*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NURSING 2115 | Safety_and_infection_Control_Study___Manual__NCLEX[133] (2) | Rasmussen College - NUR (All)
NURSING 2115 | Safety_and_infection_Control_Study___Manual__NCLEX[133] (2) | Rasmussen College - NURSING 2115 RATED A+
Document Content and Description Below
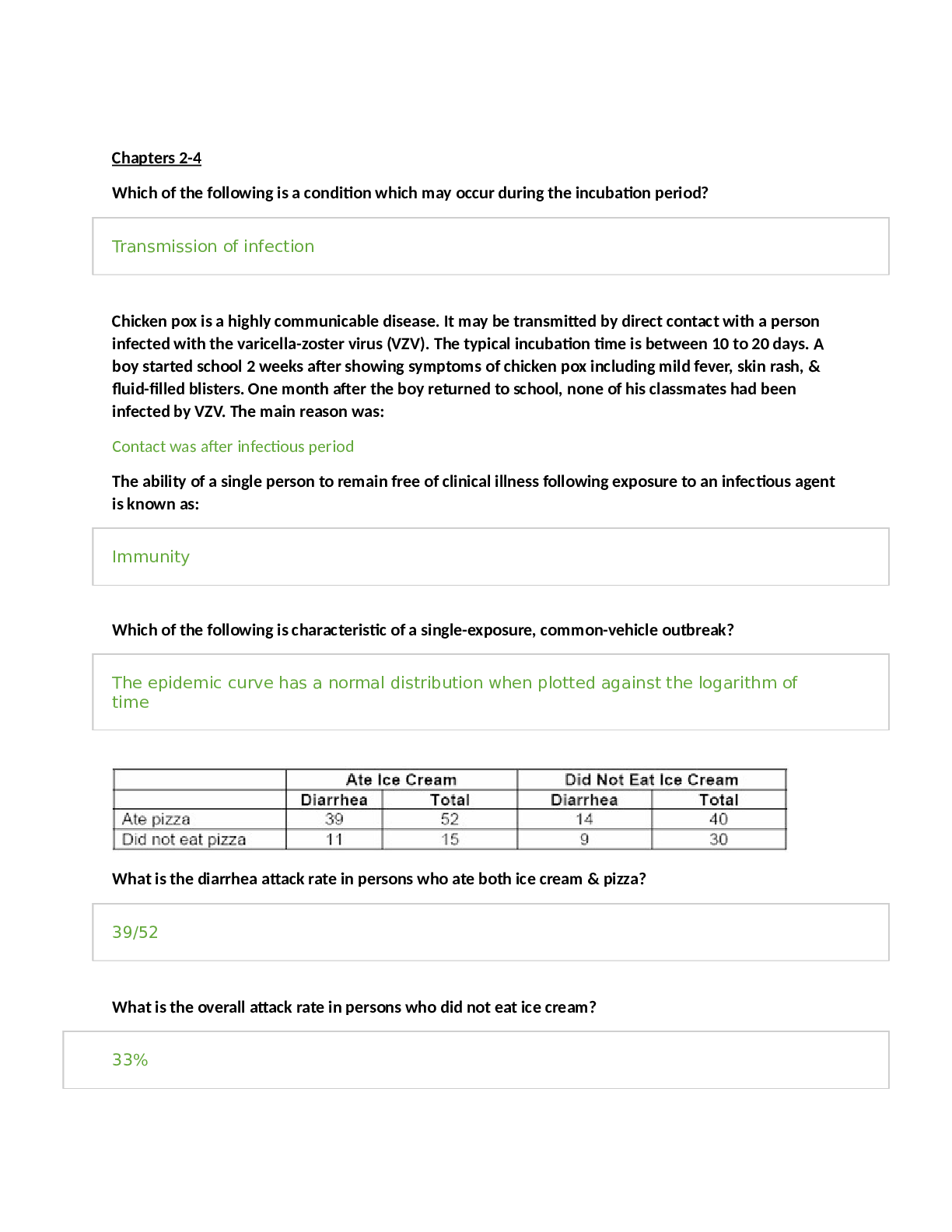
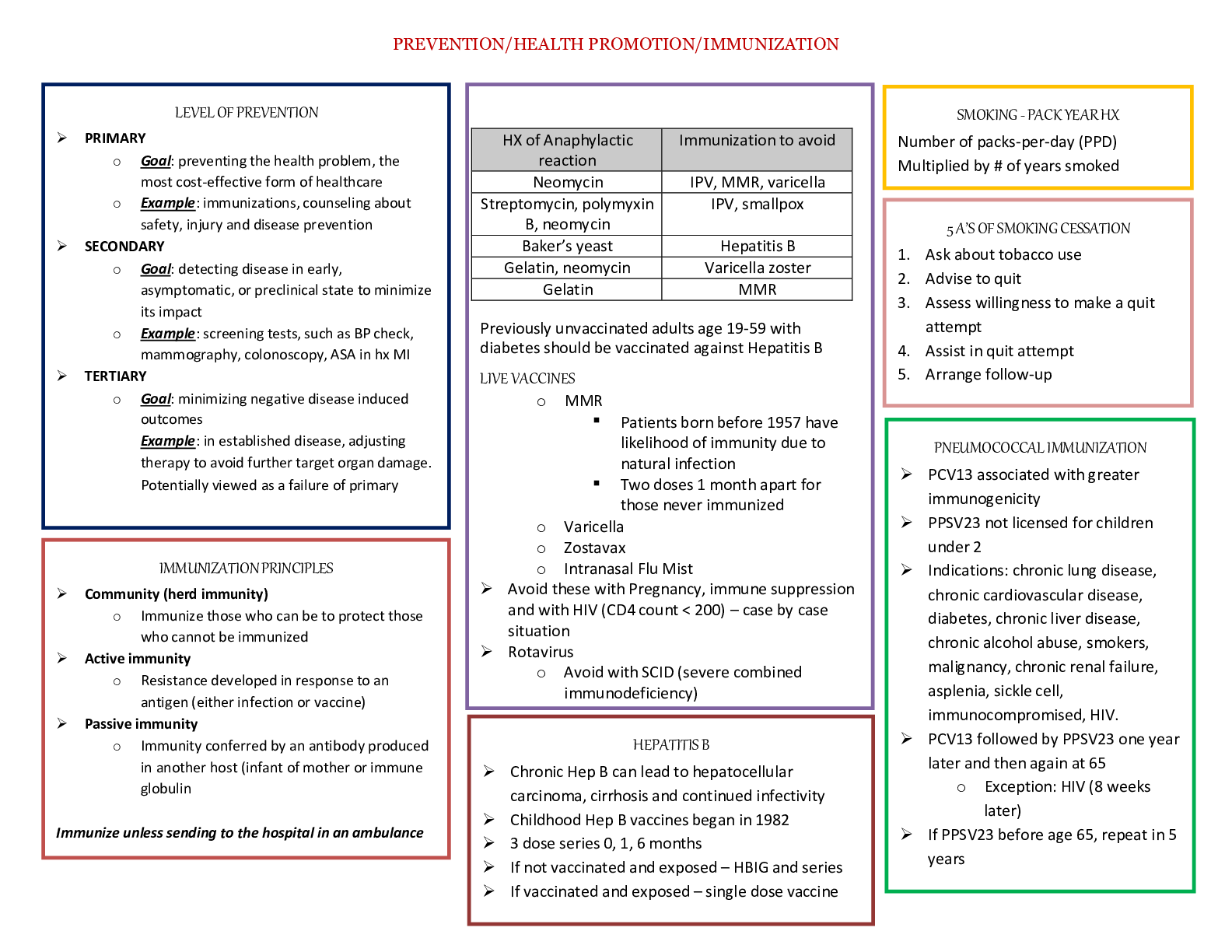
SAFETY AND INFECTION STUDY GUIDE Safety and infection Control – the nurse protect clients and health care personnel from health and environmental hazards. NCLEX TEST PLAN- Safety and Infection Contr... ol 9-15% Accident/Error/injury Prevention A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. Assess client for allergies and intervene as needed (e.g., food, latex, environmental allergies) * Determine client/staff member knowledge of safety procedures Identify factors that influence accident/injury prevention (e.g., age, developmental stage, lifestyle, Mental status) Identify deficits that may impede client safety (e.g., visual, hearing, sensory/perceptual) Identify and verify prescriptions for treatments that may contribute to an accident or injury (does not include medication) Identify and facilitate correct use of infant and child car seats Provide client with appropriate method to signal staff members Protect client from injury (e.g., falls, electrical hazards) * Review necessary modifications with client to reduce stress on specific muscle or skeletal groups (e.g., frequent changing of position, routine stretching of the shoulders, neck, arms, hands, fingers) Implement seizure precautions for at-risk clients Make appropriate room assignments for cognitively impaired clients Ensure proper identification of client when providing care* Verify appropriateness and/or accuracy of a treatment order* Emergency Response Plan A. B. C. D. E. Determine which client(s) to recommend for discharge in a disaster situation Identify nursing roles in disaster planning Use clinical decision-making/critical thinking for emergency response plan Implement emergency response plans (e.g., internal/external disaster) * Participate in disaster planning activities/drills Ergonomic Principles A. Assess client ability to balance, transfer and use assistive devices prior to planning care (e.g., crutches, walker) B. Provide instruction and information to client about body positions that eliminate potential for repetitive stress injuries C. Use ergonomic principles when providing care (e.g., safe client handling, proper lifting) * Handling Hazardous and infectious Materials A. B. C. D. Identify biohazardous, flammable and infectious materials Follow procedures for handling biohazardous materials* Demonstrate safe handling techniques to staff and client Ensure safe implementation of internal radiation therapy Home safety A. B. C. D. Assess need for client home modifications (e.g., lighting, handrails, kitchen safety) Apply knowledge of client pathophysiology to home safety interventions Educate client on home safety issues (e.g., home, school, transportation) * Encourage the client to use protective equipment when using devices that can cause injury E. Evaluate client care environment for fire/environmental hazard 1 Reporting of incident/Event/ A. irregular Occurrence/Variance B. Identify need/situation where reporting of incident/event/irregular occurrence/variance is appropriate C. Acknowledge and document practice error (e.g., incident report for medication error) * D. Evaluate response to error/event/occurrence Safe Use of Equipment Inspect equipment for safety hazards (e.g., frayed electrical cords, loose/missing parts) Teach client about the safe use of equipment needed for health care Facilitate appropriate and safe use of equipment* Remove malfunctioning equipment from client care area and report the problem to appropriate Personnel Security Plan Use clinical decision making/critical thinking in situations related to security planning Apply principles of triage and evacuation procedures/protocols Follow security plan and procedures (e.g., newborn nursery security, violence, controlled access) * Standard Precautions/ Transmission-Based Precautions/surgical asepsis A. Assess client care area for sources of infection B. Understand communicable diseases and the modes of organism transmission (e.g., airborne, droplet, contact) C. Apply principles of infection control (e.g., hand hygiene, surgical asepsis, isolation, sterile technique, universal/standard precautions) * D. Follow correct policy and procedures when reporting a client with a communicable disease E. Educate client and staff regarding infection control measures* F. Utilize appropriate precautions for immunocompromised clients G. Use appropriate technique to set up a sterile field/maintain asepsis (e.g., gloves, mask, sterile supplies) H. Evaluate infection control precautions implemented by staff members I. Evaluate whether aseptic technique is performed correctly Use of Restraints/safety devices A. Assess appropriateness of the type of restraint/safety device used B. Follow requirements for use of restraints and/or safety device (e.g., least restrictive restraints, timed client monitoring) * C. Monitor/evaluate client response to restraints/safety device 2 A. The Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN) project The overall goal for the Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN) project is to meet the challenge of preparing future nurses who will have the knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSAs) necessary to continuously improve the quality and safety of the healthcare systems within which they work. Using the Institute of Medicine 1 competencies, QSEN faculty, a National Advisory Board, and 17 representatives from 11 professional organizations representing advanced nursing practice defined quality and safety competencies for nursing and proposed targets for the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to be developed in nursing graduate programs for each competency. These definitions are shared in the six guidelines below Patient-centered Care: Definition: Recognize the patient or designee as the source of control and full partner in providing compassionate and coordinated care based on respect for patient’s preferences, values, and needs Teamwork and Collaboration: Definition: Function effectively within nursing and interprofessional teams, fostering open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making to achieve quality patient care. Evidence-based Practice (EBP): Definition: Integrate best current evidence with clinical expertise and patient/family preferences and values for delivery of optimal health care. Quality Improvement (QI): Definition: Use data to monitor the outcomes of care processes and use improvement methods to design and test changes to continuously improve the quality and safety of health care systems. Safety: Definition: Minimizes risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance. Informatics: Definition: Use information and technology to communicate, manage knowledge, mitigate error, and support decision making 2. KSA for Safety: minimize the risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance 3. Safety is the primary concern when caring for clients In patient safety, critical thinking is an ongoing process. Standards have been developed by American Nurses Association and The Joint Commission. Use of the nursing process when planning care promotes safety 3 Using QSEN goals helps because it NCLEX PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A nurse is caring for an older-adult couple in a community-based assisted living facility. During the family assessment he notes that the couple has many expired medications and multiple medications for their respective chronic illnesses. They note that they go to two different health care providers. The nurse begins to work with the couple to determine what they know about their medications and helps them decide on one care provider rather than two. This is an example of which Quality and Safety in the Education of Nurses (QSEN) competency? A. Patient-centered care B. Safety C. Teamwork D. Informatics Answer B -Safety: Definition: Minimizes risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance 2. A critical care nurse is using a computerized decision support system to correctly position her ventilated patients to reduce pneumonia cause by accumulated respiratory secretions. This is an example of which Quality and Safety in the Education of Nurses (QSEN) competency? A. B. C. D. Patient-centered care Safety Teamwork and collaboration Informatics Answer D- Informatics: Definition: Use information and technology to communicate, manage knowledge, mitigate error, and support decision making 4 Environmental Hazards includes Physical hazards: Lighting Obstacles Bathroom hazards Motor vehicle accidents Poison Fires Falls Transmission of pathogens Pollution Disasters- Natural and Man-made Chemical Hazards NCLEX The nurse has investigated safety hazards and recognizes that which one of the following statements is accurate regarding safety needs? A) Bacterial contamination of foods is uncontrollable. B) Fire is the greatest cause of unintentional death. C) Carbon monoxide levels should be monitored in home settings. D) Temperature extremes seldom affect the safety of clients in acute care facilities. Correct Answer: C Explanation: Annual inspections of heating systems, chimneys, and appliances should be done in private homes. Carbon monoxide detectors are available but should not be used as a replacement for proper use and maintenance of fuel-burning appliances. A. Bacterial contamination of foods is controllable. The FDA is a federal agency responsible for the enforcement of federal regulations regarding the manufacture, processing, and distribution of foods, drugs, and cosmetics to protect consumers against the sale of impure or dangerous substances. B. Motor vehicle accidents are the leading cause of unintentional death, not fire. D. Temperature extremes 5 Providing a Secure and Safe Environme nt 6 Fire Safety There were 386,500 reported home fires in the United States in 2008, resulting in 2,755 deaths and 13,160 injuries (National Fire Protection Association, 2010b). The leading cause of fire-related death is careless smoking, especially when people smoke in bed at home. The improper use of cooking equipment and appliances, particularly stoves, are the main sources for in-home fi res and fi re injuries. Patients should have smoke detectors along with carbon monoxide detectors, placed strategically throughout their homes. Multipurpose fire Extinguishers need to be near the kitchen and any workshop areas. Prevention -Fire extinguishers are divided into four categories, based on different types of fires for which they are used. The most common water extinguishers are suitable for class A fires only. Never use water to extinguish class C fires due to the risk of electrical shock. The most common water extinguishers are suitable for class A fires only. Never use water to extinguish class C fires due to the risk of electrical shock. Dry chemical extinguishers come in a variety of types and are suitable for a combination of class A, B, and C fires (liquids and electrical fires) o filled with foam or powder and pressurized with nitrogen o may leave a harmful residue that reduces the likelihood of re-ignition Carbon dioxide (CO ) extinguishers 2 o used for class B and C fires o do not work well on class A fires because they may not be able to displace oxygen to put the fire out and the fire may re-ignite do not leave a harmful residue MATCH 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Fire Extinguisher Type A can be used for? Fire Extinguisher Type B can be used for? Fire Extinguisher Type C can be used for? Fire Extinguisher Type ABC can be used for? Fire Extinguisher Type D can be used for? ANSWERS A -Paper, wood cloth B- Flammable liquid, grease C- Electrical D-Everything #1 #2 #3 #4 7 E.- Combustible metals #5 Response to Fire All employees need to know: 1. the institution's fire evacuation routine 2. the location of fire alarms 3. the location of fire extinguishers 4. how to use the fire extinguisher? 5. the location of fire exits The following things are important 1. The "hang tag" should be checked for date of last inspection (usually annually) 2. 3. A. B. C. List the phone number for reporting fires close to all phones in the facility Depending on facility policy, the nurse’s actions in a fire will include one of the following: PRC ARCE RACE Acronym PRC ARCE RACE P= R= C= A= R= C= E= R= Action Protect clients from injury Report the fire Contain the fire Activate fire alarm system Rescue or remove clients Contain fire by closing windows and doors Extinguish flames with fire extinguishers Rescue or remove clients 8 A= C= E= Activate fire alarm system Contain fire by closing windows and doors Extinguish flames with fire extinguishers Electrical Safety Safety issues in health care facilities are addressed in specific standards and directives by the federal Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) Electrical safety overview for health care facilities According to the Joint Commission, health care organizations need to have a policy related to clients using of any electrical equipment brought from home. A. Ensure that cords are in good condition; old and damaged cords must be replaced. B. If any defective equipment is noted, or if a tingle is sometimes felt when using a piece of equipment, this is a signal to: Stop using the equipment Report the problem Note: An electrical shock is always unpleasant, but it can be lethal in the intensive care unit (ICU) or an operating suite C. Always check the ground wire before plugging in a piece of electrical equipment. D. Electrical equipment must be maintained in good working order and should be properly grounded. E. Inform the client that any electrical equipment that the client brings into the healthcare facility must be inspected for safety before it is used. F. Check electrical cords and outlets for exposed, frayed, or otherwise damaged wires and loose or missing parts. G. Do no overload electrical circuits. H. Read warning labels on all equipment; never operate unfamiliar equipment. I. Use safety-type extension cords only when absolutely necessary and secure them to the floor with the use of electrical tape. J. Never run electrical wiring under a carpet. K. Never pull a plug by the cord; always grasp the plug itself. L. Never use electrical appliances near sinks, bathtubs, or other water sources. M. Always disconnect a plug from the outlet before cleaning equipment or appliances. N. If a client sustains an electrical shock, turn off the electricity before touching the client. O. A malfunctioning piece of equipment must be removed from the client’s vicinity, and the appropriate hospital maintenance personnel must be notified Electrical safety overview for home settings A. To reduce the risk of electric shock, make sure that ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection is provided for outlets at kitchen counters, in bathrooms, and at outdoor receptacles; test GFCIs regularly B. Check the wattage of light fixtures and lamps to make sure they are the correct wattage; incorrect wattage can cause overheating that can lead to a fire C. Use safety closures to "child-proof" electrical outlets 9 D. Many avoidable electrical fires can be traced to misuse of electric cords, e.g., overloading circuits or extension cords, running cords under rug 10 GFCI In case of Facility Fire I. II. III. IV. Ambulatory clients may be directed to walk on their own to a safe area and may be able to help move clients in wheelchairs. Bedridden clients are generally moved from the scene of a fire on stretchers, in their beds, or in wheelchairs. Appropriate transfer techniques must be used to carry a client from the area of a fire. Fire department personnel at the scene of a fire can help evacuate clients. NCLEX QUESTIONS 1. On entering the client’s room, the nurse sees a fire burning in the trash can next to the bed. The nurse removes the client and calls in the fire. The next action of the nurse is to: A) Extinguish the fire B) Remove all the other clients from the unit C) Close all the doors of client rooms D) Move the trash can into the bathroom Correct Answer: C Explanation: The next action the nurse should take is to confine the fire by closing doors and windows and turning off oxygen and electrical equipment. A. The nurse should extinguish the fire by using an extinguisher after closing the doors of the client rooms. 11 B. After activating the alarm, the nurse should close all the doors, not remove all the other clients from the unit. D. This would not be an appropriate action, as the nurse could get burned in attempting to move the trash can. 2. The workmen cause an electrical fire when installing a new piece of equipment in the intensive care unit. A client is in the next room. The first action the nurse should take is to: A) Pull the fire alarm B) Attempt to extinguish the fire C) Call the physician to obtain orders to take the client off the ventilator D) Remove the client from the area Correct Answer: D Explanation: If there is a fire, the nurse should move the client away from the fire. A. The first action of the nurse is not to pull the fire alarm. The workmen could do that. B. The workman can attempt to extinguish the fire. The nurse should attend to the client who is closest to the fire in the next room. C. The nurse should not call the doctor to obtain orders to take the client off the ventilator, as this will take valuable time. The client must be moved away from the fire and the source of oxygen must be discontinued, as it is combustible. The client will need to be manually resuscitated with an Ambu-bag. 3. A nurse is setting up an intravenous pump that will be used for a client who will be receiving a continuous intravenous infusion of normal saline solution containing heparin. As the nurse prepares to plug the pump’s electrical cord into the wall socket, she notes that no socket is available because of other medical equipment being used in the room. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? 1. Allowing the pump to run in battery mode 2. Obtaining an extension cord from the nurses’ lounge 3. Moving the client into the hallway, near a wall socket 4. Calling the hospital’s electrical department for assistance RATIONALE D-The nurse would most appropriately contact the hospital’s electrical department for assistance in safely setting up electrical equipment. Safety-type extension cords are used only if necessary, and although this may be an option, it is not the most appropriate one. Electrical outlets should not be overloaded, because this presents an electrical hazard. The nurse would not allow the pump to run on its battery for an extended period. It is inappropriate to place a client in a hallway. This would constitute an invasion of the client’s privacy. 12 Read the test let below and answer the questions Mary Houder, a new nursing graduate, has been hired to work as a staff nurse on a medical nursing unit in a large hospital. Mary is required to complete the hospital's orientation program, which includes a fire safety program. During the program, each new employee is given a scenario and expected to demonstrate how he or she would respond to the situation set forth in the scenario. Mary's case scenario reads: You are working on a medical nursing unit and are delivering medications to a client who is ambulatory, is under respiratory precautions, and is receiving oxygen by nasal cannula. When you enter the client's room, you discover a fire blazing in the laundry basket, caused when the client used a match to light a candle. The case scenario asks Mary to respond to the questions that follow 4. a. b. c. d. When the fire is discovered, what will you do first? Activate the fire alarm Assist the client in leaving the room Get the fire extinguisher located outside the client's room Assist the client into a corner of the room, as far away from the fire as possible, and shut the oxygen off RATIONALE- Answer B-In the event of a fire, the nurse would use the mnemonic RACE to set priorities. The nurse'... [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 237 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$24.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 16, 2021
Number of pages
237
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 16, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
52