
ATI TEAS 7 TEST 2023 BANK WITH ANSWER KEY AND EXPLANATION.
Marketing > EXAM > University of Maryland, University CollegeMRKT 602MRKT 602_Consumer Behavior_FINAL exam_all Answers (All)
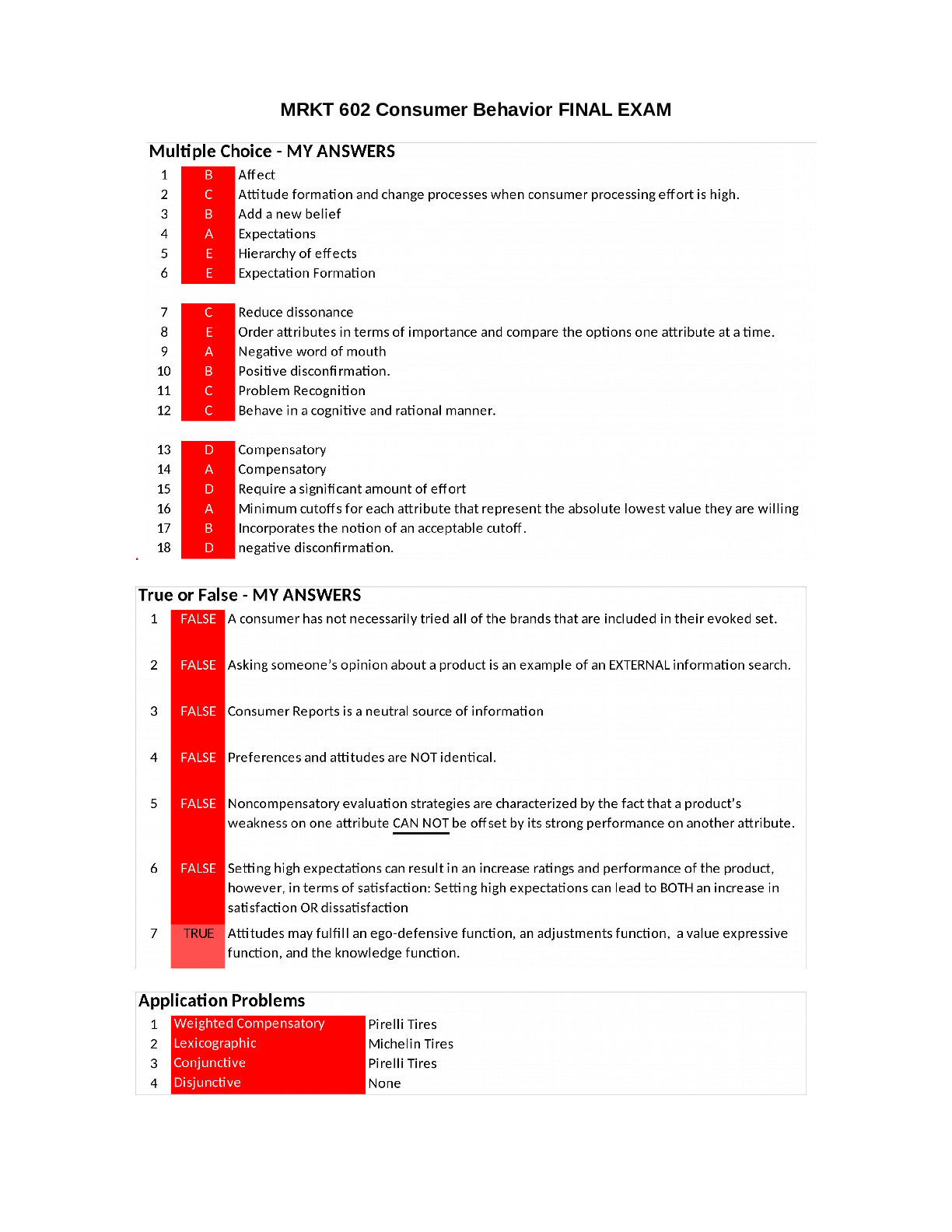
MRKT 602 Consumer Behavior FINAL EXAM . Instructions: Choose the best answer from the alternatives provided. Please answer on the exam. Circle the best possible answer or write it down next to the ... question number. There is only one possible answer per question. Each of the 18 multiple choice and 7 true/false questions are worth 1 point. (B) | 1. Lily didn’t like liver because of its appearance. Her bad attitude toward liver was based ona. motivation. b. affect. c. involvement. d. cognition. e. pre-attitude. (C) 2. Central-route processing describes a. when message processing is not elaborated, but is simply remembered in a direct or central way from the source. b. exclusive affective treatments of information directly from the source rather than indirectly from secondary sources. c. attitude formation and change processes when consumer processing effort is high. d. the superficial analysis and processing of a message. (B) 3. The Canon Xapshot camera, which records pictures on a computer disk, introduces several new beliefs, including “seeing your pictures instantly on your TV” and “the ability to erase unwanted photos.” This is best thought of as an example of an attitude-change strategy to a. target normative beliefs. b. add a new belief. c. change beliefs. d. make attitudes toward the object more important than subjective norms. e. change evaluations. (A) 4. Within the disconfirmation paradigm, __________ are desired product and service outcomes and include “pre-consumption beliefs about overall performance, or the levels or attributes possessed by a product (service).” a. expectations b. purchases c. performances d. confirmations e. cognitions (E) | 5. ___________ refers to the progression of thinking (Cognitive), feeling (Affective) and doing (Behavioral). a. Sequential system b. Satisficing c. Flowing structure d. Progressive system e. Hierarchy of effects (E) 6. All of the following phenomena occur after a purchase is made except a. performance. b. dissatisfaction. c. satisfaction. d. learning about products by direct experience. e. expectation formation. (C) 7. After Ned bought an IBM desktop computer, he felt uneasy and sought out information from magazines and friends that was favorable to IBM and unfavorable to Compaq or Apple. Ned was probably trying to a. increase brand awareness for IBM. b. decrease brand awareness for the other brands. c. reduce dissonance. d. increase brand knowledge for that product category. e. increase his involvement in processing information about other brands. (E) 8. With the lexicographic model, consumers a. evaluate one brand at a time. b. immediately reject the brand or service from the consideration set. c. compare brands by attribute, two at a time. d. choose the brand with the greatest number of positive features. e. order attributes in terms of importance and compare the options one attribute at a time. (A) 9. The most damaging form of behavior that dissatisfied customers can engage in is a. negative word of mouth. b. complaining. c. repeat purchasing. d. discontinuing purchasing. (B) 10. Nathan was pleasantly surprised with his computer game. It had better graphics than he expected and good playability. This is an example of a. negative disconfirmation. b. positive disconfirmation. c. objective expected outcome. d. reinforcement. e. subjective expected outcome. (C) 11. _________ is a critical stage in the decision process because it motivates the consumer to action. a. Information storage b. External search c. Problem recognition d. Purchase e. Internal search (C) 12. A basic assumption underlying many models of consumer decision making when effort is high is that consumers a. have a low need for cognition. b. will usually use simplifying cues, or heuristics. c. behave in a cognitive and rational manner. d. make conjunctive probability assessments. (D) 13. When using the __________ model, consumers choose the brand that has the greatest number of positive features relative to the negative. a. classification b. brand c. attribute d. compensatory e. noncompensatory (A) 14. For some U.S. consumers, a negative feature of Japanese products is that these products are foreign. However, this shortcoming can be overcome if they are rated highly on other aspects, such as reliability and price. This is an example of a(n) __________ model of decision making. a. compensatory b. brand c. classification d. noncompensatory e. attribute (D) 15. Consumers might often not choose to use compensatory models primarily because they a. result in a negativity bias in evaluations. b. are not accurate. c. result in a positivity bias in evaluations. d. require a significant amount of effort. e. do not fit with most product or service decision-making situations. (A) 16. With a conjunctive model, consumers set up a. minimum cutoffs for each attribute that represent the absolute lowest value they are willing to accept. b. ordinal values that automatically compare attributes with others in memory to determine the lowest value. c. maximum cutoffs for each attribute that represent the absolute highest value they are willing to accept. d. ordinal values that automatically compare attributes with others in memory. (B) 17. The elimination-by-aspects model is similar to the lexicographic model except that it a. includes only negative information. b. incorporates the notion of an acceptable cutoff. c. incorporates overall evaluations. d. includes only positive information. (D) 18. AT&T’s advertising tries to set up the expectation that it provides the highest quality phone service. In recent years, however, phone service has gone dead for large blocks of consumers on a number of occasions. This is an example of a. a disconfirmatory subjunctive experience. b. objective unexpected outcome. c. positive disconfirmation. d. negative disconfirmation. True or False (7 points) | 1. A consumer has always tried all the brands that are included in his evoked set. 2. Asking someone’s opinion about a product is an example of internal information search. 3. Consumer Reports is an example of a marketer-dominated information source. 4. Preferences and attitudes are identical. | 5. Non compensatory evaluation strategies are characterized by the fact that a product’s weakness on one attribute can be offset by its strong performance on another attribute. 6. Based on the disconfirmation paradigm, by setting high expectations, companies increase the odds of consumers being satisfied. 7. Attitudes may fulfill an ego-defensive function. TRUE APPLICATION PROBLEM (10 points) John wants to buy four new tires for his car. He decides to make his choice among the four following brands: Firestone, Pirelli, Goodyear and Michelin.The following table summarizes the information that he found regarding these brands. He thinks that the most important attributes to consider, in order to make an appropriate decision, are durability, safety, availability and warranty. He ranked these attributes by giving them a specific weight ranging from 1 to 4 (1 being the least important and 4 the most important). He also evaluates each brand for each attribute considered. These evaluations appear in the following table and range from 1 to 10 (1 being the worst evaluation whereas 10 is the best possible score). In case he needed it, John fixed 6.1 as a cut-off threshold for each attribute. Considered Brands Attributes | Importance (weight) of Attributes . If John decides to use a Multi-attribute (Weighted additive) compensatory model to make his decision, what brand will he choose? Explain briefly (demonstration or calculations). (2.5 points) Pirelli tires. 2. If John decides to use a lexicographic model to make his decision, what brand will he choose? Explain briefly (demonstration or calculations). (2.5 points) Michelin tires. 3. If John decides to use a Conjunctive model to make his decision, what brand will he choose? Explain briefly (demonstration or calculations). (2.5 points) Pirelli tires. 4. If John decides to use a disjunctive model to make his decision, what brand will he choose? Explain briefly (demonstration or calculations). (2.5 points) N/A - None Development Question (15 points) Instructions: Please answer carefully each part of the question in the allocated space. Please explain Weber’s law as discussed during the perception lecture. Give an example if necessary. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 15, 2021
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
86
Scholarfriends.com Online Platform by Browsegrades Inc. 651N South Broad St, Middletown DE. United States.
We're available through e-mail, Twitter, Facebook, and live chat.
FAQ
Questions? Leave a message!
Copyright © Scholarfriends · High quality services·