*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Seidels Guide to Physical Examination-9th edition test-bank | NURS 6501 Advanced Practice_ Test Bank (All)
Seidels Guide to Physical Examination-9th edition test-bank | NURS 6501 Advanced Practice_ Test Bank (2) Q&As Complete Guide to Boost Your Grades
Document Content and Description Below
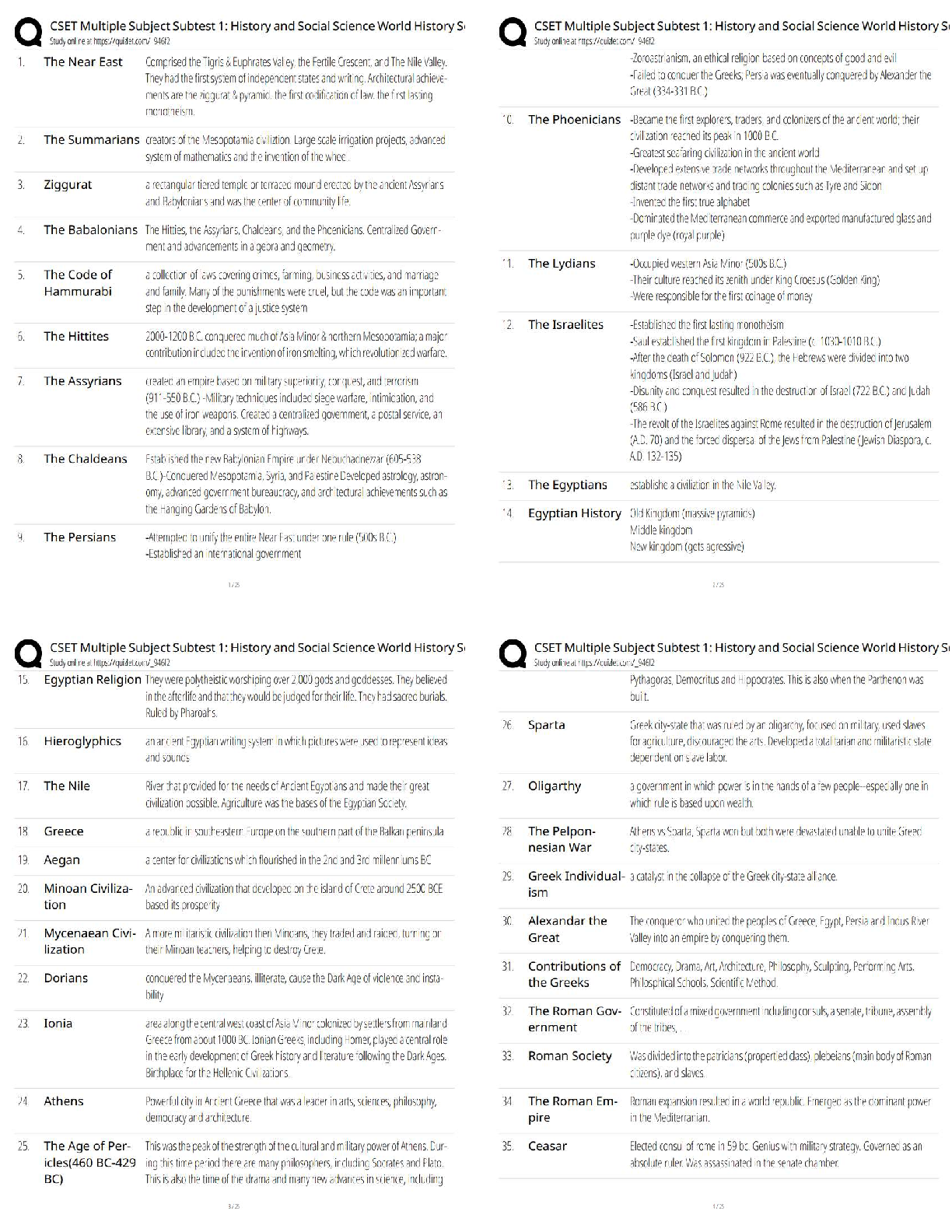
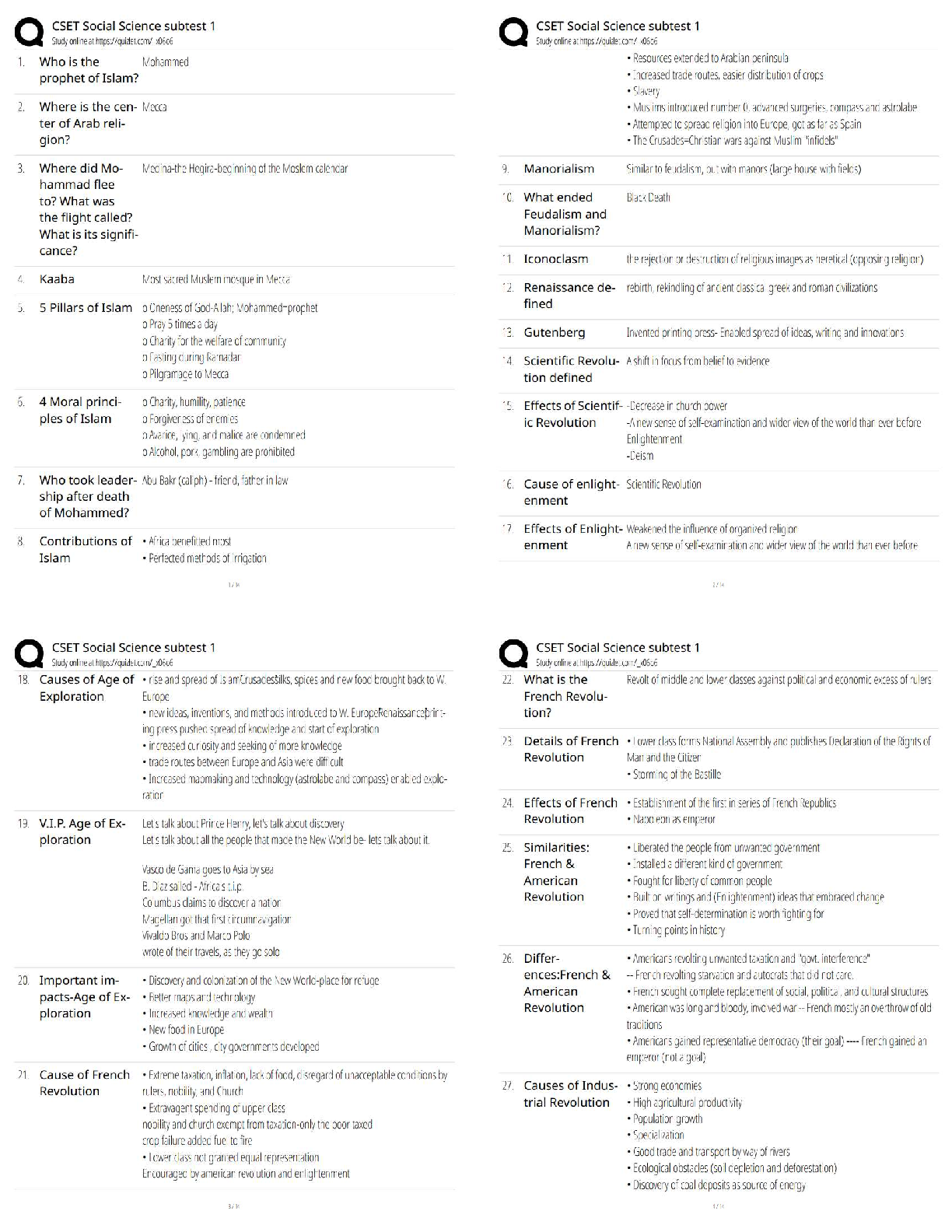
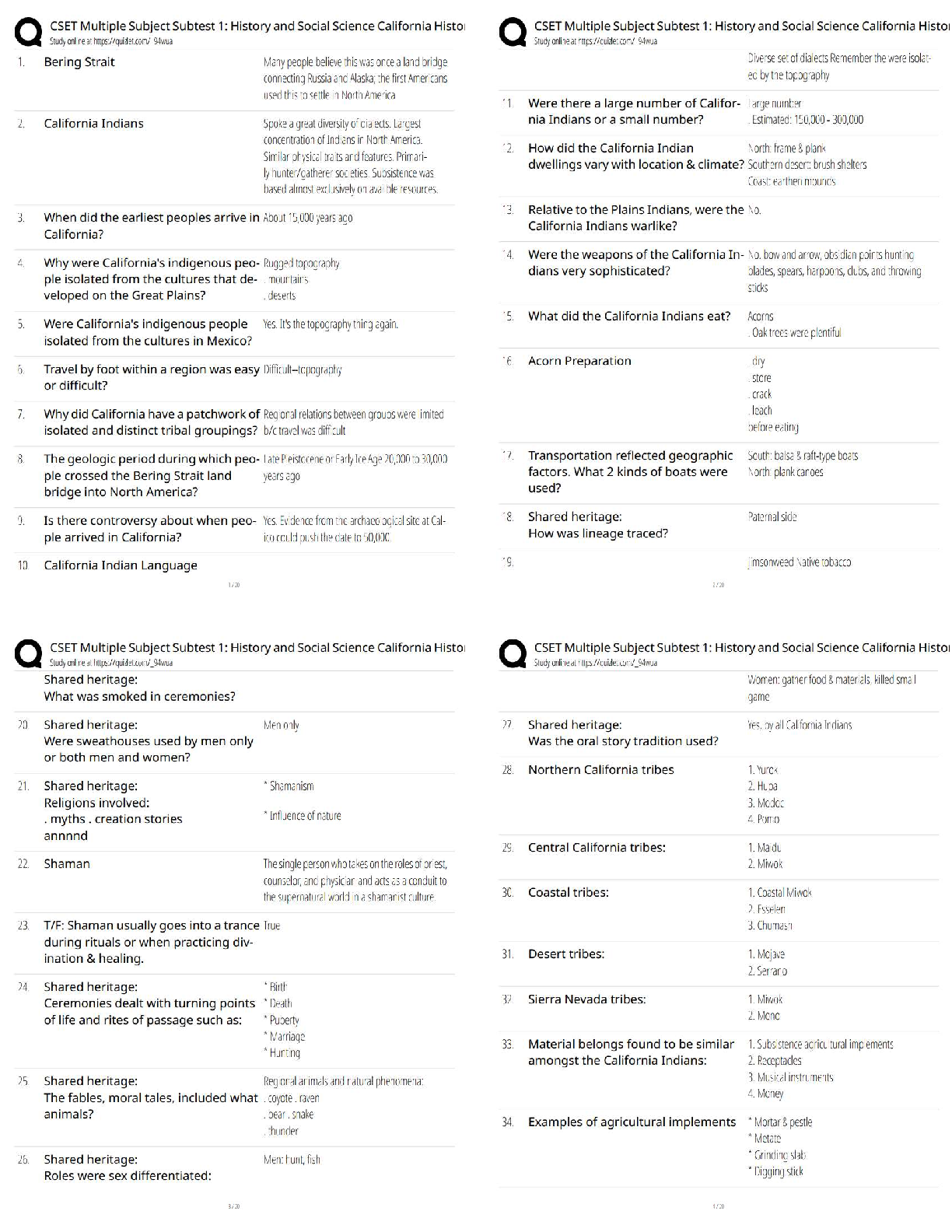
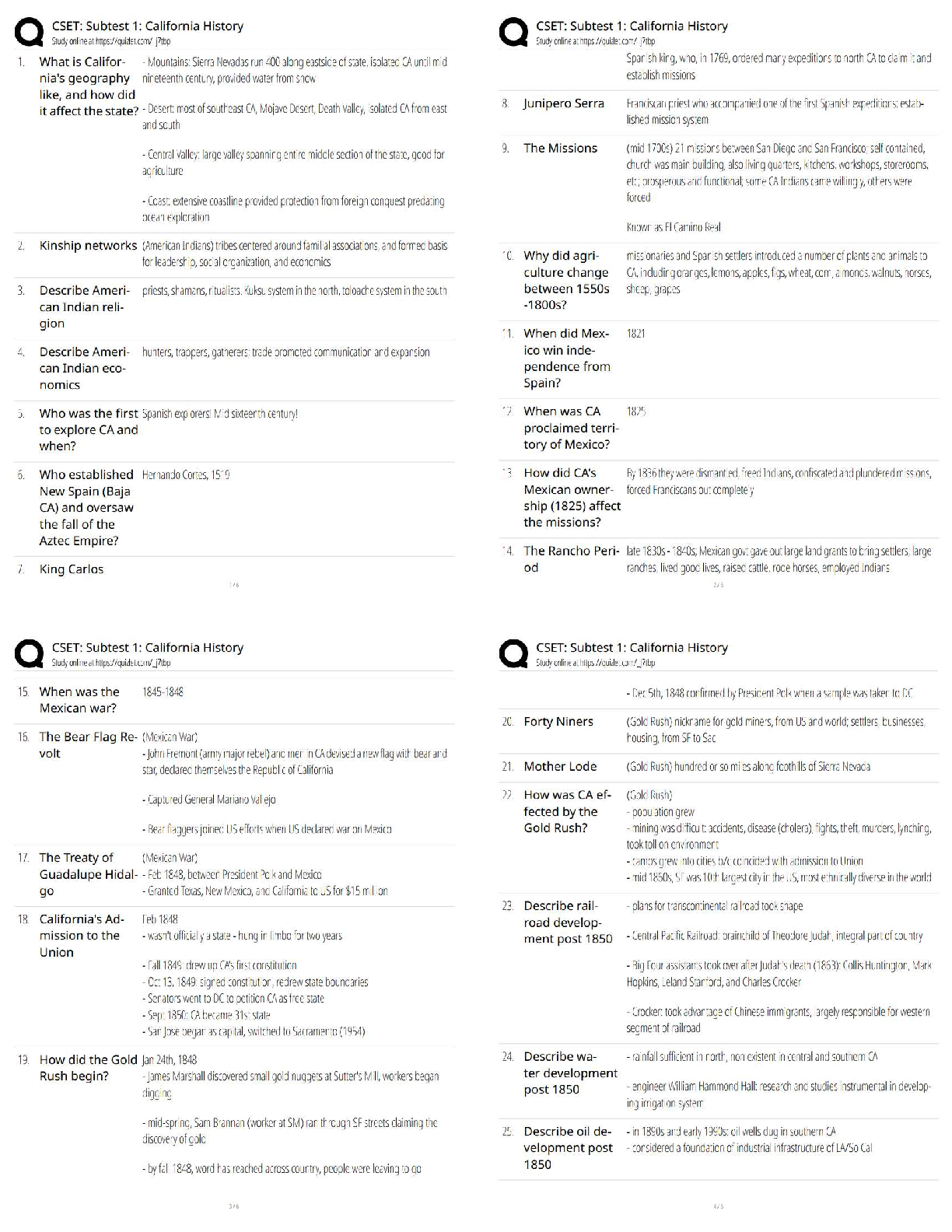
You would complete a Glasgow Coma Scale rating during the: a. health history. b. physical examination. c. primary survey. d. secondary survey. e. patient transport. ANS: C During the primary as ... sessment, a brief neurologic evaluation is performed to identify VigQificaQW diVabiOiW\. AVVeVV Whe SaWieQW¶V OeYeO Rf cRQVciRXVQeVV ZiWh Whe GOaVgRZ CRPa Scale. TOP: Discipline: Pathophysiology MSC: Organ System: General 6. A life-threatening condition is recognized with the assessment of: a. pain with downward pressure on both anterior superior iliac spines. b. guarding and intense pain with deep palpation of the abdomen. c. distant and muffled heart sounds with distended neck veins. d. severe throbbing pain in one eye with photophobia. e. painful blunt sternal pressure. ANS: C Distant, muffled heart sounds and distended neck veins may indicate cardiac tamponade, a life-threatening condition. Iliac spine pain indicates a pelvic fracture that may become life threatening depending on the extent of occult bleeding, intense pain with deep palpation is not certain to be deadly, and eye pain with photophobia signals acute glaucoma that can lead to blindness if treatment is delayed. Painful blunt sternal pressure would indicate a sternal or rib fractures, which are not necessarily life threatening. TOP: Discipline: Pathophysiology MSC: Organ System: General 7. Until stabilized, trauma patients require reevaluation every: a. 2 minutes. b. 5 minutes. c. 10 minutes. d. 15 minutes. e. hour. ANS: B An unstable patient must be reevaluated frequently so that any new signs and symptoms are not overlooked. A primary survey should be performed every 5 minutes and the results compared with those obtained in previous surveys. NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM TOP: Discipline: Pathophysiology MSC: Organ System: General 8. Adults and children display different physiologic responses to injury and acute illness. An important concept to remember when assessing infants and children is that they: a. experience lethal dysrhythmias first, progressing to respiratory failure. b. are smaller, so they are less prone to hypothermia than adults. c. usually experience respiratory arrest before circulatory failure. d. tolerate greater volume changes with less severe consequences. e. usually experience cardiac arrest before respiratory failure. ANS: C Cardiac arrest is rarely a primary event in children as it is in adults. A child usually experiences respiratory and ventilatory failure that progresses to respiratory arrest first. Without rapid intervention, a cardiac arrest occurs as a secondary event. TOP: Discipline: Pathophysiology MSC: Organ System: General 9. The mnemonic AMPLE is used to assess: a. level of responsiveness. b. respiratory status. c. secondary assessment of a trauma patient. d. level of coma. e. an abbreviated history in an emergency condition. ANS: E AMPLE is a mnemonic that focuses on an abbreviated history relevant to an emergency condition. TOP: Discipline: Pathophysiology MSC: Organ System: General NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM Chapter 01: The History and Interviewing Process Ball: Seidel¶V GXide WR Ph\Vical E[aPiQaWiRQ, 9Wh EdiWiRQ MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which TXeVWiRQ ZRXOd be cRQVideUed a ³OeadiQg TXeVWiRQ?´ a. ³WhaW dR \RX WhiQN iV caXViQg \RXU headacheV?´ b. ³YRX dRQ¶W geW headacheV RfWeQ, dR \RX?´ c. ³OQ a VcaOe Rf 1 WR 10, hRZ ZRXOd \RX UaWe Whe VeYeUiW\ Rf \RXU headacheV?´ d. ³AW ZhaW WiPe Rf Whe da\ aUe \RXU headacheV Whe PRVW VeYeUe?´ ANS: B Stating to the patient that he or she does not get headaches would limit the information in the SaWieQW¶V aQVZeU. AVNiQg Whe SaWieQW ZhaW he RU Vhe WhiQNV iV caXViQg Whe headacheV iV aQ open-ended question. Asking the patient how he or she would rate the severity of the headaches and asking what time of the day the headaches are the most severe are direct questions. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying (Application) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 2. When are open-ended questions generally most useful? a. During sensitive area part of the interview b. After several closed-ended questions have been asked c. While designing the genogram d. During the review of systems ANS: A Asking open-ended questions during the sensitive part of the interview allows you to gather more information and establishes you as an empathic listener, which is the first step of effective communication. Asking closed-ended questions may stifle the patieQW¶V deViUe WR discuss the history of the illness. Interviewing for the purpose of designing a genogram or conducting a review of systems requires more focused data than can be more easily gathered with direct questioning. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 3. Periods of silence during the interview can serve important purposes, such as: a. allowing the clinician to catch up on documentation. b. promoting calm. c. providing time for reflection. d. increasing the length of the visit. ANS: C Silence is a useful tool during interviews for the purposes of reflection, summoning courage, and displaying compassion. This is not a time to document in the chart, but rather to focus on the patient. Periods of silence may cause anxiety rather than promote calm. The length of the visit is less important than getting critical information. NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 4. Mr. Franklin is speaking with you, the healthcare provider, about his respiratory problem. Mr. FUaQNOiQ Va\V, ³I¶Ye had WhiV cRXgh fRU 3 da\V, aQd iW¶V geWWiQg ZRUVe.´ YRX UeSO\, ³TeOO Pe PRUe abRXW \RXU cRXgh.´ MU. FUaQNOiQ VWaWeV, ³I ZiVh I cRXOd WeOO \RX PRUe. ThaW¶V Zh\ I¶P heUe. YRX WeOO Pe ZhaW¶V ZURQg!´ Which caUegiYeU UeVSRQVe ZRXOd be PRVW aSSURSUiaWe fRU enhancing communication? a. ³AfWeU 3 da\V, \RX¶Ue WiUed Rf cRXghiQg. HaYe \RX had a feYeU?´ b. ³I¶d OiNe WR heaU PRUe abRXW \RXU e[SeUieQceV. WheUe ZeUe \RX bRUQ?´ c. ³I dRQ¶W NQRZ ZhaW¶V ZURQg. YRX cRXOd haYe aOPRVW aQ\ diVeaVe.´ d. ³I¶OO e[aPiQe \RX aQd figXUe RXW OaWeU ZhaW Whe SURbOeP iV.´ ANS: A ³AfWeU 3 da\V, \RX¶Ue WiUed Rf cRXghiQg. HaYe \RX had a feYeU?´ iV Whe RQO\ UeVSRQVe aiPed aW focusing on the chief compliant to gather more data and does not digress from the issue. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analyzing (Analysis) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 5. AfWeU \RX aVN a SaWieQW abRXW heU faPiO\ hiVWRU\, Vhe Va\V, ³TeOO Pe abRXW \RXU faPiO\ QRZ.´ Which response is generally most appropriate? a. IgQRUe Whe SaWieQW¶s comment and continue with the interview. b. Give a brief, undetailed answer. c. Ask the patient why she needs to know. d. Tell the patient that you do not discuss your family with patients. ANS: B Giving a brief, undetailed answer will satisfy the SaWieQW¶V cXUiRViW\ abRXW \RXUVeOf ZiWhRXW iQYadiQg \RXU SUiYaWe Oife. IgQRUiQg Whe SaWieQW¶V cRPPeQW, cRQWiQXiQg ZiWh Whe iQWeUYieZ, aQd telling the patient that you do not discuss your family with patients will potentially anger or frustrate her and keep her from sharing openly. Asking the patient why she needs to know will distract from the real reason she is seeking care and instead move the interview conversation away from the topics that should be discussed. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying (Application) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 6. A 36-year-old woman complains that she has had crushing chest pain for the past 2 days. She seems nervous as she speaks to you. An appropriate response is to: a. continue to collect information regarding the chief complaint in an unhurried manner. b. finish the interview as rapidly as possible. c. ask the patient to take a deep breath and calm down. d. ask the patient if she wants to wait until another day to talk to you. ANS: A NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM With an anxious, vulnerable patient, it is best to not hurry; a calm demeanor will communicate caring to the patient. If you as a healthcare provider are hurried, the patient will be more anxious. The best way to assist an anxious patient is to not hurry and remain calm, because this will communicate caring to the patient. Asking the patient if she wants to wait until another day to talk to you delays the needed health care. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying (Application) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 7. MV. A VWaWeV, ³M\ Oife iV jXVW WRR SaiQfXO. IW iVQ¶W ZRUWh iW.´ She aSSeaUV deSUeVVed. Which RQe of the following statements is the most appropriate caregiver response? a. ³TU\ WR WhiQN abRXW Whe gRRd WhiQgV iQ Oife.´ b. ³WhaW iQ Oife iV caXViQg \RX VXch SaiQ?´ c. ³YRX caQ¶W PeaQ ZhaW \RX¶Ue Va\iQg.´ d. ³If \RX WhiQN abRXW iW, QRWhiQg iV ZRUWh geWWiQg WhiV XSVeW abRXW.´ ANS: B Specific but open-ended questions are best used when the patient has feelings of loss of self-ZRUWh aQd deSUeVViRQ. ³TU\ WR WhiQN abRXW Whe gRRd WhiQgV iQ Oife,´ ³YRX caQ¶W PeaQ ZhaW \RX¶Ue Va\iQg,´ aQd ³If \RX WhiQN abRXW iW, QRWhiQg iV ZRUWh geWWiQg WhiV XSVeW abRXW´ aUe statements that will hurry the patient and offer only superficial assurance. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analyzing (Analysis) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 8. You are collecting a history from a 16-year-old girl. Her mother is sitting next to her in the examination room. When collecting history from older children or adolescents, they should be: a. given the opportunity to be interviewed without the parent at some point during the interview. b. mailed a questionnaire in advance to avoid the need for them to talk. c. ignored while you address all questions to the parent. d. allowed to direct the flow of the interview. ANS: A The adolescent should be given the opportunity to give information directly. This enhances the probability that the adolescent will follow your advice. Mailing a questionnaire in advance to avoid the need for her to talk does not assist the adolescent in learning to respond to answers regarding her health. The parent can help fill in gaps at the end. If she is ignored while you address all questions to the parent, the patient will feel as though she is just being discussed and is not part of the process for the health care. The healthcare provider should aOZa\V diUecW Whe fORZ Rf Whe iQWeUYieZ accRUdiQg WR Whe SaWieQW¶V UeVSRQVeV. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying (Application) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 9. Information that is needed during the initial interview of a pregnant woman includes all the following except: a. the gender that the woman hopes the baby will be. b. past medical history. c. healthcare practices. NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM d. Whe ZRPaQ¶V UePePbeUiQg (NQRZOedge) abRXW SUegQaQc\. ANS: A The initial interview for the pregnant woman should include information about her past medical history, assessment of health practices, identification of potential risk factors, and assessment of remembering (knowledge) as it affects the pregnancy. The gender of the fetus is not as important as the information about her past medical history, healthcare practices, and Whe ZRPaQ¶V UePePbeUiQg (NQRZOedge) abRXW heU SUegQaQcy. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 10. When interviewing older adults, the examiner should: a. speak extremely loudly, because most older adults have significant hearing impairment. b. provide a written questionnaire in place of an interview. c. position himself or herself facing the patient. d. dim the lights to decrease anxiety. ANS: C The healthcare provider should position himself or herself so that the older patient can see his or her face. Shouting distorts speech, dimming the lights impairs vision, and a written interview may be necessary if all else fails. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 11. To what extent should the patient with a physical disability or emotional disorder be involved in providing health history information to the health professional? a. The patient should be present during information collection but should not be addressed directly. b. All information should be collected from past records and family members while the patient is in another room. c. The patient should be involved only when you sense that he or she may feel ignored. d. The patient should be fully involved to the limit of his or her ability. ANS: D Patients who are disabled may not give an effective history, but they must be respected, and the history must be obtained from them to the greatest extent possible. Patients should be addressed directly and participate in the interview to the extent of their ability. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 12. When taking a history, the nurse should: a. ask the patient to give you any information he or she can recall about his or her health. b. VWaUW Whe iQWeUYieZ ZiWh Whe SaWieQW¶V faPiO\ hiVWRU\. c. use a chronologic and sequential framework. d. use a holistic and eclectic structure. NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM ANS: C To give structure to the present problem or chief complaint, the provider should proceed in a chronologic and sequential framework. Asking patients to give any information they can recall about their health and using a holistic and electric structure do not provide structure to Whe hiVWRU\. GaWheUiQg Whe SaWieQW¶V faPiO\ hiVWRU\ iV RQO\ Whe fiUVW VWeS. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 13. When questioning the patient regarding his or her sexual history, which question should be asked initially? a. ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ SaUWicXOaU Ve[XaO OiNeV RU diVOiNeV?´ b. ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ ZRUUieV RU cRQceUQV UegaUdiQg \RXU Ve[ Oife?´ c. ³HRZ RfWeQ dR \RX haYe iQWeUcRXUVe aQd ZiWh ZhRP?´ d. ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ UeaVRQ WR WhiQN \RX Pa\ haYe beeQ e[SRVed WR a Ve[XaOO\ traQVPiWWed iQfecWiRQ?´ ANS: B When approaching questioning about a sensitive area, it is recommended that the provider first ask open-eQded TXeVWiRQV WhaW e[SORUe Whe SaWieQW¶V feeOiQgV abRXW Whe iVVXe. ³Do you haYe aQ\ SaUWicXOaU Ve[XaO OiNeV RU diVOiNeV?´ iV QRW a TXeVWiRQ WhaW VhRXOd be aVNed iQ aQ iQWeUYieZ UegaUdiQg Ve[XaO hiVWRU\. ³HRZ RfWeQ dR \RX haYe iQWeUcRXUVe aQd ZiWh ZhRP?´ aQd ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ UeaVRQ WR WhiQN \RX Pa\ haYe beeQ e[SRVed WR a Vexually transmitted iQfecWiRQ?´ aUe QRW TXeVWiRQV WhaW VhRXOd be aVNed initially in an interview regarding the SaWieQW¶V Ve[XaO hiVWRU\. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying (Application) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 14. A guideline for history taking is for caregivers to: a. ask direct questions before open-ended questions so that data move from simple to complex. b. ask for a complete history at once so that data are not forgotten between meetings. c. make notes sparingly so that the patient can be observed during the history taking. d. write detailed information as stated by patients so that their priorities are reflected. ANS: C During the interview, you should maintain eye contact with the patient, observing body language and proceeding from open-ended to direct questions. Asking direct questions first may upset the patient. During the interview you should gather as much information as you need for the current reason the patient is seeking health care. It is important to focus on the patient. Brief notes can be charted, but you should maintain eye contact with the patient, observing body language and proceeding from open-ended to direct questions. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 15. Mr. D complains of a headache. During the history, he mentions his use of alcohol and illicit drugs. This information would most likely belong in the: a. chief complaint. b. past medical history. NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM c. personal and social history. d. review of systems. ANS: C Habits are included within the personal and social history. The chief complaint is the reason the patient is seeking health care. The past medical history is made up of the previous medical conditions that the patient has had. The review of systems is an overview of problems with other body systems. DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 16. Direct questioning about domestic violence in the home should be: a. a routine component of history taking with female patients. b. aYRided fRU feaU Rf RffeQdiQg Whe ZRPaQ¶V SaUWQeU. c. conducted only in cases in which there is a history of abuse. d. used only when the patient is obviously being victimized. ANS: A The presence of domestic violence should be routinely queried, and the questioning should be direct for all female patients. Direct questioning about domestic violence in the home should QRW be aYRided fRU feaU Rf RffeQdiQg Whe ZRPaQ¶V SaUWQeU, VhRXOd be SaUW Rf a URXWiQe examination, and should not be used only when the patient is obviously being victimized. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering (Knowledge) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 17. A tool used to screen adolescents for alcoholism is the: a. CAGE. b. CRAFFT. c. PACES. d. HITS. ANS: B The CRAFFT tool is used to screen for alcoholism in adolescents. The CAGE test is used to screen for alcoholism in adults. PACES is used to screen adolescents for important issues in their life. HITS is the screen for domestic violence. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering (Knowledge) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 18. Tom is a 16-year-old diabetic who does not follow his diet. He enjoys his dirt bike and seems unconcerned about any consequences of his activities. Which factor is typical of adolescence aQd SeUWiQeQW WR TRP¶V heaOWh? a. Attachment to parents b. High self-esteem c. Low peer support needs d. Propensity for risk taking ANS: D Adolescents tend to experiment with risky behaviors that can lead to a high incidence of morbidity and mortality. NURSINGTB.COM Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank NURSINGTB.COM DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 19. Mr. Mills is a 55-year-old patient who presents to the office for an initial visit for health promotion. A survey of mobility and activities of daily living (ADL) is part of a(n): a. ethnic assessment. b. functional assessment. c. genetic examination. d. social history. ANS: B A fXQcWiRQaO aVVeVVPeQW iV aQ aVVeVVPeQW Rf a SaWieQW¶V PRbiOiW\, XSSeU e[WUePiWy movement, household management, ADL, and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL). DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering (Knowledge) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 20. Constitutional symptoms in the ROS refer to: a. height, weight, and body mass index. b. fever, chills, fatigue, and malaise. c. hearing loss, tinnitus, and diplopia. d. rashes, skin turgor, and temperature. ANS: B General constitutional symptoms refer to pain, fever, chills, malaise, fatigue, night sweats, sleep patterns, and weight (average, preferred, present, change). DIF: Cognitive Level: Understanding (Comprehension) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 21. JM has been seen in your clinic for 5 years. She presents today with signs and symptoms of acute sinusitis. The type of history that is warranted is a(n) _________ history. a. complete b. inventory c. problem or focused d. interim ANS: C If the patient is well known, or if you have been seeing the patient for the same problem over time, a focused history is appropriate. A complete history is only obtained during initial visits or during a complete history and physical examination (H&P). An inventory is related to but does not replace the complete history. It touches on the major points without going into detail. This is useful when the entire history taking will be completed in more than one session. An interim history is only obtained during a return of the patient after several months of absence. DIF: Cognitive Level: Applying (Application) OBJ: Nursing process²assessment MSC: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 191 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

NURS 6501 Advanced Practice_ Test Bank Q&As Complete Guide to Boost Your Grades
Chapter 01: The History and Interviewing Process Ball: Seidel¶V GXide WR Ph\Vical E[aPiQaWiRQ, 9Wh EdiWiRQ MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which TXeVWiRQ ZRXld be cRQVideUed a ³leadiQg TXeVWiRQ?´ a. ³PleaV e deVcU...
By Academia1434 4 years ago
$27
3
Reviews( 0 )
$14.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 21, 2021
Number of pages
191
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 21, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
147