*NURSING > EXAM > NR 509 Advanced physical assessment quiz 4 (2020) – Chamberlain College of Nursing | NR509 Advance (All)
NR 509 Advanced physical assessment quiz 4 (2020) – Chamberlain College of Nursing | NR509 Advanced physical assessment quiz 4 (2020)
Document Content and Description Below
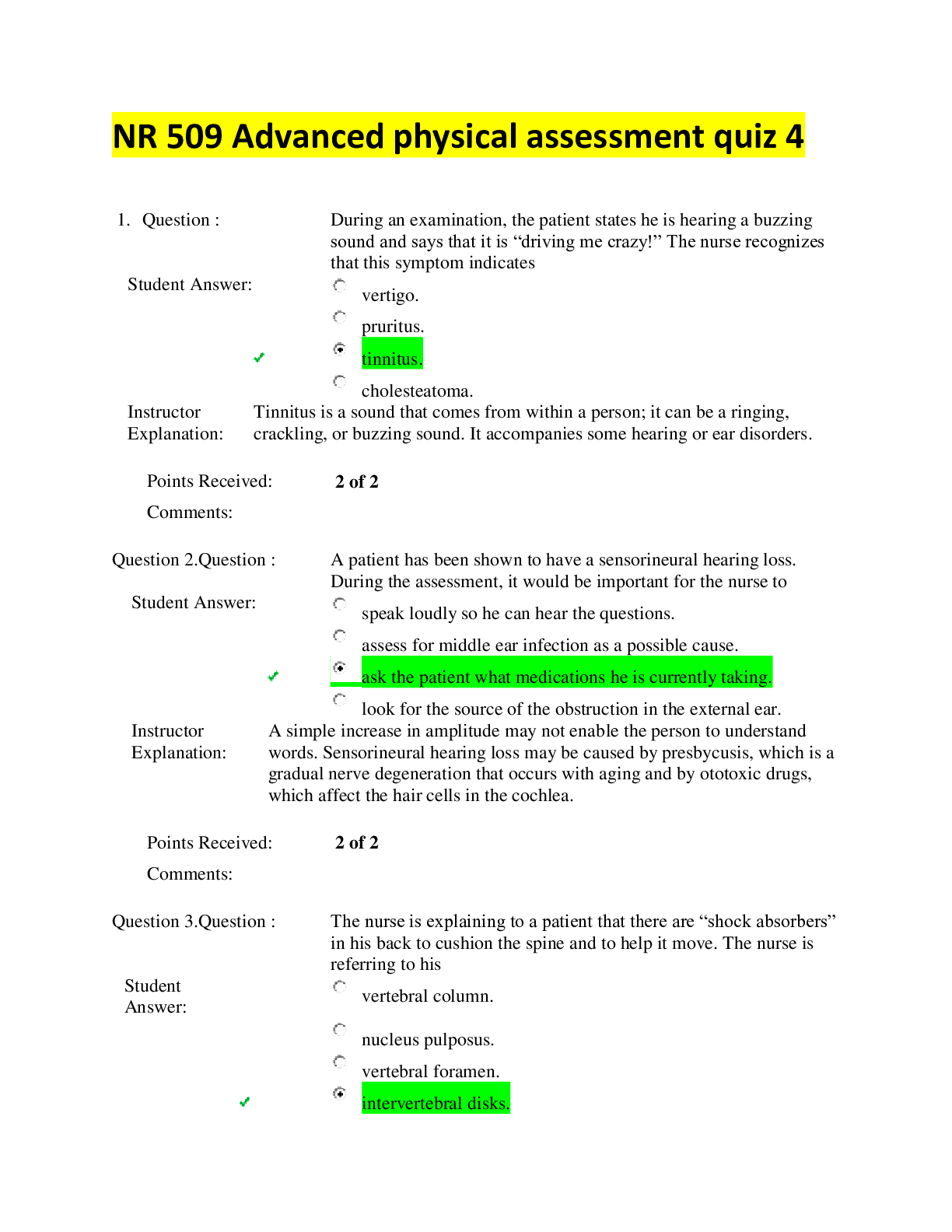
NR 509 Advanced physical assessment quiz 4 (2020) – Chamberlain College of Nursing Advanced physical assessment quiz 4 1. Question : During an examination, the patient states he is hea... ring a buzzing sound and says that it is “driving me crazy!” The nurse recognizes that this symptom indicates Student Answer: vertigo. pruritus. tinnitus. cholesteatoma. Instructor Explanation: Tinnitus is a sound that comes from within a person; it can be a ringing, crackling, or buzzing sound. It accompanies some hearing or ear disorders. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 2. Question : A patient has been shown to have a sensorineural hearing loss. During the assessment, it would be important for the nurse to Student Answer: speak loudly so he can hear the questions. assess for middle ear infection as a possible cause. ask the patient what medications he is currently taking. look for the source of the obstruction in the external ear. Instructor Explanation: A simple increase in amplitude may not enable the person to understand words. Sensorineural hearing loss may be caused by presbycusis, which is a gradual nerve degeneration that occurs with aging and by ototoxic drugs, which affect the hair cells in the cochlea. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 3. Question : The nurse is explaining to a patient that there are “shock absorbers” in his back to cushion the spine and to help it move. The nurse is referring to his Student Answer: vertebral column. nucleus pulposus. vertebral foramen. intervertebral disks. Instructor Explanation: Intervertebral disks are elastic fibrocartilaginous plates that cushion the spine like shock absorbers and help it move. The vertebral column is the spinal column itself. The nucleus pulposus is located in the center of each disk. The vertebral foramen is the channel, or opening, for the spinal cord in the vertebrae. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 4. Question : The nurse educator is preparing an education module for the nursing staff on the epidermal layer of skin. Which of these statements would be included in the module? The epidermis is Student Answer: highly vascular. thick and tough. thin and nonstratified. replaced every 4 weeks. Instructor Explanation: The epidermis is thin yet tough, replaced every 4 weeks, avascular, and stratified into several zones. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 5. Question : The nurse is examining a 6-month-old infant and places the infant’s feet flat on the table and flexes his knees up. The nurse notes that the right knee is significantly lower than the left. Which of these statements is true of this finding? Student Answer: This is a positive Allis sign and suggests hip dislocation. The infant probably has a dislocated patella on the right. This is a normal finding for the Allis test for an infant of this age. The infant should return to the clinic in 2 weeks to see if this has changed. Instructor Explanation: Finding one knee significantly lower than the other is a positive Allis sign and suggests hip dislocation. Normally, the tops of the knees are at the same elevation. The other statements are not correct. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 6. Question : A patient drifts off to sleep when she is not being stimulated. The nurse can arouse her easily when calling her name, but she remains drowsy during the conversation. The best description of this patient’s level of consciousness would be Student Answer: lethargic. obtunded. stuporous. semialert. Instructor Explanation: Lethargic (or somnolent) is when the person is not fully alert, drifts off to sleep when not stimulated, and can be aroused when called by name in a normal voice but looks drowsy. He or she responds appropriately to questions or commands, but thinking seems slow and fuzzy. He or she is inattentive and loses train of thought. Spontaneous movements are decreased. See Table 5-3 for definitions of the other terms. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 7. Question : A 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after he was found dazed and incoherent, alone in his apartment. He has an enlarged liver and is moderately dehydrated. When evaluating his serum albumin level, the nurse must keep in mind that Student Answer: serum albumin levels will increase as liver function decreases. serum albumin levels are a sensitive measure of early protein malnutrition. low serum albumin levels may be caused by reasons other than protein-calorie malnutrition. the results of the serum albumin measurement along with the patient’s hemoglobin level should be considered. Instructor Explanation: Low serum albumin levels may be caused by reasons other than protein-calorie malnutrition, such as an altered hydration status and decreased liver function. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 8. Question : The nurse is checking the range of motion in a patient’s knee and knows that the knee is capable of which movement(s)? Student Answer: Flexion and extension Supination and pronation Circumduction Inversion and eversion Instructor Explanation: The knee is a hinge joint, permitting flexion and extension of the lower leg on a single plane. The knee is not capable of the other movements listed. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 9. Question : A patient has been admitted after an accident at work. During the assessment, the patient is having trouble hearing and states, “I don’t know what the matter is. All of a sudden, I can’t hear you out of my left ear!” What should the nurse do next? Student Answer: Make note of this finding for report to the next shift. Prepare to remove cerumen from the patient’s ear. Notify the patient’s healthcare provider. Irrigate the ear with rubbing alcohol. Instructor Explanation: Any sudden loss of hearing in one or both ears that is not associated with an upper respiratory infection needs to be reported at once to the patient’s healthcare provider. Hearing loss associated with trauma is often sudden. It is not appropriate to irrigate the ear or remove cerumen at this time. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 10. Question : A 40-year-old man has come into the clinic with complaints of “extreme tenderness in my toes.” The nurse notices that his toes are slightly swollen, reddened, and warm to the touch. His complaints would suggest Student Answer: osteoporosis. acute gout. ankylosing spondylitis. degenerative joint disease. Instructor Explanation: Acute gout occurs primarily in men over 40 years of age. Clinical findings consist of redness, swelling, heat, and extreme tenderness. Gout is a metabolic disorder of disturbed purine metabolism, associated with elevated serum uric acid. See Table 22-1 for descriptions of the other terms. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 11. Question : A 19-year-old college student is brought to the emergency department with a severe headache he describes as “like nothing I’ve ever had before.” His temperature is 104° F, and he has a stiff neck. The nurse looks for other signs and symptoms of which problem? Student Answer: Head injury Cluster headache Migraine headache Meningeal inflammation Instructor Explanation: Acute onset of neck stiffness and pain along with headache and fever occurs with meningeal inflammation. A severe headache in an adult or child who has never had it before is a red flag. Head injury and cluster or migraine headaches are not associated with a fever or stiff neck. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 12. Question : A mother brings her newborn baby boy in for a checkup; she tells the nurse that he doesn’t seem to be moving his right arm as much as his left and that he seems to have pain when she lifts him up under the arms. The nurse suspects a fractured clavicle and would observe for Student Answer: a negative Allis test. a positive Ortolani’s sign. limited range of motion during the Moro’s reflex. limited range of motion during Lasègue’s test Instructor Explanation: For a fractured clavicle, the nurse should observe for limited arm range of motion and unilateral response to the Moro’s reflex. The other tests are not appropriate for this problem. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 13. Question : While performing the otoscopic examination of a 3-year-old boy who has been pulling on his left ear, the nurse finds that his left tympanic membrane is bright red and that the light reflex is not visible. The nurse interprets these findings to indicate Student Answer: a fungal infection. acute otitis media. perforation of the ear drum. cholesteatoma. Instructor Explanation: Absent or distorted light reflex and a bright red color of the eardrum are indicative of acute otitis media. See Table 15-5 for descriptions of the other conditions. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 14. Question : The nurse is teaching a class on osteoporosis prevention to a group of postmenopausal women. Which of these actions is the best way to prevent or delay bone loss in this group? Student Answer: Taking calcium and vitamin D supplements Taking medications to prevent osteoporosis Performing physical activity, such as fast walking Assessing bone density annually Instructor Explanation: Physical activity, such as fast walking, delays or prevents bone loss in perimenopausal women. The faster the pace of walking, the higher the preventive effect on the risk of hip fracture. The other options are not correct. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 15. Question : The nurse is examining a 2-year-old child and asks, “May I listen to your heart now?” Which critique of the nurse’s technique is most accurate? Student Answer: Asking questions enhances the child’s autonomy. Asking the child for permission helps to develop a sense of trust. This is an appropriate statement because children at this age like to have choices. Children at this age like to say “no.” The examiner should not offer a choice when there is none. Instructor Explanation: Children at this age like to say “no.” Do not offer a choice when there really is none. If the child says “no,” and the nurse does it anyway, then the nurse loses trust. Autonomy is enhanced by offering a limited option, “Shall I listen to your heart next or your tummy?” Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 16. Question : Which of these assessment findings would the nurse expect to see when examining the eyes of a black patient? Student Answer: Increased night vision A dark retinal background Increased photosensitivity Narrowed palpebral fissures Instructor Explanation: There is an ethnically based variability in the color of the iris and in retinal pigmentation, with darker irides having darker retinas behind them. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 17. Question : A 50-year-old patient has been brought to the emergency department after a housemate found that he could not get out of bed alone. He has lived in a group home for years, but for several months he has not participated in the activities and has stayed in his room. The nurse assesses for signs of undernutrition, and x-rays reveal that he has osteomalacia, which is a deficiency of Student Answer: iron. riboflavin. vitamin D and calcium. vitamin C. Instructor Explanation: Osteomalacia results from vitamin D and calcium deficiency in adults. Iron deficiency would result in anemia, riboflavin deficiency would result in “magenta tongue,” and vitamin C deficiency would result in scurvy. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 18. Question : A patient who has had rheumatoid arthritis for years comes to the clinic to ask about changes in her fingers. The nurse will assess for signs of what problems? Student Answer: Heberden’s nodes Bouchard’s nodules Swan neck deformities Dupuytren’s contractures Instructor Explanation: Changes in the fingers caused by chronic rheumatoid arthritis include swan neck and boutonniere deformities. Heberden’s nodes and Bouchard’s nodules are associated with osteoarthritis. Dupuytren’s contractures occur because of chronic hyperplasia of the palmar fascia and causes contractures of the digits (see Table 22-4). Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 19. Question : The nurse notices that a patient has a solid, elevated, circumscribed lesion that is less than 1 cm in diameter. When documenting this finding, the nurse would report this as a Student Answer: bulla. wheal. nodule. papule. Instructor Explanation: A papule is something one can feel, is solid, elevated, circumscribed, less than 1 cm in diameter, and is due to superficial thickening in the epidermis. A bulla is larger than 1 cm, superficial, and thin-walled. A wheal is superficial, raised, transient, erythematous, and irregular in shape due to edema. A nodule is solid, elevated, hard or soft, and larger than 1 cm. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 20. Question : Just before going home, a new mother asks the nurse about the infant’s umbilical cord. Which of these statements is correct? Student Answer: “It should fall off by 10 to 14 days.” “It will soften before it falls off.” “It contains two veins and one artery.” “Skin will cover the area within 1 week.” Instructor Explanation: At birth, the umbilical cord is white and contains two umbilical arteries and one vein inside the Wharton jelly. The umbilical stump dries within a week, hardens, and falls off by 10 to 14 days. Skin will cover the area by 3 to 4 weeks. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 21. Question : The nurse is assessing a patient with a history of intravenous drug abuse. In assessing his mouth, the nurse notices a dark red confluent macule on the hard palate. This could be an early sign of Student Answer: AIDS. measles. leukemia. carcinoma. Instructor Explanation: Oral Kaposi sarcoma is a bruise-like, dark red or violet, confluent macule that usually occurs on the hard palate. It may appear on the soft palate or gingival margin. Oral lesions may be among the earliest lesions to develop with AIDS. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 22. Question : When observing a patient’s verbal and nonverbal communication, the nurse notices a discrepancy. Which statement is true regarding this situation? The nurse should Student Answer: ask someone who knows the patient well to help interpret this discrepancy. focus on the patient’s verbal message and try to ignore the nonverbal behaviors. try to integrate the verbal and nonverbal messages and then interpret them as an “average.” focus on the patient’s nonverbal behaviors because these are often more reflective of a patient’s true feelings. Instructor Explanation: When nonverbal and verbal messages are congruent, the verbal message is reinforced. When they are incongruent, the nonverbal message tends to be the true one because it is under less conscious control. Thus, it is important to study the nonverbal messages of patients and examiners and to understand their meanings. The other statements are not true. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 23. Question : The nurse is assessing a 75-year-old man. As the nurse begins the mental status portion of the assessment, the nurse expects that this patient Student Answer: will have no decrease in any of his abilities, including response time. will have difficulty on tests of remote memory because this typically decreases with age. may take a little longer to respond, but his general knowledge and abilities should not have declined. will have had a decrease in his response time because of language loss and a decrease in general knowledge. Instructor Explanation: The aging process leaves the parameters of mental status mostly intact. There is no decrease in general knowledge and little or no loss in vocabulary. Response time is slower than in youth. It takes a bit longer for the brain to process information and to react to it. Recent memory, which requires some processing, is somewhat decreased with aging, but remote memory is not affected. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 24. Question : When reviewing the demographics of ethnic groups in the United States, the nurse recalls that the largest and fasting growing population is Student Answer: Hispanic. Black. Asian. American Indian. Instructor Explanation: Hispanics are the largest and fastest growing population in the United States, followed by Asians, blacks, American Indians, Alaska natives, and other groups. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 25. Question : During an examination, the nurse asks a patient to bend forward from the waist and notices that the patient has lateral tilting. When his leg is raised straight up, he complains of a pain going down his buttock into his leg. The nurse suspects Student Answer: scoliosis. meniscus tear. herniated nucleus pulposus. spasm of paravertebral muscles. Instructor Explanation: Lateral tilting and sciatic pain with straight leg raising are findings that occur with a herniated nucleus pulposus. The other options are not correct. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 26. Question : During an examination of a 3-year-old child, the nurse will need to take her blood pressure. What might the nurse do to try to gain the child’s full cooperation? Student Answer: Tell the child that the blood pressure cuff is going to give her arm a big hug. Tell the child that the blood pressure cuff is asleep and cannot wake up. Give the blood pressure cuff a name and refer to it by this name during the assessment. Tell the child that by using the blood pressure cuff, we can see how strong her muscles are. Instructor Explanation: Use short, simple sentences with a concrete explanation. Take time to give a short, simple explanation for any unfamiliar equipment that will be used on the child. Preschoolers are animistic; they imagine inanimate objects can come alive and have human characteristics. Thus, a blood pressure cuff can wake up and bite or pinch. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 27. Question : Which of these statements is true regarding the use of standard precautions in the healthcare setting? Student Answer: Standard precautions apply to all body fluids, including sweat. Use alcohol-based hand rub if hands are visibly dirty. Standard precautions are intended for use with all patients regardless of their risk or presumed infection status. Standard precautions are to be used only when there is nonintact skin, excretions containing visible blood, or expected contact with mucous membranes. Instructor Explanation: Standard precautions are designed to reduce the risk of transmission of microorganisms from both recognized and unrecognized sources. They are intended for use for all patients, regardless of their risk or presumed infection status. They apply to blood and all other body fluids, secretions and excretions except sweat, regardless of whether they contain visible blood, nonintact skin, or mucous membranes. Hands should be washed with soap and water if visibly soiled with blood or body fluids; alcohol-based hand rubs can be used if hands are not visibly soiled. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 28. Question : Which term refers to a wound produced by the tearing or splitting of body tissue, usually from blunt impact over a bony surface? Student Answer: Abrasion Contusion Laceration Hematoma Instructor Explanation: The term laceration fits this definition. An abrasion is caused by the rubbing of the skin or mucous membrane. A contusion is an injury to tissues without breakage of skin, and a hematoma is a localized collection of extravasated blood. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 29. Question : A 70-year-old man has a blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg in a lying position, 130/80 mm Hg in a sitting position, and 100/60 mm Hg in a standing position. How should the nurse evaluate these findings? Student Answer: This is a normal response due to changes in the patient’s position. The change in blood pressure readings is called orthostatic hypotension. The blood pressure reading in the lying position is within normal limits. The change in blood pressure reading is considered within normal limits for the patient’s age. Instructor Explanation: Orthostatic hypotension is a drop in systolic pressure of more than 20 mm Hg, which occurs with a quick change to a standing position. Aging people have the greatest risk of this problem. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 30. Question : A patient with a middle ear infection asks the nurse, “What does the middle ear do?” The nurse responds by telling the patient that the middle ear functions to Student Answer: maintain balance. interpret sounds as they enter the ear. conduct vibrations of sounds to the inner ear. increase amplitude of sound for the inner ear to function. Instructor Explanation: Among its other functions, the middle ear conducts sound vibrations from the outer ear to the central hearing apparatus in the inner ear. The other responses are not functions of the middle ear. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 31. Question : Which statement is best for the nurse to use when preparing to administer the Abuse Assessment Screen? Student Answer: “We are required by law to ask these questions.” “We need to talk about whether you feel you have been abused.” “We are asking these questions because we suspect that you are being abused.” “We ask the following questions because domestic violence is so common in our society.” Instructor Explanation: Such an introduction both alerts the woman that questions about domestic violence are coming and makes sure that the woman knows she is not being singled out for these questions. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 32. Question : A professional tennis player comes into the clinic complaining of a sore elbow. The nurse will assess for tenderness at the Student Answer: olecranon bursa. annular ligament. base of the radius. medial and lateral epicondyle. Instructor Explanation: The epicondyles, the head of radius, and tendons are common sites of inflammation and local tenderness, or “tennis elbow.” The other locations are not affected. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 33. Question : The nurse is assessing the mental status of a child. Which of these statements about children and mental status is true? Student Answer: All aspects of mental status in children are interdependent. Children are highly labile and unstable until the age of 2 years. Children’s mental status is largely a function of their parents’ level of functioning until the age of 7 years. A child’s mental status is impossible to assess until the child develops the ability to concentrate. Instructor Explanation: It is difficult to separate and trace the development of just one aspect of mental status. All aspects are interdependent. For example, consciousness is rudimentary at birth because the cerebral cortex is not yet developed. The infant cannot distinguish the self from the mother’s body. The other statements are not true. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 34. Question : A 19-year-old woman comes to the clinic at the insistence of her brother. She is wearing black combat boots and a black lace nightgown over the top of her other clothes. Her hair is dyed pink with black streaks throughout. She has several pierced holes in her nares and ears and is wearing an earring through her eyebrow and heavy black makeup. The nurse concludes Student Answer: she probably doesn’t have any problems at all. she is just trying to shock people and her dress should be ignored. she has manic syndrome because of her abnormal dress and grooming. that more information should be gathered to decide whether her dress is appropriate. Instructor Explanation: Grooming and hygiene should be noted: the person is clean and well groomed, hair is neat and clean, women have moderate or no makeup, men are shaved or their beards or moustaches are well groomed. Use care in interpreting clothing that is disheveled, bizarre, or in poor repair because these sometimes reflect the person’s economic status or a deliberate fashion trend. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 35. Question : A patient is visiting the clinic for an evaluation of a swollen, painful knuckle. The nurse notices that the knuckle above his ring on the left hand is swollen and that he is unable to remove his wedding ring. This joint is called the _____ joint. Student Answer: interphalangeal tarsometatarsal metacarpophalangeal tibiotalar Instructor Explanation: The joint located just above the ring on the finger is the metacarpophalangeal joint. The interphalangeal joint is located distal to the metacarpophalangeal joint. The tarsometatarsal and tibiotalar joints are found in the foot and ankle. See Figure 22-10 for a diagram of the bones and joints of the hand and fingers. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 36. Question : A 52-year-old patient describes the presence of occasional “floaters” or “spots” moving in front of his eyes. The nurse should Student Answer: examine the retina to determine the number of floaters. presume the patient has glaucoma and refer him for further testing. consider this an abnormal finding and refer him to an ophthalmologist. know that floaters are usually not significant and are caused by condensed vitreous fibers. Instructor Explanation: Floaters are a common sensation with myopia or after middle age owing to condensed vitreous fibers. Usually they are not significant, but acute onset of floaters may occur with retinal detachment. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 37. Question : A mother brings in her newborn infant for an assessment and tells the nurse that she has noticed that whenever her newborn’s head is turned to the right side, she straightens out the arm and leg on the same side and flexes the opposite arm and leg. After finding this on examination, the nurse would tell her that this is Student Answer: abnormal and is called the atonic neck reflex. normal and should disappear by the first year of life. normal and should disappear between 3 and 4 months of age. abnormal. The baby should be flexing the arm and leg on the right side of his body when the head is turned to the right. Instructor Explanation: By 2 weeks, the infant shows the tonic neck reflex when supine and the head is turned to one side (extension of same arm and leg, flexion of opposite arm and leg). The tonic neck reflex disappears between 3 and 4 months of age. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 38. Question : A patient comes to the clinic complaining of neck and shoulder pain and is unable to turn her head. The nurse suspects damage to cranial nerve (CN) _____ and proceeds with the examination by _____. Student Answer: XI; palpating the anterior and posterior triangles XI; asking the patient to shrug her shoulders against resistance XII; percussing the sternomastoid and submandibular neck muscles XII; assessing for a positive Romberg sign Instructor Explanation: The major neck muscles are the sternomastoid and the trapezius. They are innervated by CN XI, the spinal accessory. The innervated muscles assist with head rotation and head flexion, movement of the shoulders, and extension and turning of the head. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 39. Question : The nurse is testing a patient’s visual accommodation, which refers to which action? Student Answer: Pupillary constriction when looking at a near object Pupillary dilation when looking at a far object Changes in peripheral vision in response to light Involuntary blinking in the presence of bright light Instructor Explanation: The muscle fibers of the iris contract the pupil in bright light and accommodate for near vision, which also results in pupil constriction. The other responses are not correct. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 40. Question : The nurse is assessing the skin of a patient who has AIDS and notices multiple patch-like lesions on the temple and beard area that are faint pink in color. The nurse recognizes these lesions as Student Answer: measles (rubeola). Kaposi’s sarcoma. angiomas. herpes zoster. Instructor Explanation: Kaposi’s sarcoma is a vascular tumor that, in early stages, appears as multiple, patch-like, faint pink lesions over the patient’s temple and beard areas. Measles is characterized by a red-purple maculopapular blotchy rash which appears on third or fourth day of illness. Rash appears first behind ears and spreads over face, then over neck, trunk, arms, and legs. Cherry (senile) angiomas are small (1 to 5 mm), smooth, slightly raised bright red dots that commonly appear on the trunk in all adults over 30 years old. Herpes zoster causes vesicles that are elevated with a cavity containing clear fluid, up to 1 cm in size. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 41. Question : The nurse is assessing the vital signs of a 20-year-old male marathon runner and documents the following vital signs: temperature—97 F; pulse—48 beats per minute; respirations—14 per minute; blood pressure—104/68 mm Hg. Which statement is true about these results? Student Answer: The patient is experiencing tachycardia. These are normal vital signs for a healthy, athletic adult. The patient’s pulse rate is not normal—his physician should be notified. On the basis of today’s readings, the patient should return to the clinic in 1 week. Instructor Explanation: In the adult, a heart rate less than 50 beats per minute is called bradycardia. This occurs normally in the well-trained athlete whose heart muscle develops along with the skeletal muscles. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 42. Question : The nurse is planning health teaching for a 65-year-old woman who has had a cerebrovascular accident, or stroke, and is aphasic. Which of these questions is most important to use when assessing mental status in this situation? Student Answer: “Please count back from 100 by seven.” “I will name three items and ask you to repeat them in a few minutes.” “Please point to articles in the room and parts of the body as I name them.” “What would you do if you found a stamped, addressed envelope on the sidewalk?” Instructor Explanation: Additional tests for persons with aphasia include word comprehension (asking the individual to point to articles in the room or parts of the body), reading (asking the person to read available print), and writing (asking the person to make up and write a sentence). Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 43. Question : The nurse is unable to identify any changes in sound when percussing over the abdomen of an obese patient. What should the nurse do next? Student Answer: Ask the patient to take deep breaths to relax the abdominal musculature. Consider this a normal finding and proceed with the abdominal assessment. Increase the amount of strength used when attempting to percuss over the abdomen. Decrease the amount of strength used when attempting to percuss over the abdomen. Instructor Explanation: The thickness of the person’s body wall will be a factor. The nurse will need a stronger percussion stroke for persons with obese or very muscular body walls. The force of the blow determines the loudness of the note. The other actions are not correct. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 44. Question : A 35-year-old pregnant woman comes to the clinic for a monthly appointment. During the assessment, the nurse notices that she has a brown patch of hyperpigmentation on her face. The nurse continues the skin assessment aware that another finding may be Student Answer: keratoses. xerosis. chloasma acrochordons. Instructor Explanation: In pregnancy, skin changes can include striae, linea nigra (a brownish black line down the midline), chloasma (brown patches of hyperpigmentation), and vascular spiders. Keratoses are raised, thickened areas of pigmentation that look crusted, scaly, and warty. Xerosis is dry skin. Acrochordons, or “skin tags” occur more often in the aging adult. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 45. Question : During a session on substance abuse, the nurse is reviewing statistics with the class. For persons aged 12 years and older, which of these illicit substances was the one most commonly used? Student Answer: Crack cocaine Heroin Marijuana Hallucinogens Instructor Explanation: In persons age 12 and older who reported past month use, marijuana (hashish) was the most commonly used illicit drug reported. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 46. Question : A 92-year-old patient has had a stroke. The right side of his face is drooping. The nurse might also suspect which of these assessment findings? Student Answer: Epistaxis Rhinorrhea Dysphagia Xerostomia Instructor Explanation: Dysphagia is difficulty with swallowing and may occur with a variety of disorders, including stroke and other neurologic diseases. Rhinorrhea is a runny nose; epistaxis is a bloody nose. Xerostomia is a dry mouth. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 47. Question : The nurse is assessing the body weight as a percentage of ideal body weight on an adolescent patient who was admitted for suspected anorexia nervosa. The patient’s usual weight was 125 pounds, but today she weighs 98 pounds. The nurse calculates the patient’s ideal body weight, and reaches which conclusion? Student Answer: She is experiencing mild malnutrition. She is experiencing moderate malnutrition. She is experiencing severe malnutrition. Her current weight is still within expected parameters. Instructor Explanation: By dividing her current weight by her usual weight, then multiplying by 100, a percentage of 78.4% is obtained. This means that her current weight is 78.4% of her ideal body weight. A current weight of 80% to 90% of ideal weight suggests mild malnutrition; a current weight of 70% to 80% of ideal weight suggests moderate malnutrition; a current weight of less than 70% of ideal weight suggests severe malnutrition. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 48. Question : The nurse knows that one advantage of the tympanic thermometer is that Student Answer: its rapid measurement is useful for uncooperative younger children. it is the most accurate method for measuring temperature in newborn infants. it is an inexpensive means of measuring temperature. studies strongly support use of the tympanic route in children under age 6 years. Instructor Explanation: The tympanic thermometer (TMT) is useful for younger children who may not cooperate for oral temperatures and fear rectal temperatures. Keep in mind that TMT use with newborn infants and young children is conflicting. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 49. Question : The nurse recognizes that an example of a person who is heritage-consistent would be a Student Answer: woman who has adapted her clothing to the clothing style of her new country. woman who follows the traditions that her mother followed regarding meals. man who is not sure of his ancestor’s country of origin. child who is not able to speak his parents’ native language. Instructor Explanation: Someone who is heritage-consistent lives a lifestyle that reflects his or her traditional heritage, not the norms and customs of the new country. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 50. Question : During an assessment of an infant, the nurse notes that the fontanels are depressed and sunken. The nurse suspects which condition? Student Answer: Rickets Dehydration Mental retardation Increased intracranial pressure Instructor Explanation: Depressed and sunken fontanels occur with dehydration or malnutrition. Mental retardation and rickets have no effect on fontanels. Increased intracranial pressure would cause tense or bulging, and possibly pulsating fontanels. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 51. Question : When considering a nutritional assessment, the nurse is aware that the most common anthropometric measurements include Student Answer: height and weight. leg circumference. biceps skinfold thickness. hip and waist measurement. Instructor Explanation: The most commonly used anthropometric measures are height, weight, triceps skinfold thickness, elbow breadth, and arm and head circumferences. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 52. Question : The nurse is providing nutrition information to the mother of a 1-year-old child. Which of these statements represents accurate information for this age group? Student Answer: It is important to maintain adequate fat and caloric intake. The recommended dietary allowances for an infant are the same as for an adolescent. At this age, the baby’s growth is minimal so caloric requirements are decreased. The baby should be placed on skim milk to decrease the risk of coronary artery disease when older. Instructor Explanation: Because of rapid growth, especially of the brain, infants and children younger than 2 years should not drink skim or low-fat milk or be placed on low-fat diets—fat (calories and essential fatty acids) is required for proper growth and central nervous system development. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 53. Question : The nurse needs to palpate the temporomandibular joint for crepitation. This joint is located just below the temporal artery and anterior to the Student Answer: hyoid. vagus nerve. tragus. mandible. Instructor Explanation: The temporomandibular joint is just below the temporal artery and anterior to the tragus. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 54. Question : The physician reports that a patient with a neck tumor has a tracheal shift. The nurse is aware that this means that the patient’s trachea is Student Answer: pulled to the affected side. pushed to the unaffected side. pulled downward. pulled downward in a rhythmic pattern. Instructor Explanation: The trachea is pushed to the unaffected side with an aortic aneurysm, a tumor, unilateral thyroid lobe enlargement, and pneumothorax. The trachea is pulled to the affected side with large atelectasis, pleural adhesions, or fibrosis. Tracheal tug is a rhythmic downward pull that is synchronous with systole and occurs with aortic arch aneurysm. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 55. Question : The nurse is incorporating a person’s spiritual values into the health history. Which of these questions illustrates the “community” portion of the FICA questions? Student Answer: “Do you believe in God?” “Are you a part of any religious or spiritual congregation?” “Do you consider yourself to be a religious or spiritual person?” “How does your religious faith influence the way you think about your health?” Instructor Explanation: The “community” is assessed when the nurse asks whether a person is part of a religious or spiritual community or congregation. The other areas assessed are faith, influence, and addressing any religious or spiritual issues or concerns. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 56. Question : The patient’s record, laboratory studies, objective data, and subjective data combine to form the Student Answer: data base. admitting data. financial statement. discharge summary. Instructor Explanation: Together with the patient’s record and laboratory studies, the objective and subjective data form the data base. The other items are not composed of the patient’s record, laboratory studies, and data. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 57. Question : During an interview, the patient states, “I can feel this bump on the top of both of my shoulders—it doesn’t hurt but I am curious about what it might be.” The nurse should tell the patient, “That is Student Answer: your subacromial bursa.” your acromion process.” your glenohumeral joint.” the greater tubercle of your humerus.” Instructor Explanation: The bump of the scapula’s acromion process is felt at the very top of the shoulder. The other options are not correct. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 58. Question : After completing an initial assessment on a patient, the nurse has charted that his respirations are eupneic and his pulse is 58. This type of data would be Student Answer: objective. reflective. subjective. introspective. Instructor Explanation: Objective data are what the health professional observes by inspecting, percussing, palpating, and auscultating during the physical exam. Subjective data is what the person says about himself or herself during history taking. The terms “reflective” and “introspective” are not used to describe data. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 59. Question : During a class on religion and spirituality, the nurse is asked to define spirituality. Which answer is correct? “Spirituality is Student Answer: a personal search to discover a supreme being.” an organized system of beliefs concerning the cause, nature, and purpose of the universe.” a belief that each person exists forever in some form, such as a belief in reincarnation or the afterlife.” that which arises out of each person’s unique life experience and his or her personal effort to find purpose in life.” Instructor Explanation: Spirituality arises out of each person’s unique life experience and his or her personal effort to find purpose and meaning in life. The other definitions reflect the concept of religion. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 60. Question : In the hot/cold theory, illnesses are believed to be caused by hot or cold entering the body. Which of these patients’ conditions is most consistent with a “cold” condition? Student Answer: Diabetic patient with renal failure Teenager with an abscessed tooth Child with symptoms of itching and a rash Elderly male with gastrointestinal discomfort Instructor Explanation: Illnesses believed to be caused by cold entering the body include earache, chest cramps, gastrointestinal discomfort, rheumatism, and tuberculosis. Those illnesses believed to be caused by heat, or overheating, include sore throats, abscessed teeth, rashes, and kidney disorders. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 61. Question : A woman is leaving on a trip to Hawaii and has come in for a checkup. During the examination, the nurse notices that she is diabetic and takes oral hypoglycemic agents. The patient needs to be concerned about which possible effect of her medications? Student Answer: An increased possibility of bruising Skin sensitivity as a result of exposure to salt water Lack of availability of glucose monitoring supplies The importance of sunscreen and avoiding direct sunlight Instructor Explanation: Drugs that may increase sunlight sensitivity and give a burn response include sulfonamides, thiazide diuretics, oral hypoglycemic agents, and tetracycline. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 62. Question : Symptoms, such as pain, are often influenced by a person’s cultural heritage. Which of the following is a true statement regarding pain? Student Answer: Nurses’ attitudes toward their patients’ pain are unrelated to their own experiences with pain. Nurses need to recognize that many cultures practice silent suffering as a response to pain. A nurse’s area of clinical practice is most likely to determine his or her assessment of a patient’s pain. A nurse’s years of clinical experience and current position are a strong indicator of his or her response to patient pain. Instructor Explanation: Silent suffering is a potential response to pain in many cultures. The nurse’s assessment of pain needs to be embedded in a cultural context. The other responses are not correct. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 63. Question : Because hair for humans is no longer needed for protection from cold or trauma, it is called Student Answer: vellus. vagus. vestigial. vestibule. Instructor Explanation: Hair is vestigial for humans. It no longer is needed for protection from cold or trauma. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 64. Question : During an assessment of a 20-year-old patient with a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting, the nurse notices dry mucosa and deep vertical fissures in the tongue. These findings are reflective of Student Answer: dehydration. irritation by gastric juices. a normal oral assessment. side effects from nausea medication. Instructor Explanation: Dry mouth occurs with dehydration or fever. The tongue has deep vertical fissures. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 65. Question : In response to a question about stress, a 39-year-old woman tells the nurse that her husband and mother both died in the past year. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate? Student Answer: “This has been a difficult year for you.” “I don’t know how anyone could handle that much stress in one year!” “What did you do to cope with the loss of both your husband and mother?” “That is a lot of stress; now let’s go on to the next section of your history.” Instructor Explanation: Questions about coping and stress management include questions regarding the kinds of stresses in one’s life, especially in the last year, any change in lifestyle or any current stress, methods tried to relieve stress, and whether these have been helpful. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 66. Question : The nurse is preparing to perform a physical assessment. Which statement is true about the inspection phase of the physical assessment? Student Answer: Inspection usually yields little information. Inspection takes time and reveals a surprising amount of information. Inspection may be somewhat uncomfortable for the expert practitioner. Inspection requires a quick glance at the patient’s body systems before proceeding on with palpation. Instructor Explanation: A focused inspection takes time and yields a surprising amount of information. Initially, the examiner may feel uncomfortable “staring” at the person without also “doing something.” A focused assessment is much more than a “quick glance.” Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 67. Question : The nurse is performing an eye assessment on an 80-year-old patient. Which of these findings is considered abnormal? Student Answer: A decrease in tear production Unequal pupillary constriction in response to light The presence of arcus senilis seen around the cornea Loss of the outer hair on the eyebrows due to a decrease in hair follicles Instructor Explanation: Pupils are small in old age, and the pupillary light reflex may be slowed, but pupillary constriction should be symmetric. The assessment findings in the other responses are considered normal in older persons. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 68. Question : The nurse is reviewing for a class in age-related changes in the eye. Which of these physiological changes is responsible for presbyopia? Student Answer: Degeneration of the cornea Loss of lens elasticity Decreased adaptation to darkness Decreased distance vision abilities Instructor Explanation: The lens loses elasticity and decreases its ability to change shape to accommodate for near vision. This condition is called presbyopia. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 69. Question : A student is late for his appointment and has rushed across campus to the health clinic. Before assessing his vital signs, the nurse should Student Answer: allow him 5 minutes to relax and rest before checking his vital signs. check the blood pressure in both arms, expecting a difference in the readings because of his recent exercise. monitor his vital signs immediately on his arrival at the clinic, then 5 minutes later, and notice any differences. check his blood pressure in the supine position because this will give a more accurate reading and will allow him to relax at the same time. Instructor Explanation: A comfortable, relaxed person yields a valid blood pressure. Many people are anxious at the beginning of an examination; the nurse should allow at least a 5-minute rest before measuring his blood pressure. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 70. Question : During an oral assessment of a 30-year-old African-American patient, the nurse notices bluish lips and a dark line along the gingival margin. What would the nurse do in response to this finding? Student Answer: Check the patient’s hemoglobin for anemia. Assess for other signs of insufficient oxygen supply. Proceed with assessment, knowing that this is a normal finding. Ask if he has been exposed to an excessive amount of carbon monoxide. Instructor Explanation: Some African-Americans normally may have bluish lips and a dark line on the gingival margin. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 71. Question : After a symptom is recognized, the first effort at treatment is often self-care. The nurse recognizes that which of the following statements about self-care is true? Self-care is Student Answer: not recognized as valuable by most healthcare providers. usually ineffective and may delay more effective treatment. always less expensive than biomedical alternatives. influenced by the accessibility of over-the-counter medicines. Instructor Explanation: After a symptom is identified, the first effort at treatment is often self-care. The availability of over-the-counter medications, relatively high literacy level of Americans, and influence of the mass media in communicating health-related information to the general population have contributed to the high percentage of cases of self-treatment. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 72. Question : In using verbal responses to assist the patient’s narrative, some responses focus on the patient’s frame of reference and some focus on the healthcare provider’s perspective. An example of a verbal response that focuses on the healthcare provider’s perspective would be Student Answer: empathy. reflection. facilitation. confrontation. Instructor Explanation: When the healthcare provider uses the response of confrontation, the frame of reference shifts from the patient’s perspective to the healthcare provider’s, and the healthcare provider starts to express his or her own thoughts and feelings. Empathy, reflection, and facilitation responses focus on the patient’s frame of reference. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 73. Question : The nurse recognizes that the concept of prevention in describing health is essential because Student Answer: disease can be prevented by treating the external environment. the majority of deaths among Americans under age 65 years are not preventable. prevention places emphasis on the link between health and personal behavior. the means to prevention is through treatment provided by primary healthcare practitioners. Instructor Explanation: A natural progression to prevention now rounds out our concept of health. Guidelines to prevention place emphasis on the link between health and personal behavior. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 74. Question : The nurse notices that a patient’s submental lymph nodes are enlarged. In an effort to identify the cause of the node enlargement, the nurse would assess the patient’s Student Answer: infraclavicular area. supraclavicular area. area distal to the enlarged node. area proximal to the enlarged node. Instructor Explanation: When nodes are abnormal, the nurse should check the area they drain for the source of the problem. Explore the area proximal (upstream) to the location of the abnormal node. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 75. Question : A patient tells the nurse that he is allergic to penicillin. What would be the nurse’s best response to this information? Student Answer: “Are you allergic to any other drugs?” “How often have you received penicillin?” “I’ll write your allergy on your chart so you won’t receive any penicillin.” “Please describe what happens to you when you take penicillin.” Instructor Explanation: Note both the allergen (medication, food, or contact agent, such as fabric or environmental agent) and the reaction (rash, itching, runny nose, watery eyes, difficulty breathing). With a drug, this symptom should not be a side effect but a true allergic reaction. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 45 pages
 – Chamberlain College of Nursing.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 16, 2020
Number of pages
45
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 16, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
137








 – University of the People.png)