Gerald Green _ iHuman patient_2020 | NR 442 iHuman patient Gerald Green
$ 5.5

Conflict and Intervention_Argument Framing Tool
$ 8
GREEK DOCUMENT WITH Q&A. SCORE 100.
$ 10
PEARSON EDEXCEL AS LEVEL FURTHER MATHS PAPER 21: Further Pure Mathematics 1 June 2023 | QUESTION PAPER
$ 7

NHA EXAM CORRECTLY SOLVED GUIDE.
$ 12

OCR GCE Mathematics B MEI H640/03: Pure Mathematics and Comprehension A Level Mark Scheme for June 2023
$ 11.5

University of Pennsylvania-CIS 501midterm13-solutions-REVIEWED BY EXPERTS 2021-ALL ANSWERS CORRECT
$ 8.5

NUR 1211 Med Surg Hesi key point both semesters_Grade A | NUR1211 Med Surg Hesi key point both semesters_School Graded
$ 10.5

CHEM 409
$ 10
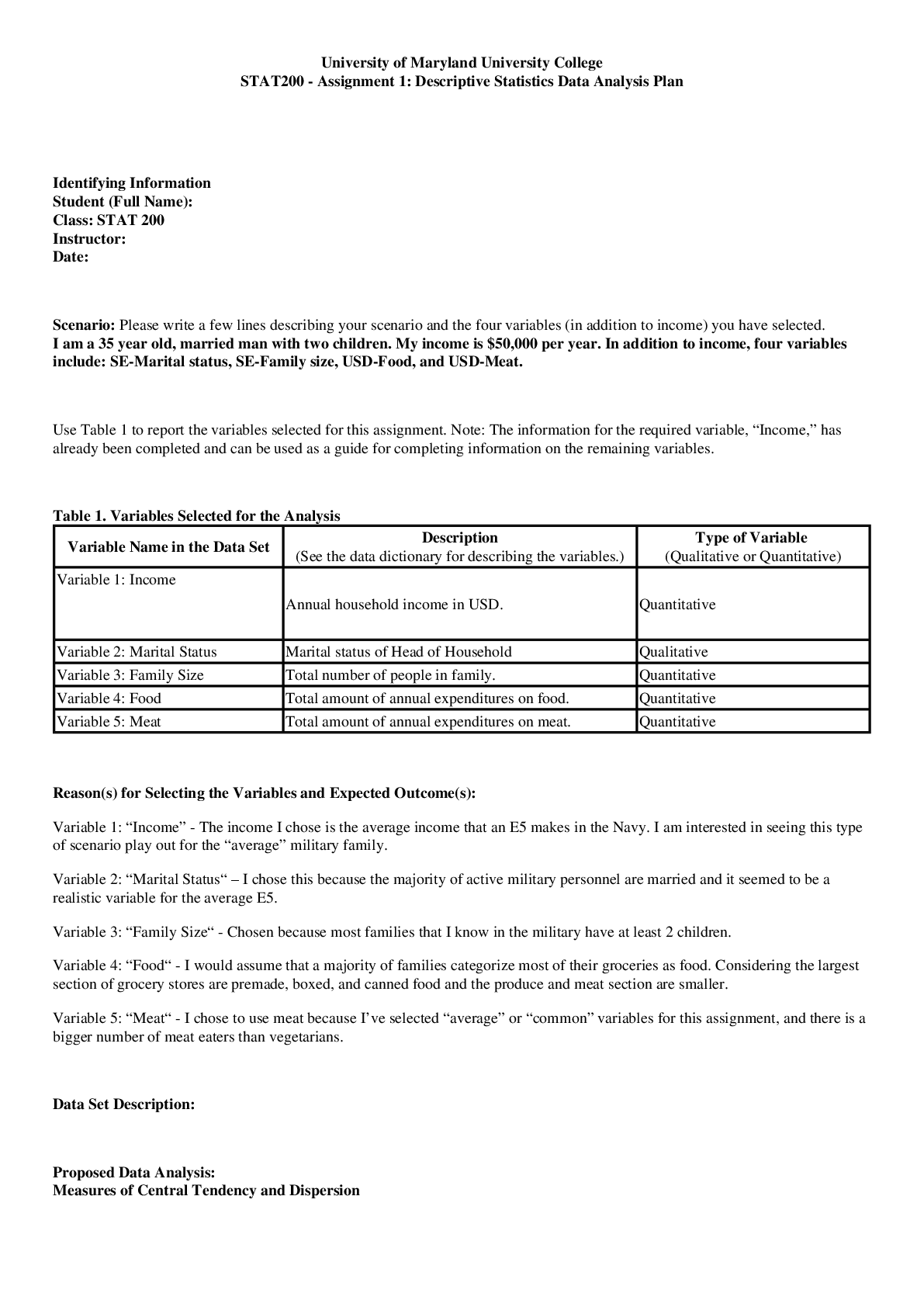
STAT200 - Assignment 1: Descriptive Statistics Data Analysis Plan
$ 10

New Generation (2025)- ATI Mental Health Proctored Exam
$ 70.5

ATI NURSING MISC EXAM (LATEST UPDATE)
$ 15

HESI BIO
$ 7

A Level History A_Y216/01 Question Paper Nov 2020 | The USA in the 19th century: Westward expansion and Civil War 1803-c.1890
$ 6.5

East Carolina University - COMM 2410Chapter 14 Lecture(1)
$ 7

GCE Further Mathematics A Y540/01: Pure Core 1 Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for Autumn 2021
$ 6.5

AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS Higher Tier Paper 3 MS 2021
$ 13.5

AQA A LEVEL PHYSICS PAPER 3 SECTION B MS 2020/ COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 15
.png)
WGU C175 Final+1+2 Latest 2022 Already Passed
$ 6
Linda Waterfall _ Feedback Log & Score_2020 | Diagnosis: Left Mastectomy_Linda_Waterfall_Graded A
$ 8

All Lines Adjuster Exam Questions and Answers 100% Pass

.png)


.png)


.png)