NUR 2092 Final Exam Study Guide
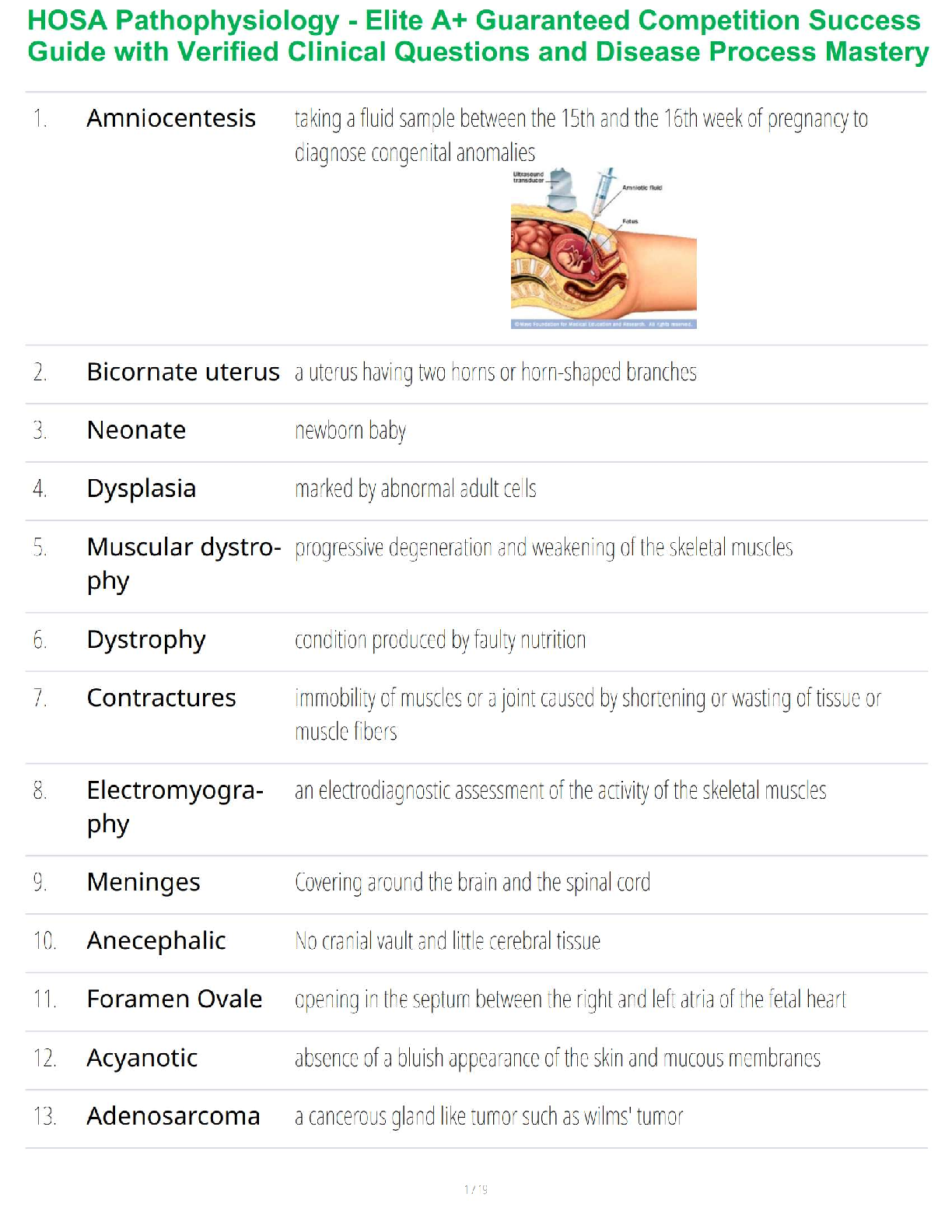
1. History taking/symptom analysis – components of a health history (what is in each component, for ex. Past medical history); subjective vs objective data; examples of open and closed e
...
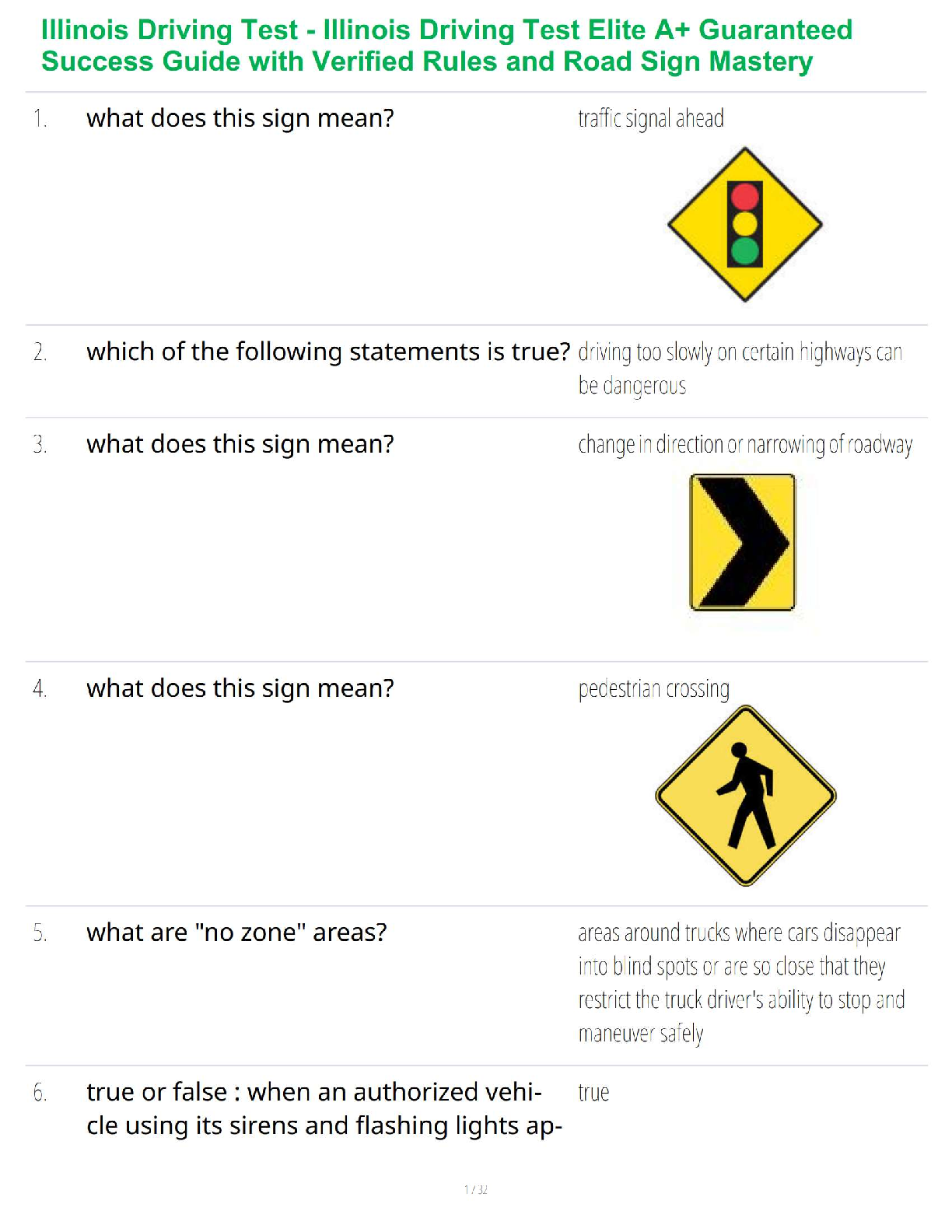
NUR 2092 Final Exam Study Guide
1. History taking/symptom analysis – components of a health history (what is in each component, for ex. Past medical history); subjective vs objective data; examples of open and closed ended questions; history first; signs vs symptoms; health promotion levels
2. Therapeutic communication: examples of effective and ineffective (barriers) techniques e.g. clarification, sequencing, reflection, blaming, etc.; questions; preparing for interviews
3. Cultural assessment: culturally competent care; religion vs spirituality;
4. Nursing process steps
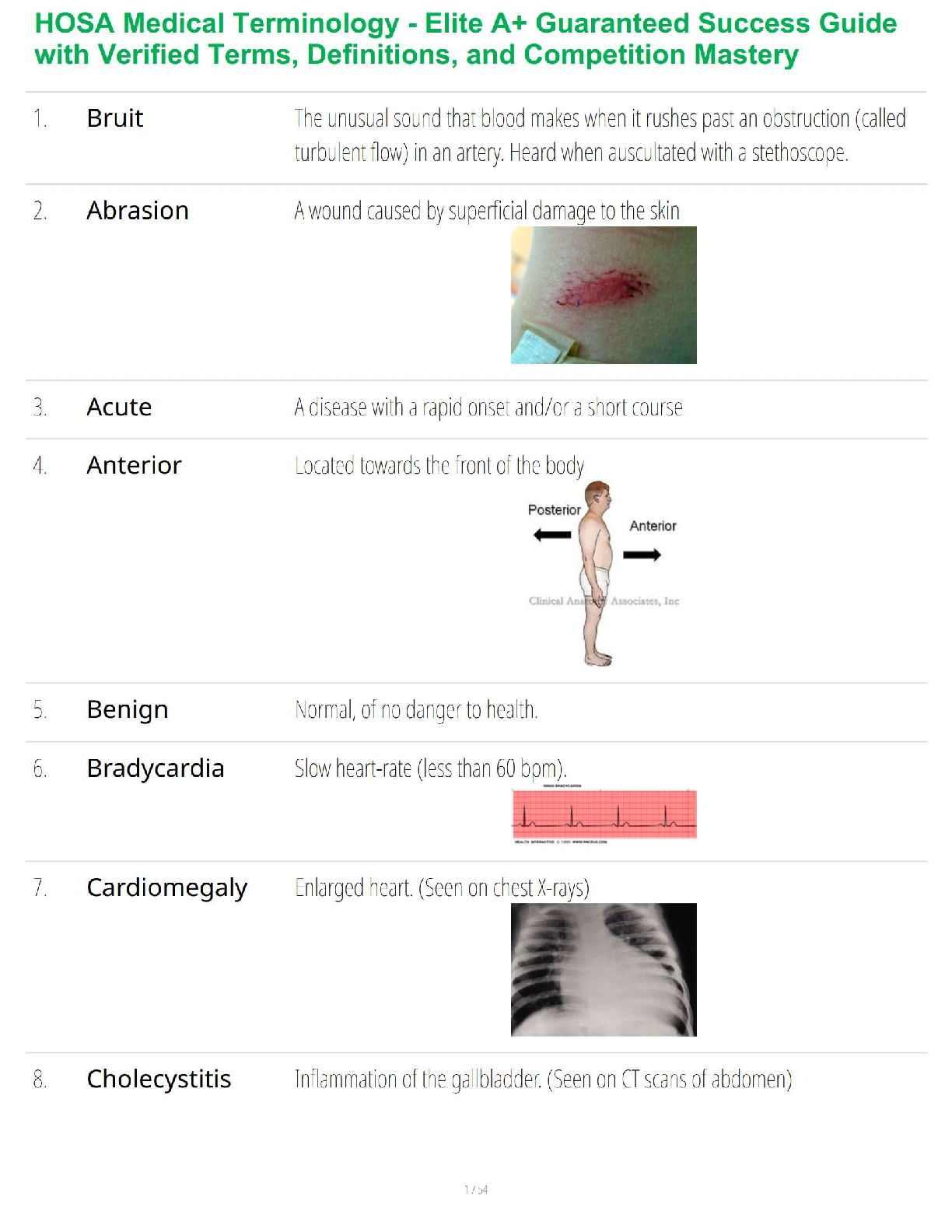
5. General survey – what is included?
6. Vital signs: BP – proper method, findings if not done properly; normal ranges-adults; terminology used, e.g. bradycardia, tachypnea, etc.
7. Pain assessment techniques; 4 classical techniques of assessment
8. Nutrition: Dietary assessment methods fastest vs most comprehensive vs frequency; abnormal eating patterns, for example, anorexia.
9. Skin: measurement; staging of decubitus ulcers, primary skin lesions like nodules, pustules, etc.; common skin lesions, for ex. Psoriasis, contact dermatitis; signs of malignant skin lesions; color differences seen in dark skinned individuals; lesion configurations, like annular, petechiae, linear, etc.;
10. HEENT: eye examination techniques; PERRLA; hearing tests; lymph nodes; problems seen in head, ears, eyes, nose, and throat, ex. cataracts, tonsillitis, glaucoma
11. Thorax/Respiratory assessment – auscultation, palpation; normal sounds and locations; abnormal sounds & when you might hear them; proper method of auscultation; methods- e.g. voice sounds such as egophony, thoracic expansion, etc.; chest shapes; respiratory vocabulary
12. Heart: cardiac cycle; auscultation sites; what causes the heart sounds; use of apical pulse; bruit vs murmur
13. Breasts: Risk factors for cancer
14. Abdomen – methods and order of assessment, anatomy, expected findings; colon cancer risk factors
15. GU: testicular cancer; assessing
16. Pulses- where are they, how do you document information about them, including rate, amplitude, rhythm; peripheral vascular assessment, edema – appearance, scale; arterial vs venous insufficiency
17. Musculoskeletal – range of motion techniques; points for comparison; osteoporosis risk factors; spinal assessment findings; testing various joints including jaw; types of fractures; osteoarthritis risk factors; problems such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, etc.; movements like abduction/adduction, flexion/extension
18. Neuro – Glasgow coma scale; reflexes; cranial nerves – how do you test each one; testing for cerebellar function; tests such as graphesthesia, position sense, stereo gnosis, etc., part of the brain being tested? headache types;
19. Geriatrics: functional assessment-what is it, what is being tested, best approach to testing; caregiver concerns/burnout; IADLs, ADLs; disability concerns; expected changes in the elderly; fall risk factors
20. Pediatrics – best methods for assessing; pain assessment
[Show More]