*NURSING > Lab Experiment > Chamberlain College of Nursing BIOS 242 Lab5_DifferentialStainupdated. (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing BIOS 242 Lab5_DifferentialStainupdated.
Document Content and Description Below
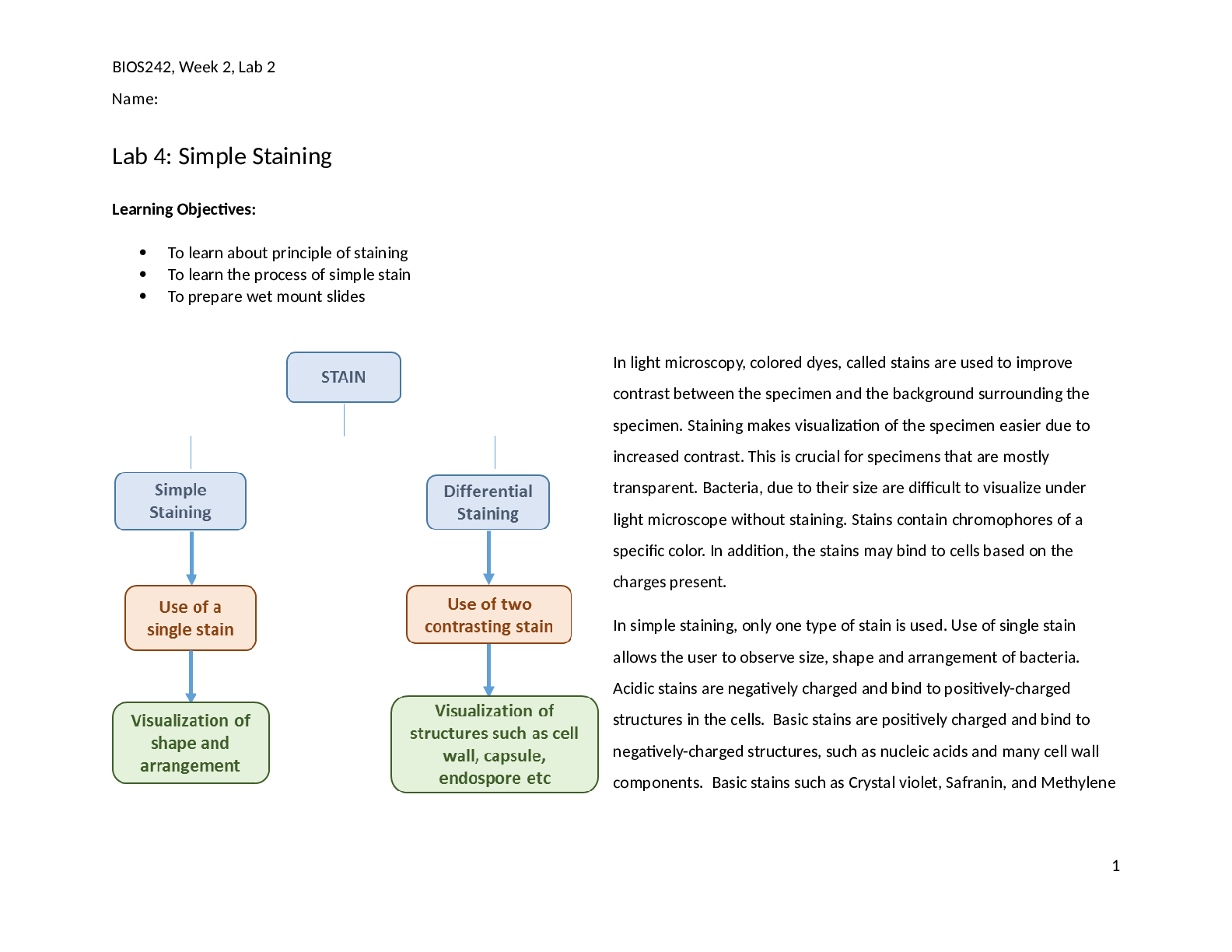
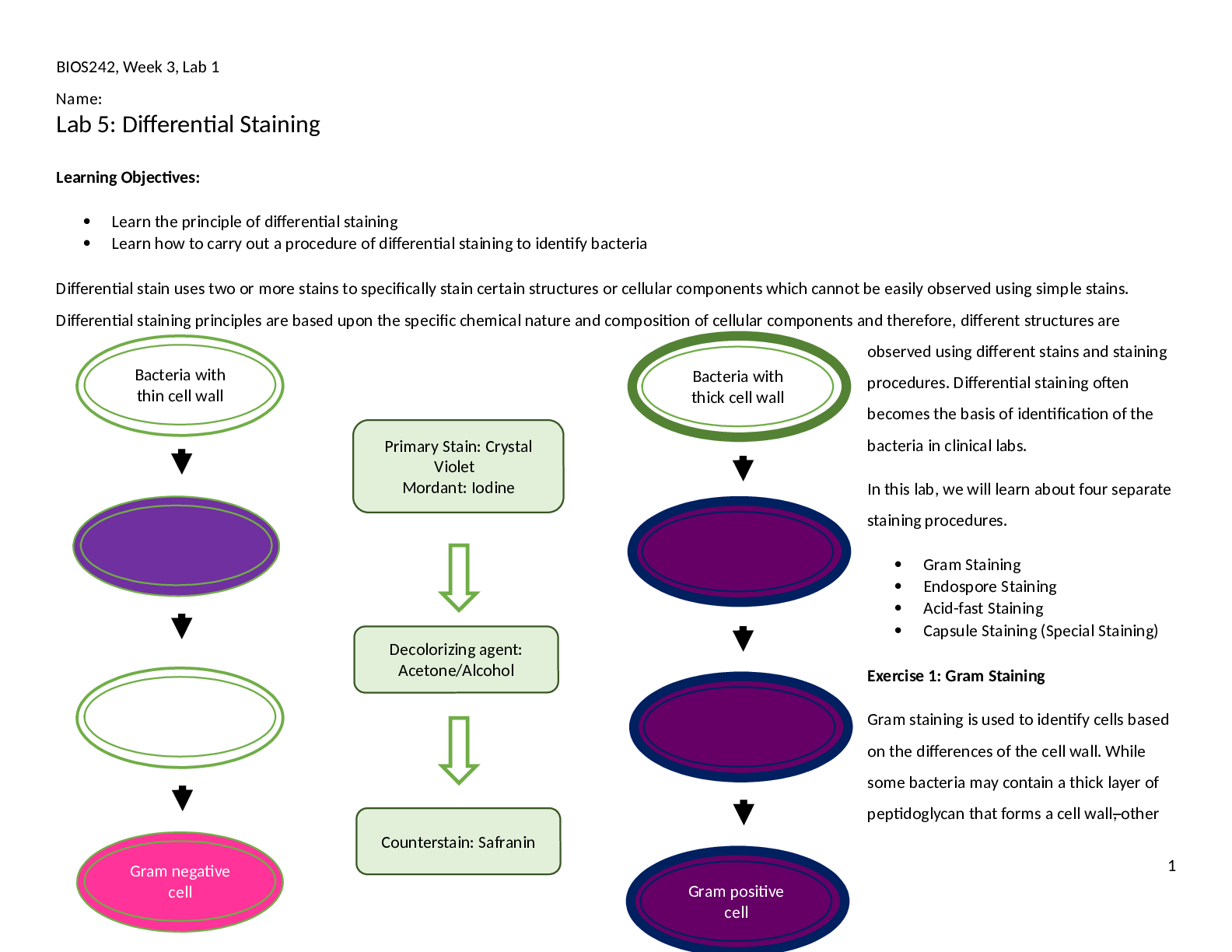
BIOS242, Week 3, Lab 1 Name: Lab 5: Differential Staining Learning Objectives: Learn the principle of differential staining Learn how to carry out a procedure of differential staining to ... identify bacteria Differential stain uses two or more stains to specifically stain certain structures or cellular components which cannot be easily observed using simple stains. Differential staining principles are based upon the specific chemical nature and composition of cellular components and therefore, different structures are observed using different stains and staining procedures. Differential staining often becomes the basis of identification of the bacteria in clinical labs. In this lab, we will learn about four separate staining procedures. Gram Staining Endospore Staining Acid-fast Staining Capsule Staining (Special Staining) Exercise 1: Gram Staining Gram staining is used to identify cells based on the differences of the cell wall. While some bacteria may contain a thick layer of peptidoglycan that forms a cell wall, other 1 Bacteria with thin cell wall Bacteria with thick cell wall Primary Stain: Crystal Violet Mordant: Iodine Counterstain: Safranin Decolorizing agent: Acetone/Alcohol Gram positive cell Gram negative cell BIOS242, Week 3, Lab 1 Name: bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan forming a cell wall sandwiched between two cell membranes. The outer membrane is rich in lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Gram staining takes advantage of these differences in the cell wall of bacteria. Using two different stains that offer a lot of contrast, bacteria containing a thick cell wall are stained purple. They are called Gram-positive cells. Bacteria containing a thin cell wall are stained pink and are called Gram-negative cells. In Gram staining, bacteria are first treated with a primary stain, crystal violet. Upon treatment with crystal violet, all cells are stained purple irrespective of presence of cell wall or LPS. Stained bacteria are then treated with a mordant, Iodine. Iodine helps crystalize crystal violet on the cell surface and therefore, cells retain crystal violet with higher affinity. After that, cells are rinsed with a decolorizing agent, a solution of acetone and alcohol. Decolorizing agent dissolves lipids and peptidoglycan from both gram positive and gram negative cell walls. However, the thicker cell wall of the gram positive bacteria will be able to retain some of the crystal violet. Over decolorization can completely decolorize gram positive bacteria as well. Under decolorization will make gram negative bacteria appear as gram positive. This step is the most CRITICAL step in the staining process. Lastly, bacteria are stained with a counterstain, safranin. Both gram positive and gram negative cells will stain with safranin but the purple crystal violet will override the pick color in gram positive cells. Gram negative cells, which are colorless cells after decolorization, are stained pink using safranin. Materials: Broth cultures of S. epidermidis, E. coli, a mixed culture containing one gram positive and one gram negative bacteria; sterile loop, Gram staining kit, glass slides, Incinerator, DI water, marker, immersion oil, lens paper, bibulous paper, Microscope Note to students: Wear gloves and use PPE before starting the lab work. Use aseptic technique to prevent contamination. Use only 1-2 drops of stain per slide. Avoid using excess. x Method: 1. Obtain glass slides and pure cultures. Write the name of the bacteria on the side of the glass slide. 2. Using aseptic technique make a thin smear. Allow it to air dry and then heat fix it. 3. Add a drop or two of crystal violet and allow staining for 1 minute. 4. Gently wash of crystal violet using a few drops of DI water. 5. Add a few drops of Iodine solution to the slide and wait for 1 minute. 6. Wash iodine solution using a few drops of water. 7. Rinse the slide with decolorizer until no more color washes off. 2 BIOS242, Week 3, Lab 1 Name: 8. Rinse the slide gently with a few drops of water. 9. Add a few drops of safranin and allow to stain for 1 minute. 10. Rinse the slide gently with a few drops of water. 11. Blot the slide dry. 12. Observe using 10X, and 40X objective lenses. Record the observations made using 40X objective in Lab report. a. Use 100X lens if needed. Don’t forget to use oil with it. After completing the observation, clean the oil immersion lens with lens wipes to remove oil. Be careful to not contaminate other lenses (4X, 10X, 40X) with oil. 13. Repeat the steps for all assigned cultures [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$6.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 08, 2021
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
269