MULTIPLE CHOICE
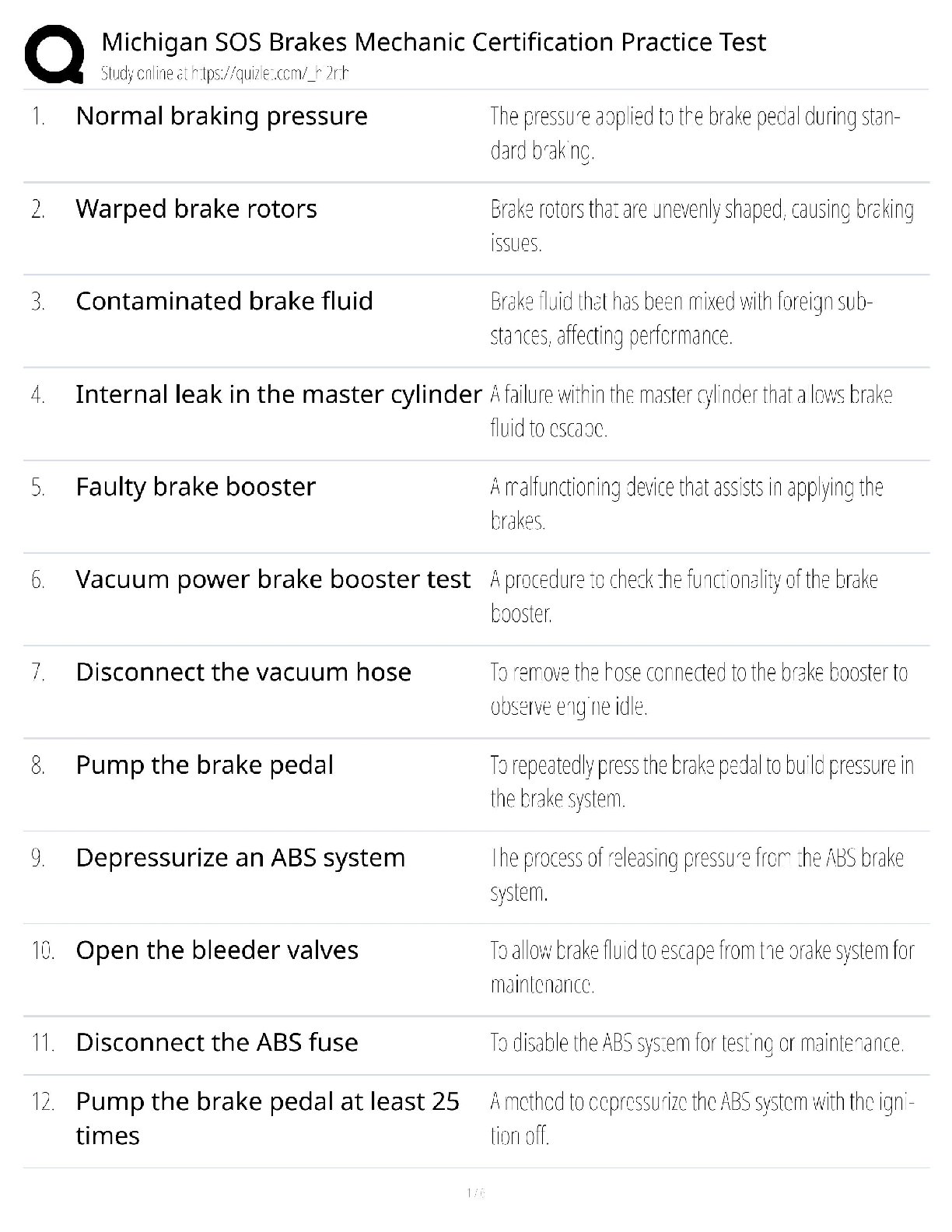
1. A basic principle of probability sampling is that a sample will be representative of
the population from which it is drawn if _____.
a. all members of the population have an equal chance of being se
...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A basic principle of probability sampling is that a sample will be representative of
the population from which it is drawn if _____.
a. all members of the population have an equal chance of being selected for the
sample
b. the researcher uses a method of selection based upon convenience
c. every nth person is selected for the sample
d. if the researcher follows rules.
2. The purpose of sampling is to select a set of elements from a population so that the
descriptions of the sample statistics accurately portray the parameters of the
population. This is best achieved through _____.
a. use of a convenience sample
b. use of random selection
c. use of the sampling element
d. use of sampling error
3. Which of the following is not a reason for using random selection methods in
selecting samples?
a. Random selection is a check on conscious or unconscious bias.
b. Random selection gives access to probability theory.
c. Random selection allows for estimates of error.
d. Random selection allows the researcher to selects cases on an intuitive basis
4. Which of the following are true concerning sampling error?
a. If many independent random samples are drawn from a population, then the
sample statistics from those samples are distributed in a predictable way around the
population parameter.
b. Probability theory does not allow us to use a formula to estimate how closely the
sample statistics are clustered.
c. The standard error cannot identify how spread out of clustered the sample statistics
are around the population parameter.
d. The standard error generally similar to the standard deviation.
5.Which of the following statements is true concerning the relationship between standard
error and sample size?
a. there is a positive relationship
b. there is an inverse relationship
c. As sample size decreases, the standard error decreases.
d. As sample size increases, the standard error increases. (decreases p 143
This study source was downloaded by 100000823742721 from CourseHero.com on 08-12-2021 09:41:39 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/15235906/CHAPTER-6-Practice-Test/
This study resource was
shared via CourseHero.com
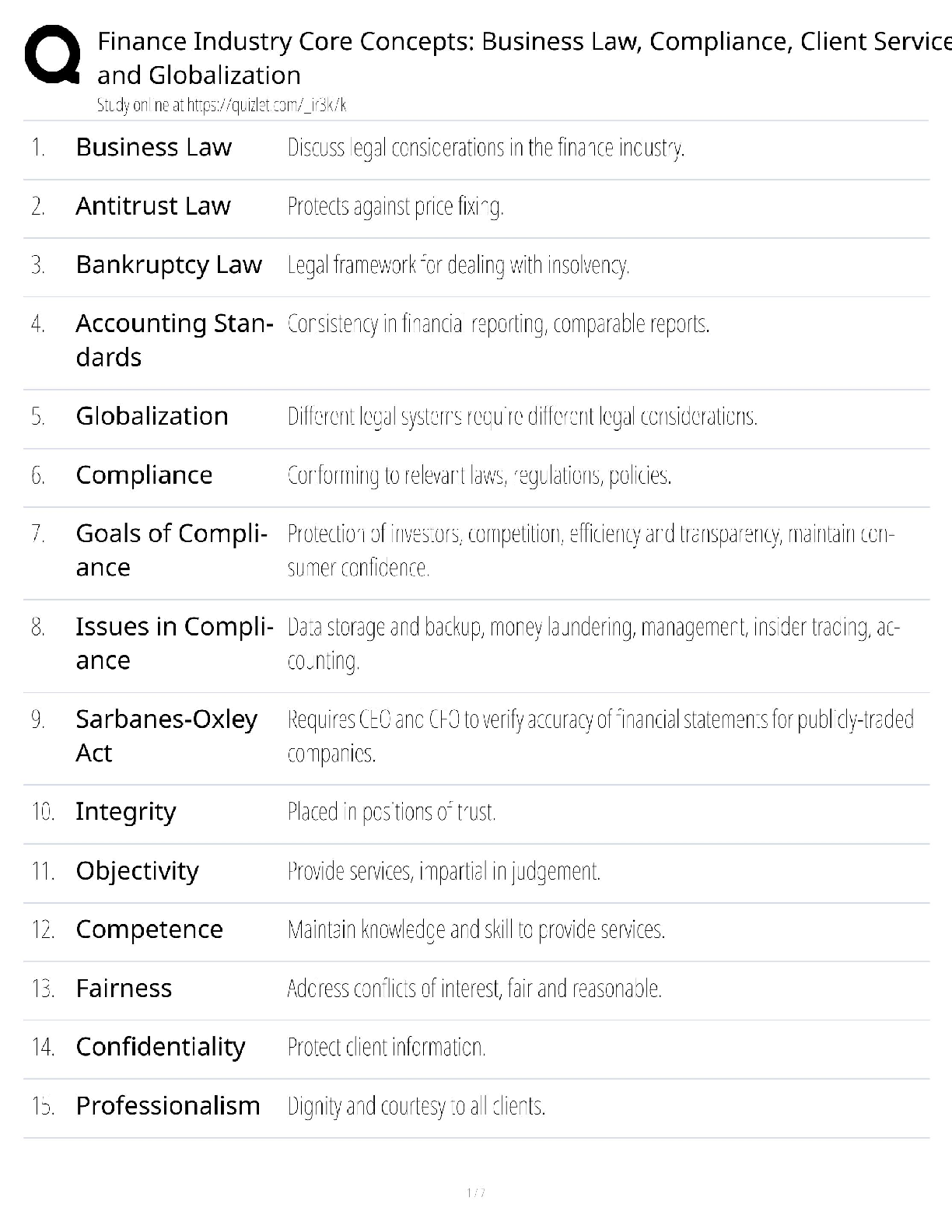
6. Confidence levels allow the researcher to have some idea of how closely their
samples reflect the parameter. Which of the following statements about confidence
levels is true?
a. If a simple random sample is used, probability theory suggests that researchers can
be 95 percent sure the estimates of that sample fall within one standard error of the
parameter.
b. If a simple random sample is used, probability theory suggests that researchers can
be 68 percent sure that estimates of that sample fall within two standard errors of
the parameter.
c. If a simple random sample is used, probability theory suggests that researchers can
almost be positive (99+ percent) that estimates of that sample fall within three
standard errors of the true value.
d. If a simple random sample is used, probability theory suggests that researchers can
be positive that sample mean is equivalent to population mean.
7. Which of the following is not appropriate for use as a sampling frame?
a. telephone directories when you wish to sample attitudes toward a new law
b. lists of licensed drivers when you wish to ask juveniles their opinions about
drinking prohibitions
c. taxpayer rolls when the researcher is interested in public concerns about school
appropriations in their community
d. American Medical Association membership lists to survey doctors about their
attitudes concerning HMOs
8. Which of the following is accurate concerning the use of systematic sampling?
a. systematic sampling is a poor example of simple random sampling
b. systematic sampling is often used as a substitute for stratified sampling
c. systematic sampling is frequently used rather than a simple random sample
d. systematic sampling is a non-probability sampling
9. When a researcher uses a stratified sampling technique, they _____.
a. do not select elements from homogeneous subsets of a population
b. recognize the extent that subsets that are homogeneous on stratified variables will
generally result in homogeneity on other variables as well
c. cannot estimate that a stratified sample is likely to be more representative on a
number of variables than a simple random sample
d. do not use probability sampling method.
10. When researching a population where it is impossible or impractical to compile a
list of the elements, what is the proper sampling technique to use?
a. stratified sample
b. systematic sample
c. cluster sample
d. simple random sample
This study source was downloaded by 100000823742721 from CourseHero.com on 08-12-2021 09:41:39 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/15235906/CHAPTER-6-Practice-Test/
This study resource was
shared via CourseHero.com
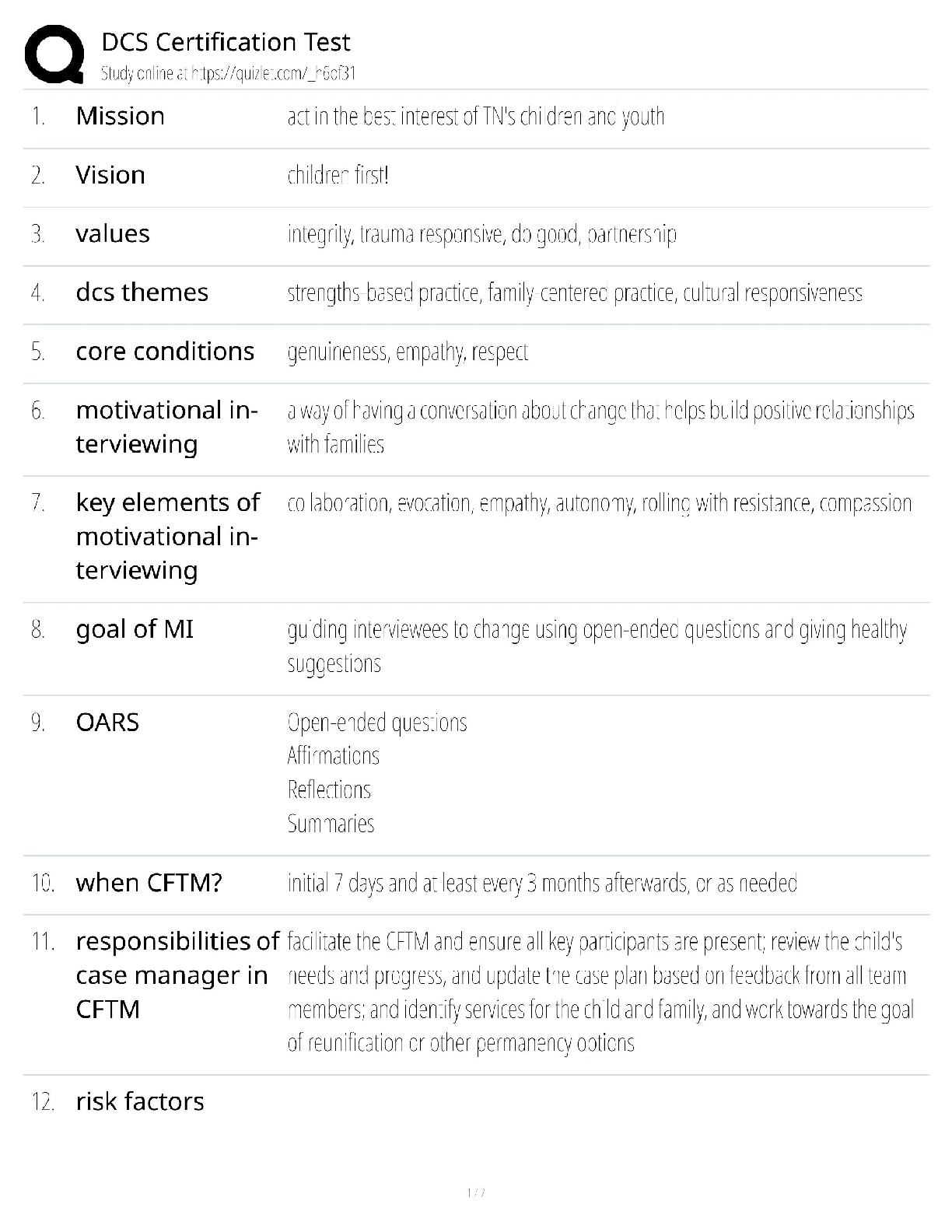
11. Which of the following illustrates a population where cluster sampling would be the best
choice?
a. law enforcement officers in the United States
b. Uniform Crime Reports
c. convicted violent criminals
d. news paper reports
12. Which of the following is an example of a multistage cluster sample?
a. the Self Report Survey
b. the National Crime Victimization Survey
c. Uniform Crime Reports
d. Court records
13. When considering probability sampling in general, it is usually the preferred
method for selecting study elements because _____.
a. probability sampling sanctions intuition on the part of the researcher
b. probability sampling permits the researcher to estimate the sampling error
c. probability sampling allows unconscious biases in the selection process
d. probability sampling allows selection of the best subjects
14. In order to study active criminals who have not been arrested for their criminal
acts, the researcher would be wise to employ which type of sampling technique?
a. purposive sampling
b. snowball sampling
c. convenience sampling
d. stratified random sampling
15. The true list of elements in the population is called the _____.
a. parameter
b. sampling frame
c. population
d. sample
[Show More]
.png)











.png)