*NURSING > EXAM > C157 and C128 combined test with 70 Questions Answers with Rationales,100% CORRECT (All)
C157 and C128 combined test with 70 Questions Answers with Rationales,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
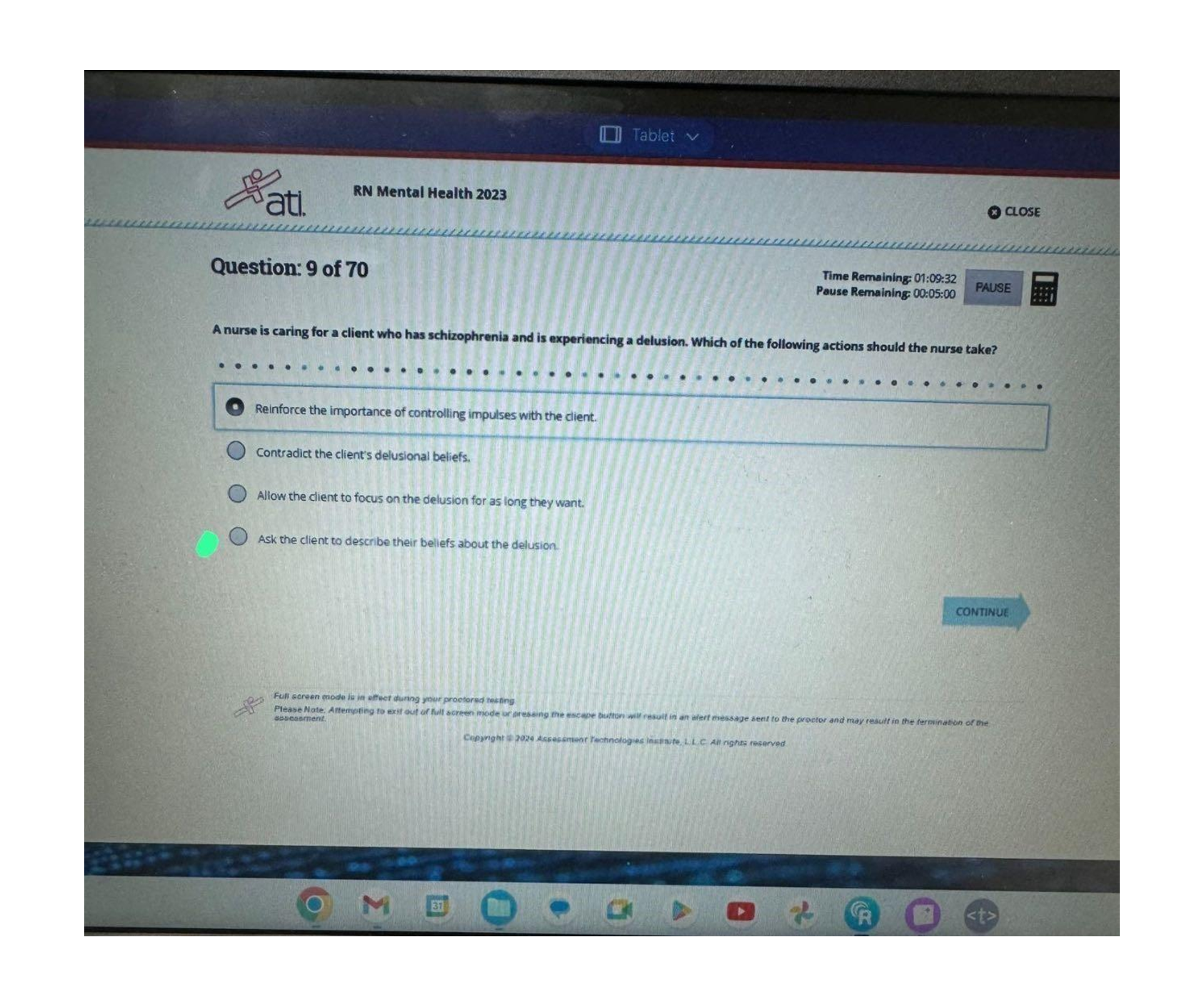
C157 and C128 combined test with 70 Questions Answers with Rationales Analyze each question and choose the best response. Record your rationale for each choice. 1. Quality improvement assumes that... : a. Most problems with service delivery result from process difficulties, not individuals. b. Frequent inspection is necessary to improve quality. c. Employees generally try to avoid work. d. Top management leads all quality improvement activities. Response A is correct. QI starts with the assumption that errors occur as a result of system failures, not individual errors. We should eliminate response C. In response B, frequent inspection might help ensure quality control over the process we have now, but will not help us exceed the capability of the existing process to improve quality. In response D, top management would be the CEO and senior management—there is not enough of them to go around to lead ‘all’ QI activities. 2. The term “quality” as used in quality improvement usually refers to: a. Characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. b. A product or service free of deficiencies. c. Having a high degree of excellence. d. All of the above. Although each of the definitions provided are different ways in which we think of attribute of “quality”, quality improvement focuses on delivering quality services or products as determined by the customer. Therefore, in QI, high “quality” rests on the ability to satisfy customer needs. A product or service that is free of deficiencies or has a high degree of excellence but does not meet the customer needs would not be considered a “quality” result (we would think of it as wasteful). Note also the IHI “Triple Aim”: • Improving the patient experience of care (including quality and satisfaction); • Improving the health of populations; and • Reducing the per capita cost of health care. 3. The major difference between traditional “quality assurance” activities (e.g., keeping track of the total number of different procedures conducted in your practice, rates of adverse outcomes) and “quality improvement” activities is that quality improvement also focuses on: a. People and competency. b. Analysis of data. c. Performance measures. d. Systems and processes. While quality improvement strategies also stress the importance of data analysis, rely on performance measures to benchmark progress, and occasionally assess individual capabilities, one of its key principles is the focus on systems and processes (rather than individuals or products) to introduce positive change to an organization’s performance. 4. Effective quality improvement does not require: a. Leadership and commitment from management with long-term vision. b. An increased emphasis on inspection of individuals’ work. c. Increased investment on employee education and training. d. Scientific redesign of processes/services Quality improvement strategies focus primarily on systems and process changes, but this does not mean that inspection of the results of individuals’ work or how well people perform in the existing systems should be ignored. Note: We’re talking about inspecting ‘work’ not a person. Inspection or observation is a scientific method used in evaluating how systems and processes are working and can provide clues on how or where to improve. So while we wouldn’t ignore the need to inspect individuals work, we also wouldn’t increase our emphasis on this aspect of the process. Strong leadership, team commitment, and enhanced education and training are all very necessary for effective QI interventions to succeed. 5. A leadership style that is said to motivate employees, and that optimizes the introduction of change is: a. Autocratic – A clear top-down approach where a single individual has complete power of decision-making and little discussion is had for external input. b. Consultative – A style where leaders engage subordinates/peers in the decision-making and problem-solving process, but ultimately make the final decisions for the team. c. Participatory – An approach where leaders interact with other participants as peers, engaging them in the decision-making process and playing an equal role in the process as others and jointly carrying out the problem solving activities. d. Democratic – An open style of running a team where leaders facilitate discussion among all members, encourage ideas to be shared, and consider everyone’s input in order to make final decisions for the team. Bringing about change in health care settings often involves the participation of all staff. Each professional plays a role in satisfying the organization’s customer (i.e., patients) since the responsibility for the care provided is shared. Therefore, whoever leads a quality effort practice should be prepared to take a central but equal (team-oriented) role in the activities identified for establishing change. Shared governance is a feature of Magnet hospital status; this is a staff-leader peer partnership that promotes collaboration, participative decision making and shared accountability for improving quality of care, safety, and enhancing work life 6. Which representatives of a CV practice should be included on a quality improvement team to implement a new practice: a. Cardiologists only. b. Cardiologists and nurse practitioners. c. Cardiologists, nurse practitioners, quality improvement staff, and practice administrator. d. All staff directly affected by the quality improvement practice to be implemented. This is important because successful implementation of an intervention most often occurs when all relevant or affected parties are aware of the changes being made or tested, have been bought into the endeavor, are willing participants, and understand what their role will be in bringing about necessary changes. This is also important because these are the people who likely know the most about the process or system being changed. 7. When is it appropriate to collect and use data? a. Before the QI project, to prove a problem exists. b. During the QI project, to answer questions about the cause and help prioritize the implementation of improvements. c. After the implementation of the improvement to maintain the gain. d. All of Above. Because quality improvement is intended to be continuous, and because data gathering and analysis is a key activity of assessing performance and areas for improvement, it is always appropriate to collect and use data to inform these processes. It is up to team members to evaluate if ceasing to collect data for a QI intervention is reasonable at any point. Or to state another way, we need to substantiate the need for a particular improvement (and its associated cost) with data. We need to collect data and analyze it during the PDSA cycles. And we often want to continue monitoring to ensure we have sustained the improvement. 8. Which of the following concerns would be best solved by a QI team? a. A computer systems issue with linking the clinical database to the hospital ADT system. b. A discipline issue with a problem employee. c. An individual customer complaint regarding lengthy wait time. d. A financial variance in cost per left heart cath procedure over the past 6 months. Substantial variation in cost for a procedure is a problem that directly affects customers and could have implications for organizational processes. It is an ideal concern for a QI team to handle. Response A is a one-time technical fix that requires little QI analysis to solve. Response B is an employee concern, best handled by senior management. Although customer complaints about long waits could warrant a situation handled by a QI team, one customer complaint is usually insufficient for establishing and investing in a QI intervention. 9. The first step in problem solving is to: a. Assume the worst. b. Establish responsibility for change. c. Collect and analyze data. d. Define the problem issue. In order to embark on any quality improvement activity, a problem that can benefit from an intervention must first be identified. In the IHI model, we identify the aim. Data collection and analysis would occur later during the PDSA cycle. We should eliminate responses A and B—neither of which are very useful. 10. After assessing current work flow and processes, a clinical team presumes that a delay can occur anywhere along the process of their tasks. Data is inadequate at this point to identify a particular time of day, day of week, type of patient, and/or step in the process that is largely responsible for the delays. Further data collection is necessary. What should the team “product” be for the next meeting? a. A prioritization matrix. b. A finalized data collection tool and instruction sheet for implementation. c. A list of questions to be answered and a draft data collection tool. d. A listing of possible solutions. Because no root causes have been identified at this point for the problem at hand, developing a list of possible solutions or a finalized data collection tool to measure activities in specific areas would be premature. A prioritization matrix would be less helpful at this point since it is more of a decision tool intended to “rank” a list of problems or metrics to focus on next. In this case, because yet more data is needed to determine what intervention to put through the PDSA cycle, a list of additional questions that the team would like answered should be created along with a draft of how to capture data that would help them drill down to a root cause or a specific process to focus on. 11. As a building block for determining whether or not quality has been improved, the use of basic descriptive statistics in applying QI is critical. Which of the following is not a strictly quantitative description of the basic features of a study? a. Mean data values. b. Frequency counts. c. Hospital ratings. d. Standard deviations. Although hospitals ratings are one way to describe a hospital’s performance or a way to compare hospitals against each other, it is not a basic component of general descriptive statistics. Mean data values, frequency counts, and standard deviations are all foundational elements of typical data analysis. Hospital ratings are usually based on a suite of indicators—some built from quantitative data and some from qualitative data. 12. Of the following, two statistics are essential for identifying opportunities for performance improvement. These are: a. Frequency counts and modes. b. Variance and distributions. c. Mean and median values. d. Data ranges and standard deviations. Unlike the other responses listed (which are also important elements of analysis for QI), variance and distribution data are key for discerning areas with the greatest potential for improvement. The greater the variance and the more varied the distribution of services provided, the greater the opportunity for improvement – more bang for the buck! The goal being to implement processes that minimize variance in performance and make higher, yet achievable, results more consistent. 13. Comparisons of your data against the top performers in your region/industry describe the process(es) of: a. External benchmarking. b. Internal benchmarking. c. Neither external nor internal benchmarking. d. Both internal and external benchmarking. External benchmarking is when an organization compares its performance data to that of a similar organization in the region (or competitor in the market). Internal benchmarking is when an organization compares its own current performance to its past performance in order to assess its improvement over time. Both approaches are good for setting desired performance targets. 14. Benchmarking creates objective measures of performance that are based on: a. Past performance targets within an organization. b. Performance of a competing external organization. c. Some external universal performance target established by the industry. d. All of the above. Setting targets for achievement (i.e., benchmarking) can be accomplished using any of the approaches listed here. Internal benchmarking (or baseline goals) uses past performance targets to set new targets going forward, whereas external benchmarking can be done either by comparing one’s performance to that the highest performing peers, or by adopting the target set, for example, by a national effort or organization targeting in on a specific QI effort. 15. Of the following quality tools, which would be most useful for identifying a problem in a process that could benefit from a quality improvement strategy? a. Control chart b. Histogram c. Flow chart d. Run chart A flow chart (or process map) would be very useful for examining the steps in a process failure to identify a root cause. 16. A patient has a terminal illness. Against the family's wishes, the patient requests a "do not resuscitate" order. Which ethical principle supports the patient's decision? a. Autonomy b. Beneficence c. Justice d. Nonmaleficence The patient is looking for self-determination—autonomy would support this. 17. Which ethical conflict places the equitable access to health care against actions that produce the greatest good? a. Autonomy versus paternalism b. Fairness versus altruism c. Justice versus utilitarianism d. Veracity versus fidelity Responses A and D should be eliminated—we’re not talking about truth, self-determination, loyalty, or treating others like children. Fairness and altruism have more to do with our emotions and concerns about others. Justice is about equality or equity; utilitarianism deals with actions resulting in the greatest good for the greatest number of people. 18. Four strategies that promote staff empowerment are adopting a shared vision, team building, relinquishing administrative control, and: a. counseling the staff frequently. --?! b. delegating final decisions to the staff. –the leaders need to retain final authority/responsibility c. providing detailed instructions of a proposed plan.—micromanaging/needs to elicit team input d. rewarding performance that adheres to high standards. 19. The nurse executive is the chair of a new performance improvement team whose purpose is to address patient flow through the emergency department. A laboratory team member openly blames emergency department nurses for a long turnaround time in obtaining patient test results. To which phase of group development does the nurse executive attribute the blaming behavior? a. Forming—the team is brought together b. Norming—team members begin to resolve differences c. Performing—team members begin to obtain results d. Storming—refers to the conflict-ridden stage of team development 20. The nurse executive develops a balanced scorecard for nursing practice by emphasizing: a. consistency over time b. customer feedback. c. financial performance. d. internal and external benchmarks. The critical characteristics that define a Balanced Scorecard: • focus on the strategic agenda of the organization concerned • selection of a small number of data items to monitor • mix of financial and non-financial data items. 21. A nurse executive sponsors a multidisciplinary team that is charged with educating patients scheduled for total joint replacement surgery, about topics including what to expect after discharge. What is the nurse executive's response when encountering resistance from team members? a. Direct the mid-level managers to reemphasize the vision to their direct reports b. Encourage the first-level managers to reinforce the vision to the team members c. Gather together the various disciplines and listen to their concerns about the project d. Reeducate the team members about how their role affects the outcome of the team Response C is the only one that respects the perspective of the team members and engenders participation. 22. The nurse executive receives notice that critical supplies have not arrived before a three-day holiday weekend. Due to a computer system error, “just-in-time" supplies were not queued for delivery. The nurse executive's next action is to: a. conduct an internal audit of supplies, compared to patient usage and census, before requesting assistance from materials management. b. contact the materials manager to expedite the delivery of supplies before the end of the work day. c. direct the department managers to negotiate for needed supplies, and allocate resources according to department census. d. mobilize personnel to facilitate the purchase of needed supplies from the available vendors. The factor to be concerned about here is time. All other responses will take valuable time to complete and may entail unnecessary work. An order for supplies from the vendor already exists but was not delivered; delivery needs to be expedited. 23. What is the primary purpose of a policy, as opposed to a procedure? a. A policy is binding in all circumstances to which the policy relates. b. A policy is broad and durable, designating actions for matters that frequently recur. c. A policy is designed to guide actions when managing exceptional situations. d. A policy is specific and detailed so as to avoid individual interpretation. A law is binding; a regulation is an interpretation of how a law is to be applied. A policy is broad and describes how people should act in a particular situation. When usual or unplanned events occur, exceptions to policy can be granted (with good justification). A procedure has detailed steps. 24. A 14-year-old female patient, who is a practicing Jehovah's Witness, is admitted for anemia. The physician determines that blood transfusions are necessary, but the patient's parents refuse to consent. The patient states that she wishes to be treated. The advanced practice nurse action is to: a. contact local clergy for assistance in crisis intervention. b. inform the patient that her parents must consent before treatment can be administered. c. inform the patient that she is a minor and incapable of such decisions under state law. d. request that the administration contact the hospital attorney for legal counsel All of these might occur simultaneously, but the advanced role of advocate is best displayed by answer ‘a’. 25. Which statement is an outcome indicator for an educational strategy? a. The nurse working in a coronary care unit has successfully completed an advanced coronary care course. b. The nursing care plan outlines a strategy for each patient problem c. The patient names all medications to be taken after discharge. d. The patient who is newly diagnosed with diabetes receives 10 hours of instruction. Response B should be eliminated due to no focus on any educational strategy (this is a care strategy). Completing a course or receiving instruction indicates successful completion of the material but the individual in these is not actively demonstrating competency—which we do see in response C. 26. The data obtained for quantitative research would best be used for what purpose? a. To gain insight into cultural practices b. To investigate the "why and how" of decision-making c. To predict future clinical outcomes d. To understand the meaning of events Gaining insight into a person’s culture, asking why, and understanding the meaning of things are all referring to qualitative data. We can make predictions about clinical outcomes using quantitative data. 27. Research suggests that a nurse executive most effectively improves employee job satisfaction by: a. increasing employee salaries. b. increasing staff autonomy. c. offering more educational assistance. d. providing a clinical advancement program. Money is a short term fix for employee satisfaction. Intrinsic motivation, such as increasing autonomy, will produce long term results. 28. The first step in a remedial action program for an employee whose clinical performance does not meet standards is to: a. determine whether the employee will be more receptive to self-learning modalities or referral to a staff development educator. b. determine whether the problem is related to a lack of competency or a lack of productivity. c. refer the employee to a staff development educator for further education and training. d. determine whether the problem is related to a lack of knowledge or a lack of skill. We need to identify the problem first. If the problem is related to competency, then we could pursue the interventions listed in responses A, C, and/or D. 29. A committee in a large urban hospital is appointed to plan improvements in patient care. The committee members include the: a. chief nursing officer and the chief medical officer. b. institution's strategic planning committee members. c. medical, nursing, and ancillary staff personnel. d. senior management and the budget adviser. The stakeholders of the processes need to be involved. The other personnel are too far removed from patient care. 30. Which of the following describe examples of patient safety barriers? a. Persistent fear and hierarchical authority b. Complexity and deficient measures c. Reporting systems and safety culture—this is the only item that would support patient safety! d. Diffuse accountability and lack of leadership e. All of the above f. A, B, and D g. B, C, and D 31. If data are plotted over time, the resulting chart will be a (A) Run chart (B) Histogram (C) Pareto chart (D) Poisson distribution Improvement takes place over time. Determining whether an improvement has actually happened and if it has been sustained requires observing data to determine patterns over time. Run charts typically use a line graph to show data over time. The run chart below depicts a baseline measurement and the response to steps in the improvement process: Pareto charts and Histograms (the next two graphs shown below) look very similar. Both typically involve bar graphs and help depict the frequency or distribution of data. A Poisson distribution can help us look at recurring events over a fixed timeframe: 32. The following diagram is best described as a: (A) Run chart (B) Flow chart (C) Control chart (D) Checklist A flow chart is basically an illustration of the steps in a process. It can help us better understand all the factors (human, environmental, organizational, etc.) that are involved. We’ve already see a run chart in question #1. A checklist is essentially a list of prompts that serve as a reminder of the critical elements that must be completed in a process. A control chart is a special kind of run chart that helps us determine if a process is out of control or not. The chart below includes upper and lower control limits (UCL & LCL): 33. Using the diagram (in item number 2), which of the following statements is correct? (A) The purpose of this chart is to show how data in a process are distributed. (B) Steps in a highly complex process are outlined. (C) Only one decision can be made in this process. (D) Three potential activities or interventions can occur in this process. Again, the purpose of a flow chart is to outline or illustrate the steps in a process and will not help us see how data are distributed. This flow chart is not very complex and contains 2 decisions (indicated by the diamond shapes). The interventions are illustrated by the green rectangular shapes. 34. Before selecting a vendor of a particular healthcare equipment or supply, the masters prepared nurse should do which of the following first? (A) Conduct vendor surveys. (B) Define departmental needs. (C) Determine which vendors are industry leaders. (D) Get feedback from team members about how various vendors and their supplies are performing (E) Decide which vendor is most cost effective. Determining needs (or to think about it this way—determining the aim) is necessary before attending to any of the other activities—until we know what the department needs; we can’t determine who (which vendor) can meet those needs. 35. Which of the following is a priority for the MSN in planning quality improvement training? (A) Establishing specific training evaluation tools. (B) Developing short-term training plans. (C) Scheduling training for managers. (D) Connecting training to organizational needs. Again, we start with needs (the aim) before any training is actually planned, scheduled, or evaluated. 36. To be effective, quality initiatives must be (A) Developed by stakeholders. (B) Free from cost and profit considerations. (C) An integral part of the overall organizational strategic plan. (D) A&C (E) All of the above The IHI is one organization that states that quality and safety must occupy a prominent place in the strategic plans of health care organizations. What we want to avoid is a long list of worthwhile projects and measures that are not well coordinated, or that are not capable of achieving system-level results. Having the stakeholders (people who have a vested interest in the systems that are being improved or that are in need of improvement) involved in quality initiatives is a great way to help ensure success. Quality improvement is not free from cost and profit considerations. In fact, improvement initiatives should seek to improve efficiency and reduce costs. 37. Which of the following is NOT an appropriate goal for quality improvement education of MSNs? (A) Develop an understanding of the fundamentals of quality. (B) Integrate quality into decision-making processes. (C) Define the chain of command for approving quality procedures. (D) Provide tools and information to help MSNs build and utilize quality systems and processes. Responses a, b, and d are reasonable goals for QI education of MSNs. Individual healthcare organizations and settings have their own mechanisms for initiating QI activities and providing approval. 38. Rank order, from first to last, the following training design steps. 1. Prepare training materials. 2. Define training objectives. 3. Determine course structure and sequence. 4. Establish consensus on needs. (A) 2, 1, 4, 3 (B) 2, 4, 1, 3 (C) 4, 2, 3, 1 (D) 4, 3, 1, 2 Determining needs (the aim) is the first step again. After that, we can define objectives, develop the course structure, and then prepare the training materials. 39. An MSN wants to implement Leadership Rounds in the hospital, to include participation of the CEO. This initiative would provide an informal way for senior leaders to talk with front-line staff about safety issues in the organization and to encourage reporting of errors. All of the following are benefits of having the CEO involved in these rounds EXCEPT (A) Increased understanding by the CEO of the organization’s state of affairs. (B) Improved motivation of subordinates through personal participation of the CEO. (C) Improved human relations between the CEO and front line staff. (D) Improved dissemination of information throughout the organization. Leadership Rounds are basically an opportunity for senior leaders, like the CEO, to demonstrate their organization’s commitment to building a culture of safety by engaging in direct communication with frontline staff—it is not an optimal method for disseminating information. For more information, see the IHI website: http://www.ihi.org/resources/pages/tools/patientsafetyleadershipwalkrounds.aspx 40. In order to be successful in the role of change agent, an MSN should do all but one of the following? (A) Understand and respect peoples’ needs. (B) Learn from previous unsuccessful efforts to transform the organization. (C) Maintain commitment to the mission and vision of the organization. (D) Communicate change initiatives only to senior management. Dissemination of information in a change initiative should not be limited to senior management. Responses a through c will help ensure success of the project as well as success of the change agent. 41. Which of the following is the first priority when starting a quality improvement initiative? (A) Assign team goals. (B) Develop strategies. (C) Identify an aim. (D) Make sweeping organizational changes to support quality. We first need to develop a time-specific, measurable aim or goal. For more see: http://www.ihi.org/resources/Pages/HowtoImprove/ScienceofImprovementHowtoImprove.aspx 42. Which of the following is the LEAST effective safety approach for a patient-centered healthcare organization to take? (A) Urge employees to do it right the first time. (B) Establish a quality council that includes patients. (C) Implement team-building throughout the organization. (D) Examine processes and establish controls to increase efficiency, reliability, and safety. Response ‘a’ is not a systems approach to improving patient safety—the focus should not be on individuals. Response ‘b’ is good because it includes patients as a stakeholder. Team-building and examining processes are good approaches to improving systems. 43. Which of the following is one advantage of team decision-making? (A) Ease of arriving at a decision (B) Reduced potential for conflict (C) Increased acceptance of decisions (D) Increased productivity Team work is not always easy and does not guarantee a reduction in conflict. In fact, “storming” is one of the early phases in team development (phases are form-storm-norm-perform). We hope that team decision-making will eventually increase our productivity, but finding time to participate in team meetings or other activities often does the opposite (at least in the short term). C is the best response. 44. The wide scale collection of patient weight into a large dataset is primarily used to measure and improve healthcare for which type of group? (A) Family health (B) Extended family health (C) Population health (D) Individual health The keywords here are “wide-scale” and “large dataset”. C is the best response—the others (involving a single family or individual) are too limited. 45. In interpreting the run chart below, all of the following are true EXCEPT (A) More than a year of data is represented in the chart. (B) The highest rate of infection reported was about 8%. (C) The data points in red indicate a rise in infection rates from April through December. (D) The data points in green indicate a decrease in infection rates over two separate time periods. (E) The green dotted line is located at about a 4.5% infection rate; this is the target or benchmark. (F) The blue dotted line is located at about a 3% infection rate; this is the target or benchmark. Response ‘e’ is located at about the 4.5% infection rate, but this is the “mean” or average of the values presented in the chart. The blue line at the 3% mark is the actual target rate—the rate that helps to describe the aim of this project. Only four data points are on or below the target rate. 46. A primary care provider refers a patient to a specialist. The specialist treats the patient and then sends the patient with a report back to the primary care provider. A manual (paper-based) system was used in this referral process. Which of the following statements about manual systems is true? Manual systems for referrals or other transitions in care: (A) Decrease the complexity of the referral process and reduce opportunities for human error. (B) Often result in more efficient work-flow processes. (C) Never result in missed appointments and lost revenue. (D) Are known to reduce delays in patient care. (E) Often involve no agreement on who is responsible for closing the loop (ensuring that referral information is exchanged provider-to-provider). Paper-based systems for referral often do the opposite of responses a through d. Closing the loop is a significant problem, not only for referrals, but for other transitions in care that involve hand-offs between providers of different healthcare institutions. 47. A patient's right to make informed decisions includes all of the following except: (A) Right to participate in the development of his/her plan of care. (B) Right to consent to treatment. (C) Right to refuse to consent to treatment. (D) Right to receive care that is not medically necessary. (E) Right to participate in planning for post-hospitalization care. Most healthcare organizations issue a notification to patients of their rights and responsibilities upon admission or initial contact. While these may differ somewhat in content, the right to make informed decisions is included universally. However, while obtaining adequate information to make a decision about care that is not medically necessary is important, receipt of such care is not considered a right. In fact, most healthcare insurance companies will not cover the costs of care deemed medically unnecessary. 48. Medicare and Medicaid Electronic Health Care Record (EHR) Incentive Programs provide financial incentives for the Meaningful Use of certified EHR technology. To receive payment, providers have to show that they are “meaningfully using” this technology by meeting certain measurement thresholds. In Stage 1, 18 out of a total of 22 Meaningful Use objectives must be met. Stage 1 requirements must be met for a 90-day period in the 1st year of Meaningful Use and for a full year in the 2nd year of Meaningful Use. Stage 2 requirements must then be met for two full years. Below is a table outlining the two incentive programs. Medicare EHR Incentive Program Medicaid EHR Incentive Program Run by CMS Run by Your State Medicaid Agency Maximum incentive amount is $44,000 Maximum incentive amount is $63,750 Payments over 5 consecutive years Payments over 6 years, does not have to be consecutive Payment adjustments will begin in 2015 for providers who are eligible but decide not to participate No payment adjustments for providers who are only eligible for the Medicaid program Providers must demonstrate Meaningful Use every year to receive incentive payments. In the first year providers can receive an incentive payment for adopting, implementing, or upgrading EHR technology. Providers must demonstrate Meaningful Use in the remaining years to receive incentive payments. An MSN practice manager is trying feverishly to meet the Meaningful Use requirements for a newly implemented EHR system for the practice. She is behind on her work. Which approach is best for solving this problem? (A) Seek vendor input on how to optimally manage this transition period for implementing the EHR and meeting the Meaningful Use requirements. (B) Re-prioritize her own workload since she knows what to do and can do it all herself. (C) Meet with the medical director of the practice, explain the situation, and ask for help in selecting priorities. (D) Meet with the medical director of the practice, explain the situation, and request additional short-term help since the deadlines for attestation and reporting periods in this incentive program are fixed. A practice manager is a leadership role that an MSN might fill. A practice manager administers the business and financial activities of a medical practice. While a vendor could provide great information about implementation of an EHR, they should not be relied upon as a subject matter expert on the meaningful use requirements. Ultimately, the vendor will not hold any responsibility (or liability) for a failure to meet these requirements. Response b is basically continuing to do what has already been done (and probably getting the same results). It should additionally be noted that re-prioritization (either self-directed or directed by someone else) may not cure the problems of inadequate time or resources. Response c is potentially a strategy to shift responsibility for failure onto, and is a decision that will likely result in relinquishing some authority to the medical director—who may not have the knowledge base or motivation to correctly select priorities for the practice manager. So will the practice manager be the subordinate or the equal of the medical director if response c is chosen? D is the best response—the practice manager is alerting the medical director to the problem and suggesting a solution. This decision places the practice manager in the best possible light, retains decision-making authority, and will help create a culture conducive to teamwork. For more information on requirements and incentives for the Meaningful Use of certified EHR technology, see this site: http://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and- Guidance/Legislation/EHRIncentivePrograms/Getting_Started.html 49. Based on patient survey data that indicate patients were dissatisfied with the level of noise on the patient care unit, the QI team has recommended the use of a sound machine in each patient room to muffle the ambient noise on the unit. How should the MSN respond to this recommendation? (A) The MSN should serve as a champion & role model during the implementation of the recommendation. (B) The MSN should search the literature to confirm that the recommendation is evidence-based. (C) The MSN should support the recommendation, as it is an effort that will improve patient care. (D) The MSN should clarify how the data were collected and how the team developed its recommendation. Responses a and c are pretty much saying the same thing—it would be better to throw support toward and be a role model for an initiative that we have good assurance will result in a positive change. Since we know the recommendation is based on patient survey data, response d seems a little redundant (and may strictly be a strategy to invalidate or undermine a quality improvement initiative). B is the best response—we want to know that the recommendation will be a cure for the problem. Here is an article: http://www.hermanmiller.com/research/research-summaries/sound-practices-noise-control-in-the- healthcare-environment.html 50. Historically, which group is closely aligned with the financial success of healthcare organizations and therefore is designated the leader for most clinically-based innovations? (A) Nurses (B) Administration (C) Physicians (D) Admitting Administration & admitting can be eliminated as having no direct clinical role—they might assume a leadership role in business innovations. Nurses typically don’t earn the revenue; providers do (although this is changing somewhat). 51. The Health & Human Services dept established a National Strategy for QI in Healthcare. This national quality strategy (NQS) has the triple aim of better care, healthy people/healthy communities, and affordable care. To further this triple aim, one of the NQS priorities is to promote effective communications and coordination of care. The following goals were established: 1 Improve the quality of care transitions and communications across care settings. 2 Improve the quality of life for patients with chronic illness and disability by following a current care plan that anticipates & addresses pain and symptom management, psychosocial needs, and functional status. 3 Establish shared accountability and integration of communities and health care systems to improve quality of care & reduce health disparities. Nursing leadership in a 750 bed tertiary care facility has been advised that quality measures affecting reimbursement are going to be captured to assess progress toward these goals, so a program is needed to improve the coordination of care as patients transition to other care settings. What role should the QI team have in a program to improve communication and care transitions? (A) Determine if current practice meets the metrics established for the measure or if this is a QI program needed to improve the quality of care delivered. (B) Determine whether facilities receiving patients are interested in a QI program initiated by the sending facility. (C) Check with patient families of discharged patients to ensure home care contacted them in a timely fashion and had the necessary information to provide high quality care. (D) Check each patient discharged for a two-week period to a skilled nursing facility or an assisted living facility to be sure the correct paperwork was sent or transmitted to the facility. Some key words/phrases are underlined in this question. This is a huge facility—having the QI team check discharges even for just a 2-week period (as in response d) could be a time-consuming activity and would still not solve the problem of “shared accountability” in care transitions. In addition, sent or transmitted doesn’t mean actually received by a human being—this is often the problem with care transitions. It’s called closing the loop. The first response would tend to check on how well we’re meeting reimbursement requirements or possibly the care delivered in the facility—it doesn’t address communication or care transitions. The third one is either limited to only home care patients (which doesn’t include the healthcare facilities some patients get discharged to) or potentially we’d be checking every discharged patient (and we know not all patients need home care). In questions like this, make sure that your response will fully address the actual problem (or in this case, problems). 52. In reflecting on the role of MSN mentor, which of the following statements is not true? (A) The mentor nurtures and develops the mentee’s capacity for self-reflection and self-direction. (B) Mentoring relationships are task focused; when the tasks are completed the relationship comes to a close. (C) A mentor who understands how to provide vision and how to support and challenge the mentee can help the mentee grow and develop. (D) The mentoring relationship is a learning partnership that focuses on developing the mentee’s abilities and thinking. (E) Some preceptors are also mentors; being a mentor is not dependent on being a preceptor. The preceptor relationship is task focused (not the mentor relationship). A mentor typically holds an unofficial role as a new nurse’s trusted advisor. The mentor supports and nurtures the new nurse, usually checking in frequently to see how he/she is progressing. But there are no specific milestones or deadlines that must be met. The mentor is concerned about the nurse becoming an asset to the nursing profession as a whole, more than becoming an asset to any specific organization, unit, or job. A preceptor typically has an assigned duty of monitoring the training and evaluating the performance of a new nurse. A preceptor works with the new nurse for a defined period of time to assist the novice in acquiring new competencies required for safe, ethical and quality practice on a particular unit or for a particular type of job. At the end of the defined period of time, the preceptor is usually asked to help evaluate the novice and determine whether the individual is ready to work independently or needs additional time to train and prepare (as in an extension of the probationary time for a new job). When things go well, a preceptor may become a mentor to the new nurse (assuming that a relationship of trust has developed). 53. By focusing on the patient, we can achieve the IHI Triple Aim. The Triple Aim is, simply stated, to create: (A) better outcomes, great patient experiences, and reduced costs (B) higher revenues, reduced turnover, and lower costs (C) lower revenues, higher costs, and lower patient satisfaction (D) better outcomes, reduced costs, and higher revenues For more, see: http://www.ihi.org/Engage/Initiatives/TripleAim/Pages/default.aspx 54. An MSN needs to assign a staff member to assist a medical director in the development of a quality program for a newly established service. Which of the following staff members is MOST appropriate for this project a. a newly hired staff member who has demonstrated competence and has time to complete the task b. a knowledgeable staff member who works best on defined tasks c. a motivated staff member who is actively seeking promotion d. a competent staff member who has good interpersonal skills Rationale: This is basically a question about delegation. The objective in delegation is to give a task to someone who can handle it efficiently, effectively and without a lot of oversight--so that the delegator does not turn in to the doer! In option a, the newly hired staff member would not have the contacts necessary to start a quality program in a new service. In option b, the staff member who needs defined tasks would not have the level of initiative needed to start a new program. In option c, the motivated staff member might not be the best choice to develop a new program because they intend to move on to another position (and the MSN might need to assign someone else to this eventually). The staff member with good interpersonal skills (option d) is the best choice—this person can work with others and has demonstrated competence. 55. A surgeon’s wound infection rate is 32%. Further examination of which of the following data will provide the MOST useful information in determining the cause of this surgeon’s infection rate? a. mortality rate b. facility infection rate c. use of prophylactic antibiotics d. type of anesthesia used Rationale: This question is asking for a ‘cause’ for this particular surgeon. The cause can be found by examining process. Options a and b refer to high level outcome measures—these tell us about all patients in this facility, not just this surgeon. Option d refers to a process but it is not directly attributable to the problem of infection. Option c also refers to a process and we know that use of prophylactic antibiotics is known to reduce incidence of infection. Option c is the best response because we can use this information to inform this particular surgeon’s practice (his process). 56. Pharmacy and Nursing are having difficulty developing an action plan for medication errors. Pharmacy Services states that Nursing Services cause the majority of the problems related to errors, while Nursing Services states the opposite. The QI department’s role in resolving this problem is to a. provide them with directives on how to solve the problem b. facilitate discussion between the groups to enable them to assume ownership of their portions of the problem c. assign the task to an uninvolved manager d. refer the problem to the facility-wide quality council Rationale: While the Nursing and Pharmacy department could potentially let the QI department direct their activities, as in options a and c, they will likely choose to govern themselves. Option d is simply pawning off the problem to a (potentially) higher authority—this tactic should be taken only after all other options have been explored. Option b is the best response; the QI department would be well within their bounds to facilitate discussion and point out potential options for the two departments. This response supports development of a culture of safety and helps the QI department promote teamwork central to the idea of this culture. 57. Which of the following is MOST likely to be a benefit of concurrent ambulatory surgical case review? a. decreased medical record review at discharge b. an increase in the number of cases failing screening criteria c. an increase in reviewer competence d. decreased medical record requests Rationale: Retrospective review of records occurs after care is delivered. Concurrent case review indicates that the cases are being reviewed while care is being delivered in the ambulatory surgery dept. This should help decrease or prevent the need for medical record review at discharge (option a). Concurrent review should reduce (rather than increase) the number of cases that fail criteria, as listed in option b. It may not affect option d at all—multiple departments (not just ambulatory surgery) request medical records and a review of a patient’s current record would not reduce the need for prior records to be requested and reviewed by surgery. Concurrent review of ambulatory surgery cases might increase reviewer competence, as in option c, but there would be other factors influencing development of competence as well. 58. A well-designed patient safety program should include all of the following EXCEPT a. an annual patient safety committee meeting b. planned response to adverse events c. orientation and continuing education on patient safety issues d. review of patient safety policies and procedures for all departments. Rationale: Options b, c, and d are all important components of a patient safety program. In option a: although patient safety committee meetings are also important for a well-designed patient safety program —a once-a-year meeting would be insufficient. 59. Discharge planners regularly monitor the number of inappropriate referrals, the timeliness of discharge planning, and the number of days of discharge delays. What additional monitor should be added to evaluate the appropriateness of discharge planning interventions? a. adequacy of documentation in progress notes b. attainment of discharge planning goals c. timeliness of referrals to discharge planning d. number of discharge planning referrals from nursing Rationale: Option b is the only response that would yield outcome data to evaluate the appropriateness (and effectiveness) of discharge planning interventions—and tell us how our patients are doing! Options a, c, and d are process measures that might help us identify areas in need of improvement— these would tell us how accurately or efficiently we perform these processes. In addition, Option a would not be highly specific to discharge planning—multiple providers place documentation in progress notes and not just for purposes of discharge planning. Options c and d involve referrals to discharge planning— a referral is a notification that discharge planning is needed; this would occur prior to any interventions being implemented by a discharge planner. 60. A primary purpose of an information management system is to allow an organization to a. save time b. centralize demographics c. reduce cost d. evaluate data Rationale: Information management systems are primarily used to collect and evaluate data—of all types: patient care information, dates and times of care delivery, outcomes of care, costs of goods and services, multiple revenue streams and cost centers, payroll, etc. Such evaluation often leads to greater efficiency and cost reduction. Information management systems can also yield benefits like a centralized location of data—demographics being just one type of data centrally stored. 61. Which of the following monitors provides patient outcome information? a. healthcare-acquired infection rate b. nursing care documentation compliance c. antibiotic therapy discontinuation compliance d. equipment malfunction rate Rationale: Options b, c, and d are all referring to process measures that might tell us what we can improve our accuracy or efficiency. Option A is the only outcome measure; it will help tell us how patients are doing. 62. The surgery department's monthly case review revealed twenty-six records meeting the criteria. Six records did not meet the criteria. When calculating the incidence risk, the denominator is a. 6 b. 20 c. 26 d. 32 Rationale: This is a thought problem—it is telling you that 26 records in the review did meet criteria (compliant records), so you can’t have 6 records out of that 26 that also did not meet criteria (noncompliant records). So the 6 records that did not meet criteria would be an additional amount (6 records that did not meet criteria + 26 records that did meet criteria = 32 total records). The denominator in a calculation of rate is always the total number in the group being examined. Numerator - The upper part of a fraction - For example, the number of records that were compliant 26 Denominator - The lower part of a fraction used to calculate a rate or ratio - For example, total number of records in the audit 32 Rate Numerator/Denominator (26/32 = Compliance Rate) 81% 63. Flowcharts are primarily used in quality improvement to a. analyze causal factors of process dispersion b. understand the overall process or system being audited c. distinguish variations in a process over time d. determine process capability and uniformity Rationale: A flowchart is an illustration of a process—it allows us to understand it better (see diagram below for a simple example). Breakdowns in process or causal factors of such breakdowns can be identified in a flowchart but not before the process itself is mapped out and understood. A flowchart will not provide information of process variations that occur over time. It may help you look at process capability, efficiency, and standardization to provide insight into opportunities for improvement of the process—but again, the process itself must be mapped out and understood first. 64. In what instance is it acceptable to obtain additional time for a corrective action? a. When the auditor cannot perform the audit as scheduled b. When the group being audited determines that the proposed corrective action is not cost effective c. When the corrective action plan requires more time than originally anticipated d. When there has been a change in personnel who perform the task Rationale: In this question, it helps to dissect the issues down. In option C, additional time will definitely cure the identified problem. In the other responses, additional time may not help—we need to find a different auditor or a different schedule for the first one, we probably need more money for the second one (or the group being audited may be trying to offer an excuse to avoid the audit), and in option D, there could be several problems including time (such as the hiring and training of new personnel or some general instability in that department) that may need to be addressed. Also keep in mind that when a corrective action has been implemented, it is generally because there is a critical issue that must be addressed in an appropriate and timely fashion—additional time without good justification is delaying vital action that could potentially save a patient’s life. 65. Which of the following statistics best describes the central tendency of a sample of data? a. Mode b. Mean c. Standard deviation d. Range Rationale: Mode, mean, and median are the 3 measures of central tendency. The mode is the value that appears most often in a set of data—however, there could be more than one mode if more than one value occurs the same number of times in a data set. Example data set: 10, 5, 6, 10, 6, 7, 5, 3, 6, 4, 5, 10 Modes: 10, 6, and 5 each occurred 3 times. (The median is not one of your choices, but it is the value which occupies the middle position when all the observations are arranged in an ascending/descending order. It divides the frequency distribution exactly into two halves. Example data set: 10, 5, 6, 10, 6, 7, 5, 3, 6, 4, 5, 10 Median= 6 The mean is considered the preferred measure for central tendency. It is the average--the sum of the values in a data set divided by the number of values. Example data set: 10, 5, 6, 10, 6, 7, 5, 3, 6, 4, 5, 10 Mean= 77 divided by 12 = 6.4 Options c and d are not measures of central tendency. The Standard Deviation is a measure of how spread out a set of numbers is. The more spread apart the data, the higher the deviation. (Data plotted out in a wide bell curve represents a higher deviation than a skinny bell curve.) The range of a set of data is basically the difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set. 66. Which of the following requests is likely to obtain the most objective evidence for verification? a. “What kind of information do you receive?” b. “Who provides the information to you?” c. “Describe how you receive information.” d. “Show me the information you have received.” Rationale: In this question, responses a through c will result in limited or biased information, based on the knowledge base and motivations of the respondent. Viewing the information received gives the investigator an opportunity to objectively review the data, and then also ask these questions. This will allow comparison between what was actually received and what the level of understanding is about the data. Remember to get objective, scientific information, we need to Test it, Measure it, or Observe it. 67. The process information shown in the graph above is indicative of a a. Cycle b. Run c. Trend d. Shift Rationale: The question is asking for the information contained in the chart to be interpreted (not for the type of chart to be identified). The chart above is a control chart (a special kind of run chart) demonstrating an upward trend from the initial baseline—we clearly see more than 5 data points all going in the same direction. We don’t have enough information here to decide if the trend is positive or negative, but it is a trend nevertheless. The control chart will also tell us whether a process is out of control or not. Due to the data being plotted between the upper and lower control limits (UCL and LCL), we have good assurance that the process is in control. There are several ways to interpret the information presented in a run or control chart. We need to look for shifts, runs, and trends. For more, see this article: http://www.med.unc.edu/cce/files/education- training/The%20run%20chart%20a%20simple%20analytical%20tool.pdf/at_download/file The run chart below does not demonstrate a clear trend in the process being measured. 68. Which QI goal is most effective for the QI team to use? a. the pt satisfaction score will increase by 10% b. the pt satisfaction score will exceed national averages c. the pt satisfaction score will improve from 62% to 98% d. the pt satisfaction score will be 95% by December 1 All of the responses point to data that refer to a rate or measure of improvement. Only one (response D) provides an additional piece of information that is important in setting a SMART goal: Specific— Measureable—Achievable (or Action-Oriented)—Realistic (or Relevant)—Time-bound. A good discussion of this is located here: http://www.communicatingwithpatients.com/articles/smart_goals.html Simply put, a goal without a deadline is “just a dream”. 69. The QI team is working together to identify the primary drivers of pt satisfaction regarding the nursing care that patients receive. One of the identified primary drivers of pt satisfaction was effective communication. What is the 1st thing the QI team should do with this information? a. develop strategies for effective communication b. implement a national program for effective communication c. establish a means for measuring effective communication d. remind staff of the importance of effective communication In the “Plan” portion of the IHI PDSA cycle, after we decide what it is that we want to improve (this is the objective--in this case we want to improve “communication”), we need to establish how we’ll know a successful change occurred (our prediction needs to be based on data—a measurement that will show us that the proposed change resulted in the desired improvement in communication). Then we can brainstorm some ideas about steps we could take to accomplish the change (this would be the interventions we can implement that will result in the desired improvement in communication). Response C is the best answer. Response A is the actual intervention plan for the cycle (the who, what, when, where, etc. of how the change will be carried out). Then we would need to plan the who, what, when, where for the data collection. Response B has the keyword ‘implement’—indicating that this is part of the “Do” portion of the PDSA cycle. In response D, reminding staff puts the ‘blame’ on them when failure occurs (not a systems approach to improvement). We need to create systems and processes to support effective communication—and avoid depending solely on human memory (which will likely result in error). For more on the IHI model: http://community.wgu.edu/clearspacex/docs/DOC-13711 70. Based on observation, an NP believes that the rates of smoking and obesity are increasing in their patient population and wants to implement a program to address this issue in the ambulatory clinic. What is the 1st step the NP should take to determine if this belief is, in fact, a trend? a. work with the practice manager to determine rates of smoking and obesity in the practice b. ask the other staff if they are seeing increasing numbers of patients who are smoking and/or obese c. ask patients if they feel that either smoking or obesity is affecting their lifestyle d. work with the staff to counsel each patient on the dangers of smoking and the risk factors of obesity The NP has a “belief” based on observations—but he/she lacks actual data (scientific evidence) to support the need for a new program to be implemented. It wouldn’t help to ask other people (responses B and C) about their beliefs (still no hard data) and in response D, it is too soon to begin working on the interventions (we don’t have data to show that this is an actual problem yet). A trend is typically demonstrated with a run chart. A run chart is a graph that displays observed data in a time sequence. Obtaining actual rates of smoking & obesity in the practice (response A) to establish a trend over time is the data that is needed to support the need for development of the new program. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 56 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$17.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 02, 2021
Number of pages
56
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 02, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
57