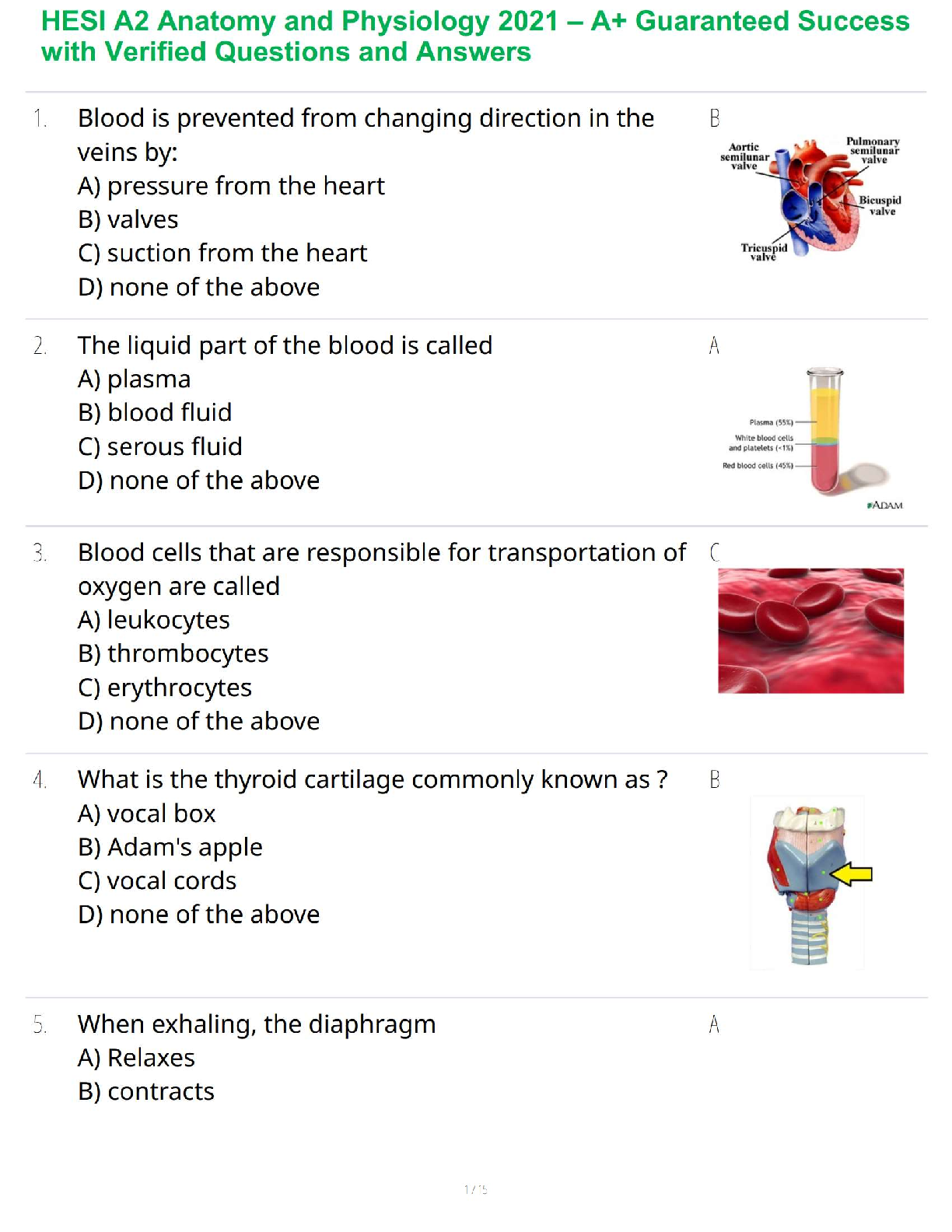
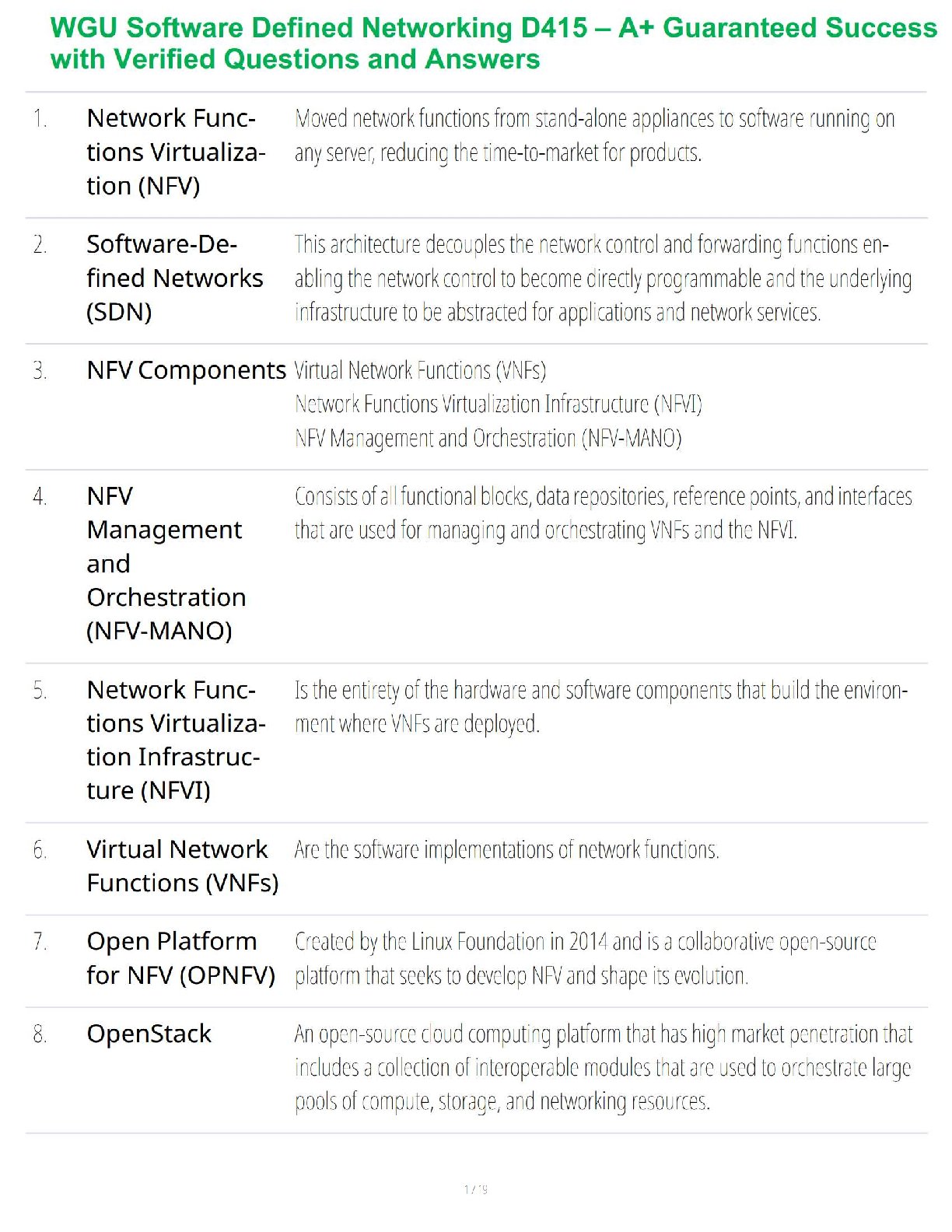
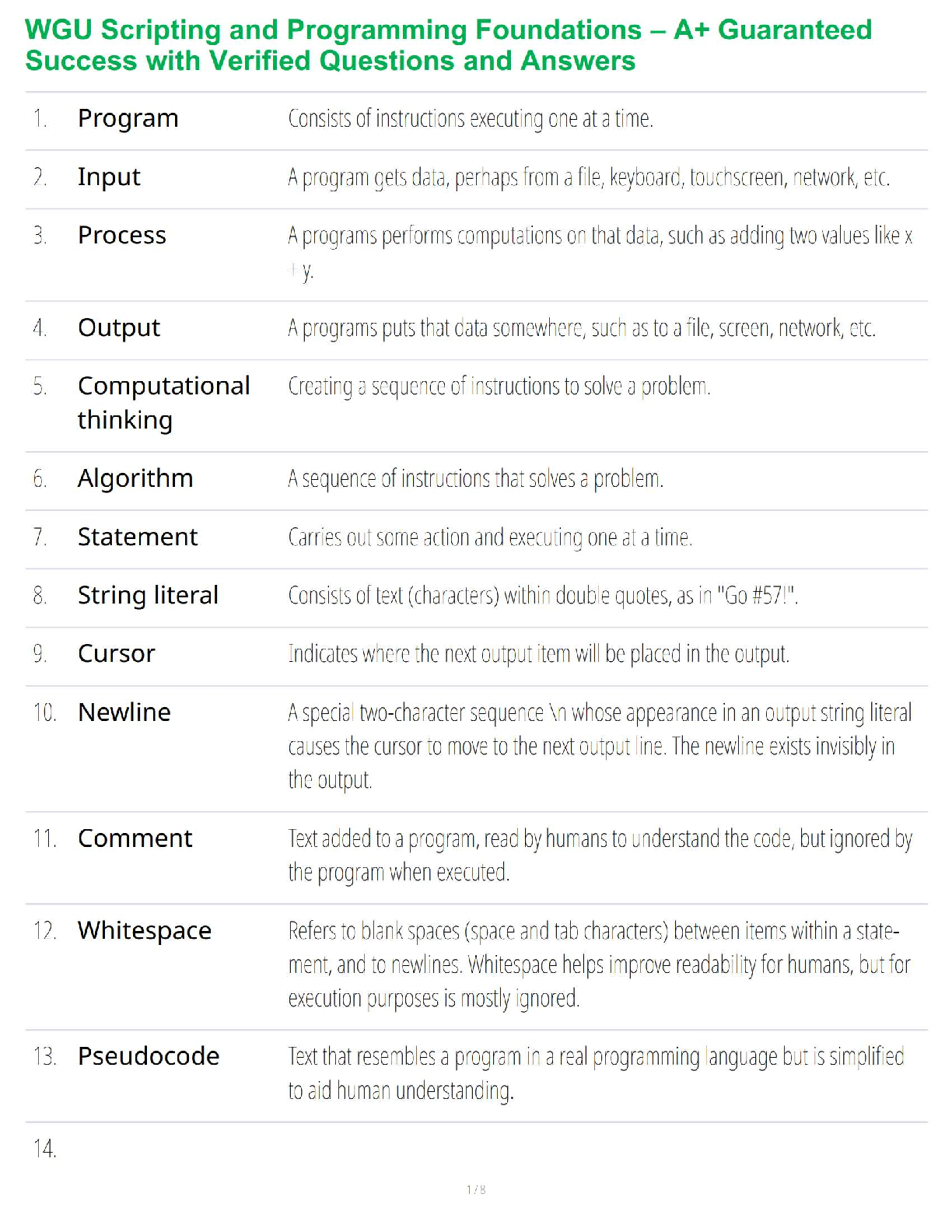
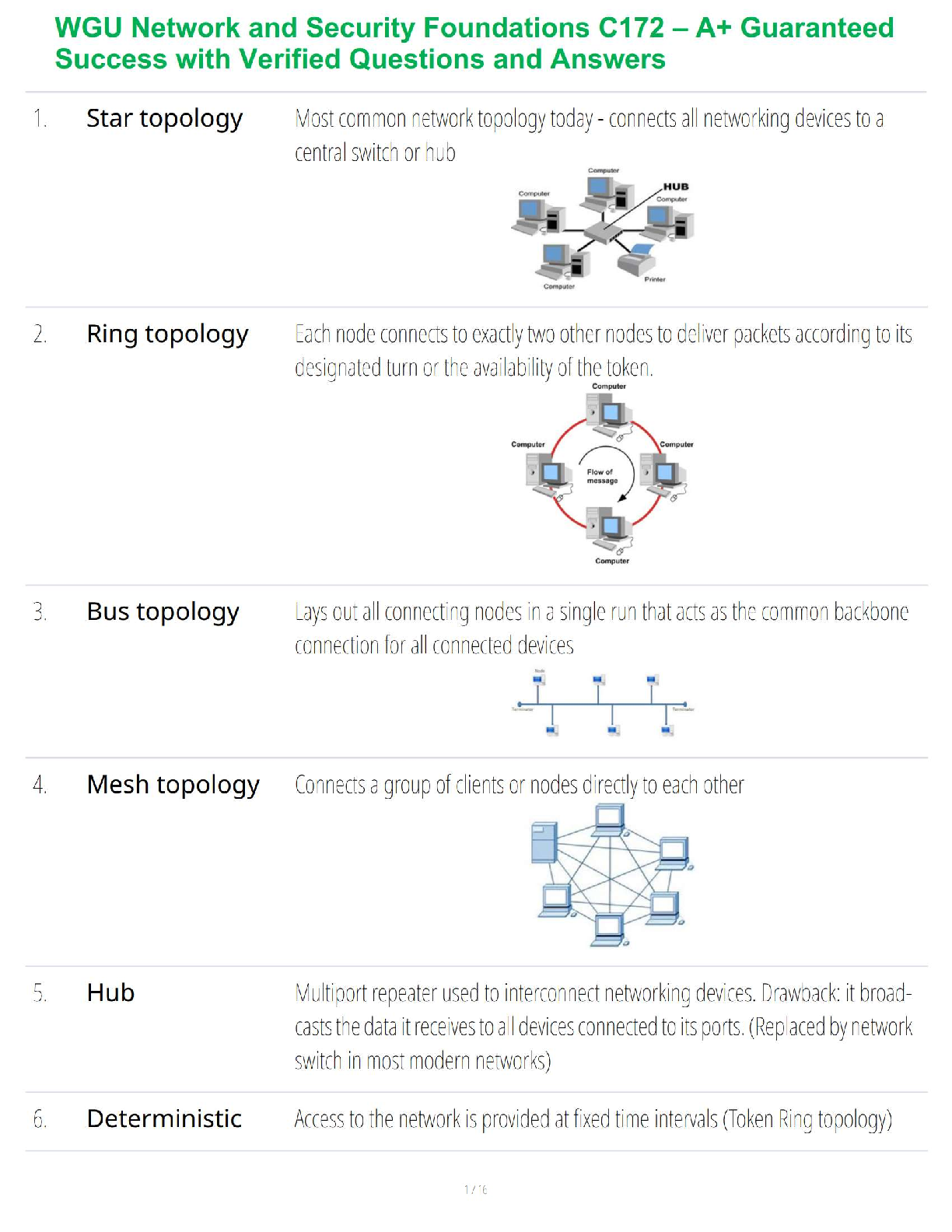
*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Mid-Term Summary & Study Guide NURS-6521 Pharmacodynamics: how the drug effects the body Pharmacokin (All)
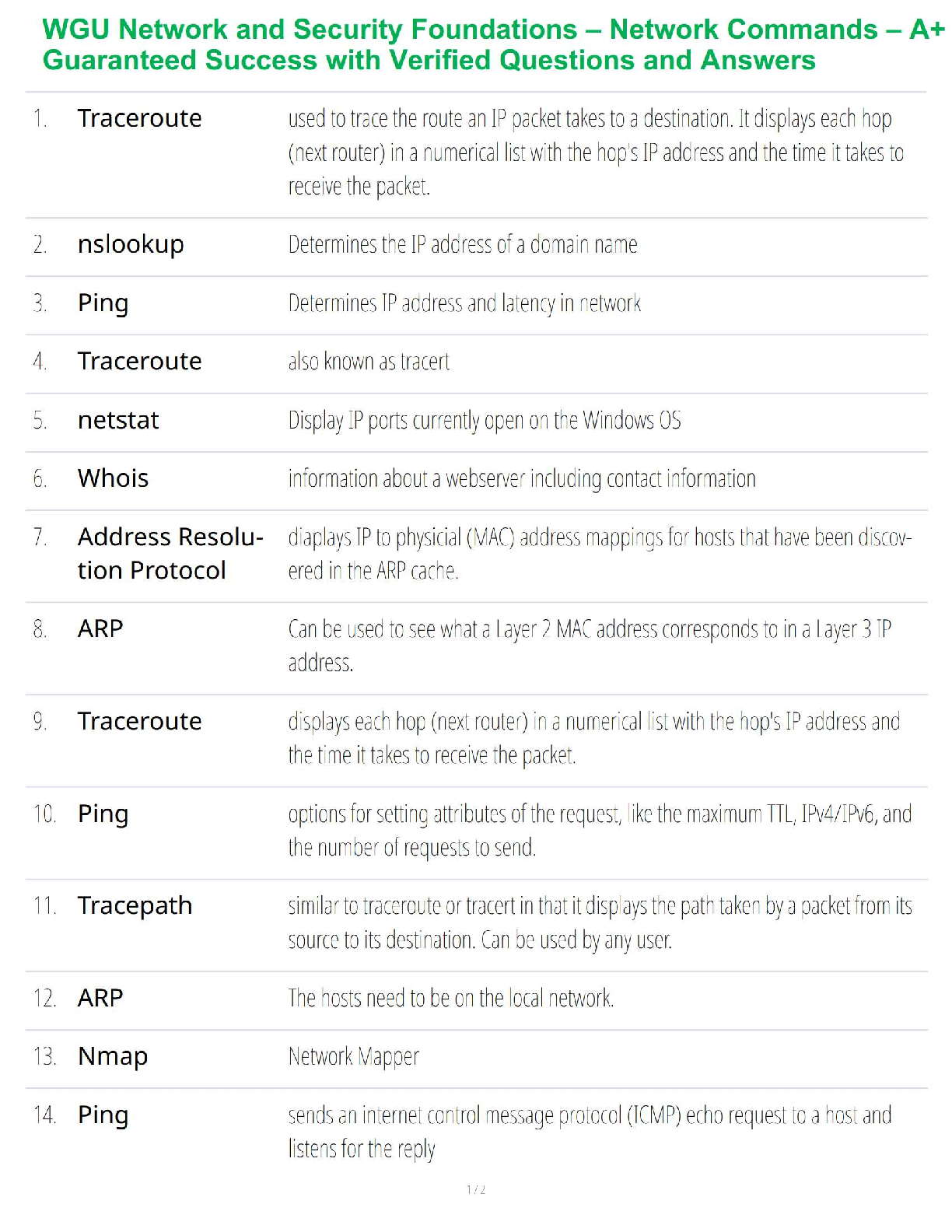
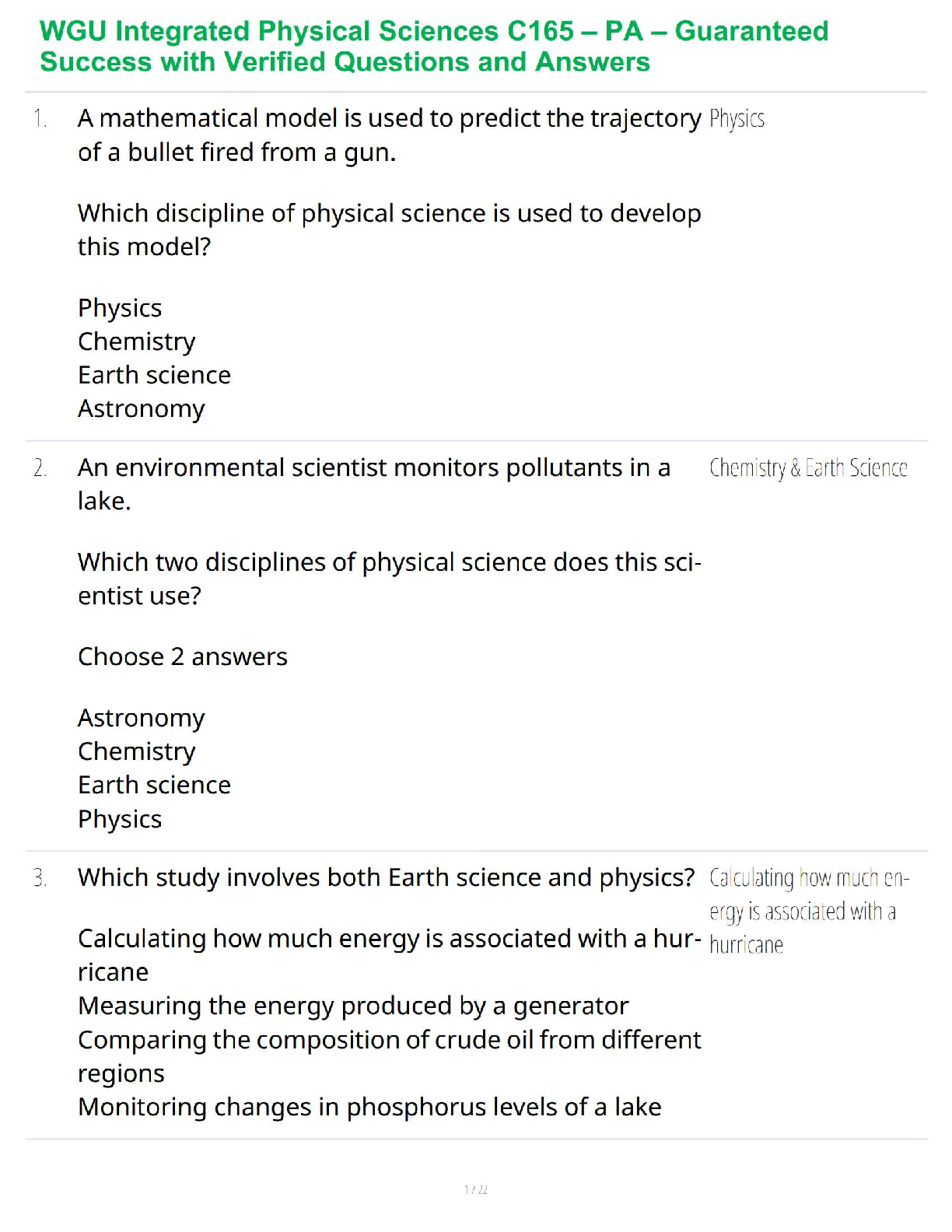
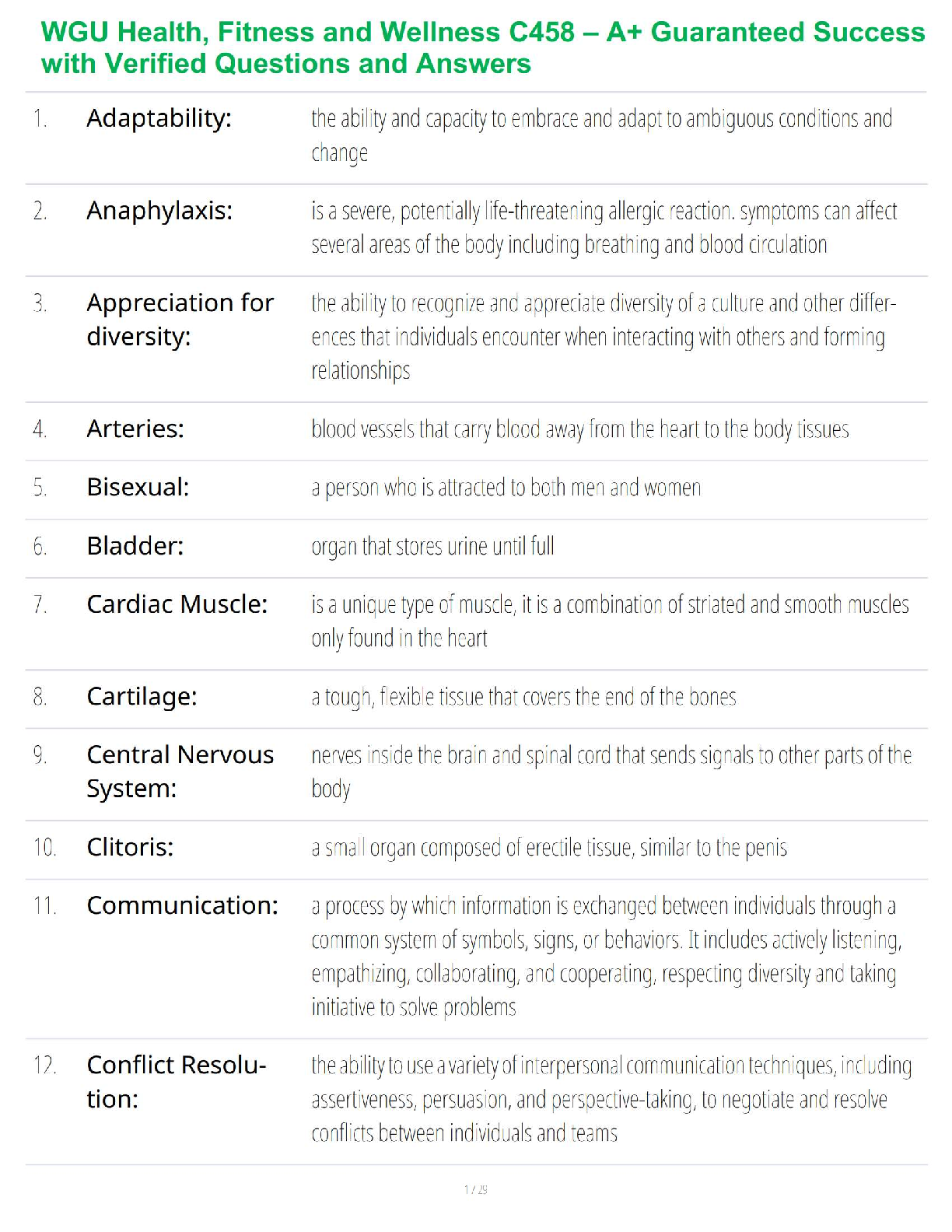
Mid-Term Summary & Study Guide NURS-6521 Pharmacodynamics: how the drug effects the body Pharmacokinetics: how the body effects the drug100-question Exam which will assess your knowledge on the Learning Resources from Weeks 1-6.
Document Content and Description Below
Mid-Term Summary & Study Guide NURS-6521 100-question Exam which will assess your knowledge on the Learning Resources from Weeks 1-6. Time limit of 2 hours. Multiple choice or multiple ... selection. Pharmacodynamics: how the drug effects the body Pharmacokinetics: how the body effects the drug Understand the implications of changing renal function on creatinine & drug dosing. Kidney/Renal functions : Filters blood = Remove Waste, Toxins, and Extra Fluid from the body Returns needed substances to the blood – & the remainder becomes urine Removes acid produced by cells of the body to maintain balanced water, salts; minerals Makes hormones that control BP, make RBCs; keeps bones strong Creatinine: Measures kidney function - byproduct of muscle metabolism (creatinine phosphate) Normal Serum Creatinine levels: 0.6-1.3 mg/dL - healthy kidney (Easily filters & excretes creatinine) More Reliable than BUN. Creatinine is Not Absorbed by the kidneys. Rises indicate renal damage or failure = Kidney is unable to properly filter & excrete waste (creatinine) = Lab Value rises in the serum. Creatinine = Kidney Function = Requires a decreased dose of medication or different dosing schedule = Renal Dosing What is the impact of the following on drug levels and dosing: Cirrhosis: a disease in which normal liver cells are replaced by scar tissue. As liver cells die, the organ makes less of the proteins that regulate fluid retention & blood clotting and the liver loses its ability to metabolize the pigment bilirubin. Liver/Hepatic functions : Produces proteins that help clot blood Removes / neutralizes poisons, drugs and alcohol Manufactures bile that helps the body absorb fats & cholesterol Helps maintain normal blood sugar levels Regulates hormones With Cirrhosis - the liver fails to detoxify the blood & it becomes less able to metabolize medications, which magnifies their effects. Eventually toxins build up in the brain & can produce: Increased sensitivity to drugs Levels of medication will be higher d/t decreased metabolism Requires decreased dose of medication Liver/Hepatic Function = Ability to metabolize medication = Requires a decreased dose of medication or different dosing schedule = Hepatic Dosing Protein binding: Drugs can form reversible bonds with various proteins in the body. Plasma albumin is the most important - large molecule - too large to leave the bloodstream! Binding is reversive & Drugs can be bound or unbound. % of drug molecules that are bound is determined by the attraction between it and albumin. Ex. Albumin & Warfarin – Strong Attraction = 99% of warfarin molecules in plasma are bound. 1% Free. Albumin & Antibiotic Gentamicin – Weak Attraction = < 10% of gentamicin molecules in plasma are bound. > 90% Free. Restricted drug distribution = Albumin is too large to leave; bound molecules cannot leave either! o Bound molecules cannot reach their site of action or undergo metabolism/excretion until drug-protein bond is broken so the is free to leave the circulation. Drug Interactions = Each Albumin molecule has only a few sites where drug molecules can bind. o Drugs will complete with 1 another for the limited binding sites = 1 drug displaces another from albumin = Free concentration of the displaced drug Rises = Increasing intensity of drug responses! o If plasma drug levels rise = Toxicity! o If the drug is highly protein bound = Need higher dose of drug to attach to/saturate all areas of the drug binding proteins & the Receptors TO GET RESULTS! o If you have Drug A in place at all drug binding protein sites, and you add Drug B (which is more protein bound), it will displace (Kick off) Drug A & take their place at the drug binding protein sites = Causing more Drug A to be free floating o Ex: Coumadin & Dilantin Both Highly Plasma Protein Bound Drugs! o 3 days prior to surgery, Coumadin in stopped – leaving more protein binding sites for Dilantin. The Dilantin binds and leaves less available to prevent Seizure o Starting or stopping drugs that bind to plasma protein changes the free drug levels of other protein bound drugs *Check Levels & Drug Effects more frequently! Drug interactions: When two drugs interact, there are three possible outcomes: (1) one drug may intensify the effects of the other (2) one drug may reduce the effects of the other (3) the combination may produce a new response not seen with either drug alone. • Medications must be prescribed at doses that will allot for the appropriate level of outcome required specifically for that patient. • Frequent monitoring of effects & levels are required Half-life: the time required for the amount of drug in the body to decrease by 50%. Metabolism & excretion cause the drug in the body to decline. Half-life of a drug determines the dosing interval (i.e., how much time separates each dose). Short half-life = Dosing interval must be correspondingly short or therapeutic effects will be lost. Long half-life = Long time can separate doses without loss of benefits. No matter what the amount of drug in the body may be, half (50%) will leave during a specified time period (the half-life). The actual amount of drug that is lost during one half-life depends on just how much drug is present: the more drug in the body, the larger the amount lost during 1 half-life. Routes of Administration and Dosage Forms: Understand when it is OK to crush (or not crush) certain dosage forms & why. OK to Crush: Immediate Release Not OK to Crush: Sustained Release/ Enteric Coated Immediate Release: Rapid absorption of a drug after ingestion ( < 30 minutes ) Extended-Release: Released over a period of time ( 8, 12, 24 hours) o Sustained Release: Maintains drug release over a sustained period but not at a constant rate o Controlled Release: Maintains drug release over a sustained period at a nearly constant rate *prolongs actions but also attempt to maintain therapeutic drug levels Delayed Release: Releases the dose after a set time. Usually enteric coated to prevent release in the stomach – it releases the dose in the intestinal track. Which Routes of administration have the fastest and slowest rates of absorption? o Fastest to Slowest: IV, IM, SC, Oral o IV, Inhaling, Snorting, Smoking, Swallowing, Rectal o IV, IM, Intranasal, Intradermal, Subcutaneous, Oral, Rectal Oral forms: Time until a pill/capsule is broken down enough to release the medication in the stomach: Crushed/Chewed Tablet = under 10 mins Chalk tablet = 10 mins & Solid tablet = 10 mins Time-release capsule = 45 minutes Gel capsule = > 60 mins ENTERAL ROUTE: to the GI/ Intestinal Tract • Oral: By Mouth: PO: Easiest & most economical way. Avoid if pt is lethargic, has N/V, or unable to swallow/NPO [Involves 1st pass effect – decreasing concentration rapidly before hits target] • Sublingual: Under Tongue to dissolve. Absorbed through the mucous membranes of the gums, Not to be Swallowed. No water until dissolved fully. • Buccal: Between the gum and cheek. Rotate sides to avoid irritation. • Rectal: Suppository or Enema: When unable to take oral meds. Avoids about 2/.3 of first-pass metabolism. • Tubes: NG/Duodenal/G-Tubes: Meds needs to be crushed, so confirm orders! MUCOUS MEMBRANE ROUTE: • Transdermal: Patch: Through the skin. Left for extended time, Extended release meds are used for longer effect. • Drops/Sprays: Via Eyes, Nose, or ears. Absorbed through Mucous Membranes, Can Cause Systemic Effects. Confirm # of drops/sprays to be administered. • Vaginal: Can cause irritation to the mucous membranes. TOPICAL ROUTE: • Eye/ Nasal Mucosa/ Skin: Usually less lipophilic to reduce systemic absorption.INHALATION ROUTE: • Inhaler: Absorption can be Very Rapid & Complete. System or Local. Pulmonary alveoli represent a large surface w/ minimal barrier to diffusion. Rapid relief of Respiratory problems, or for anesthesia. Enters directly into bloodstream & can cause SEVERE Systemic Side Effects. PARENTERAL ROUTE: Does Not involve drub absorption via the GI Tract • IV: Most reliable method to the systemic circulation. Bypasses many absorption barriers. Bioavailability of drugs is 100%. Delivered directly into vascular space. • IM: Absorption depends on muscle blood flow. [Depot IM: slowly releases drug at site of injection] • SC or SQ: For drugs with low bioavailability (ex. Insulin) • Transdermal: Drug must be highly lipophilic. Slow absorption but long-lasting effects Know the relative onset, monitoring and appropriate use of various dosage forms: Sublingual tablets: (Nitro/Subox): Immediate Systemic Onset: 1-5 Mins Peak: 10 Mins (Capsule/Tab/Liquid) ORAL: VARY! Onset: 20 Mins- 1 Hr Peak: 30 Mins- 1 Hr Duration: 4-6 Hrs Patches: Rivastigmine: (Alzheimer’s): Onset: 30-60 Mins Peak: 8-16 Hrs after 1st dose Duration: 10 Hrs Fentanyl: Onset: Unknown/ Within 24 Hrs Peak: 20-72 Hrs Duration: 72 Hrs Suppositories: (Acetaminophen): Onset: 1 Hr Peak: Duration: 2-4 Hrs Elixir - Active ingredients are mixed with liquid – syrup or alcohol (concentrated) Suspension – Med is mixed with liquid – water - it can’t d [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 29 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 26, 2021
Number of pages
29
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 26, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
204

.png)
.png)