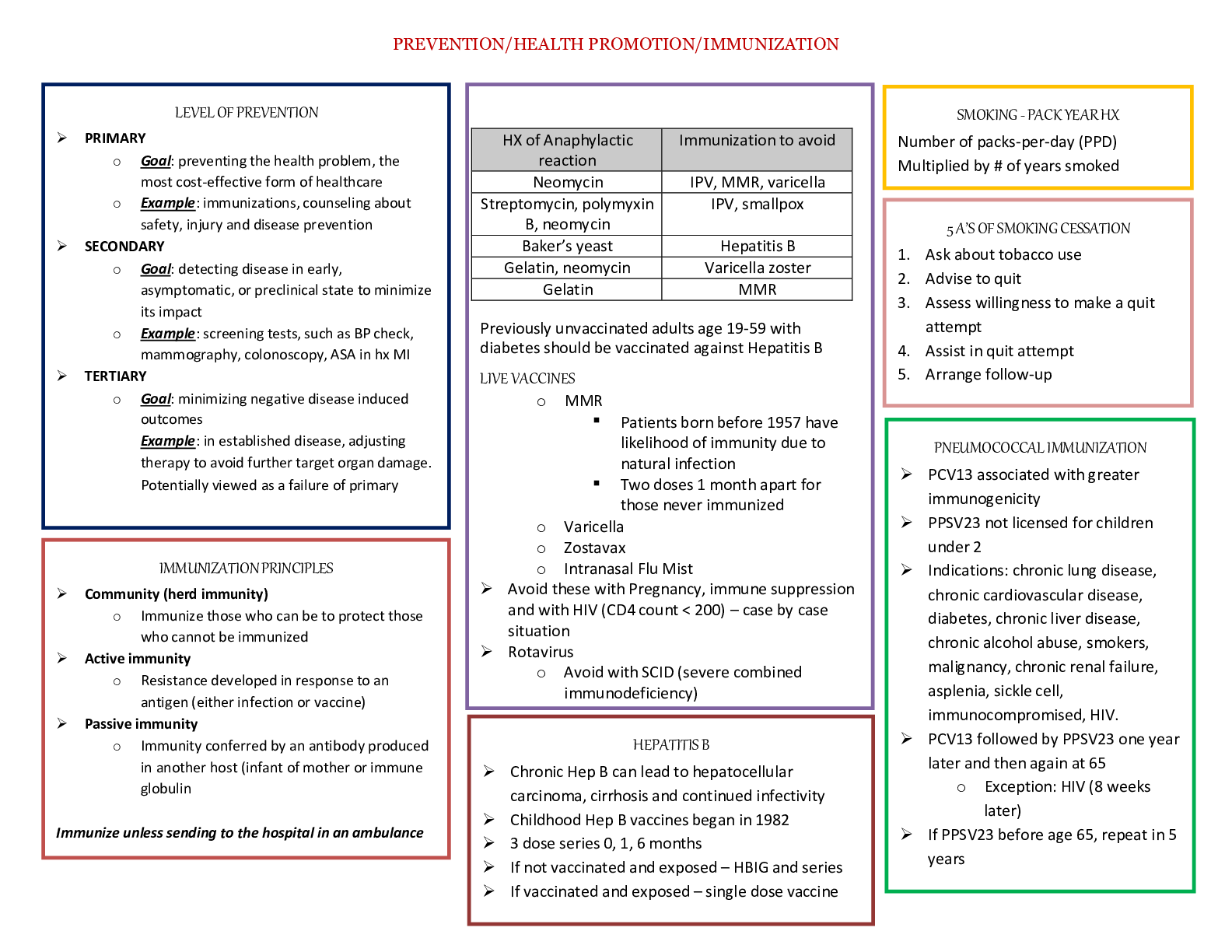
HAP Study Guide: Exam 1 WEEK 1 (5Q) The nursing process: ● Assessment ● Diagnosis ● Planning (should be SMART: Specific Measurable Attainable Reasonable Timely) ● Implementation ● Evaluation... Assessment ● Health history – subjective ● Physical assessment – objective ● Psychosocial, sociocultural, spiritual, etc. SUBJECTIVE DATA: info from patient or patient family, SYMPTOMS OBJECTIVE DATA: finds from direct observation using your senses, SIGNS ● Use inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation ● Must document findings – improves care pan, acts as legal document, baseline for evaluation ● Confidential/HIPAA ● Accuracy – legally accepted abbreviations ● SOAP: subjective, objective, assessment, plan ● SBAR (handoffs): situation, background, assessment, recommendations ● CBE: charting by exception, only document unusual findings ● PIE: problem, intervention, evaluation ● DAR: data, action, response Types of assessment ● Comprehensive – complete health history and physical assessment, annually/outpatient use, first time you see a patient ● Episodic – ex would be someone on Coumadin checking blood levels 1x/month ● Shift assessment – head to toe shift assessment ● Screening assessment - check BP or other screenings ● Focused assessments – based on health issue, involves 1 or 2 body systems, purpose is to get treatment fast o Urgent care/ER ● Emergency assessment - ABCs Frequency of assessments depends on patient needs, setting can be ICU, long term, post treatment, etc. Amount of info gathered depends on content of care, patient need, expertise of nurse Prioritize based on assessments, life threatening is #1 – patient’s #1 complaint should be one of your highest priorities Organizing data: ● Body systems format – cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, etc.… ● Conceptual format – mobility, oxygenation, etc.… Data analysis: ● ID abnormal findings ● Interpret and select appropriate plan of care ● Apply clinical judgment to make conclusions re: pt needs, concerns, or health problems ● Use PES statement: problem, etiology, signs/symptoms (defining characteristics) o Diagnosis r/t Etiology AEB signs/symptoms Diagnosis: ● Medical – disease (pneumonia) ● Nursing – judgment about patient response to health problem ● Collaborative – complication nurses monitor to detect onset of a change in patient status ● Actual diagnosis: human response to current condition ● Risk diagnosis: potential human response to condition that may develop ● Wellness diagnosis: human response to levels of wellness, promotes health Evaluation: judgment of effectiveness of nursing care in meeting pt goals and outcomes Health protection = disease prevention ● Primary – optimize health and disease prevention thru promotion of healthy lifestyle ● Secondary – ID @ early stage before too much damage ● Tertiary – minimize effects of disease (teach diabetics to eat right) HP 2020: framework for health promotion managed by US DHHS ● Addresses most important, preventable threats to health ● 4 goals: o High quality longer lives w/o disease o Equity, eliminate disparities o Social and physical environments that promote health o QOL, healthy development, healthy behavior across all life stages WEEK 2 (9Q) 2 main components of health assessment: 1. Health history – subjective 2. Physical exam – objective Subjective data can be PRIMARY (from pt) or SECONDARY (from caregivers, family, med charts) ● ID areas of concern to be addressed via physical exam, topics for teaching/health promotion (i.e. if they tell you they smoke) Goals: do a complete health hx, make database that can be used for plan, prevent disease, resolve problems, minimize limitations, build trust & rapport (contract btwn nurse is a LEGAL CONTRACT) Non-verbal behaviors form nurse: ● Appearance, posture, eye contact, gesture, facial expressions o May be culture specific (American culture uses most eye contact) o May be gender specific (Muslim female and male nurse) ● Touch – can comfort elderly with dementia, also culturally specific, more rapport more touch The interview ● Phases o Preinteraction – after you’ve gotten shift report you go into room w/ set of info you’ve been giving o Beginning – introduce self with first and last name ▪ Use statements and less questions because you don’t want to ask permission when you need to get answers o Working – biggest part, health hx and review of systems o Closing – thank for time, summarize info, discuss next time ● Therapeutic communication – single most important factor for successful interviewing, communication skill of nurse gains pt trust ● Factors effecting interview: setting, nurse behaviors, types of Q you have to ask, how you ask Q, personality and behavior of patient, how pt feels at that specific time, nature of info being discussed o Physical setting should be private, quiet, comfy, w/o distractions (TV off) o First impression w/ nurses starts with appearance and prof demeanor o Pt related variables – consider their age, physical/mental/emotional status, limit Q for pt in distress, pain, or young age ● Illicit story by asking open end Q – gives you longer answers, builds rapport, helps you diagnose because it’s more descriptive ● Use close end Q when trying to get pt back on track ● Use Y/N questions in urgent situations ● Review of systems uses direct close-end Q ● Active listening – don’t constantly write ● Confrontation – address when pt gives 2 pieces of contradicting info ● Elaboration – go on… ● Reflection – summarize main themes (“so you sound a bit nervous”) ● Restatement – use patient’s own words to get them to elaborate and so they can understand what they said ● Interpretation – make associations, repeat what you interpreted the pt is trying to say so you can confirm that it’s correct ● Explanation – give facts or info ● Summary – give final review ● Don’t interrupt pt, make value judgments, use medical jargon, mistake sympathy for empathy (“it must be hard…”, act authoritarian, use false reassurance ● Don’t’ use family members for pt with language barriers, you need to use a formal interpreter ● Space & distance – o Social distance = 4-12 ft. for interview o Personal distance = 04 ft. for exam The Health History o Patient’s statement of current and past health o Actual, potential, and resolved problems o Can be comprehensive (primary care), episodic/follow up after treatment, or problem-based focus o Biographic data: gender, address, payment, etc. o Source of Hx: hopefully primary o Reason for seeking care = chief complaint o History of present illness = HPI, use oldcarts! o Present health status: how are you? o Family health, genogram (used to review family patterns) o Social history/functional assessment – who you live with, religion, activity/exercise, nutrition, sleep, sex, drugs, alcohol, safety (care seats & helmets for kids, loose rugs & steps for elderly) Review of Systems (part of subjective information) o Evaluation of past and present health state of each body system o Yes/no questionnaire o If yes use oldcarts Pediatric variations o Additions of pregnancy (child birth issues can affect dvlpt), prenatal care, growth and development, behavioral status, immunization status, safety o Observe parent-child interactions o Include child as much as possible appropriate for age o Nurse detects if pediatric or adult database should be used o Nurse determines if interview should be with parent or alone o Teens should have chance to be questioned separately Older adult variations o Have multiple symptoms, conditions, meds o Longer health hx o Gradual change of body systems with age o Functional ability: focus on ADLs and IADLs o Focus on problems unique to elderly – fall risk, food spoilage, etc. Cultural considerations o Nurse values illness experience thru patient’s eyes o Diversity challenges w/ culture, language, beliefs, and value systems Culture vs. ethnicity o Culture: everything societal that makes person up – arts, beliefs, worldviews o Ethnicity: soc group within social and cultural system group shares common heritage o Language, hx, lifestyles, religion o Race: genetic origin w/ physical characteristics o Religion: organized system of beliefs o Spirituality: broader than religion Nurse must understand OWN cultural values BEFORE we can understand someone else’s o Understand meaning of health to patient, be knowledgeable about pt background, know their language, have interpretation resources Purnell model of cultural care: has 12 domains related to cultural competence (healthcare practices, death rituals, diet, nutrition, etc.) WEEK 3 (10Q) Order of assessment 1. Inspection 2. Palpation 3. Percussion 4. Auscultation *WITH EXCEPTION OF ABDOMEN, which has auscultation before percussion General inspection – always comes first o Must have good lighting, adequate exposure, right instruments Palpation – use to assess temp, texture, moisture, organ location/size, swelling, vibration/pulsation, abnormal lumps & masses o Finger tips – vibration o Finger and thumb – grasping to see if masses are movable, solid, squishy o Back of hands (dorsa) – temperature (warmth = DVT) o Base of fingers (ulnar surface of hands) – vibrations Enlarged organs = “—megaly” o Use moderate-deep palpation for feeling organs Percussion – produces sound or elicits tenderness o Maps out location and size of organs o Determines density of structure (air, fluid, solid filled) o Finds abnormal masses and tenderness o Deep tendon reflexes – usually on patella, hit w/ end of stethoscope o Direct percussion – used in ONLY 2 PLACES CVA (kidney inflammation) & sinuses o Indirect percussion – non-dominant hand used as sound board, tap on distal part of finger What sounds are and when you should hear them…. o Resonant: normal lung tissue o Hyper resonant: abnormal adult lung (emphysema, COPD) or normal child lung o Tympany: air filled viscous organ like stomach or intestine o Dull: dense organ like liver or spleen o Flat: large muscle, bone, tumor Auscultation – does not amplify o Use diaphragm for high pitched sounds o Use bell for low pitched o Used for heart, lung, bowel sounds o AB fistula should have whooshing sound with blood flow General survey – physical appearance, body structure, mobility, mental health o Begins with first moment of encounter and all throughout exam o Objective data collection o Physical appearance o Appears staged age, facial features normal (symmetrical and no distress), body symmetrical o Level of consciousness/speech o Skin color (tone, approp for ethnicity, discolorations like vitilago or lesions) o Hygiene, dress (can tell you mental status) o Sexual development o Body structure o Normal height range for age, gender, genetic heritage o No gigantism (too much GH), or dwarfism (too little GH) o Achondritic dwarfism – cartilage doesn’t convert to bone o Arm span = height o Nutrition – normal weight for height and build ▪ No Cushing syndrome (buffalo hump or moon face from too much steroids, pituitary gland has tumor and causes increase release of ACTH) o Posture – part of musculoskeletal system, should be erect without lordosis, kyphosis, or scoliosis ▪ Note tripod position (difficulty breathing or heart issue in children), fetal positions of pain o Build & contour ▪ Abnormal = marfans, missing extremities, shortened limbs, webbed digits ● Polydactaly = extra digits o Mobility – asses w/ neuromuscular system o Gait = how they walk o Look for shuffling, dragging, limping o Range of motion should be smooth, no involuntary movements Vital Signs ● Height, weight, BMI, waist circumference (criteria for metabolic syndrome) ● Children in lower 5-10% or upper 5-10% is abnormal o Head & chest circumference is important ● 6 vital signs = temperature, pulse, respiration, BP, O2 sat, & pain! Temperature – 98.6F or 37C is normal ● Rectal temp is ½ degree higher ● Axillary temp is ½ degree lower ● 35.8-37.3C or 96.4-99.1 ● 101.4 call the doctor [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 08, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
55