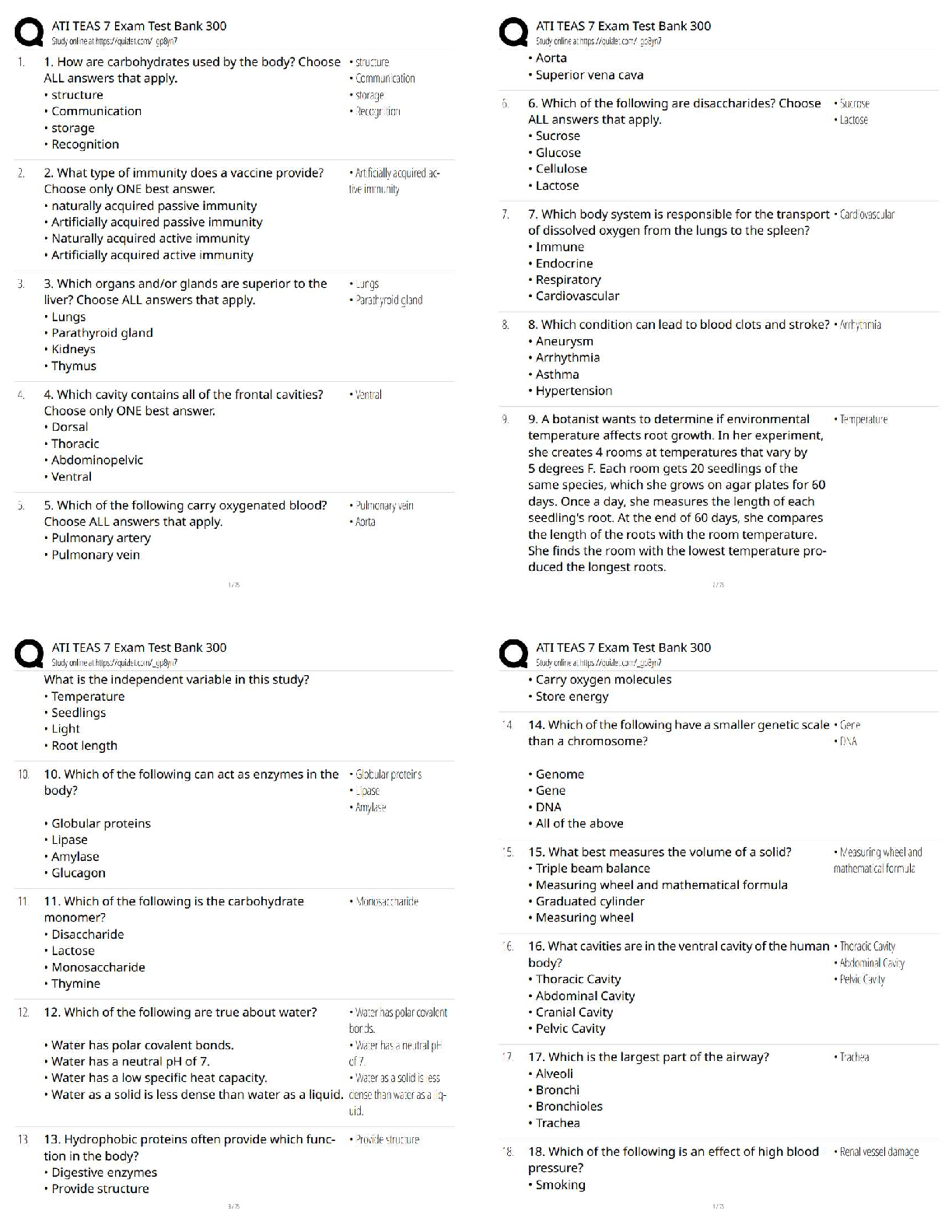
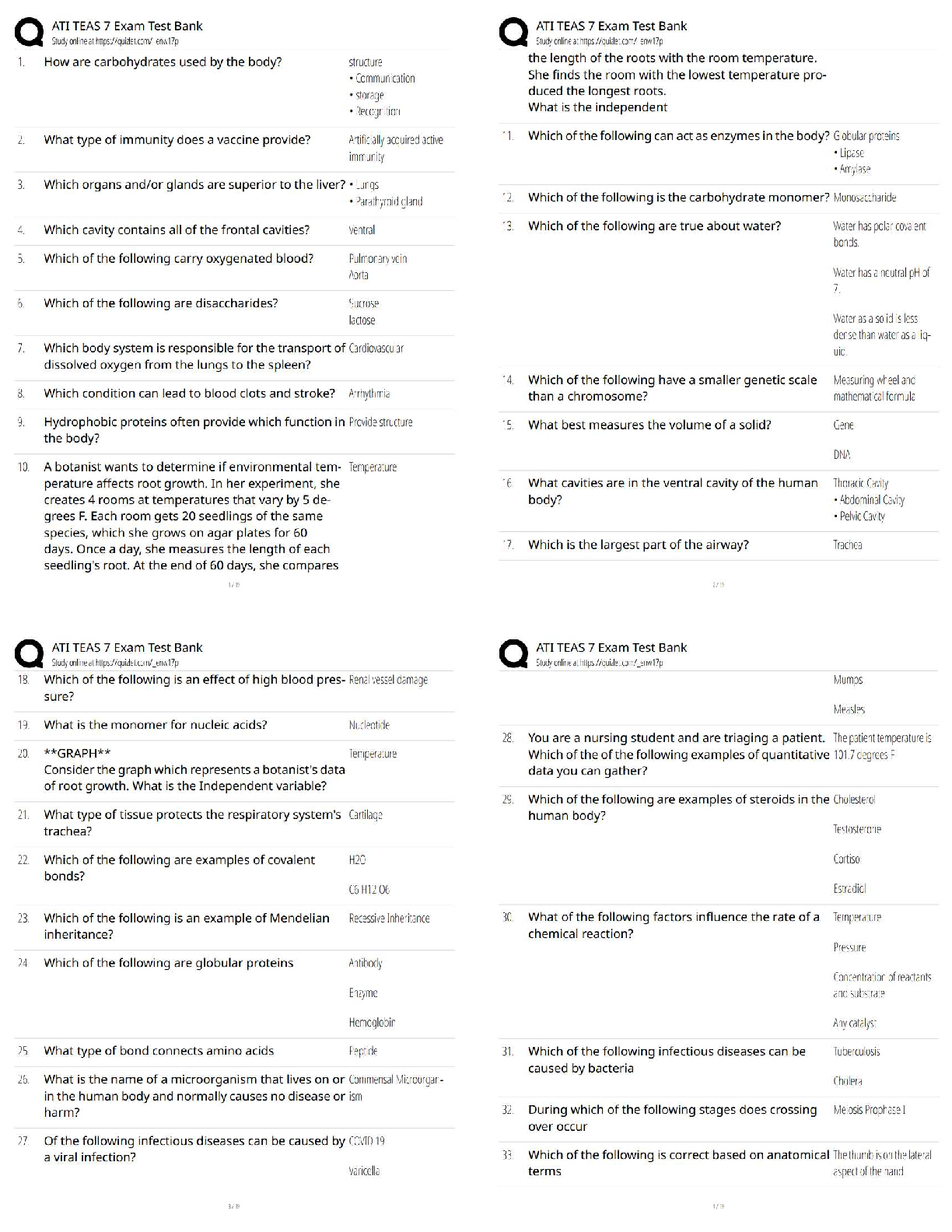
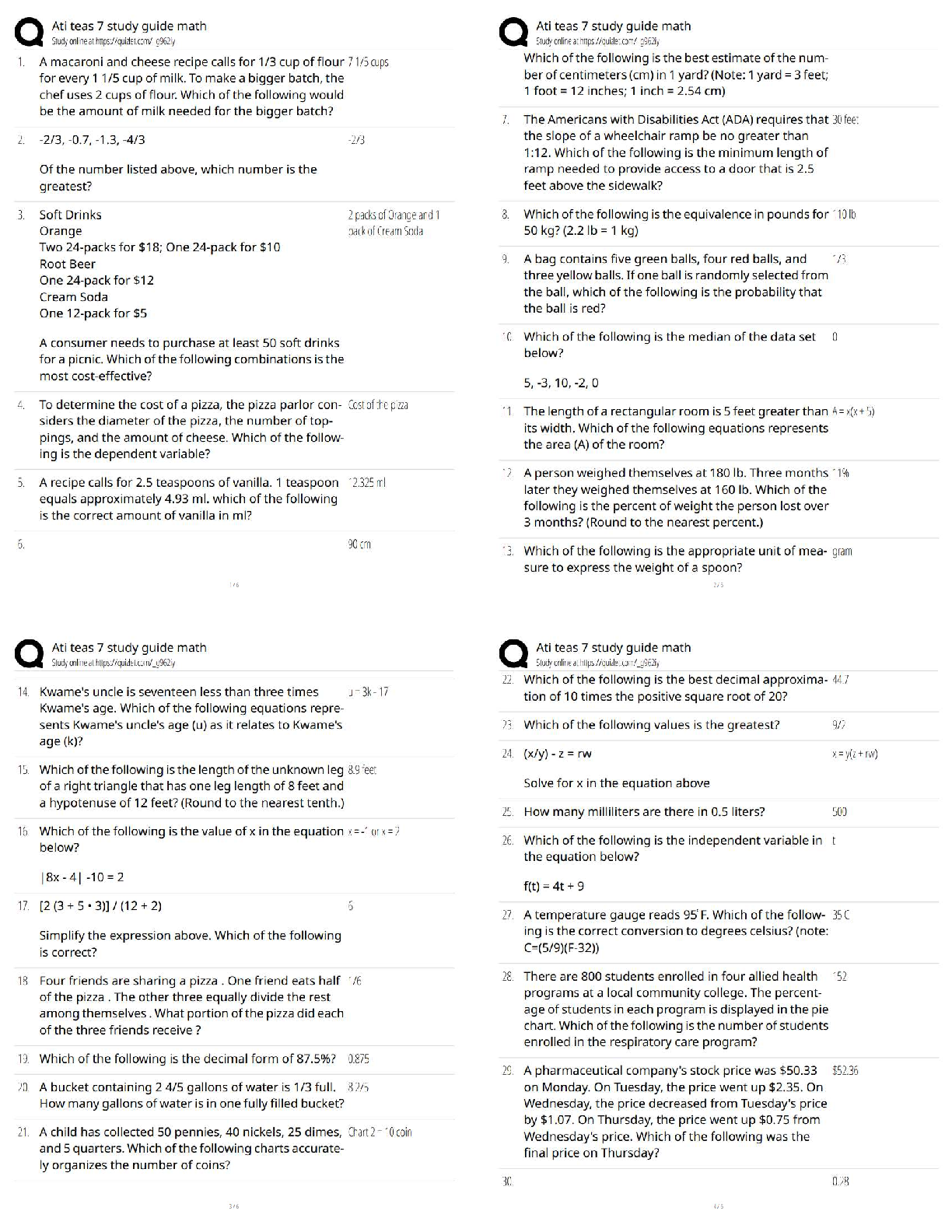
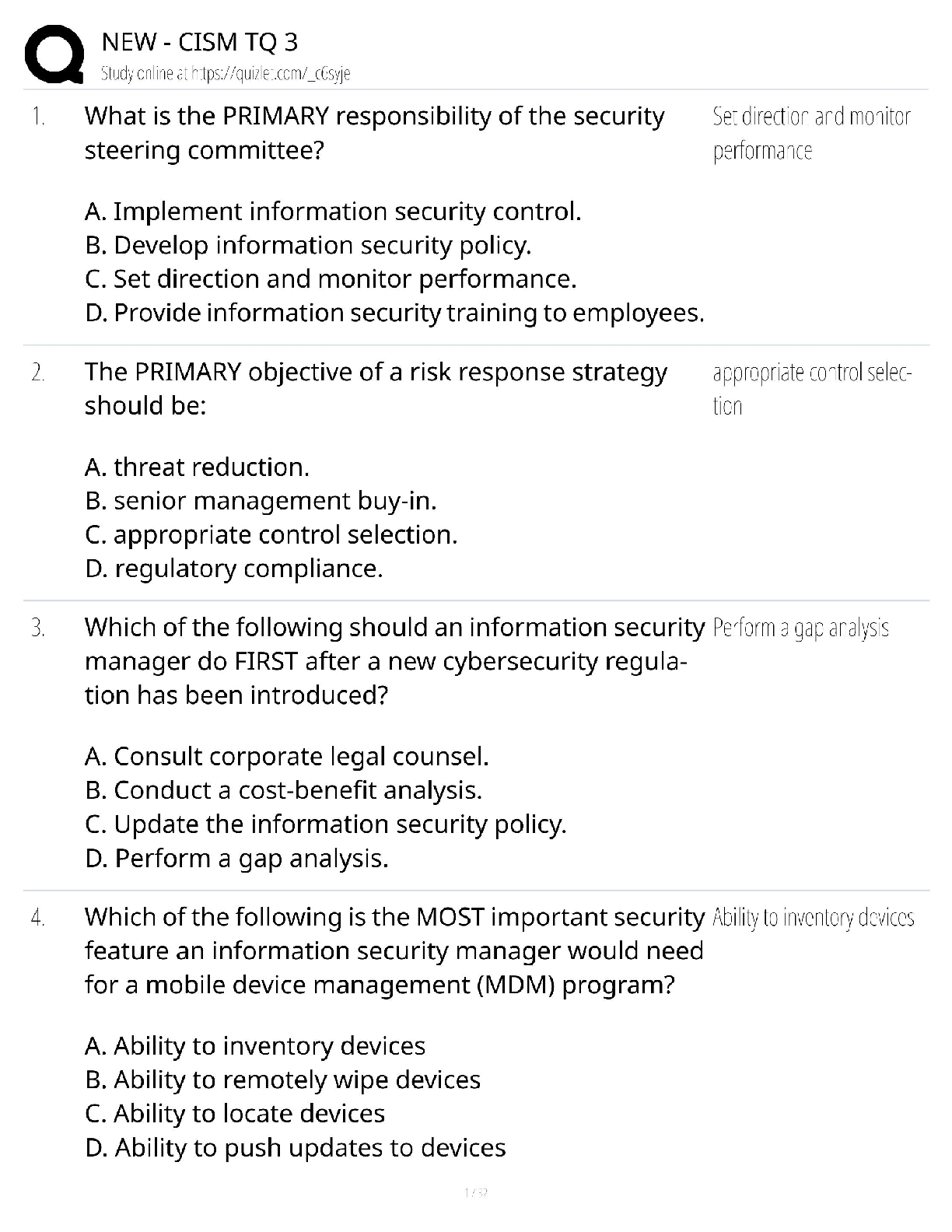
CARBOHYDRATE BIOCHEMISTRY
1 (a) Show the structural formulae of the following carbohydrates;
(i) D- Xylose
(ii) D- Erythrulose
(iii) �- D- Arabinofuranose
(iv) �- D-Galactopyranosyl (1 ->4) �- D- Glucopyranoside
(b
...
CARBOHYDRATE BIOCHEMISTRY
1 (a) Show the structural formulae of the following carbohydrates;
(i) D- Xylose
(ii) D- Erythrulose
(iii) �- D- Arabinofuranose
(iv) �- D-Galactopyranosyl (1 ->4) �- D- Glucopyranoside
(b) Using a relevant example, describe epimerism in monosaccharides.
(c) Describe the various conformations of D-glucopyranose. Which is the most
stable conformation? Explain.
(d) Which compound is formed when carbonyl group of galactose is reduced?
Show its structure.
(e) Write the chemical reaction between glucose and warmed anhydrous methanol
containing HCL.
(f) Illustrate the formation of �-D-fructofuranose
2. (a) Write the structure of milk disaccharide. Explain the medical condition
associated with its metabolism.
(b) Sucrose consumption is implicated in dental decay. Offer a biochemical
explanation for this condition.
(c) Describe the structure of and function of;
(i) Raffinose.
(ii) Galactinol. Explain the clinical implication of Galactinol.
3 (a) Like starch, cellulose is a polymer of D-glucose yet has a remarkably different
biochemical role. Explain.
(b) Write the structure of heparin and explain its application in medicine.
(c) A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor whereas a person
with blood group AB is said to be a universal recipient. Offer a biochemical
explanation.
4 (a) Chondroitin sulfate and keratin sulfate are components of cartilage which binds
the collagen. What structural features of these 2 glycosaminoglycans that suits
this function.
1
(b) The structure of the cell wall is used to categorize bacteria as either gram
positive or negative bacteria. In reference to polysaccharides, describe the
structural differences between these two categories of bacteria.
(c) Name 2 antibiotics that target bacterial cell wall as their mode of action. Explain
their mode of action.
(d) Hyaluronic acid has both functional and structural roles in the body. In reference
[Show More]
.png)