FIN 205FIN205_StudyGuide.
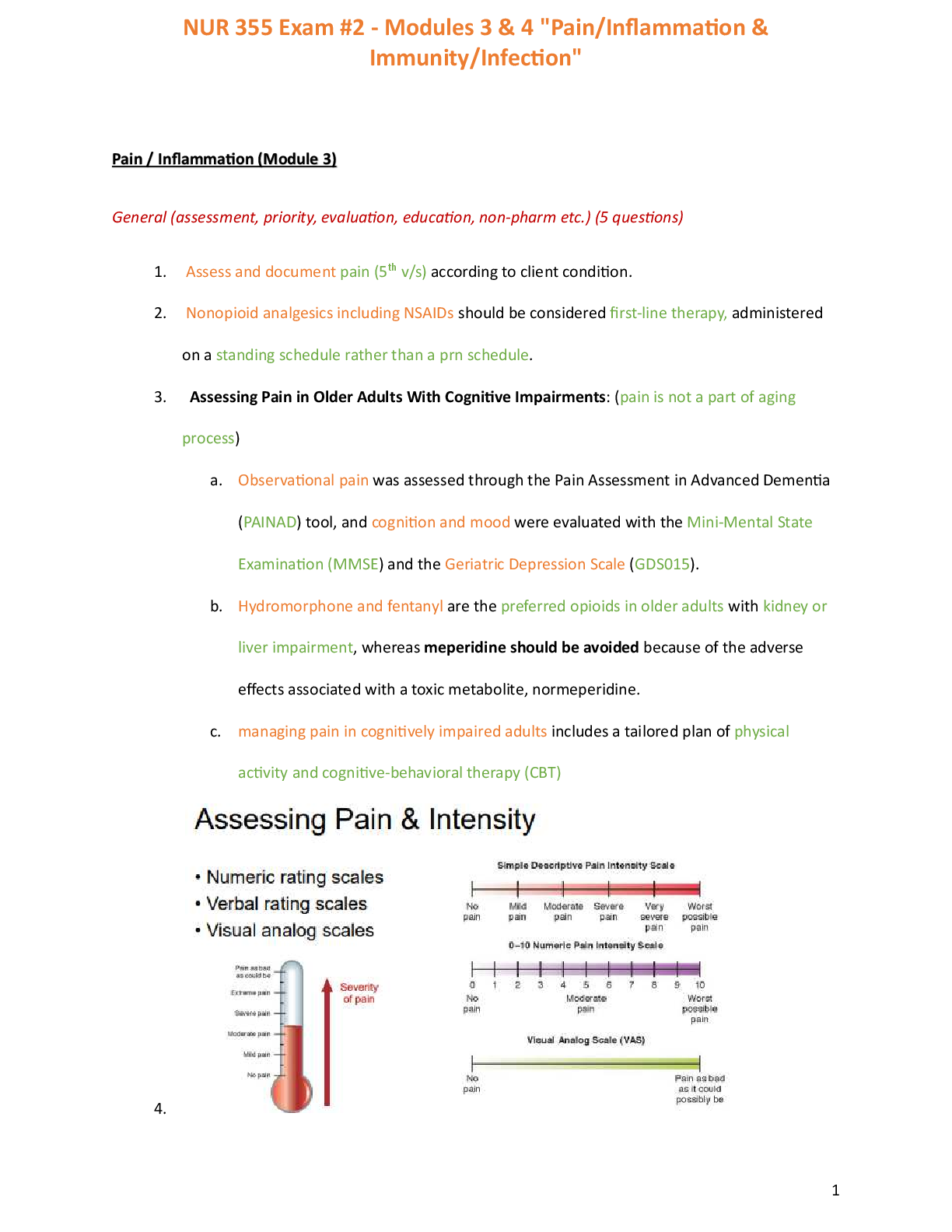
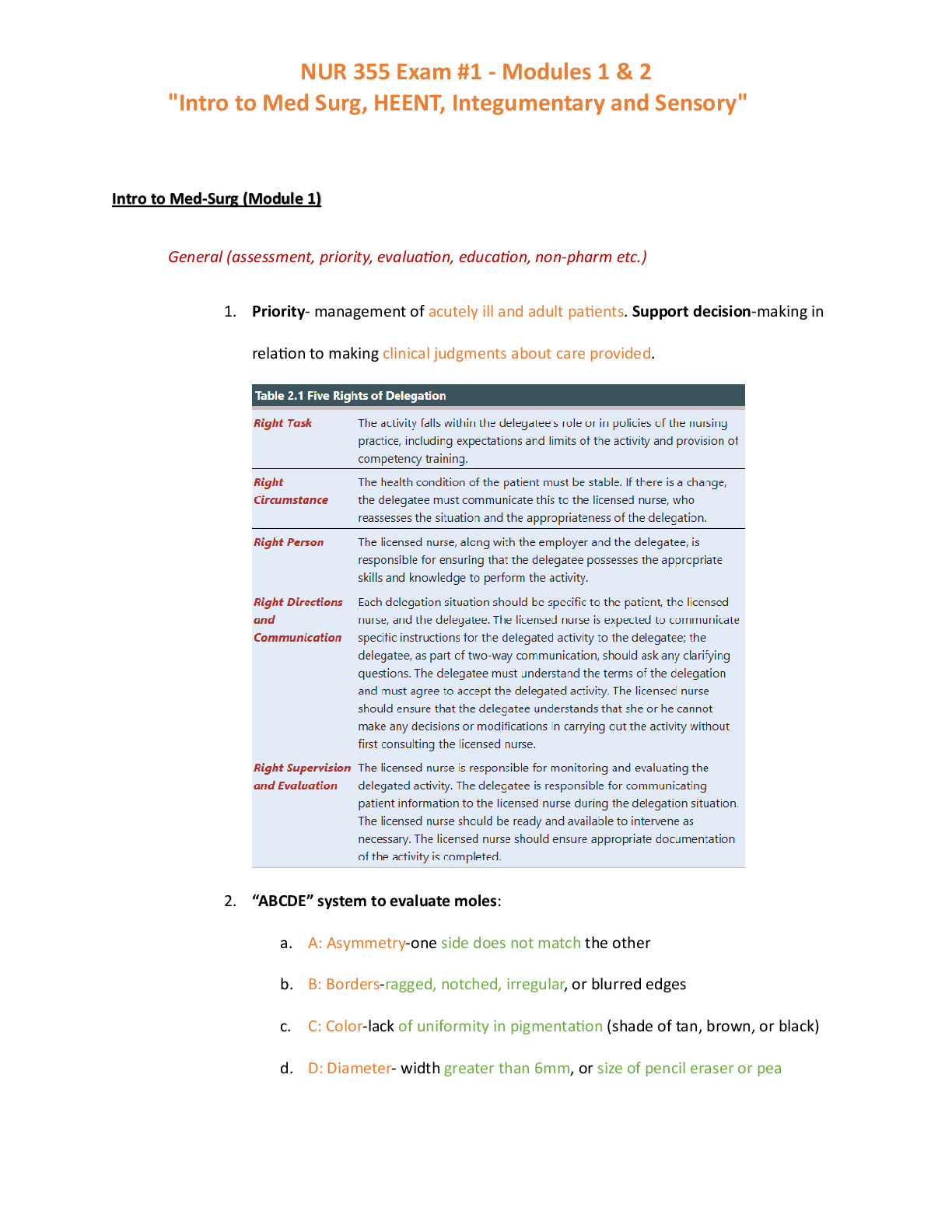
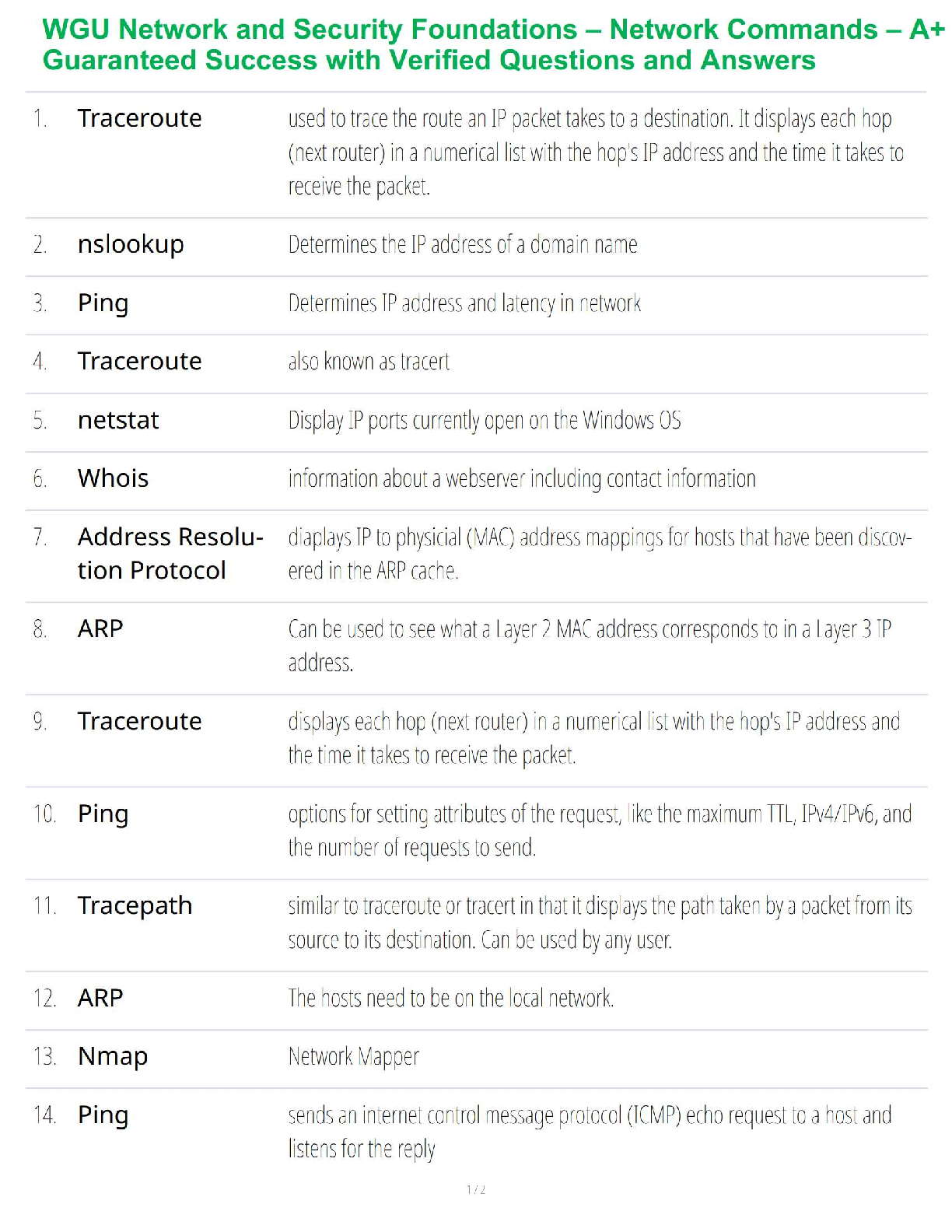
Document Content and Description Below
Chapter 1: Financial modelling
1.1 What is financial modelling?
In finance, one would come across all kinds of information and data related to the
company or the market. Financial modelling is a me
...
thod that utilises such information
and data to build a model to represent a real-world financial situation. It involves either
building a model from scratch or maintaining the existing models with new information.
Through the abstract numerical scenario, users can get a better understanding of how
different inputs and how changes in the inputs would influence the outcome.
1.2 Why is financial modelling important?
Financial modelling is very useful in the analysis and evaluation of a firm, a project,
a portfolio or an asset class, which will contribute to a more accurate and informed
investment or other strategic decisions, for both institutions and individuals. Basically, it is
a tool used to aid the decision-making process, by the companies in the cost estimation and
project benefit analysis, by financial analysts in the impact forecasts and event analysis,
by portfolio managers in risk management and portfolio allocations, or by investors in
company valuations and asset pricing.
Therefore, as a Finance student, the abilities and skills to perform analysis using financial
modelling are of great importance. Not only the understanding of accounting, financial
and business models and scenarios will be deepened, but also the competitive advantages
provided in the future working environment.
There are many scenarios that financial modelling can be applied to, both in accounting
and corporate finance, and in quantitative finance applications. The following are
common areas that financial modelling is generally used for:
• Financial statement analysis
• Business valuation (especially the discounted cash flow method)
• Restructuring situations (e.g. merger and acquisition)
• Valuation of assets (e.g. stocks, bonds, and option pricing)
• Raising capital and cost of capital calculations (i.e. weighted average cost of capital,
or WACC)
• Capital allocation
• Budgeting and forecasting
• Leveraged buyout (LBO)
• Risk management
1.3 Who would build financial models1?
Financial modelling is a tool that can be used by various people or organisations. The
person that builds financial models in different sectors or roles would have different foci
of financial models. Examples of professionals that build financial models are summarised
below.
• Investment banking analysts
The investment banking analysts help governments, enterprises, or institutions raise
capital and execute mergers and acquisitions. Financial modelling for business valuation
and financial statement analysis would be heavily used in investment banking.
• Equity research analysts
Equity research analysts usually conduct research on listed companies and share the
results with the clients to help with their investment or other corporate decisions. The
focus is mainly on equities.
1 Referring to the interactive career map developed by the Corporate Finance Institute (CFI) for more
details on the career path.
• Corporate development analysts
Corporate development generally involves executing corporate strategic decisions related
to its development, such as mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, and capital raising.
• Financial planning and analysis (FP&A) analysts
FP&A analysts usually sit within a corporate and are responsible for generating analysis
and information that senior management and executives would need for operational,
financial, and strategic decisions. Such roles usually possess strong accounting skills
and should be familiar with financial statement models, as well as the budgeting and
forecasting models.
• Accounting firm consultants (e.g. due diligence, transaction advisory, valuations,
etc.)
Accounting firms would provide services to prepare, review and audit financial
statements, and advise on other accounting related issues such as tax, accounting systems,
fundraising and M&A. In general, financial statement models would be significantly used
by consultants and analysts in accounting firms. Other models adopted frequently include
risk management (especially for financial due diligence) and business valuation.
• Credit analysts
Credit analysts perform credit analysis and evaluation of individuals, enterprises, or
securities, typically for banks, credit card rating agencies, investment firms, and credit
card issuing institutions.
• Risk analysts
Risk analysts are responsible for identifying potential risks associated with a business
decision or project to help avoid or reduce the risks.
• Data analysts
Data analyst is a general term that could represent any analysis using data. In the
finance realm, data analysts are in charge of data collection, consolidation, analysis, and
presentation, with the aim to generate information out of the data that can help companies
or clients make better business or investment decisions.
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 168 pages



.png)