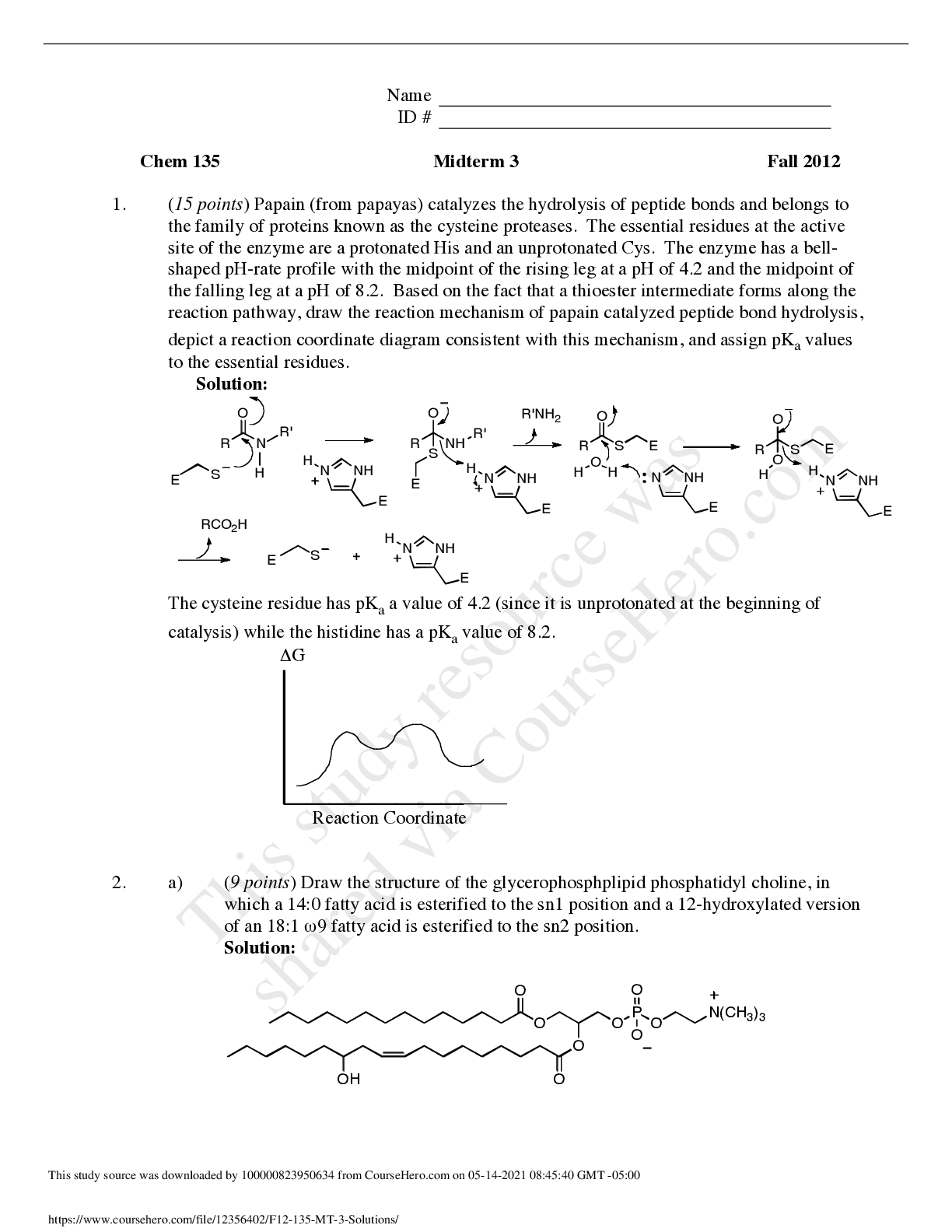
IELTS Speaking Actual Tests and Suggested Answers (September – December 2018)
$ 12

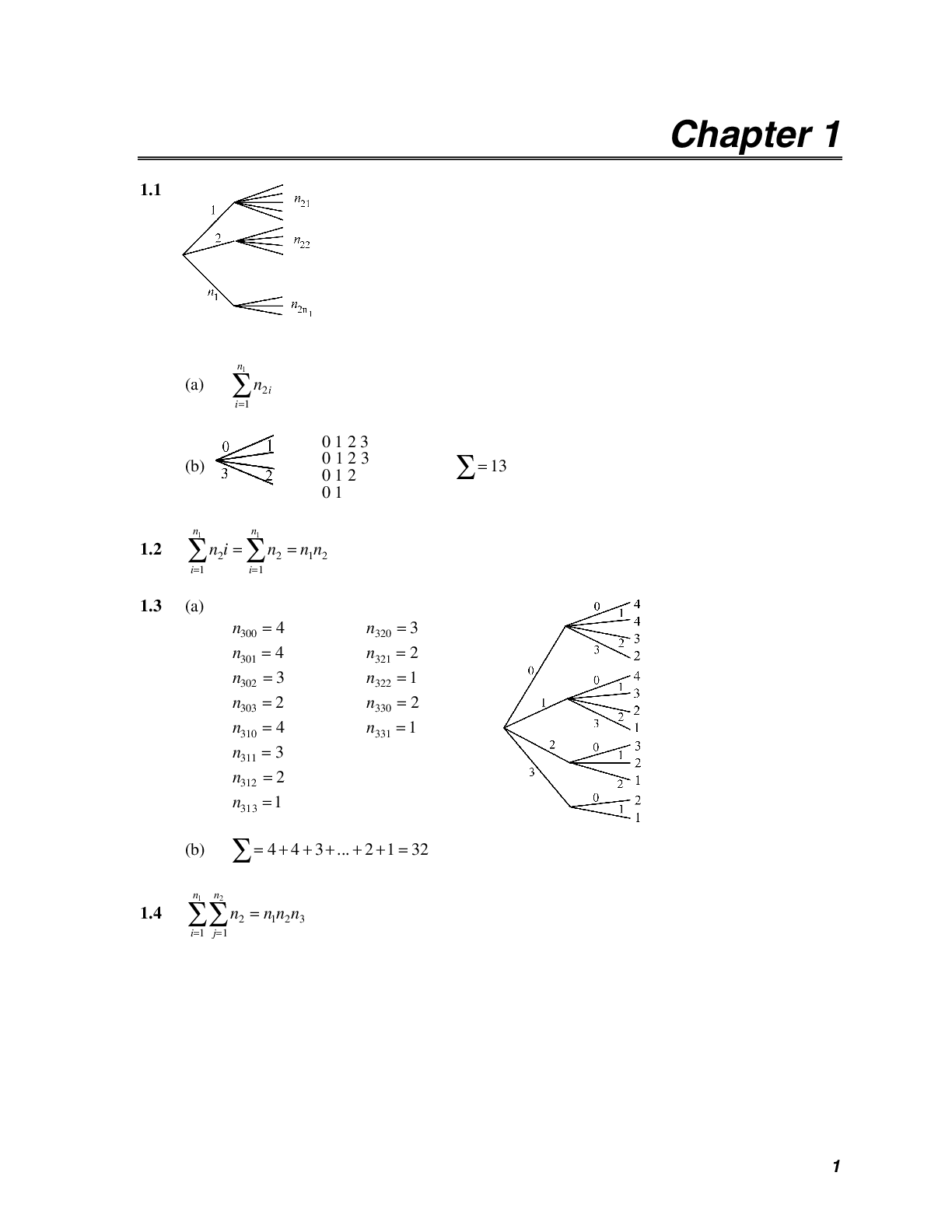
5.6.4 Journal - Designing a Mountain Landscape (Journal) University of Washington MATH MISC
$ 4

Splunk Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 10

PPI FE Civil Practice – Comprehensive Practice for the NCEES FE Civil Exam First Edition by Michael R. Lindeburg PE (Author)
$ 35

NCLEX U-World PHARMACOLOGY-TEST BANK (QUESTIONS & CORRECT ANSWERS)
$ 15

Pearson Edexcel IAL In AS/A Level Mathematics Statistics S1 WST01/01 Paper 01. Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022
$ 4

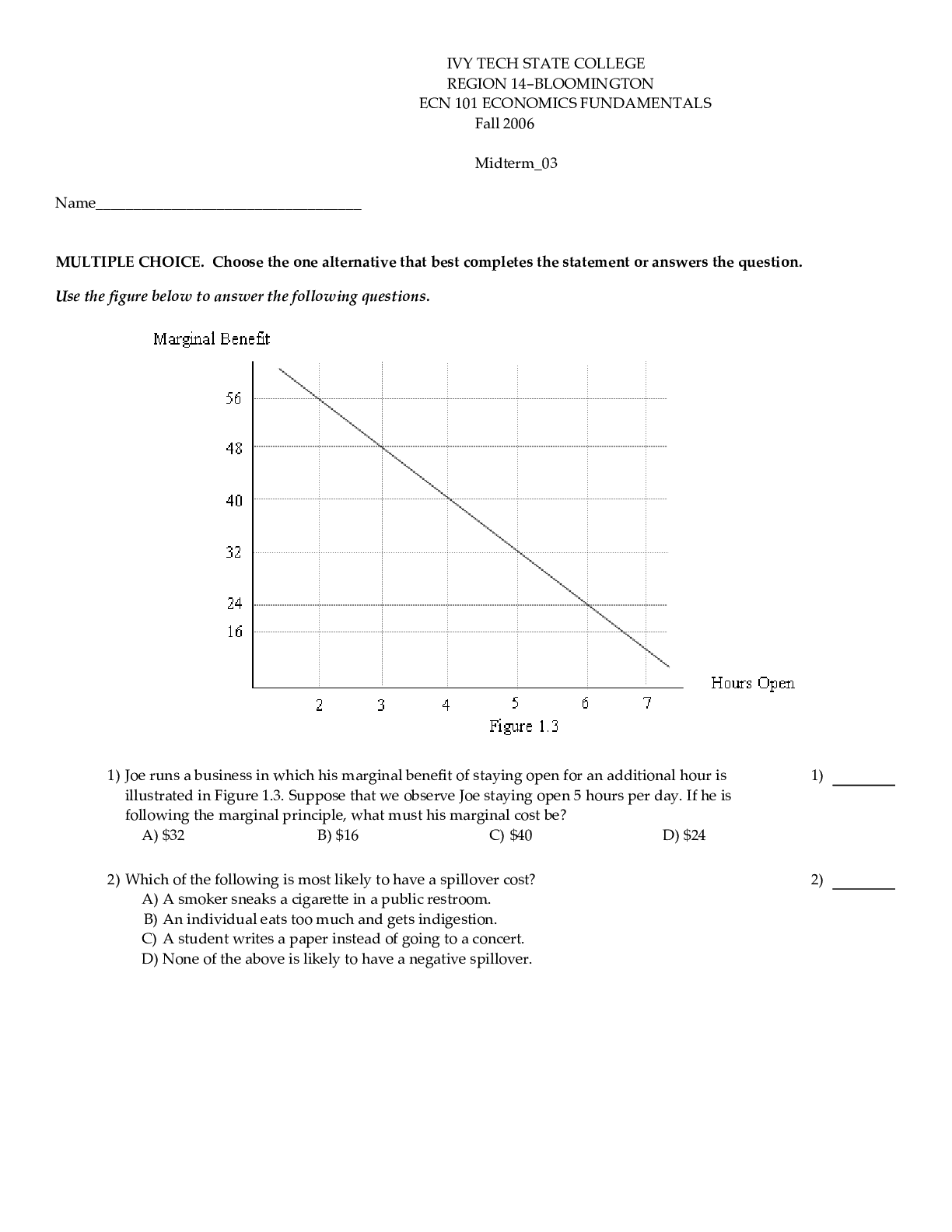
Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics B Paper 2. predictor questions. 100% approved pass rate.
$ 9

MATH 225N Week 4 Probability Questions and answers(All Correct Answers) 2021
$ 15

eBook [PDF] Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Vehicles 1st Edition By Kamal Malik, Moolchand Sharma, Suman Deswal
$ 20

Pharm 1 study guide
$ 11

eBook [PDF] Highly Efficient Thermal Renewable Energy Systems 1st Edition By Vikas Verma, Sivasakthivel Thangavel , Nitesh D
$ 20

BUSOBA 3230 Exam 2 | Questions and Answers
$ 12

ISYE 6501 Midterm 1 Part B Questions And Answers( the Complete Solution)/RATED A+
$ 10.5

4A051 CDC URE Questions & Answers 2023 2024 UPDATE
$ 18

Solutions Manual for Physics of Everyday Phenomena 10th Edition By Thomas Griffith
$ 25

eBook (ISE) Technology Of Machine Tools Paperback 8e Steve Krar, Arthur Gill, Peter Smid, Robert Gerritsen
$ 29
.png)
COMMUNICATION RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
$ 2.5

WGU Introduction to Communications C464: Competency 1
$ 4

TEST BANK for Dental Materials Foundations and Applications 11th Edition, by Powers John & Wataha John
$ 13

Progression: Field Tech III - IV Conventional With Complete Solution
$ 15.5

MATH 110 Exam 8 Statistics Questions and Answers- Portage Learning.
$ 13.5

2022-2023 ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning and Mathematics
$ 5

New-Specification-Statistics-Student-Book-1
$ 18

MATH 225N Week 4 Probability Questions and answers(All Correct Answers) 2021
$ 15

A&P Case Study Module 3
$ 8
 (1).png)
Edexcel Maths A levek paper 31 statistics Mark scheme Nov 2021
$ 12

A Level Further Mathematics A_Y543/01 Mark Scheme Oct 2021 | Mechanics
$ 6

Fluid Mechanics for Chemical Engineers 4th Edition By Noel de Nevers [TEST BANK]
$ 25

Enrolled Agent Practice Exam Questions Part 1 with 100% Correct and Answers. The following are true regarding the credit for prior-year minimum tax, EXCEPT
$ 19
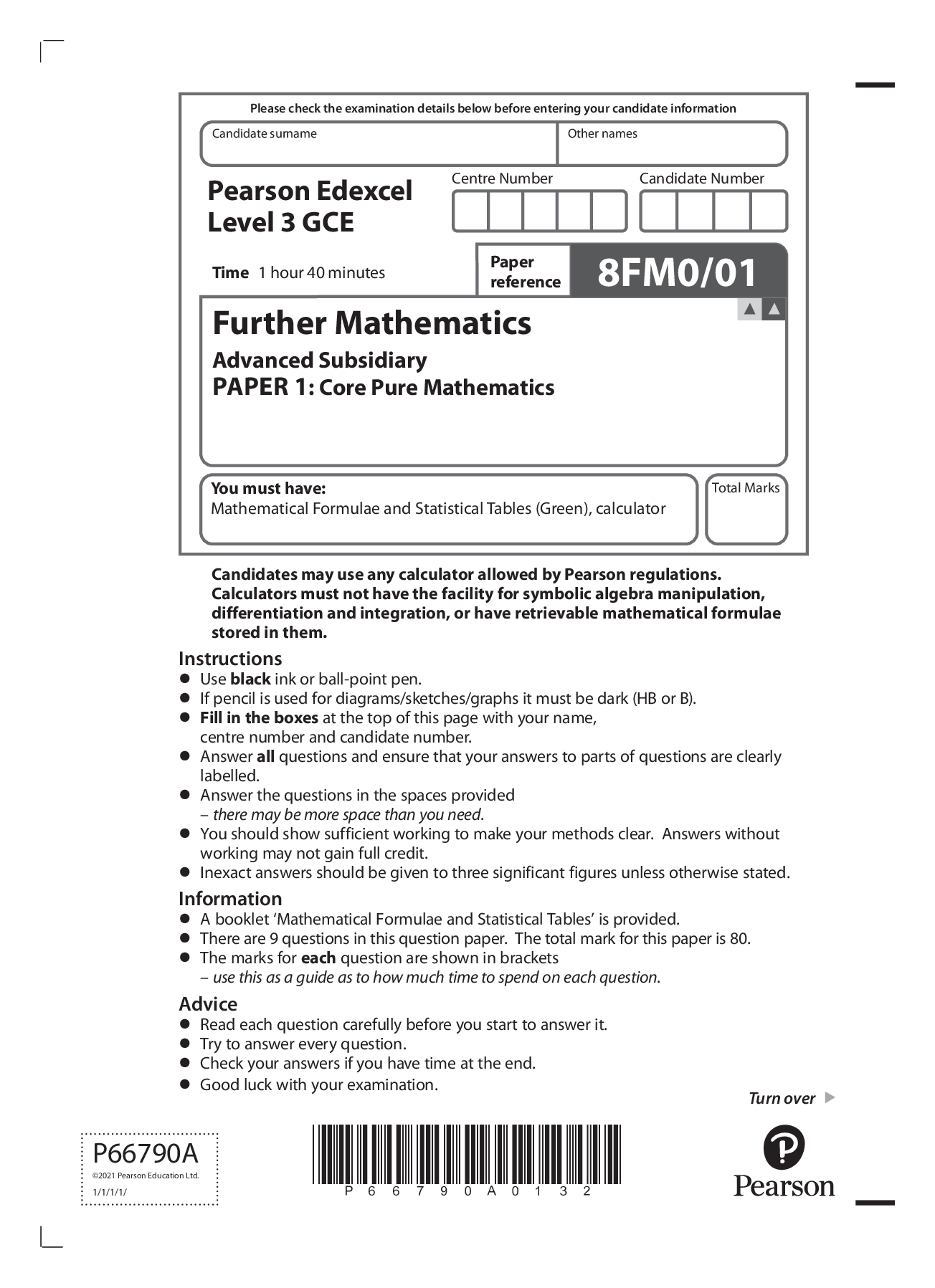
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCEFurther Mathematics Advanced Subsidiary PAPER 1: Core Pure Mathematics
$ 13
.png)
CPC Exam ICD conventions & guidelines latest 2022 100% pass
$ 7

Final Exam Study Set-SHRM-CP*/Final Exam Study Set-SHRM-CP*
$ 13

NCC-EFM Test 2023 Questions and Answers 100%
$ 5

Professional Nursing Practice & Overview of the Nursing Process Topics
$ 14
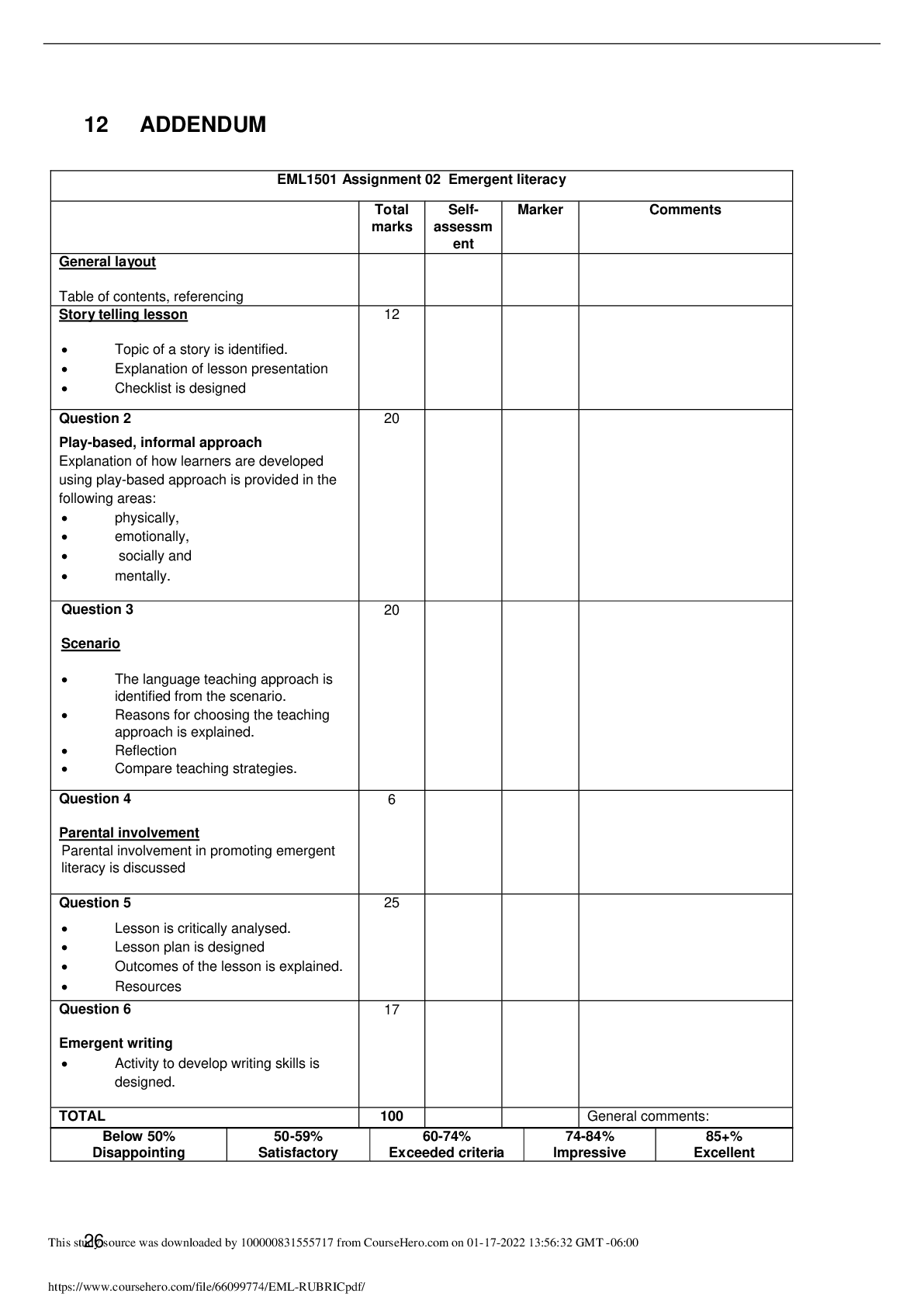
EML1501 STUDY NOTES
$ 5

Test Bank Introduction to Clinical Pharmacology 9th Edition Visovsky Chapter 1 - 19
$ 19

MATH 225N Week 8 Discussion|MATH225N Week 8 Discussion: Correlation and Regression, (Answered)
$ 10

EDEXCEL GCSE MATHS HIGHER TIER 1MA1 2H June 2025 mark scheme
$ 3.5

eBook [PDF] Class and the Uses of Poetry Symbolic Enclosures 1st Edition By Andrew Smith









.png)