PATH 370 Pathophysiology Study Guide Final – West coast University
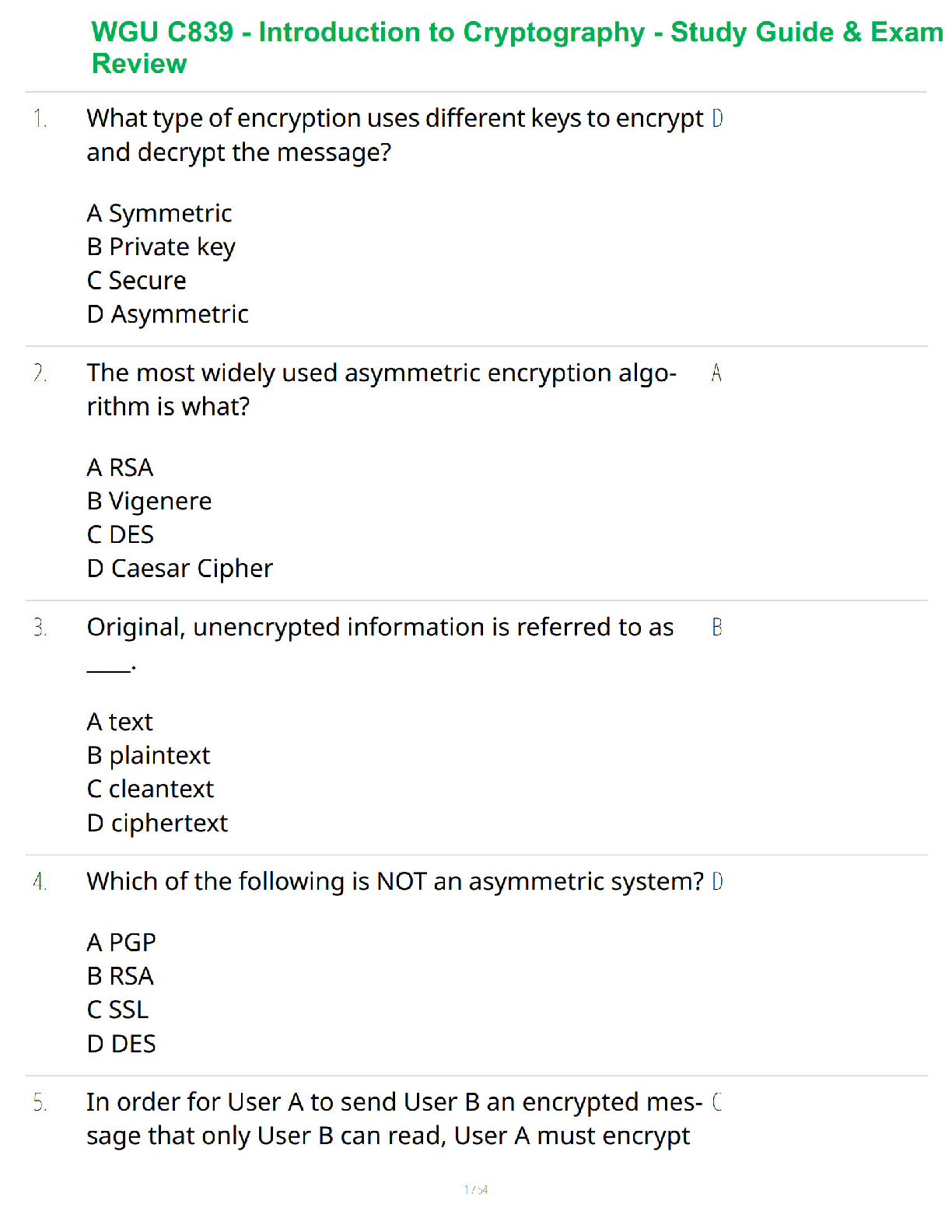
Chapter 44
¬ Brain injury (TBI) aka traumatic brain injury; head injury
o Causes: falls, sports, injuries, firearms, transportation-related trauma
...
PATH 370 Pathophysiology Study Guide Final – West coast University
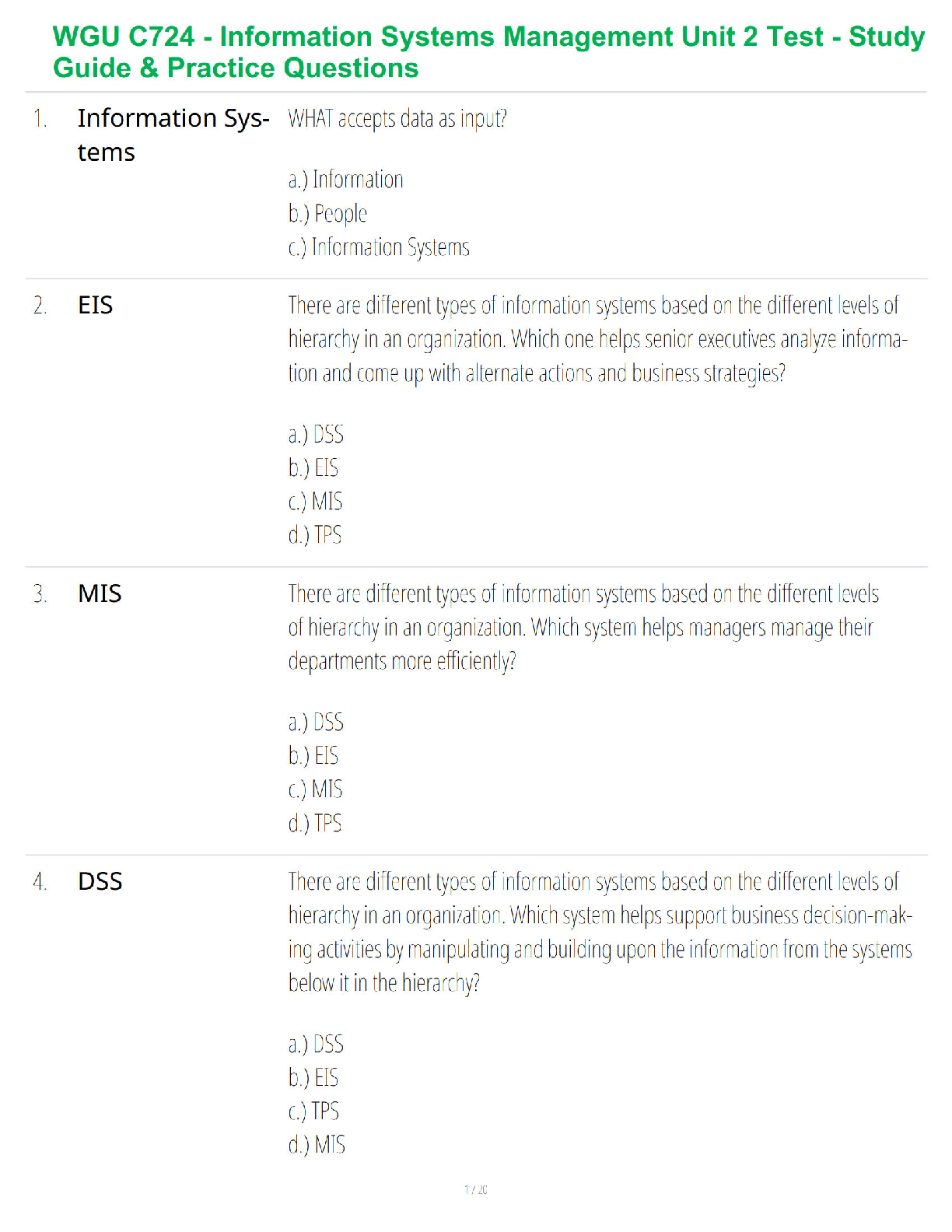
Chapter 44
¬ Brain injury (TBI) aka traumatic brain injury; head injury
o Causes: falls, sports, injuries, firearms, transportation-related trauma
♣ Males between 15-24 are 2X more likely to suffer a TBI
o Mechanism leading to damage, intracranial hypertension, cerebral edema
♣ Primary injury: (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn)
♣ Secondary injury events include damage to the blood–brain barrier, release of factors that cause inflammation, free radical overload, excessive release of the neurotransmitter glutamate (excitotoxicity), influx of calcium and sodium ions into neurons, and dysfunction of mitochondria.[55] Injured axons in the brain's white matter may separate from their cell bodies as a result of secondary injury,[55] potentially killing those neurons.
♣ Other factors in secondary injury are changes in the blood flow to the brain; ischemia (insufficient blood flow); cerebral hypoxia (insufficient oxygen in the brain); cerebral edema (swelling of the brain); and raised intracranial pressure (the pressure within the skull).[66] Intracranial pressure may rise due to swelling or a mass effect from a lesion, such as a hemorrhage.[44] As a result, cerebral perfusion pressure (the pressure of blood flow in the brain) is reduced; ischemia results.[32][67] When the pressure within the skull rises too high, it can cause brain death or herniation, in which parts of the brain are squeezed by structures in the skull.
• Direct injury or bruising (contusion) to surface brain tissue.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Chapter 51
¬ Muscle strain
o Etiology-most common, si/sx, dx, tx
¬ Ostroporosis --> fractures (classifications: simple, compound, comminuted, spiral...etc.)
o Etiology, si/sx, dx, tx, risks
¬ Osteomyelitis
o Etiology, risks
¬ Rhabdosarcoma vs Liposarcoma vs Osteosarcoma vs Chondrosarcoma
o Prefix and suffix
¬ Myasthenia gravis vs. Muscular dystrophy
o Etiology, si/sx, dx, tx
¬ Compartment syndrome
o Etiology, si/sx, dx, tx
Chapter 52
¬ Autoimmune disease
o General (Definition, si/sx, biomarker)
¬ Systemic Lupus Erythematosis (SLE)
o Etiology, si/sx, dx, tx
o SLE vs. Scleroderma
¬ Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) vs Osteoarthritis (OA)
o Etiology, si/sx, dx, tx
¬ Gouty Arthritis vs Pseudogout
o Etiology, si/sx, dx, tx
o What is tophi?
[Show More]