Biology > STUDY GUIDE > Bio201 Exam 3 Study Guide Muscular System (All)
Bio201 Exam 3 Study Guide Muscular System
Document Content and Description Below
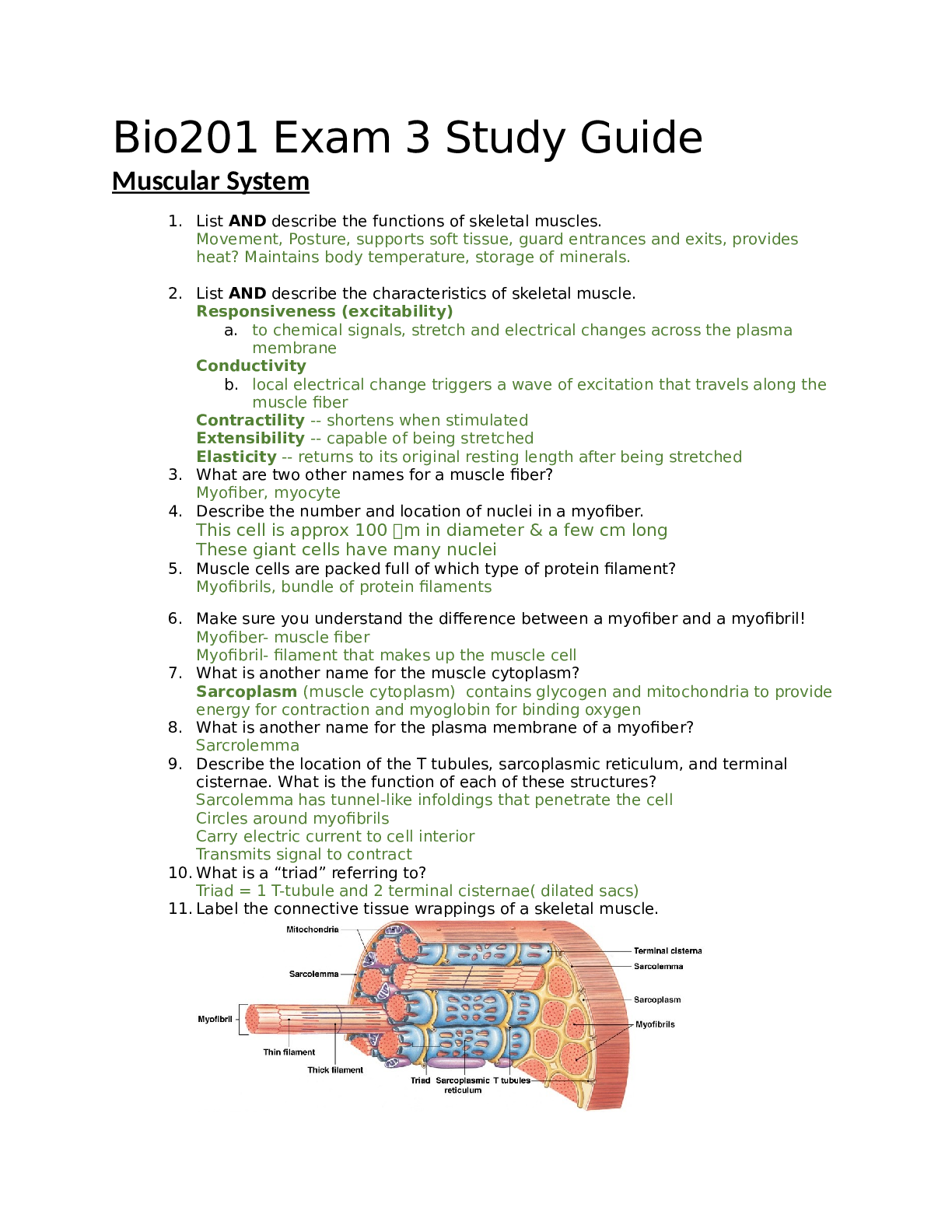
1. List AND describe the functions of skeletal muscles. Movement, Posture, supports soft tissue, guard entrances and exits, provides heat? Maintains body temperature, storage of minerals. 2. List A ... ND describe the characteristics of skeletal muscle. Responsiveness (excitability) a. to chemical signals, stretch and electrical changes across the plasma membrane Conductivity b. local electrical change triggers a wave of excitation that travels along the muscle fiber Contractility -- shortens when stimulated Extensibility -- capable of being stretched Elasticity -- returns to its original resting length after being stretched 3. What are two other names for a muscle fiber? Myofiber, myocyte 4. Describe the number and location of nuclei in a myofiber. This cell is approx 100 m in diameter & a few cm long These giant cells have many nuclei 5. Muscle cells are packed full of which type of protein filament? Myofibrils, bundle of protein filaments 6. Make sure you understand the difference between a myofiber and a myofibril! Myofiber- muscle fiber Myofibril- filament that makes up the muscle cell 7. What is another name for the muscle cytoplasm? Sarcoplasm (muscle cytoplasm) contains glycogen and mitochondria to provide energy for contraction and myoglobin for binding oxygen 8. What is another name for the plasma membrane of a myofiber? Sarcrolemma 9. Describe the location of the T tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and terminal cisternae. What is the function of each of these structures? Sarcolemma has tunnel-like infoldings that penetrate the cell Circles around myofibrils Carry electric current to cell interior Transmits signal to contract 10.What is a “triad” referring to? Triad = 1 T-tubule and 2 terminal cisternae( dilated sacs) 11. Label the connective tissue wrappings of a skeletal muscle. 12.What is an aponeurosis? Where are some regions in the human body might you find one? How does an aponeurosis differ from a tendon? Epimysium, perimysium and endomysium come together to form a tendon or aponeurosis a. Tendon – cord-like structure b. Aponeuroses – sheet-like structure (long sheet of tendon) [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 26, 2022
Number of pages
38
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 26, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
124