1. A 445 g sample of ice at –58oC is heated until its temperature reaches –29oC. Find the change in heat content of the system.
Q=C x P x ∆T
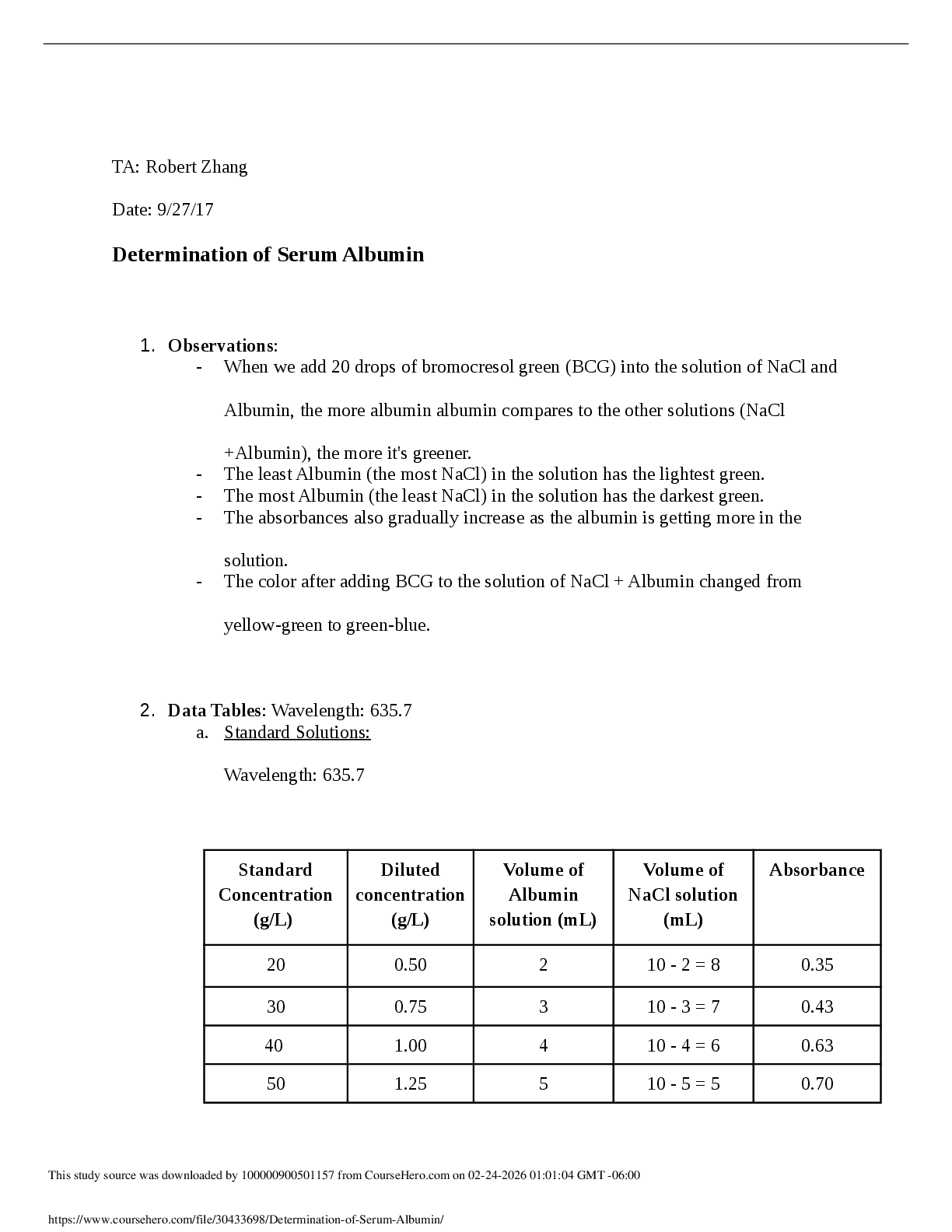
The temperature change is −29−(−58) =29
The enthalpy change is thus 445g *
...
1. A 445 g sample of ice at –58oC is heated until its temperature reaches –29oC. Find the change in heat content of the system.
Q=C x P x ∆T
The temperature change is −29−(−58) =29
The enthalpy change is thus 445g * (29’C) * 2.077 J/g-’C = 271000 Joules = 26.8 kJ
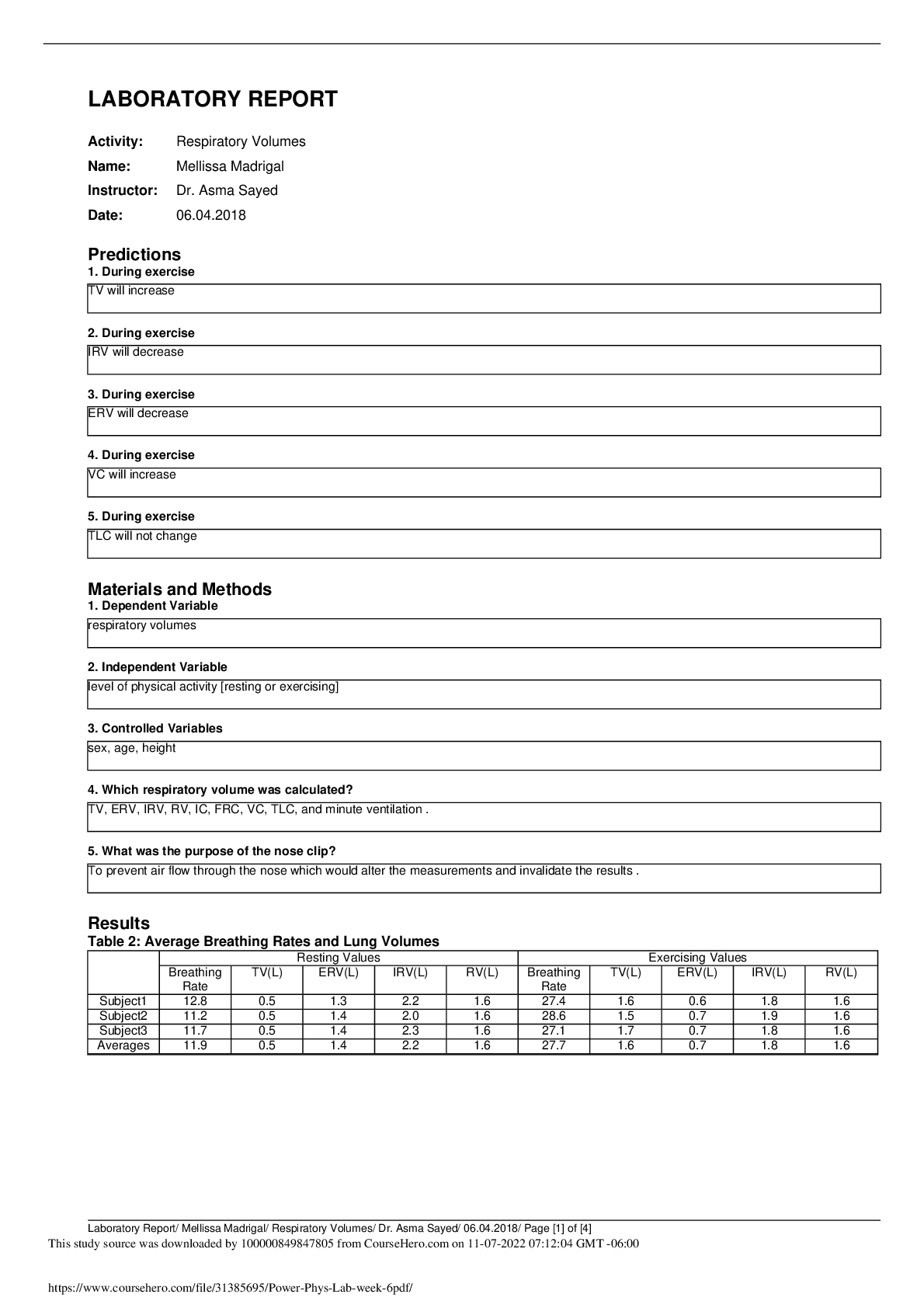
2. A 152 g sample of ice at –37oC is heated until it turns into liquid water at 0oC. Find the change in heat content of the system.
Q=C x P x ∆T+ C x m= (152x(0-(-37))x2.10)+ (332x152) = -6.23 x 104 J
3. A 218 g sample of steam at 121oC is cooled to ice at –14oC. Find the change in heat content of the system.
Q=C x P x ∆T= 218x(-14-121)x2.10= -6.71 x 104 J
4. If 161 g of water at 85oC is cooled to ice at 0oC, find the change in heat content of the system.
Q=C x P x ∆T+ C x m = 161x(0-85)x4.184 + (333 x 161) = 110871 J
5. A 79 g sample of water at 21oC is heated until it becomes steam with a temperature of 143oC. Find the change in heat content of the system.
Total Q=(C x P x ∆T)+ (C x m) + (C x m x ∆T)= –2.11 x 105 J
6. If a 348 g sample of steam at 127oC is cooled to 103oC, find the change in heat content of the system.
Q=C x P x ∆T= 348x(103-127)x1.87= –1.56 x 104 J
7. In going from ice at –34oC to steam at 138oC, a sample of water absorbs 1.41 x 105 J. Find the mass of the sample.
44.7 g
Answers: 1. 2.68 x 104 J 2. 6.23 x 104 J 3. –6.71 x 105 J 4. –1.11 x 105 J 5. 2.11 x 105 J 6. –1.71 x 104 J 7.
44.7 g
8. You find a penny in the snow. How much heat is absorbed by the penny as it warms from the temperature of the snow, which is -8.0oC, to the temperature of your body, 37oC? Assume the penny is pure copper and has a mass of 31.0 g. Use the information from question #14 for the specific heat of copper.
537.07 g
9. Consider the following specific heats of metals.
Metal Specific Heat
copper 0.385 J/(g • °C)
cobalt 0.418 J/(g • °C)
chromium 0.447 J/(g • °C)
gold 0.129 J/(g • °C)
silver 0.237 J/(g • °C)
If 100-g samples of each of the metals at 95°C are added to 100 mL of water at 25°C. Which element from the table increase the temperature of the water the greatest amount?
Heat released = heat absorbed
100 x c (95- T) = 100 x 4.18 x (T-25)
T= (9500 c + 10450)/(100c +418)
Since temperature will be lowest when the c is lower
So the correct answer is GOLD because it has the lowest specific heat And it will increase the water temperature
10. The specific heat capacity of methane gas is 2.20 J/g-°C. How many joules of heat are needed to raise the temperature of 5.00 g of methane from 36.0°C to 75.0°C?
E = 2.20 J/gK x 5g x 39K = 429
11. Which of the following processes is exothermic?
A) liquid water condensing from steam
B) the melting of ice
C) the chemical reaction in a "cold pack" often used to treat injuries
D) sweat evaporating from skin
E) None of the above are exothermic. Option D: sweat evaporating from skin
[Show More]













.png)

