*NURSING > CASE STUDY > Head Trauma Case Study-J.R Latest and Verified (All)
Head Trauma Case Study-J.R Latest and Verified
Document Content and Description Below
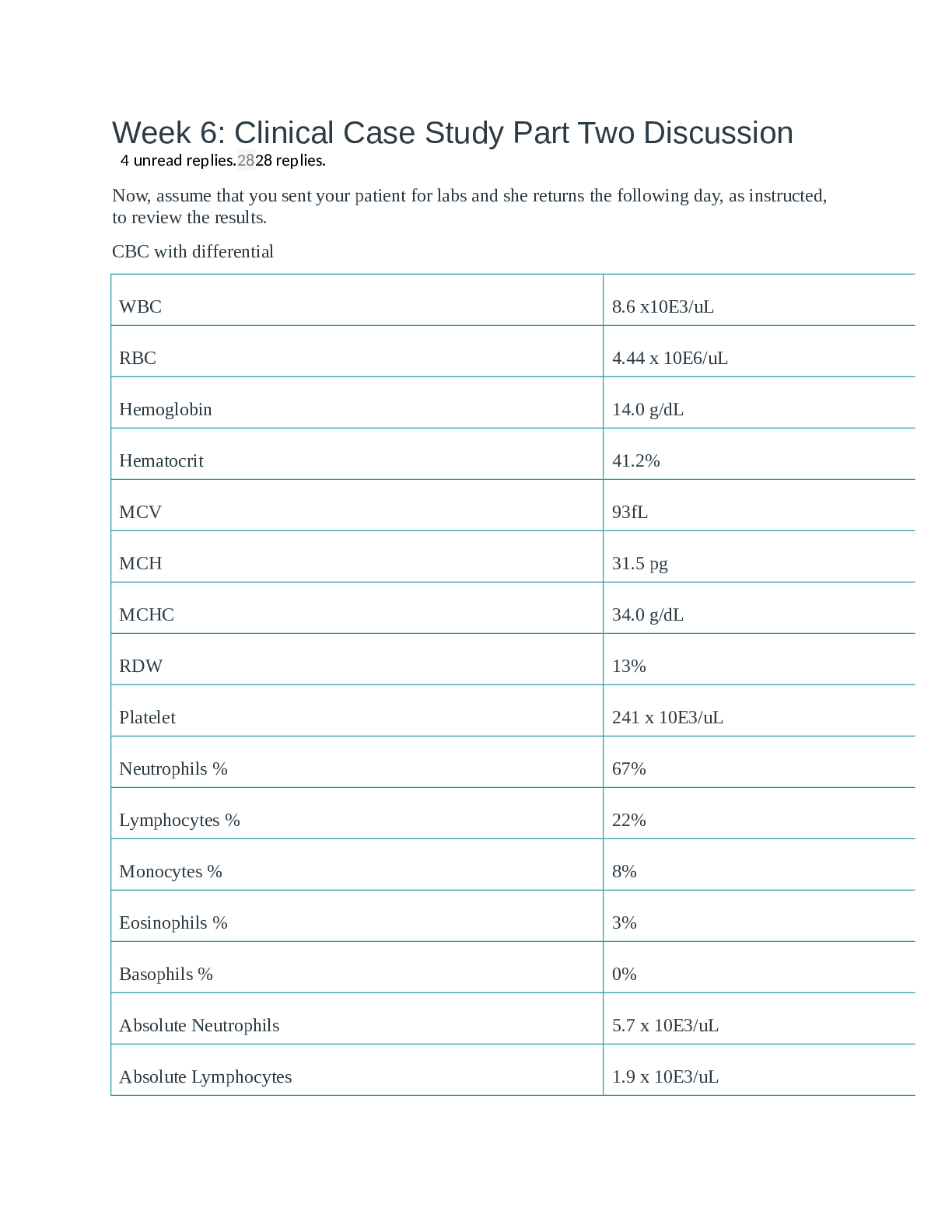
Head Trauma Case Study NUR 401 Scenario: J.R. is a 28-year-old man who was doing home repairs. He fell from the top of a 6-foot stepladder, striking his head on a large rock. He experienced a ... momentary loss of consciousness. By the time his neighbor got to him, he was conscious but bleeding profusely from a laceration over the right temporal area. The neighbor drove him to the emergency department of your hospital. As the nurse, you immediately apply a cervical collar, lay him on a stretcher, and take J.R. to a treatment room. 1. What steps will you take to assess J.R.? First I would assess his airway to make sure it is patent and nothing is prohibiting him from getting air in The I would assess his breathing to see if he is in distress, listen to lung sounds, count respirations, and assess chest expansion Check Circulation assessing blood loss from laceration, by feeling for pulses, cap refill, checking for cyanosis and checking BP Lastly I would perform Glasgow coma scale to assess LOC 2. List at least five components of a neurologic examination. Level on consciousness Motor function Pupillary function Respiratory function Vital signs 3. What types of injuries may J.R. have sustained? Due to blunt trauma from J.R. falling from a ladder and hitting his head on a rock he may have sustained some type of traumatic brain injury such as skull fracture, concussion, contusion, or cerebral hematoma. 4. What complication is common to each of these diagnoses (listed in #3) concerns you most? These injuries run the risk of increasing intracranial pressure 5. Identify at least six findings that would indicate this complication (listed in #4) is occurring. Changes in LOC 1 This study source was downloaded by 100000817113117 from CourseHero.com on 09-14-2021 06:53:25 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40258324/Head-Trauma-Case-Study-Studentdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com Changes in speech Vomiting Changes in vitals: increased SBP, decreased pulse, decreased respirations Headache Changes in pupillary functions: impaired eye movements, papilledema 6. What is the most sensitive indicator of neurologic change? The most sensitive indicator of neurologic change would be a change in level of consciousness. This is because a patients level of consciousness deteriorates before any other neuro changes are noticed. Case Study Progression You complete your neurologic examination and find the following: Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 15; pupils equal, round, reactive to light; and full sensation intact. J.R. complains of a headache and is somewhat drowsy. His vital signs (VS) are 120/72, 114, 30, 98.7 ° F (37.1 ° C) and Spo2 94%. As the radiology technician performs a portable cross-table lateral cervical spine x-ray examination, J.R. begins to speak incoherently and appears to drift off to sleep. 7. What are the next actions you will take? My next action would be to try to arouse/ wake up J.R. Next I would reassess J.R. by repeating GCS and vital signs. I would also assess for the oculocephalic reflex to see if J.R. is experiencing some brainstem injury. Case Study Progression While waiting for the physician to arrive, you find that J.R. has become unresponsive to verbal stimuli. The right pupil is larger than the left and does not respond to light. J.R. responds to painful stimuli in the manner shown in the illustration. 2 This study source was downloaded by 100000817113117 from CourseHero.com on 09-14-2021 06:53:25 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40258324/Head-Trauma-Case-Study-Studentdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com 8. What is this response called and what does it signify? The position is known as decerebrate posturing. Decerebrate occurs when there is a lesion on the brainstem this signifies that there is severe brain damage present. 9. Calculate J.R.'s GCS score. Describe the clinical implications of this score. Glasgow coma scale is a tool used for assessing level of consciousness. This score is based on eye opening, verbal response and best motor response. Lowest score to attain is 3 which signifies that patient is incompetent and in a coma , the highest score is 15. J.R. has a GCS of 4. This is because he got 1 for eye opening response due to no eye opening regardless of stimulation; 1 for verbal response due to no verbalization despite stimulation; 2 for best motor response due to decerebrate posturing in response to noxious stimuli. 10. What is the likely cause of the change in J.R.'s neurologic status? J.R. neuro change is from ICP caused by bleeding in the brain, that he acquired when he fell and hit his head on the rock, resulting in some type of hematoma. 11. What are your nursing priorities at this time? Assess the patient (neuro checks), get frequent vitals, maintain patent airway, prevent seizure and set up seizure precautions , monitor I &Os, decrease ICP, control temperature, get gastric access, and keep head of the bed elevated 12. What immediate actions will you take? Maintain airway Elevate the HOB Call HCP on status patient 3 This study source was downloaded by 100000817113117 from CourseHero.com on 09-14-2021 06:53:25 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40258324/Head-Trauma-Case-Study-Studentdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com Contact respiratory to request intubation Place catheter Get CT scan 13. His vital signs are now 160/72, 64, 10, 98.7 ° F (37.1 ° C), and Spo2 94%. What is your concern and why? I am concerned about increased intracranial pressure due to increase in blood pressure, decrease in pulse, and decreased respirations. The increase in blood pressure is due to maintaining cerebral perfusion pressure. The drop is pulse is a reflex response to hypertension. The decrease in respiration is caused by impaired brainstem function. Case Study Progression The physician arrives and gives the orders shown in the chart. 14. Outline a plan for implementing these orders. 1. Intubate 2. Get CT scan to confirm ICP 3. Start IV fluid 4. Start Mannitol 5. Start Dilantin 6. Draw labs 7. Get gastric access (NG Tube) 8. Insert Foley 15. What is Mannitol, and why is it being administered to J.R.? Mannitol is a type of osmotic diuretic that inhibits the reabsorption of water and salt. It is being administered to J.R. to decrease intracranial pressure by drawing fluid from extravascular spaces into the plasma 4 This study source was downloaded by 100000817113117 from CourseHero.com on 09-14-2021 06:53:25 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40258324/Head-Trauma-Case-Study-Studentdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com 16. What is the expected outcome associated with administering phenytoin to J.R.? Phenytoin is an anticonvulsant. The expected outcome is that it prevents J.R. from having a seizure. Case Study Progression J.R. is transported to radiology for a CT scan; he is found to have a large epidural hematoma on the right with a hemispheric shift to the left. He is taken straight to the operating room for evacuation of the hematoma. While he is in surgery, J.R.'s family arrives with their faith healer. They ask that their faith healer anoint J.R. and pray over him. 17. How should you respond? Due to J.R. emergent Dx he has to be sent to surgery immediately, however after surgery their faith healer is welcome to anoint J.R. after. Case Study Progression Postoperatively J.R. is admitted to the neurologic ICU. 18. What assessment indicators will be closely monitored in J.R.? signs of ICP, Arterial oxygenation, adequate cerebral perfusion , corneal abrasions, signs of injury, and s/s of Infection. 19. Identify eight independent nursing interventions and the rationale for each that would be used to prevent increased intracranial pressure (ICP) in the first 48 postoperative hour. 1. Position patient in semi fowlers. This will promote drainage of cerebral venous blood which will decrease ICP. 2. Maintain/ monitor blood pressure because high blood pressure can increase cerebral blood volume 3. Prevent from getting fever or to cold (shivering) because increase in metabolic rate increases blood flow to the brain. 4. Monitor Intake and output because to decrease in output can lead to fluid overload which will increase blood volume and lead to ICP 5. Maintain hyperventilation this is because CO2 is a vasodilator therefor to much retained Co2 will cause increase in blood flow to the brain. 6.Prevent seizures by administering Phenytoin this is because seizure cause metabolic requirements to increase, which results in elevation of CBF, cerebral blood volume, and ICP. 5 This study source was downloaded by 100000817113117 from CourseHero.com on 09-14-2021 06:53:25 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40258324/Head-Trauma-Case-Study-Studentdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com 7. Administer osmotic diuretics and hypertonic saline this will decrease ICP because hyperosmolar therapy is used to draw water from brain tissue into the intravascular compartment. 8. Control metabolic demand (ex. avoiding bathing, repositioning, and suctioning) this is because any noxious stimulation to the patient can cause increase in ICP. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 22, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
149