*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Central Nervous System Review Guide (All)
Central Nervous System Review Guide
Document Content and Description Below
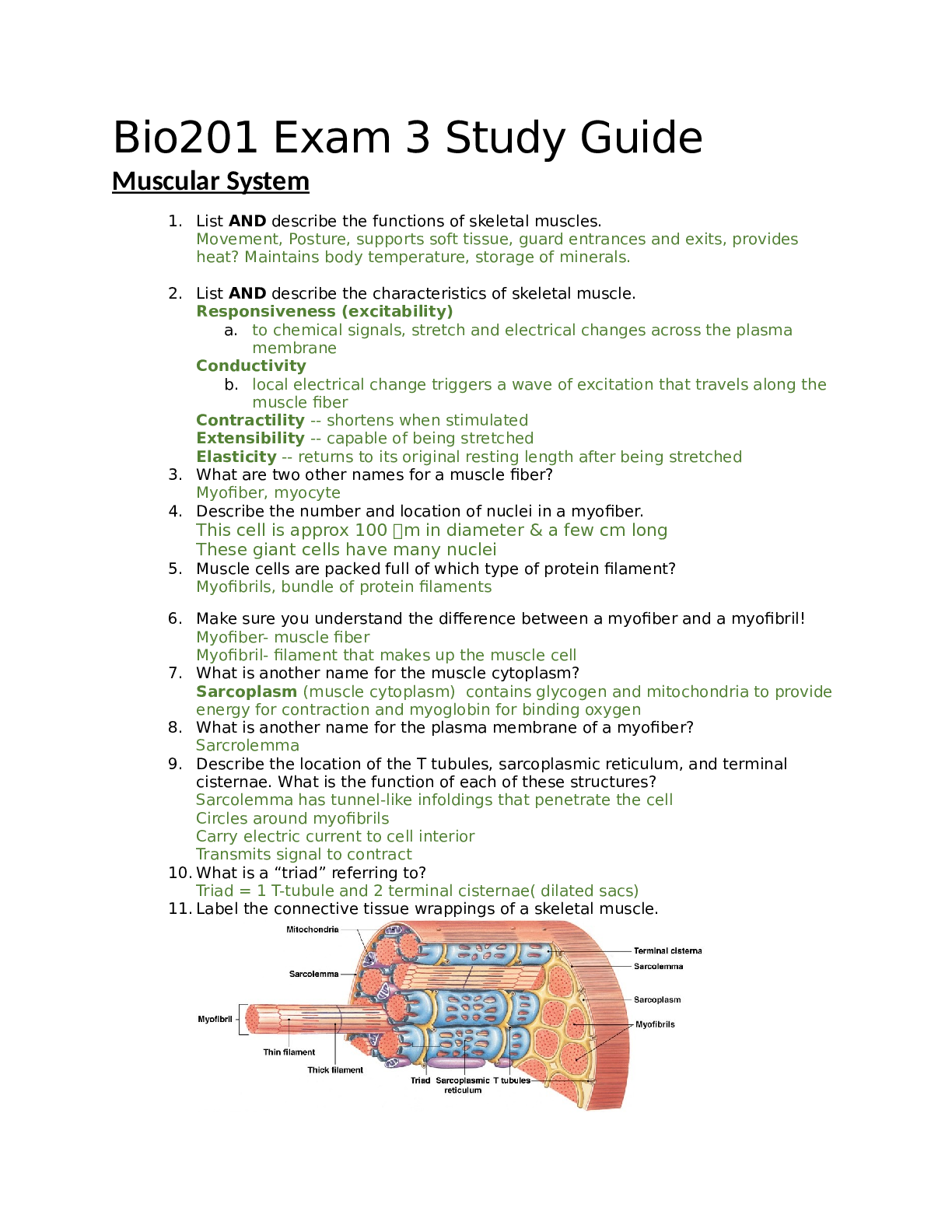
1. What two structures make up the CNS? Brain and Spinal cord 2. Describe the roles of the three types of neurons in the spinal cord (sensory, motor, and interneuron). Sensory neurons: a. about 1... 0 million b. deliver information to CNS Motor neurons: c. about 1/2 million d. deliver commands to peripheral effectors Interneurons (AKA - association neurons): a. about 20 billion b. interpret, plan, and coordinate signals in and out 3. Draw AND label (including the functions of the regions that you label) of a spinal cord cross section. The more detail that you provide, the better! Here are some regions that you should not forget to include: Sensory info Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Somatic sensory nuclei Visceral sensory nuclei Motor info Sympathetic ganglion Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus Sensory motor nuclei Visceral motor nuclei Sympathetic nerve (preganglionic and postganglionic fibers) 4. Diagram AND label the five steps that occur in a neural reflex. Make sure to keep the sensory and motor neurons straight! Step 1: Arrival of stimulus, activation of receptor a. physical or chemical changes Step 2: Activation of sensory neuron b. graded depolarization Step 3: Information processing by postsynaptic cell triggered by neurotransmitters Step 4: Activation of motor neuron action potential Step 5: Response of peripheral effector triggered by neurotransmitters 5. Compare and contrast innate and acquired reflexes. a. innate reflexes: i. basic neural reflexes ii. formed before birth b. acquired reflexes: i. rapid, automatic ii. learned motor patterns iii. tripping and falling but catching yourself 6. Compare and contrast somatic and visceral reflexes. a. somatic reflexes: i. involuntary control of nervous system 1. superficial reflexes of skin, mucous membranes 2. stretch reflexes (deep tendon reflexes) e.g., patellar reflex b. visceral reflexes (autonomic reflexes): i. control systems other than muscular system 7. Compare and contrast monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes. a. monosynaptic - sensory neuron synapses directly onto motor neuron b. polysynaptic - at least 1 interneuron between sensory neuron and motor neuron 8. Compare and contrast spinal reflexes and cranial reflexes. a. spinal reflexes: i. occurs in spinal cord (many of the reflexes that happen in the body) (majority) b. cranial reflexes: i. occurs in brain (not as many reflexes hat occur in the brain) 9. Diagram AND label a monosynaptic spinal reflex, using the stretch reflex as an example 10. Explain the roles of intrafusal and extrafusal muscle fibers in the stretch reflex as well as the adjustment of muscles tension in postural reflexes. Bundles of small, specialized intrafusal muscle fibers: a. innervated by sensory and motor neurons Surrounded by extrafusal muscle fibers: b. which maintain tone and contract muscle [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 26, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 26, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
54