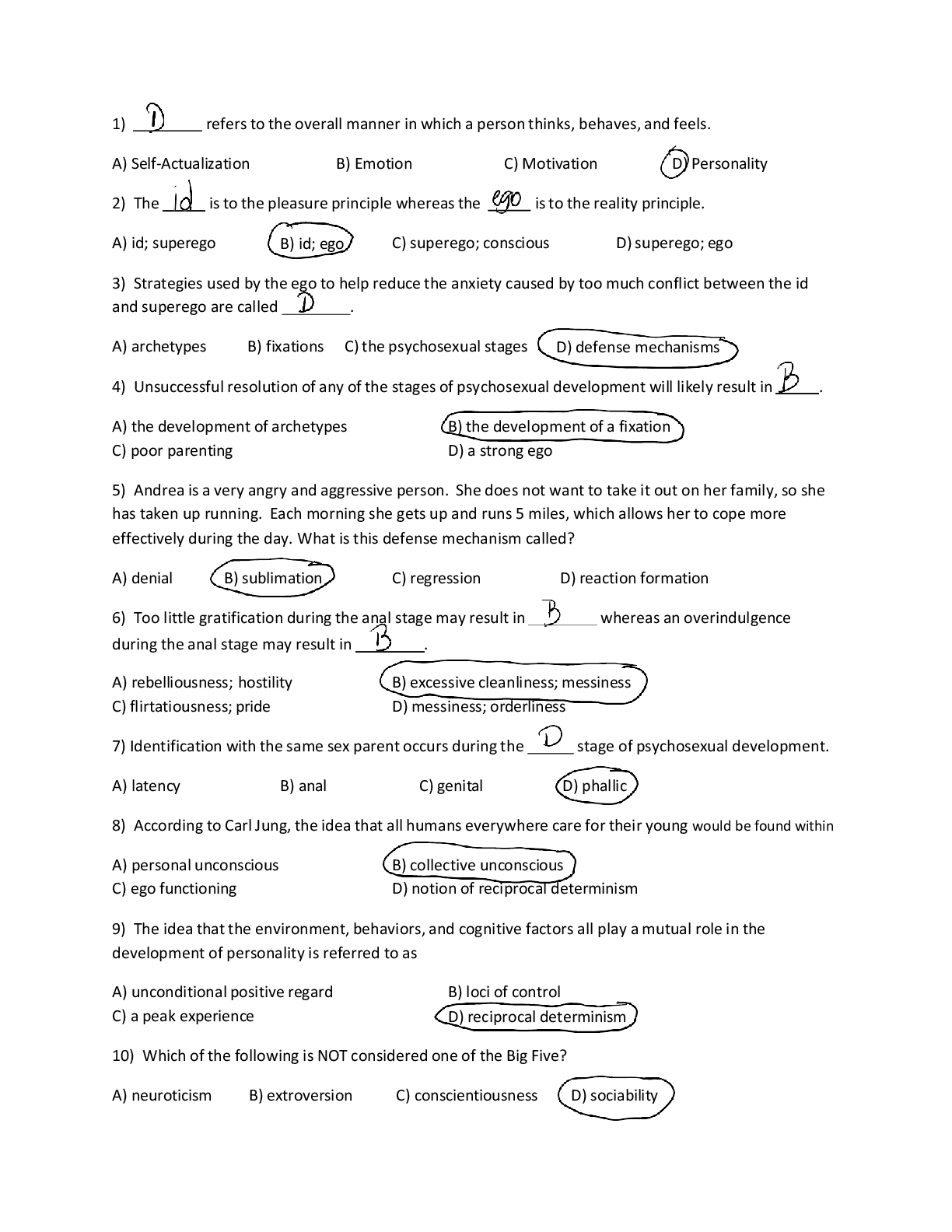
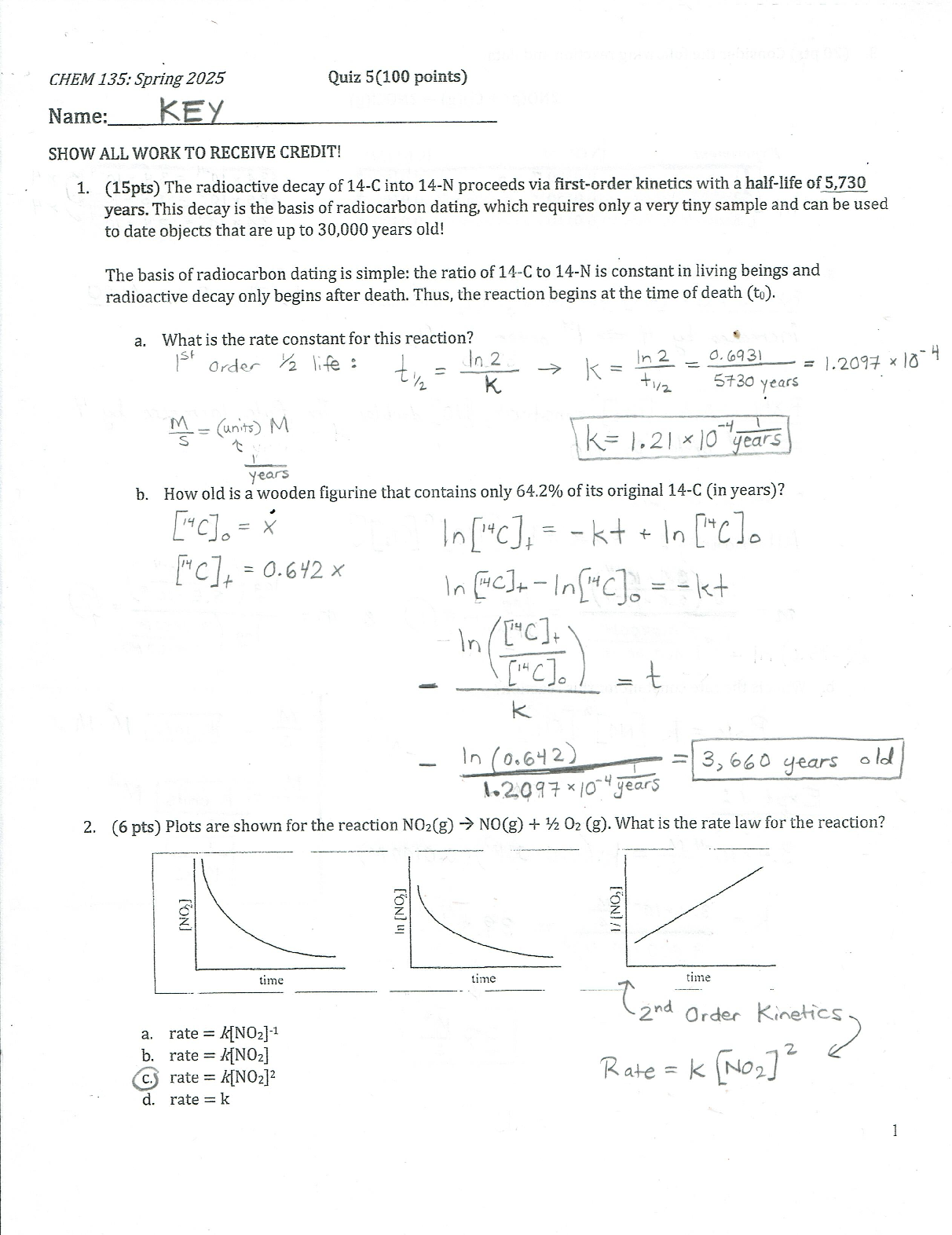
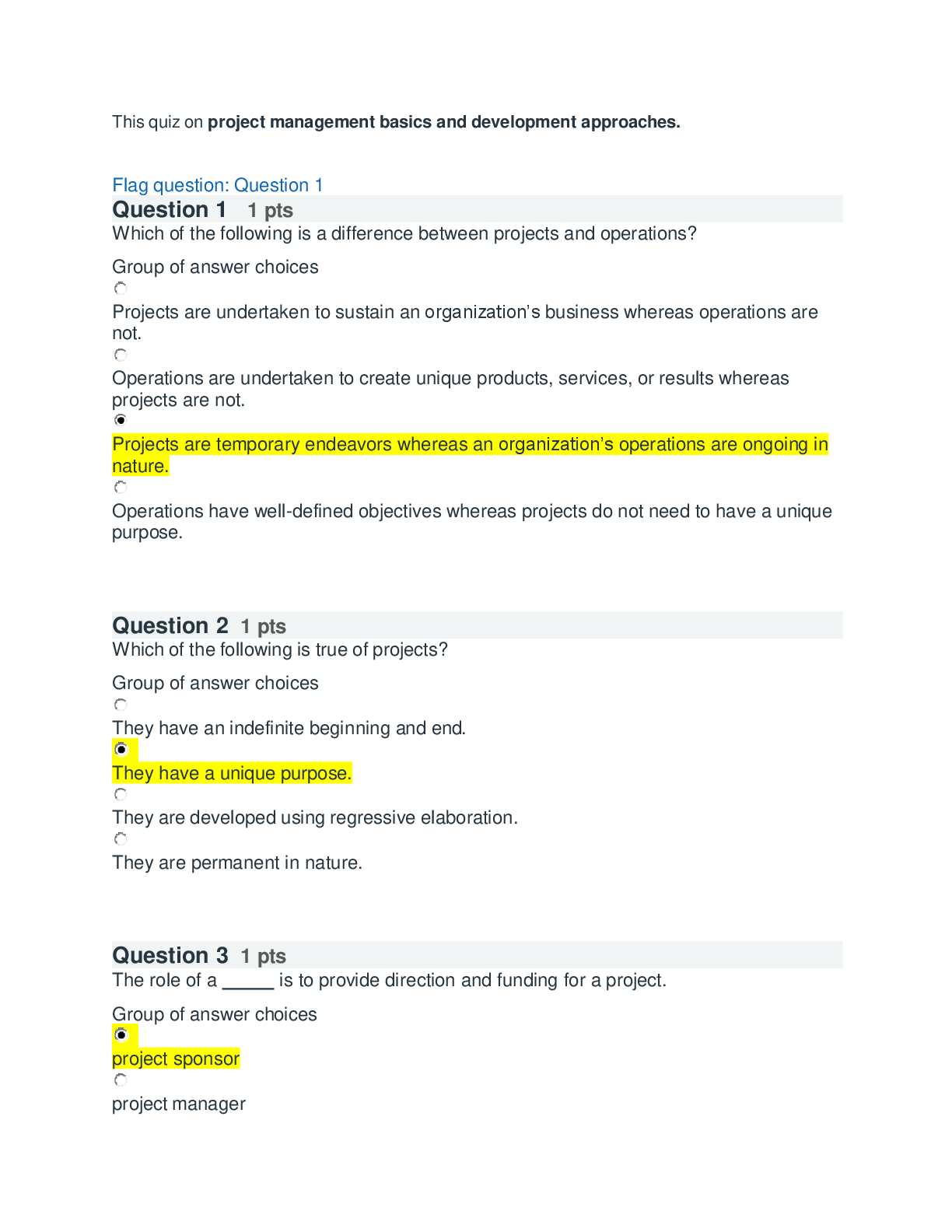
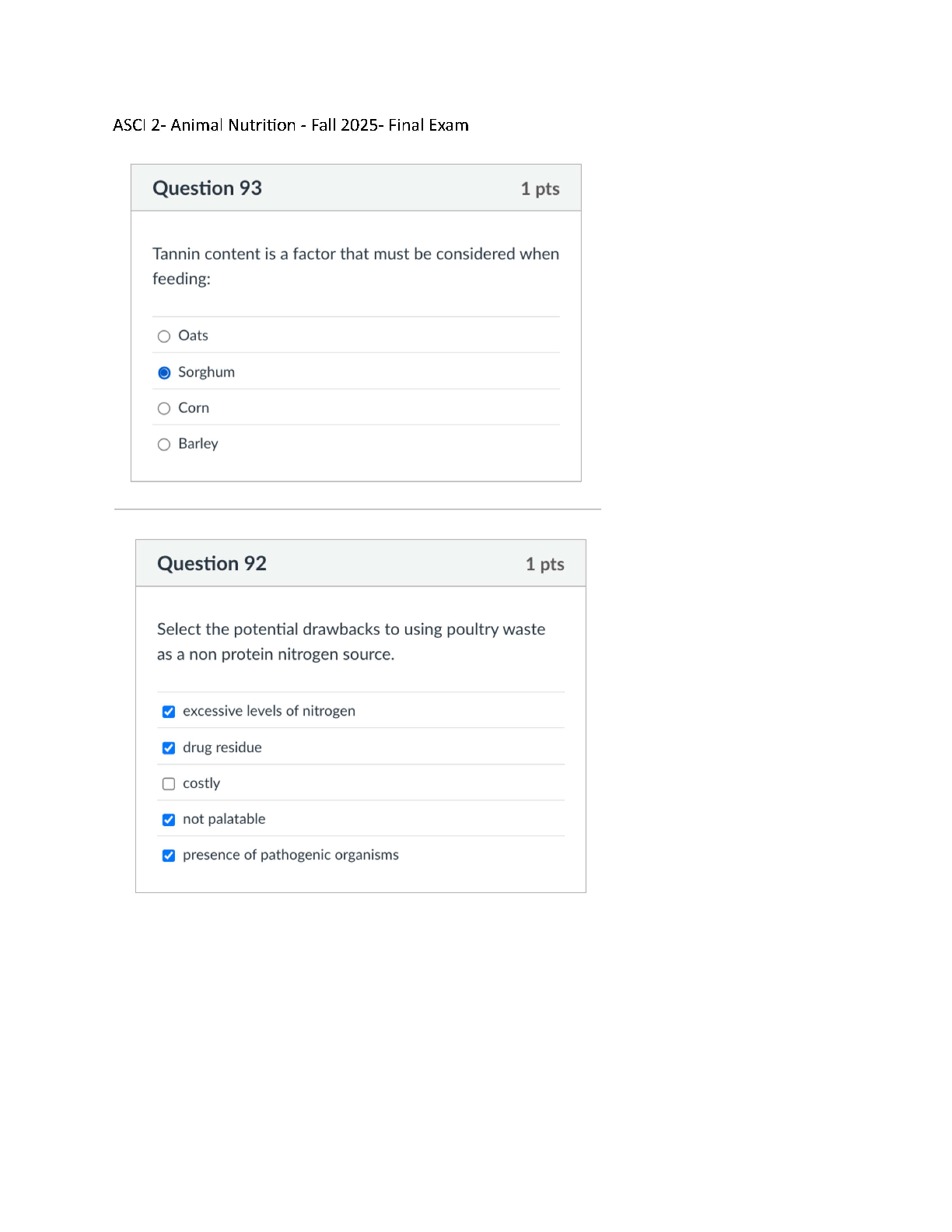
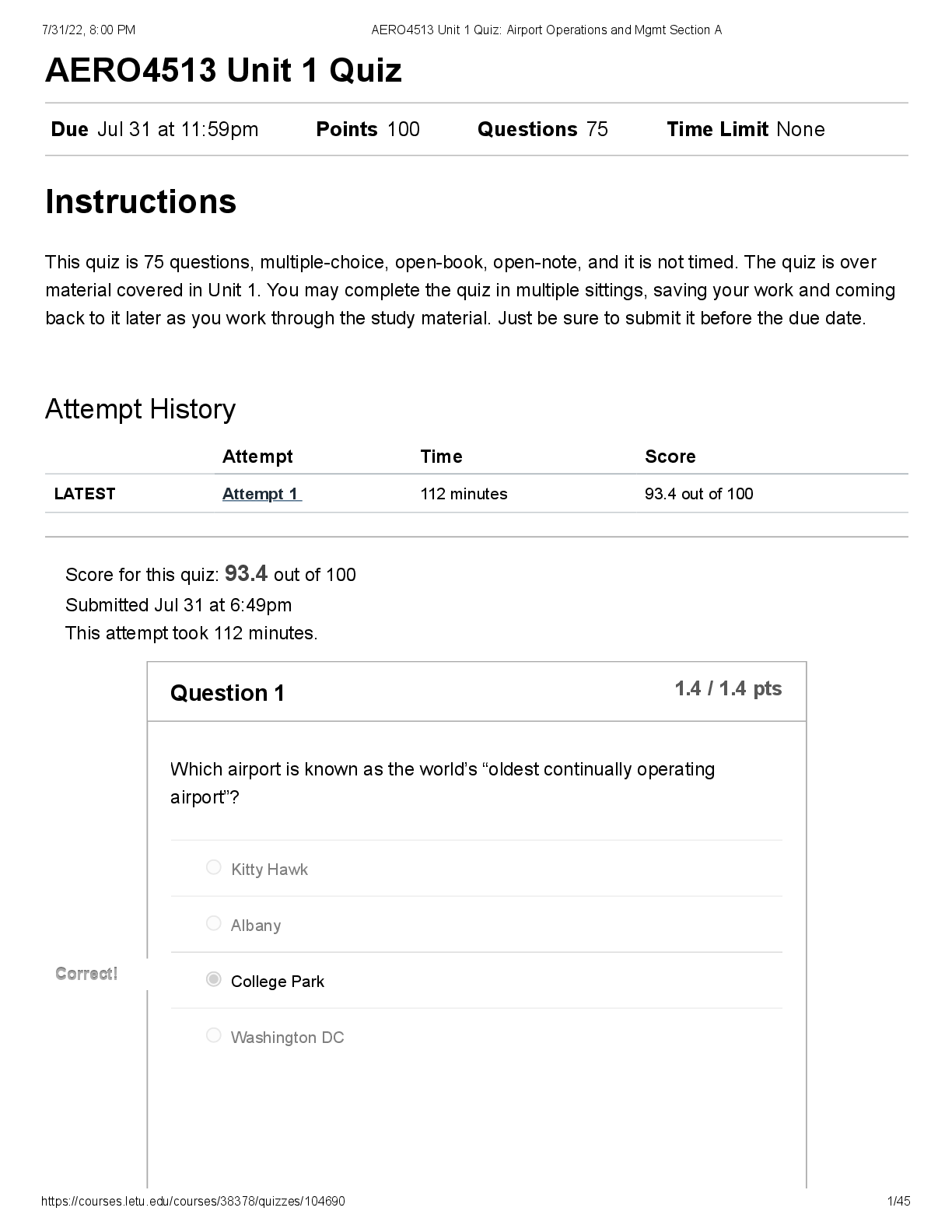
Wk6AssgnDraytonS.docx
$ 10

Drayton S WK1 Assignment.docx
$ 10

WGU C787 STUDY GUIDE
$ 5

ATI Comprehensive Predictor
$ 15
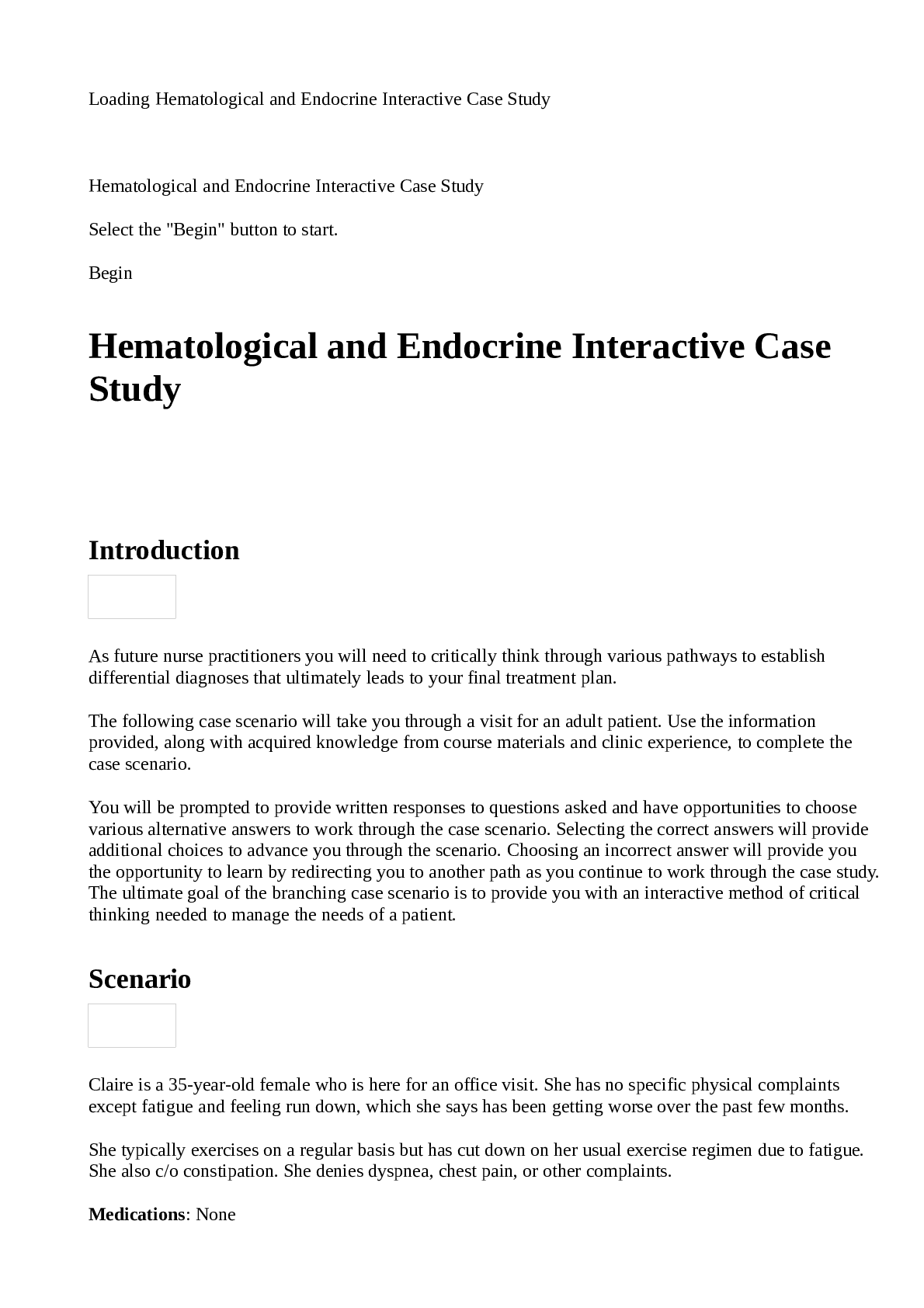
Hematological and Endocrine Interactive Case Study
$ 22

test review material
$ 39.5

NR 509 Midterm Exam Study Guide 2023
$ 11
.png)
ANCC AGPCNP Non-Clinical Terms
$ 7.5

NR565 Final Exam Study Guide
$ 10

NURS 480 - Exam 1 NOTES 2023
$ 12

BASIC LIFE SUPPORT FINAL EXAM
$ 15
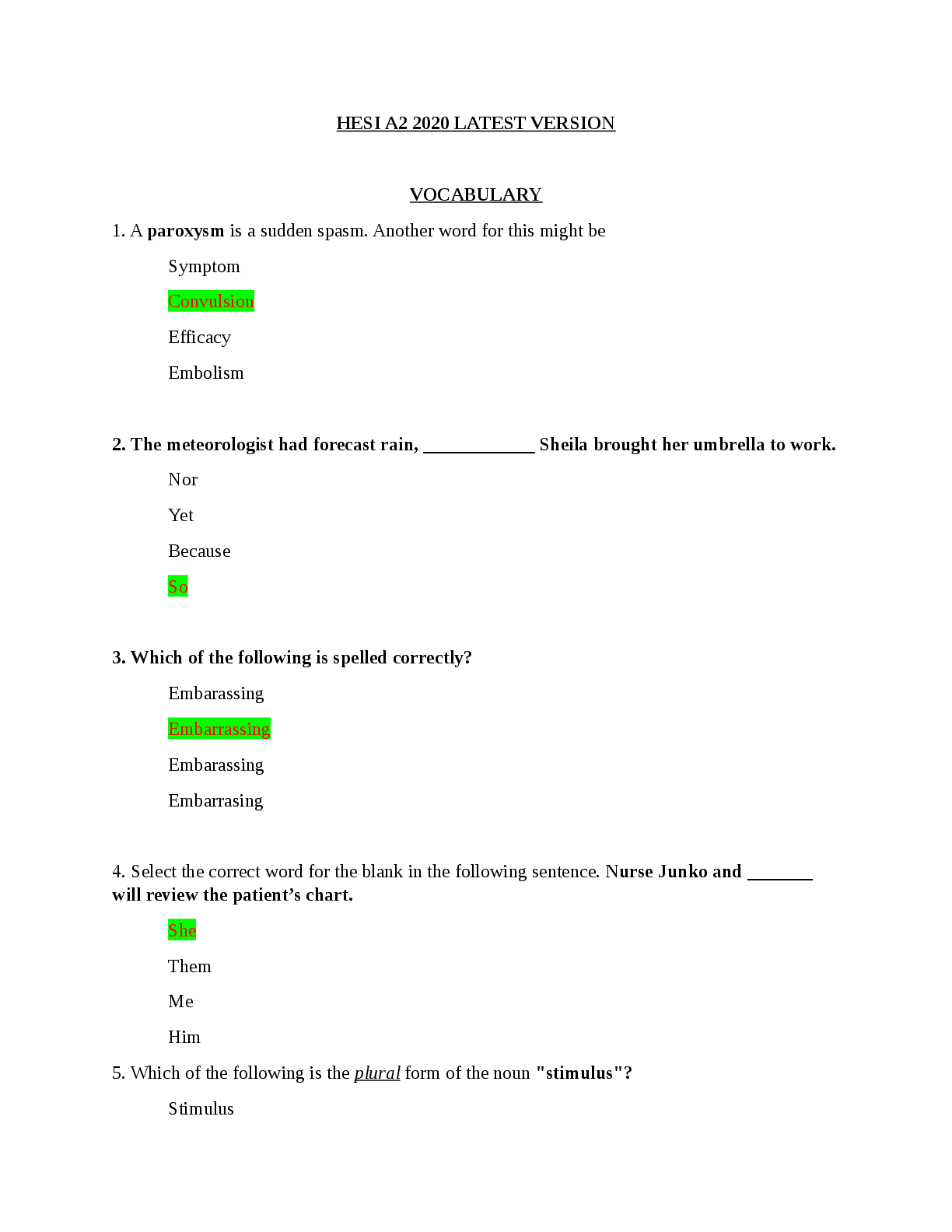
HESI A2 2023 EXAM
$ 30

VSP Foundation 2019
$ 6

PHM 326 / PHM 326 FINAL EXAM
$ 30

N2-Final-Exam-Study-Guide/Top Score
$ 11

ATI Comprehensive Predictor 2019 A
$ 8

NR 509 WEEK 3 MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE (LATEST)
$ 10

EXIT HESI Comprehensive B Evolve Practice Questions
$ 10

NR565 HTN Lipid Protocol
$ 14

CSET Spanish Subtest II
$ 9

WRK 100 Week 3 Check Your Knowledge
$ 11

NR 509 Midterm Exam Study Guide 2023
$ 11

Teas math practice tests practice 7
$ 7.5

Pumping Apparatus DriverOperator Handbook
$ 13

BIOD 121 Final Exam. | VERIFIED SOLUTION
$ 10

Lymphatic system Complete notes Handwritten Clear
$ 11

NSG 307 - Final Study Guide
$ 14.5

CS 2401 – Software Engineering I
$ 12

NURS 231 Final Exam
$ 10
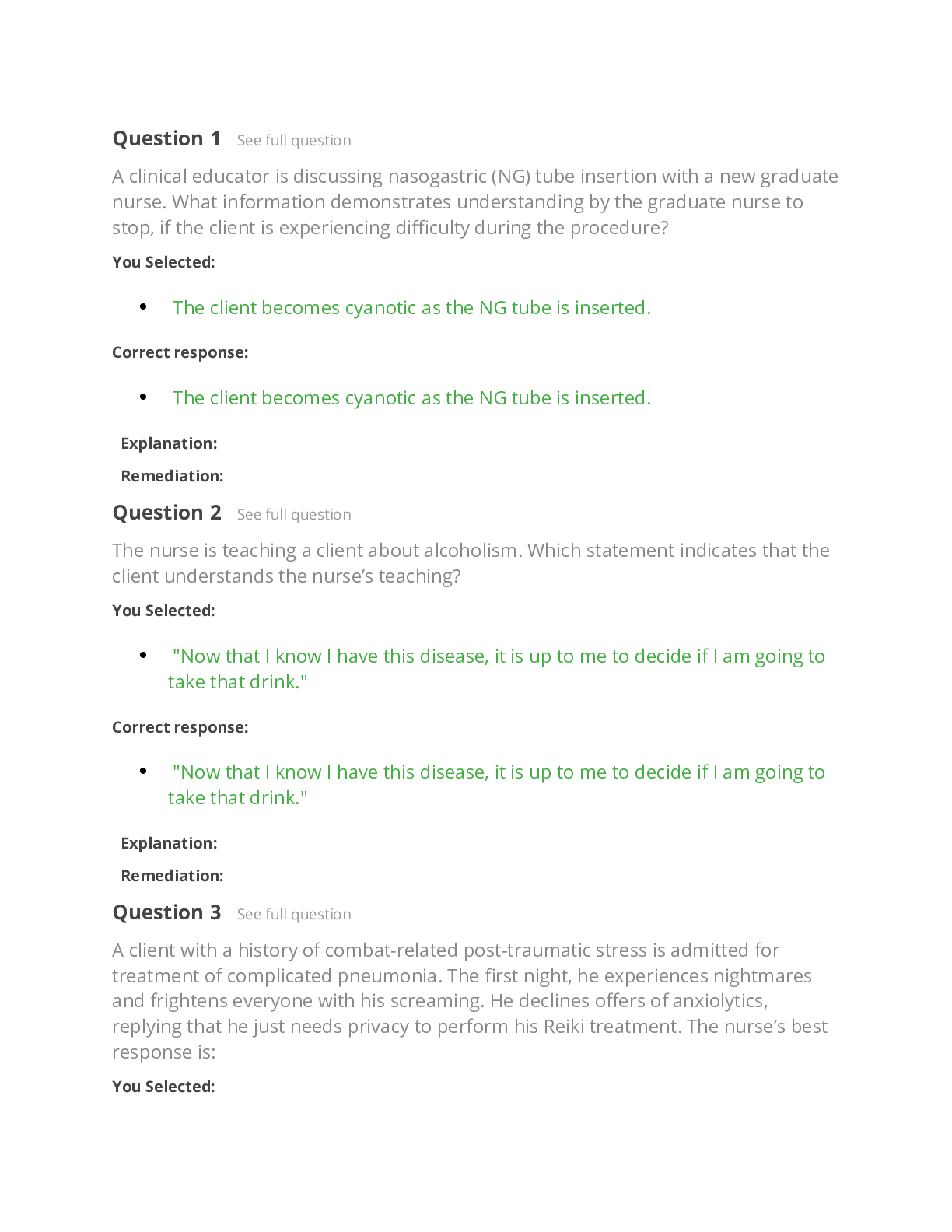
NR 322 NCLEX QNS VERSION 2
$ 14

Econ 222 First Midterm Test Study Guide
$ 11

NUR 265 Final Meds
$ 11

team_assignment__clean_draft.docx Team Assignment: Fourth Amendment Summary University o
$ 5

eBook for Intermediate Algebra 9th Edition By Richard Aufmann, Joanne Lockwood
$ 25

DCPO EXAM WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 7.5

EVIDENCE-BASED PRACTICE ASSESSMENT FOR NURSING STUDENTS VERSION 1
$ 14

HESI A2 - Critical Thinking
$ 10

NURS 231 MODULE 5 EXAM
$ 10

REAL ESTATE FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE FULL
$ 14

PSY331.WK2.Assgn.docx
$ 10

STAT Broward College 2023
$ 30

Knowledge Check I Accurate
$ 15

C236 WGU Exam Study Guide
$ 8
Passpoint Oxygenation
$ 13
Advanced Pathophysiology Week 1 Quiz
$ 10

HESI_Computerized_Adaptive_Testing 2023
$ 17
.png)
ATI CAPSTONE PEDIATRICS
$ 6

CCHT PRACTICE EXAM DAVITA
$ 8.5

Pediatrics Midterm Review 2020
$ 12

ONCOLOGY Complete Nursing Notes
$ 11

Hawaii Adjusters Practice Test



.png)







.png)