*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > RN ATI Capstone Leadership and Community Health Focused Review (All)
RN ATI Capstone Leadership and Community Health Focused Review
Document Content and Description Below
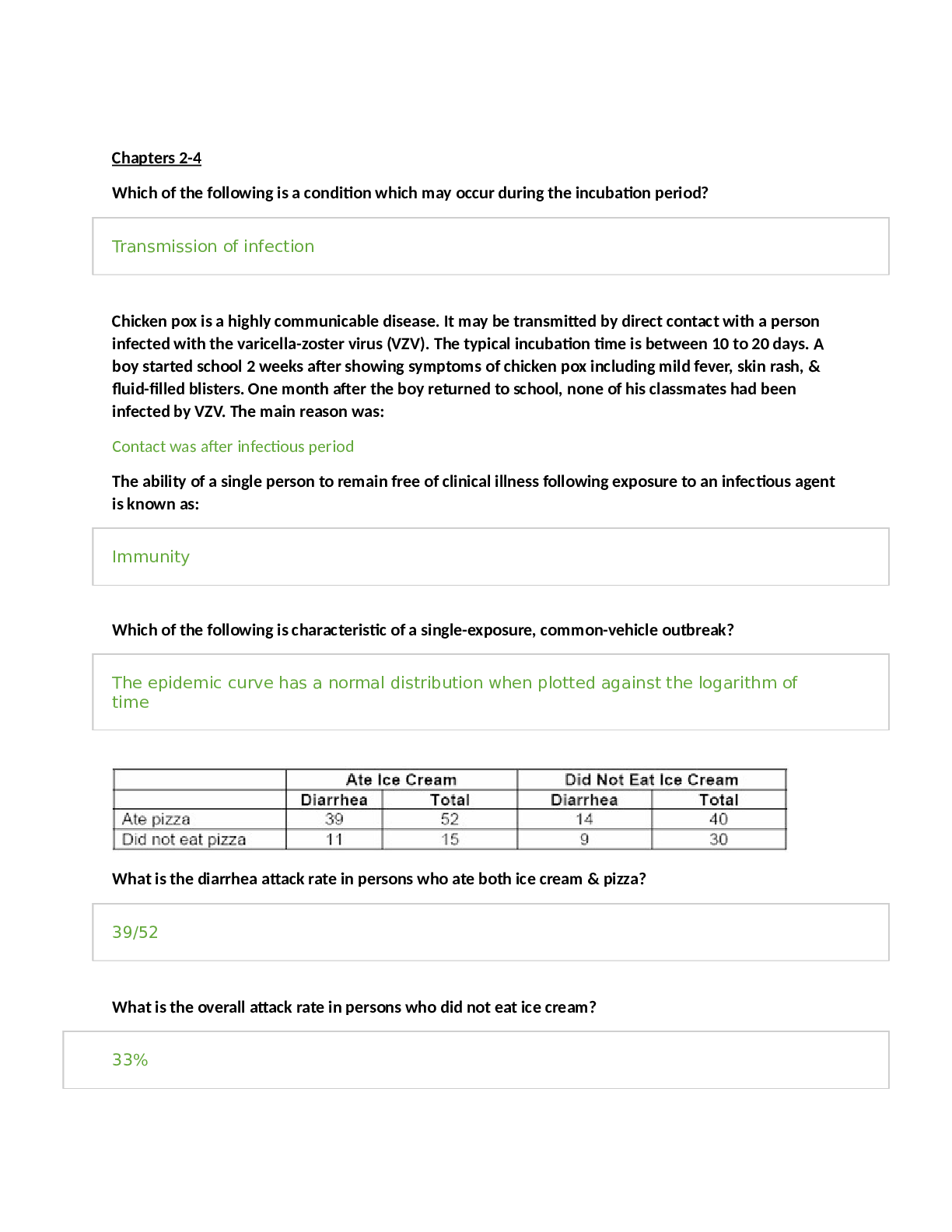
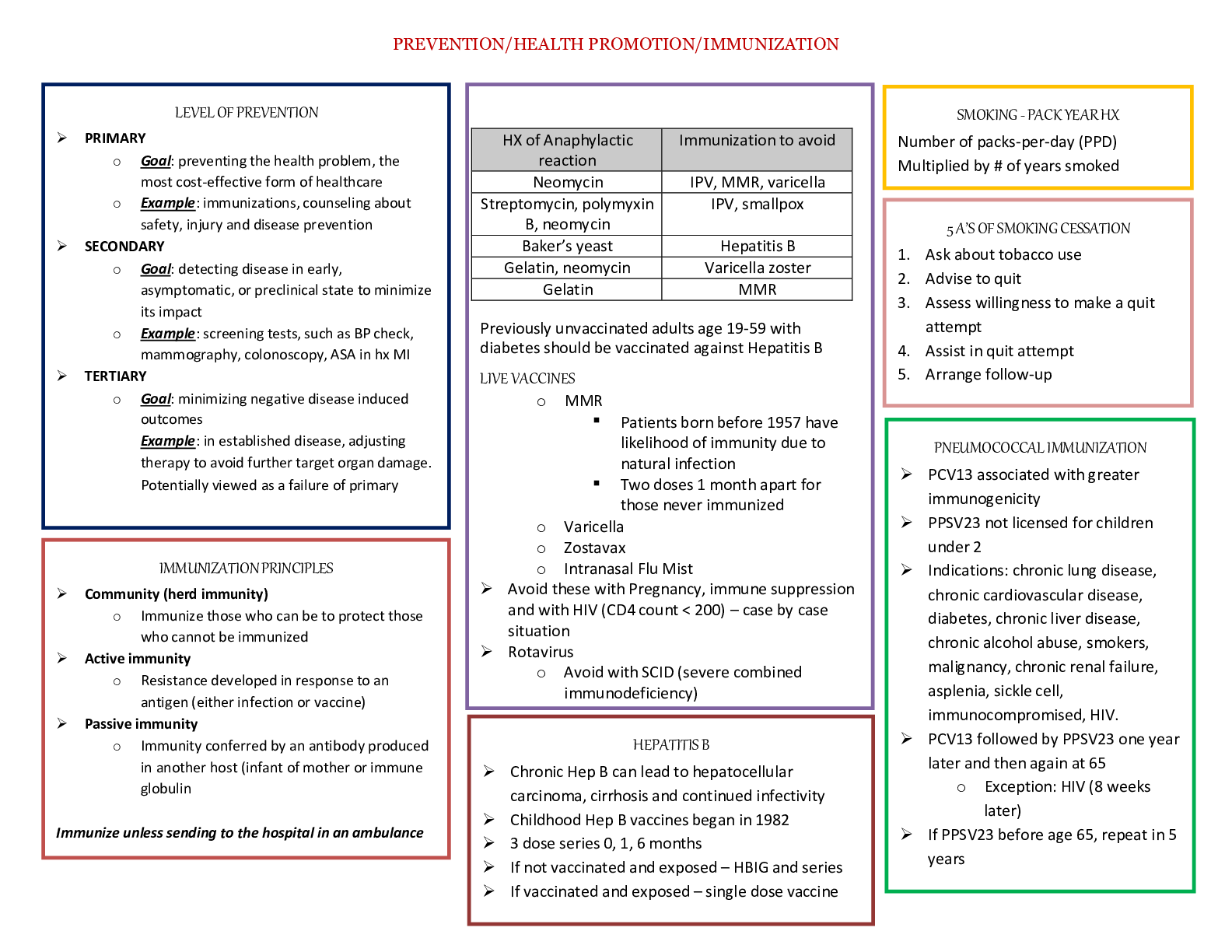
RN ATI Capstone Leadership and Community Health Focused Review Chapter 3 - Professional Responsibilities: Living Will Requirements ● Unless a do not resuscitate (DNR) or allow natural death (AND... ) prescription is written, the nurse should initiate CPR when a client has no pulse or respirations. ● Even if their will requests no resuscitation, they need a DNR prescription from the provider ● The client’s decision is respected in regard to the use of antibiotics, initiation of diagnostic tests, and provision of nutrition by artificial means. Chapter 1 - Managing Client Care: Consulting Sources When Planning Staff Education ● Research: Resources available to address learning objectives based on evidence-based practice ● Staff education, or staff development, is the process by which a staff member gains knowledge and skills. ● The goal of staff education is to ensure that staff members have and maintain the most current knowledge and skills necessary to meet the needs of clients. Chapter 1 - Managing Client Care: Preparing to Delegate Client Care Tasks ● TO PN: ○ Monitoring findings (as input to the rn’s ongoing assessment) ○ reinforcing client teaching from a standard care plan ○ Performing tracheostomy care ○ Suctioning ○ Checking ng tube patency ○ administering enteral feedings ○ inserting a urinary catheter ○ administering medication (excluding IV medication in some states) ● TO AP: ○ activities of daily living (ADLs) ○ Bathing, grooming, dressing, toileting, ambulating, feeding (without swallowing precautions), positioning, routine tasks ○ Bed making ○ Specimen collection ○ Intake and output ○ Vital signs (for stable clients) Chapter 1 - Managing Client Care: Implementing Conflict Management Strategies ● Strategy: Avoiding/Withdrawing ○ Both parties know there is a conflict, but they refuse to face it or work toward are solution. ○ Can be appropriate for minor conflicts or when one party holds more power than the other party or if the issue can work itself out over time. ● Strategy: Smoothing ○ One party attempts to “smooth” another party by trying to satisfy the other party. ● Strategy: Competing/Coercing ○ One party pursues a desired solution at the expense of others. ○ Managers can use this when a quick or unpopular decision must be made. ● Strategy: Compromising/Negotiating ○ Each party gives up something ● Strategy: Collaborating ○ Both parties set aside their original individual goals work together to achieve a new common goal. Chapter 5 - Creating and Maintaining a Therapeutic and Safe Environment: Identifying Countertransference ● Nurse overly identifies with client ● Nurse competes with client ● Nurse argues with client Chapter 2 - Coordinating Client Care: Applying the Nursing Process to Case Management ● Coordinating care, particularly for clients who have complex health care needs ● Facilitating continuity of care ● Improving efficiency of care and utilization of resources ● Enhancing quality of care provided ● Limiting unnecessary costs and lengthy stays ● Advocating for the client and family Chapter 3 - Professional Responsibilities: Providers Who Have Telephone Medication Prescriptive Authority ● physicians, ● advanced practice nurses, ● dentists, & ● physician assistants Chapter 3 - Professional Responsibilities: Organ Donation ● Donor needs to use his signature to agree ● Upon admission it is required all clients over 18 yo be questioned about organ donation ● The National Organ Transplant Act prohibits the sale and purchase of organs ● Documentation about giving permission or refusing to donate is placed in the electronic medical record Chapter 4 - Maintaining a Safe Environment: Home Safety Assessment for an Older Adult Client ● Remove items that could cause the client to trip, such as throw rugs and loose carpets. ● Place electrical cords and extension cords against a wall behind furniture. ● Monitor gait and balance, and provide aids as needed. ● Make sure that steps and sidewalks are in good repair. ● Place grab bars near the toilet and in the tub or shower, and install a stool riser. ● Use a nonskid mat in the tub or shower. ● Wear nonskid footwear. ● Place a shower chair in the shower and provide a bedside commode if needed. ● Ensure that lighting is adequate inside and outside the home. Chapter 6 - Communicable Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism: Interventions for Botulism Management ● MANIFESTATIONS ○ Double or blurred vision ○ Slurred speech ○ Difficulty swallowing ○ Progressive muscle weakness ○ Difficulty breathing ● PREVENTION: No approved vaccine ● TREATMENT ○ Airway management with possible mechanical ventilation ○ Administration of antitoxin ● ELIMINATION OF TOXIN: Induction of vomiting, enemas, surgical excision of wound tissue ● SUPPORTIVE CARE: Nutrition, fluids, prevent complications Chapter 4 - Practice Settings and Aggregates: Outcome Measures of Home Care Interventions ● Family members of clients who have tuberculosis should be screened. ● Individuals who have been exposed to TB but have not developed the disease can have latent TB. Chapter 4 - Practice Settings and Aggregates: Client Teaching About Hospice Care ● Hospice care is a comprehensive care delivery system for clients who are terminally ill. Further medical care aimed toward a cure is stopped. The focus becomes relief of pain and suffering, as well as enhancing quality of life. ● The hospice nurse provides care for the client and the client’s entire family. Hospice care includes skilled, direct services and indirect care coordination. ● The provider directs hospice care services which are then managed by the nurse. Chapter 5 - Care of Specific Populations: Teaching About Family Violence ● Assess and counsel anyone contemplating suicide or homicide, and refer the individual to the appropriate services. ● Support and educate the offender, even though a report must be made. ● Assess and help offenders address and deal with the stressors that can be causing or contributing to the abuse, such as mental illness or substance use Chapter 14 - Head Injury: Complications of a Minor Head Injury Reportable to Provider ● Deteriorating level of consciousness, restlessness, irritability ● Dilated or pinpoint nonreactive pupils ● Alteration in breathing pattern (Cheyne-Stokes respirations, central neurogenic hyperventilation,apnea) ● Deterioration in motor function, abnormal posturing (decerebrate, decorticate, flaccidity) [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 25, 2021
Number of pages
4
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 25, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
105
.png)